Fuel cell low-temperature starting system and control method
A fuel cell and start-up system technology, applied in the direction of fuel cells, fuel cell additives, fuel cell heat exchange, etc., can solve the problems of electrochemical active area loss, low battery damage, difficult recovery, etc., to improve low-temperature start-up ability, The effect of extending the parking time and prolonging the service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
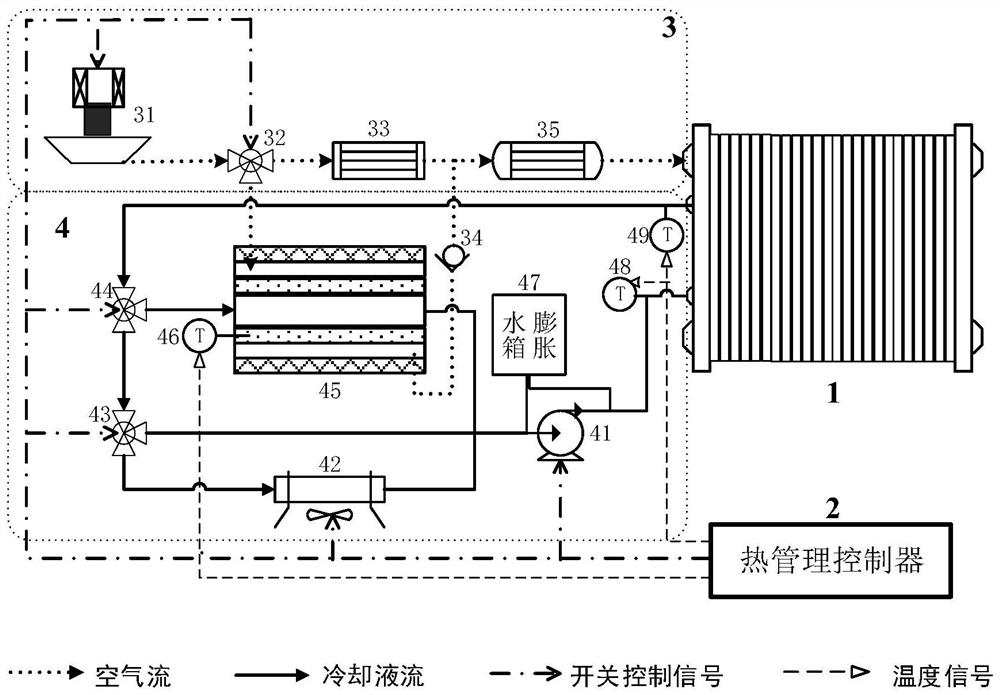
[0058] In this embodiment, the working mode of the fuel cell low-temperature start-up system based on phase change heat storage also has two implementation modes: low-temperature start-up mode and normal thermal management mode, wherein:
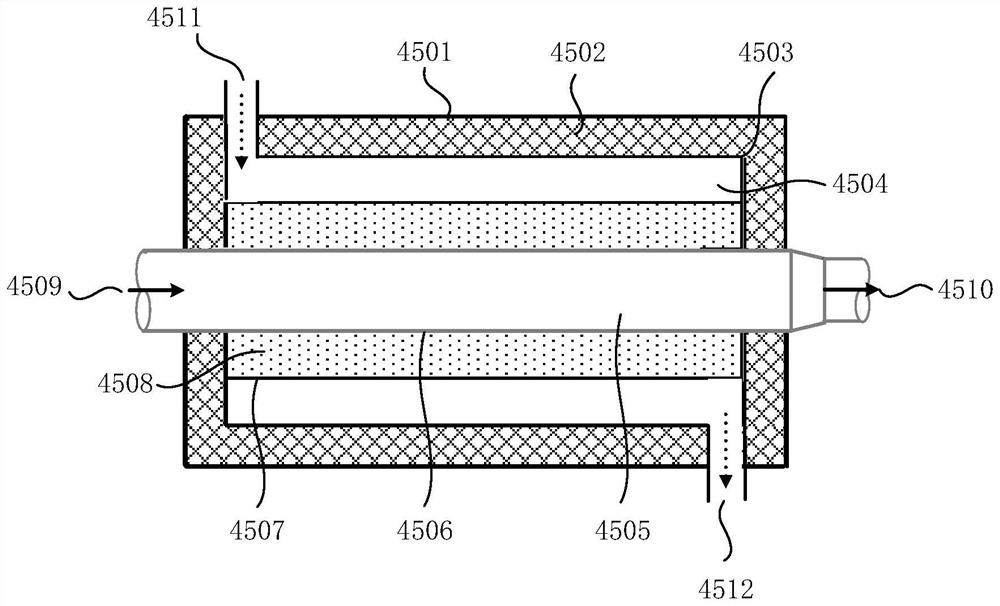
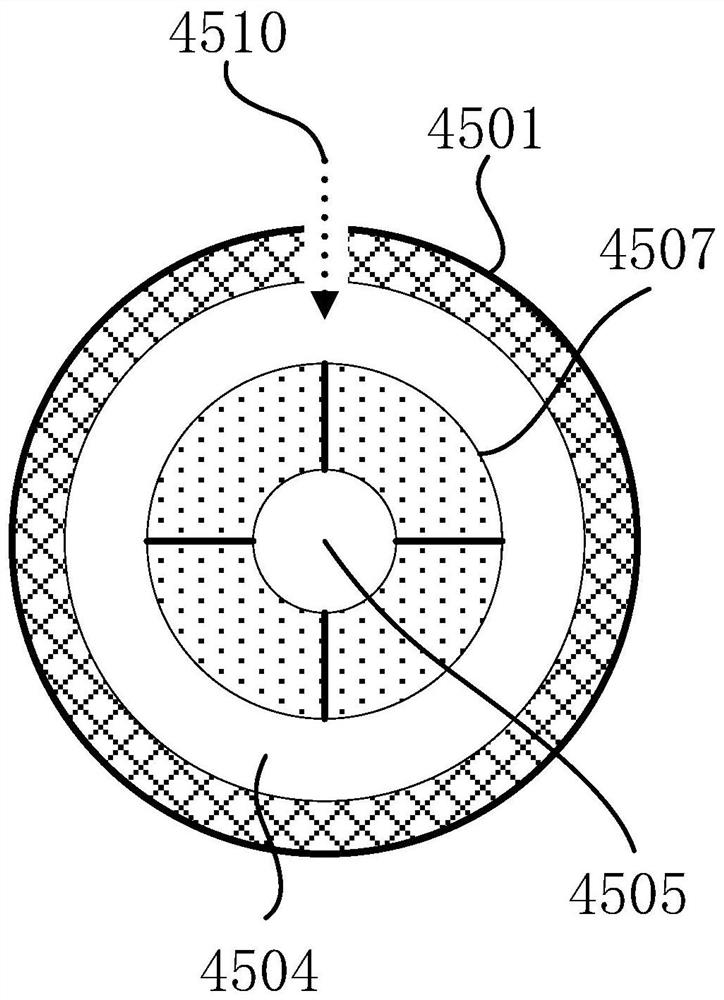
[0059] In the low temperature startup mode: the thermal management controller 2 opens the second valve of the first three-way solenoid valve 44 of the cooling liquid circulation system 4, and starts the water pump 41 to make the cooling liquid circuit of the fuel cell stack 1 run on a trajectory It is: water pump 41 → coolant temperature sensor 48 before the fuel cell stack inlet → fuel cell stack 1 → coolant temperature sensor 49 after the fuel cell stack outlet → first three-way solenoid valve 44 → cooling of the phase change heat storage device Liquid heat exchange pipe 4505 → water pump 41; at the same time, the thermal management controller 2 opens the second valve of the second three-way solenoid valve 32 of the air system 3, and starts...
Embodiment 1
[0077] A control method for a low temperature start-up system of a fuel cell, the method is realized by the following steps:
