Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Provide quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
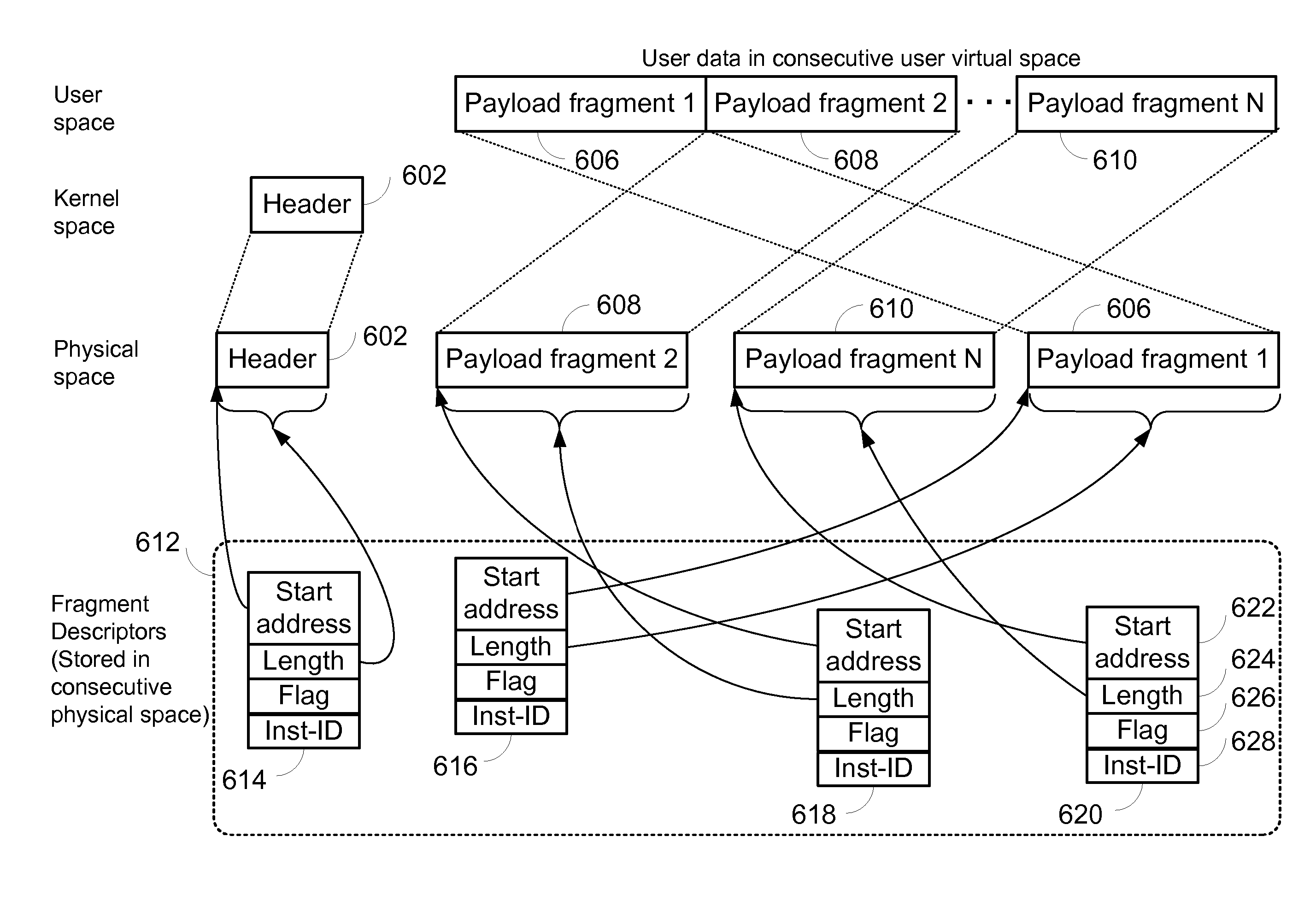
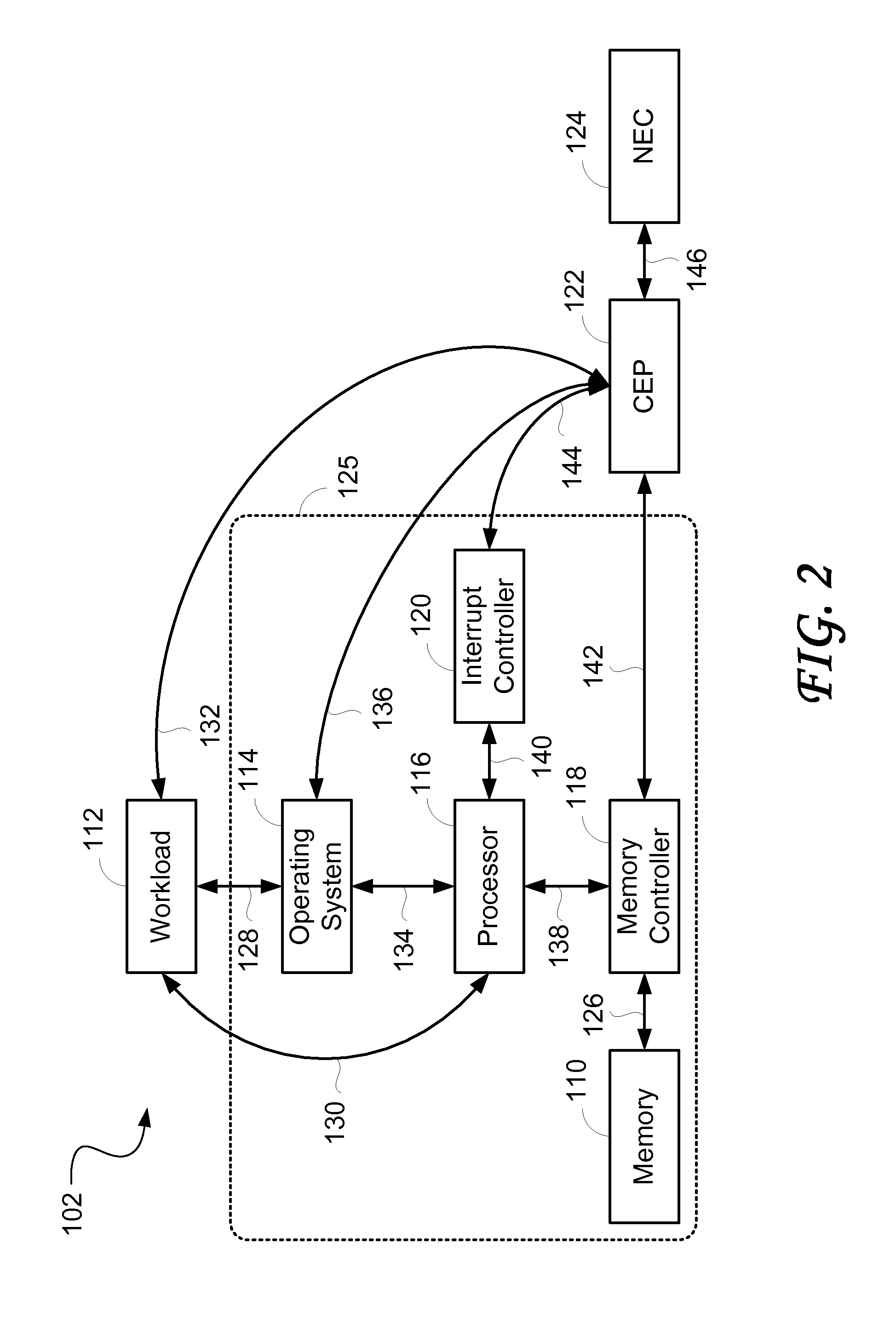
