Method for identifying and cultivating diamonds and natural diamonds by utilizing X-ray excited fluorescence and phosphorescence
A technology that excites fluorescence and X-rays. It is applied in the direction of material analysis, instruments, and measuring devices using wave/particle radiation. It can solve the problems of inability to perform a large number of inspections, anxiety, and expensive inspection instruments, and achieve maintenance technical support and avoid identification. The effect of the process and operation is simple
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
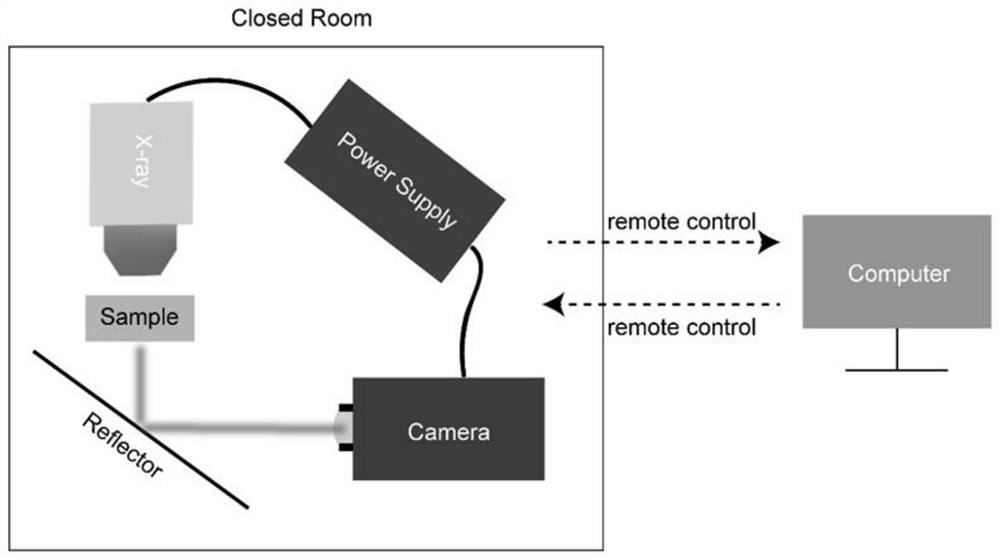
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0028] The identification principle of the present invention is:
[0029] The present invention is based on the identification of donor-acceptor impurities in diamond crystals.
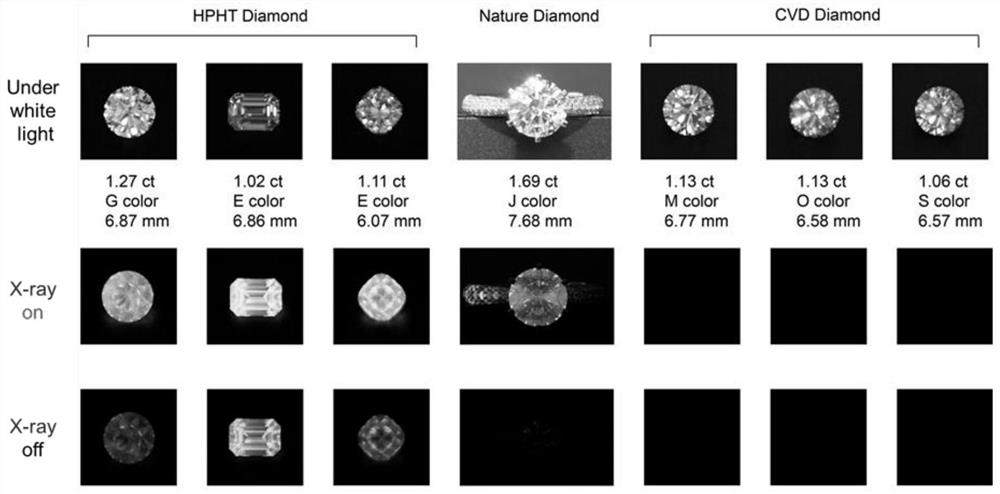
[0030] 1. Diamonds synthesized by high temperature and high pressure method (referred to as hot pressing) use metal catalysts and graphite raw materials in the synthesis process, so the produced diamond crystals inevitably contain transition metals such as iron Fe, cobalt Co, nickel Ni and so on. Elements, as well as boron B, nitrogen N and other elements, these foreign impurity elements constitute the luminescent center in the diamond crystal, which will cause the hot-pressed diamond to produce blue-green fluorescence and phosphorescence under the excitation of X-rays.
[0031] 2. Natural diamonds are grown in a complex natural geographical environment, so the natural diamond crystals will contain the above and other foreign impurity elements to varying degrees to form the luminescent center, so that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com