Construction method and application of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis mouse model based on PEDF/LDLR double-gene knockout
A gene knockout mouse, steatohepatitis technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of lack of NASH models, etc., and achieve the effect of wide promotion and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
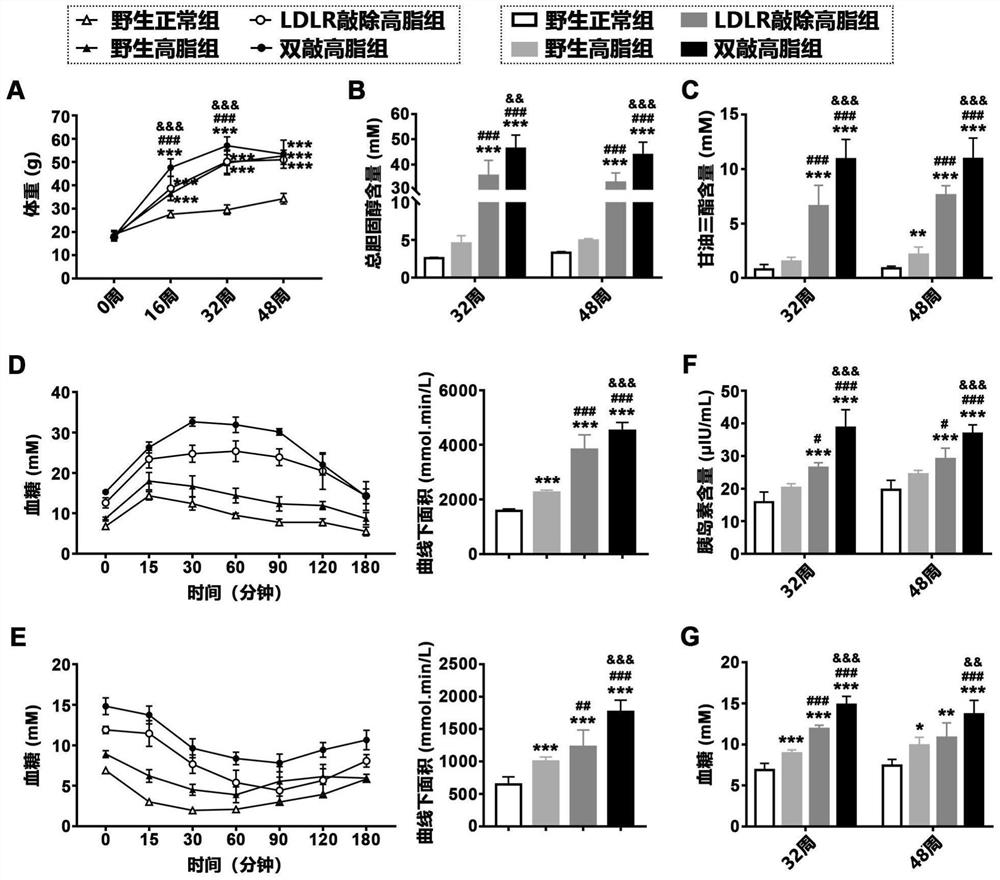
[0032] In this example, the body weight, blood lipid content, glucose tolerance, insulin tolerance, serum insulin content and blood sugar of the above-mentioned four groups of animals were measured.
[0033] The above 4 groups of animals were weighed at 0 weeks, 16 weeks, 32 weeks and 48 weeks respectively, and fasted for 12-16 hours before weighing; glucose tolerance test and insulin tolerance test were performed at 32 weeks of induction. The specific operations were as follows: Fasting for 12-16 hours, 1 g / kg glucose or 1 U / kg insulin were injected intraperitoneally, and blood glucose was measured at 0, 15, 30, 60, 90, 120, and 180 minutes after injection, and the blood glucose change curve was drawn. Calculate the area under the curve; at 32 weeks and 48 of induction, the animals were fasted for 12-16 hours, blood glucose was measured by a blood glucose meter, and the mice were dissected to collect serum samples, and commercial kits were used to detect serum total cholestero...
Embodiment 2
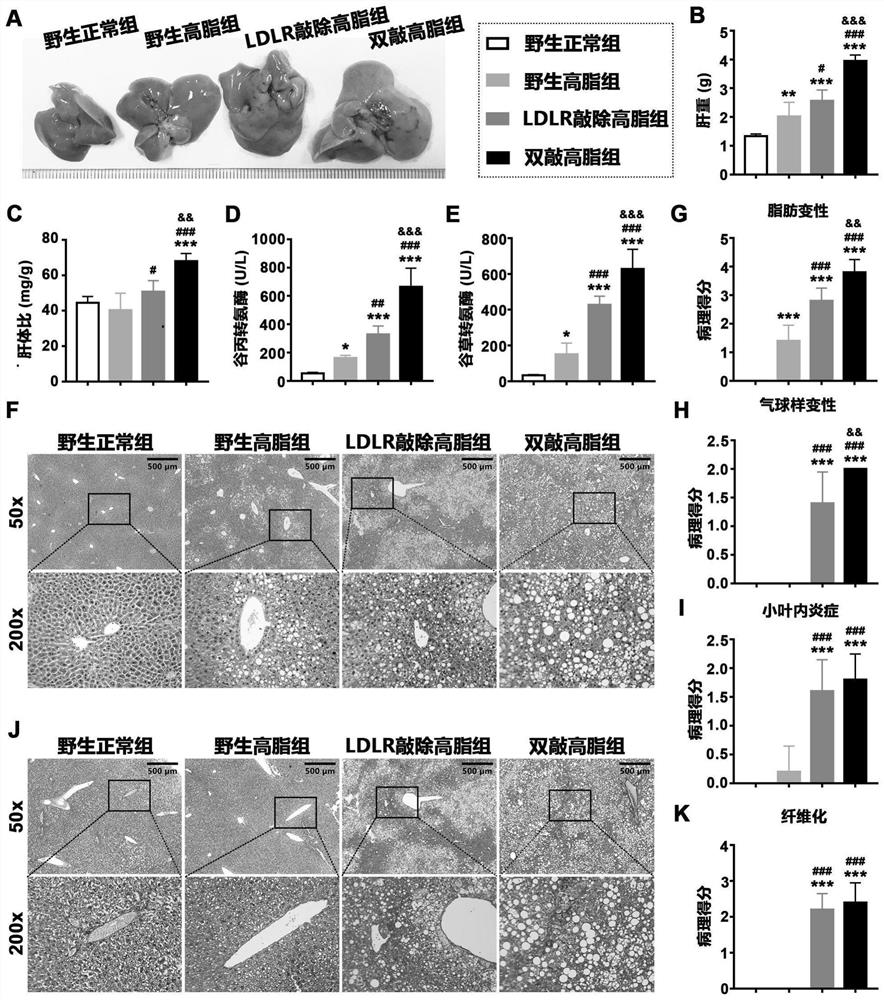
[0037] In this example, the liver weight, liver-to-body ratio, liver function enzyme level, liver steatosis, liver inflammatory response and liver fibrosis of the above-mentioned four groups of animals were evaluated at 32 weeks of induction.