[0078] Step S101, when the fuel cell needs to be started at a low temperature in an environment below 0°C, the thermal management controller detects the fuel cell stack coolant temperature T F less than the first threshold temperature T 1 When the first three-way solenoid valve of the cooling liquid circulation system and the second three-way solenoid valve of the air system are opened, they are respectively connected to the valves of the phase-change heat accumulator of the cooling liquid circulation system and start the cooling The water pump of the liquid circulation system and the air compressor of the air system make the cooling liquid and high-pressure air of the fuel cell stack flow through the cooling liquid heat exchange pipe and the air heat exchange pipe of the phase change heat storage device respectively. The phase change latent heat tran...
Embodiment 2
[0083] refer to Figure 8, On the basis of Embodiment 1, a control method for a low temperature start-up system of a fuel cell is realized by the following steps:
[0084] Step 600 : the thermal management controller 2 detects the temperature T of the coolant passing through the fuel cell stack 1 F value;
[0085] Specifically, the temperature value of the cooling liquid of the cooling liquid temperature sensor 48 in front of the fuel cell stack inlet and the cooling liquid temperature sensor 49 after the fuel cell stack outlet is detected, and the cooling liquid passing through the fuel cell stack 1 is determined accordingly. temperature T F value;
[0086] Further, compare the fuel cell stack coolant temperature T F and the first threshold temperature T 1 size and enter step 610;
[0087] Step 610: The thermal management controller 2 detects whether there is a T F 1 case where:
[0088] If yes, go to step 611;
[0089] No, go to step 614;
[0090] Step 611 : The th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com