Production method of marine fuel oil
A production method and technology for fuel oil, which are applied in the treatment of hydrocarbon oil, petroleum industry, hydrotreating process, etc., can solve the problems of increased conversion rate, high processing cost, and increased difficulty in product blending, so as to prevent excessive hydroconversion, The effect of enhancing processing flexibility and improving metal holding capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The obtained 80% hydrogenated vacuum residue is subjected to mild thermal cracking and the visbroken residue is used as a low-sulfur marine fuel oil product. The 20% hydrogenated vacuum residue is returned to the upflow reactor to be mixed with new hydrogen and then further hydrofined.
[0048] The hydrogenated vacuum residue directly enters the visbreaking heating furnace for visbreaking. The residence time in 2 minutes. The obtained visbroken products are passed through a fractionation tower to obtain visbroken gas, naphtha and visbroken residue (>165°C). Process conditions and product yields are shown in Table 9. After visbreaking, the conversion rate of visbreaking is 7.99%, and the yield of visbreaking residue is 92.01%.
[0049] Example 3
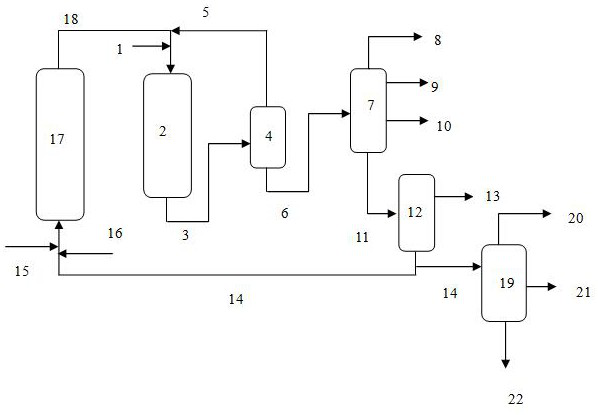
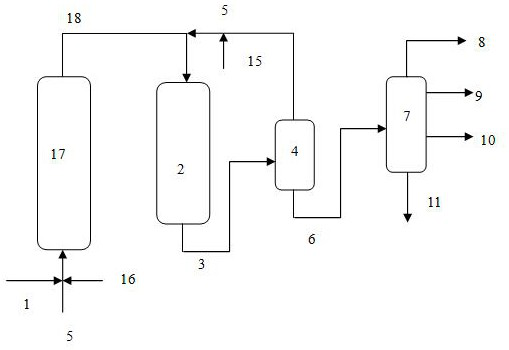
This embodiment adopts the production method of the low-sulfur marine fuel oil provided by the invention (see figure 1 ), using residue raw material A with relatively good properties and residual oil raw material B with rel...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The obtained 60% hydrogenated vacuum residue is subjected to mild thermal cracking and the visbroken residue is used as a low-sulfur marine fuel oil product. The 40% hydrogenated vacuum residue is returned to the upflow reactor to be mixed with new hydrogen and then further hydrofined.
[0055] The hydrogenated vacuum residue directly enters the visbreaking heating furnace for visbreaking. The residence time in 3 minutes. The obtained visbroken products are passed through a fractionation tower to obtain visbroken gas, naphtha and visbroken residue (>165°C). Process conditions and product yields are shown in Table 9. After visbreaking, the conversion rate of visbreaking is 6.97%, and the yield of visbreaking residue is 93.03%.
[0056] The properties of raw materials are shown in Table 1. Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6-Table 8, and Table 9 are respectively the properties of the fixed bed residue hydrotreating catalyst, the properties of the upflow hyd...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Table 11 Comparative Example 1 main operating conditions
[0063] In addition, in the hydrogenation product obtained in Comparative Example 1, the content of aromatic hydrocarbons was 22.57%, and the content of colloids was 9.65%, and the sum of the two could not reach 35%. It can be seen that in order to achieve the requirements of impurity content and viscosity, the hydrogenation depth is high, and the saturated hydrocarbon content reaches 65.84%. However, high saturated hydrocarbon content and low colloid and aromatic hydrocarbon content affect the stability of the oil system, which is not conducive to the storage and transportation of marine fuel oil, and then affects its performance.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com