[0038] At the 32nd week of induction, animals were fasted for 12-16 hours and then sacrificed by anesthesia. Serum and tissue samples were collected, and liver tissue was weighed; serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels were detected using commercial kits; Sections were stained with HE and Masson to evaluate liver lesions.
[0039] The result is as figure 2 As shown, where A: gross picture of liver; B: liver weight; C: liver body ratio; D: serum alanine aminotransferase level; E: serum aspartate aminotransferase level; F: HE staining; G: liver steatosis score; H: Liver ballooning degeneration score; I: liver lobular inflammation score; J: Masson staining; K: liver fibrosis score; *, p<0.05, vs wild-type no...
Embodiment 3
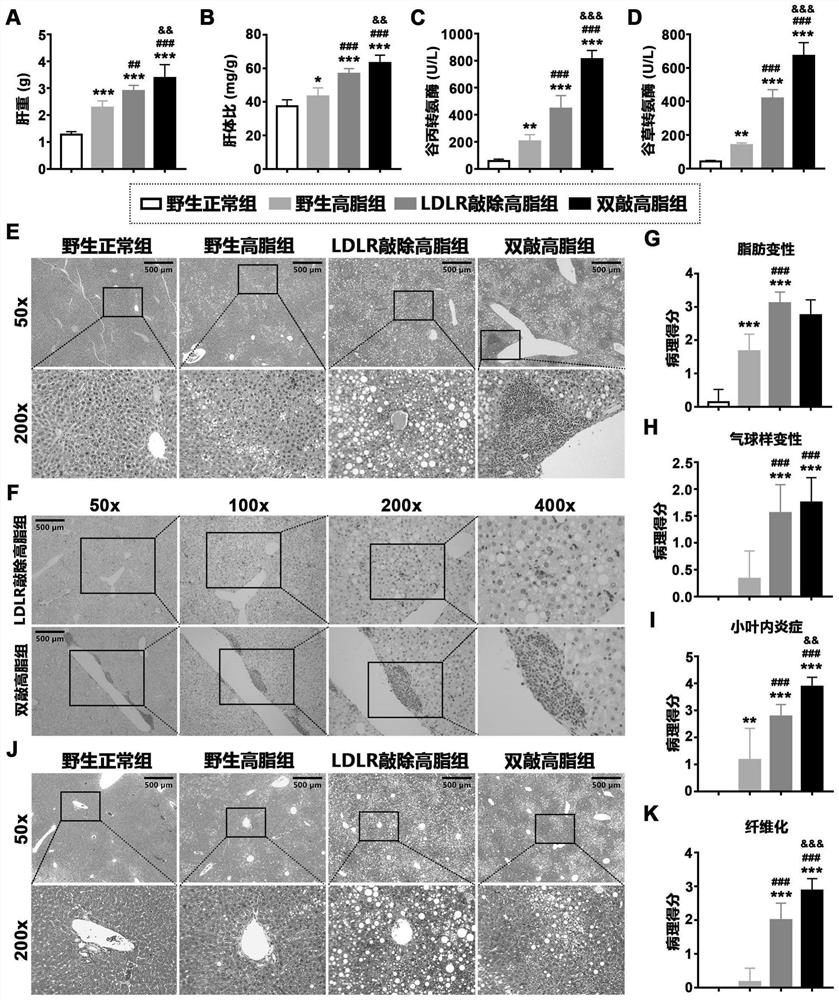
[0045] In this example, the liver weight, liver-to-body ratio, liver function enzyme level, liver steatosis, liver inflammatory response and liver fibrosis of the above-mentioned four groups of animals were evaluated at 48 weeks of induction.
[0046] At 48 weeks of induction, animals were fasted for 12-16 hours and then sacrificed by anesthesia, serum and tissue samples were collected, and liver tissue was weighed; serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels were detected using commercial kits; Sections were stained with HE and Masson to evaluate liver lesions.
[0047] The result is as image 3 As shown, where A: liver weight; B: liver body ratio; C: serum alanine aminotransferase level; D: serum aspartate aminotransferase level; E: HE staining; F: CD45 immunohistochemical staining; G: liver steatosis score; H: liver ballooning degeneration score; I: liver lobular inflammation score; J: Masson staining; K: liver fibrosis score; *, p<0.05, vs wild-ty...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com