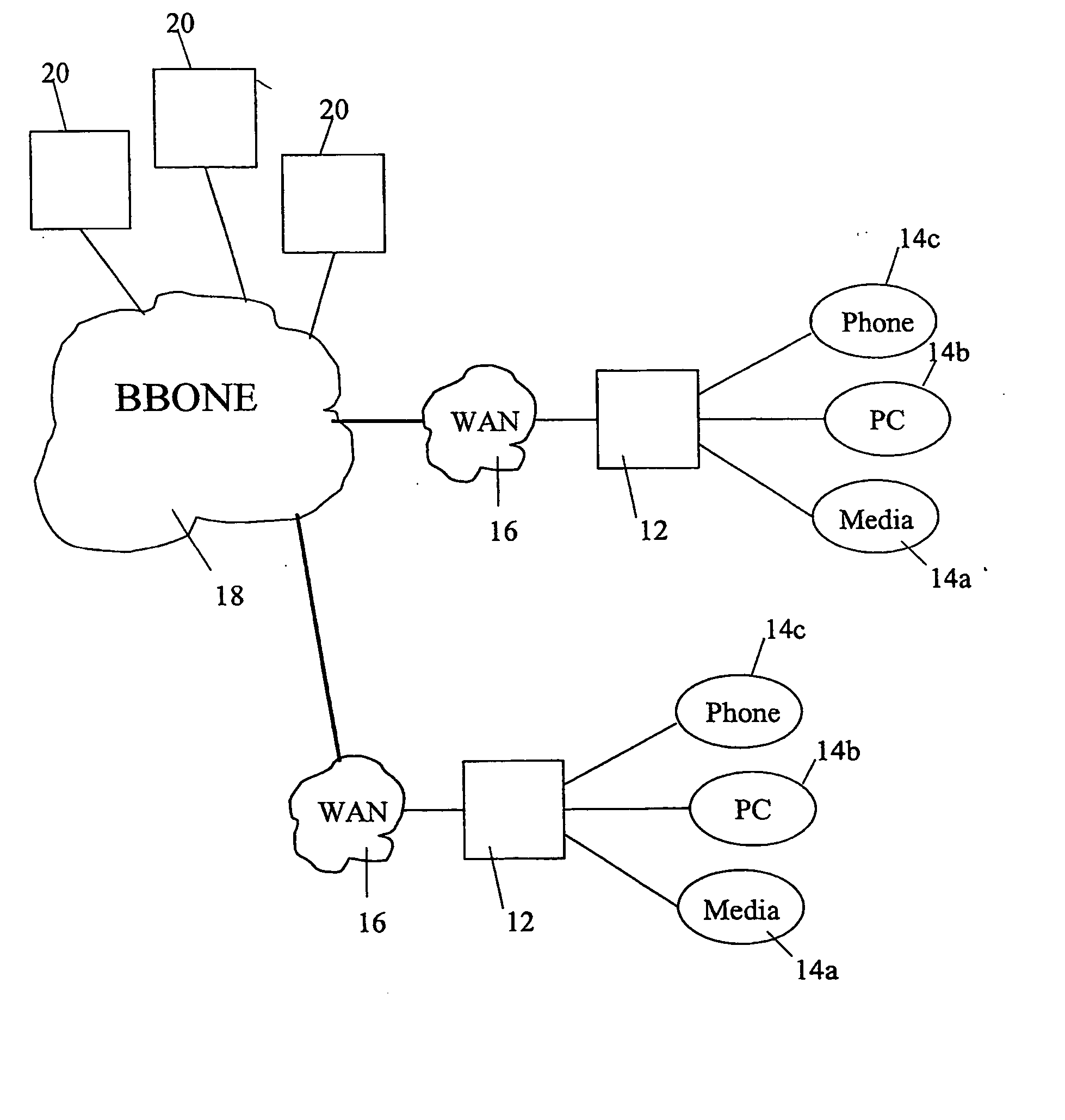
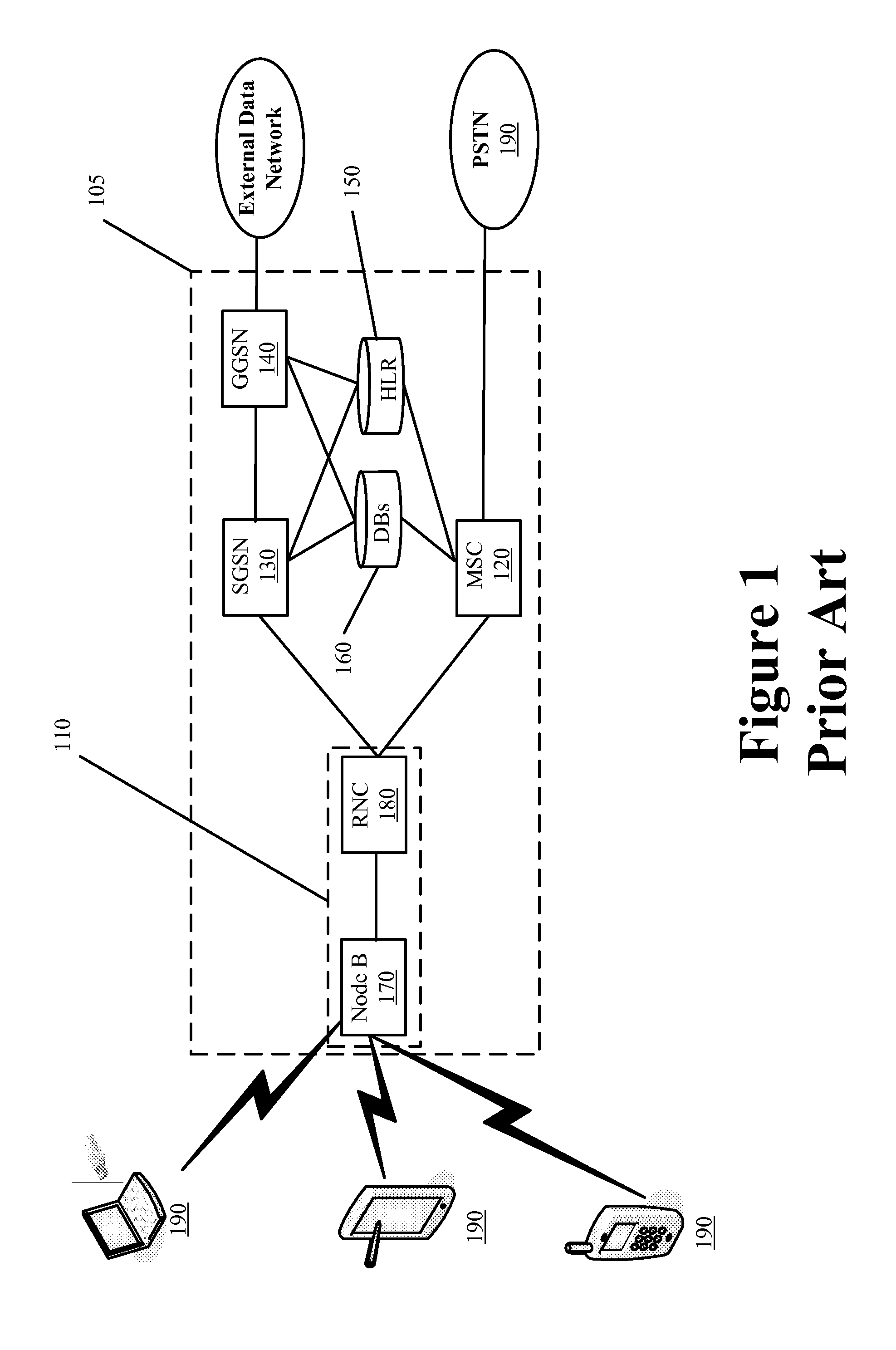
High performance memory based communications interface
ActiveUS20070223483A1Improve performanceImprove throughputTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCommunication endpointMultiple frame
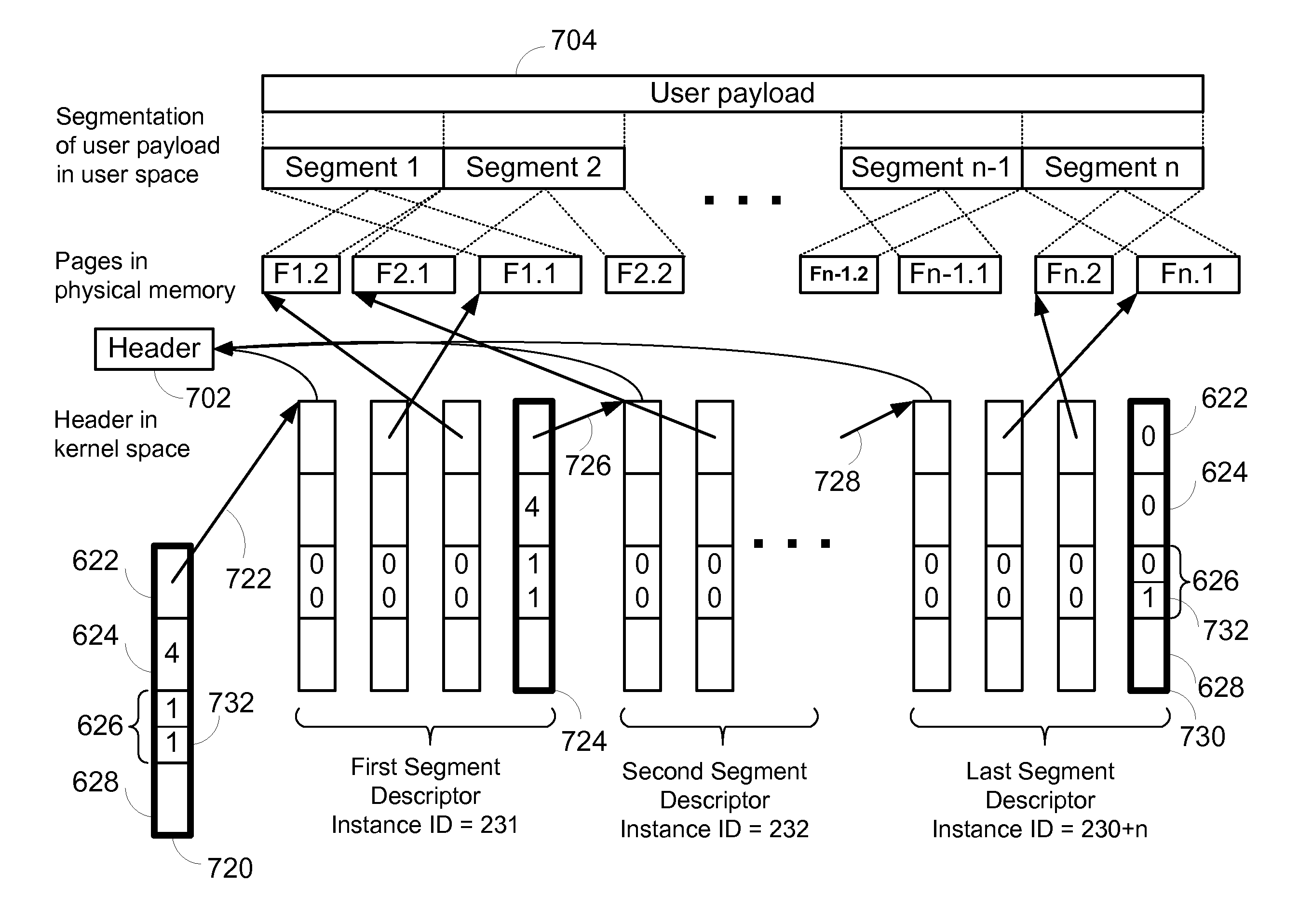
Embodiments of the present invention include enhanced functionalities and components within a Communication Endpoint Processor (CEP) that act as an interface between computational and communications domains. The embodiments disclosed herein deliver a complete memory mapped high performance interface that has the ability to support the simultaneous transmission of multiple frames of multiple sizes, and that has the ability to interrupt the transmission of lower priority frames in order to send higher priority frames.
Owner:III HLDG 1
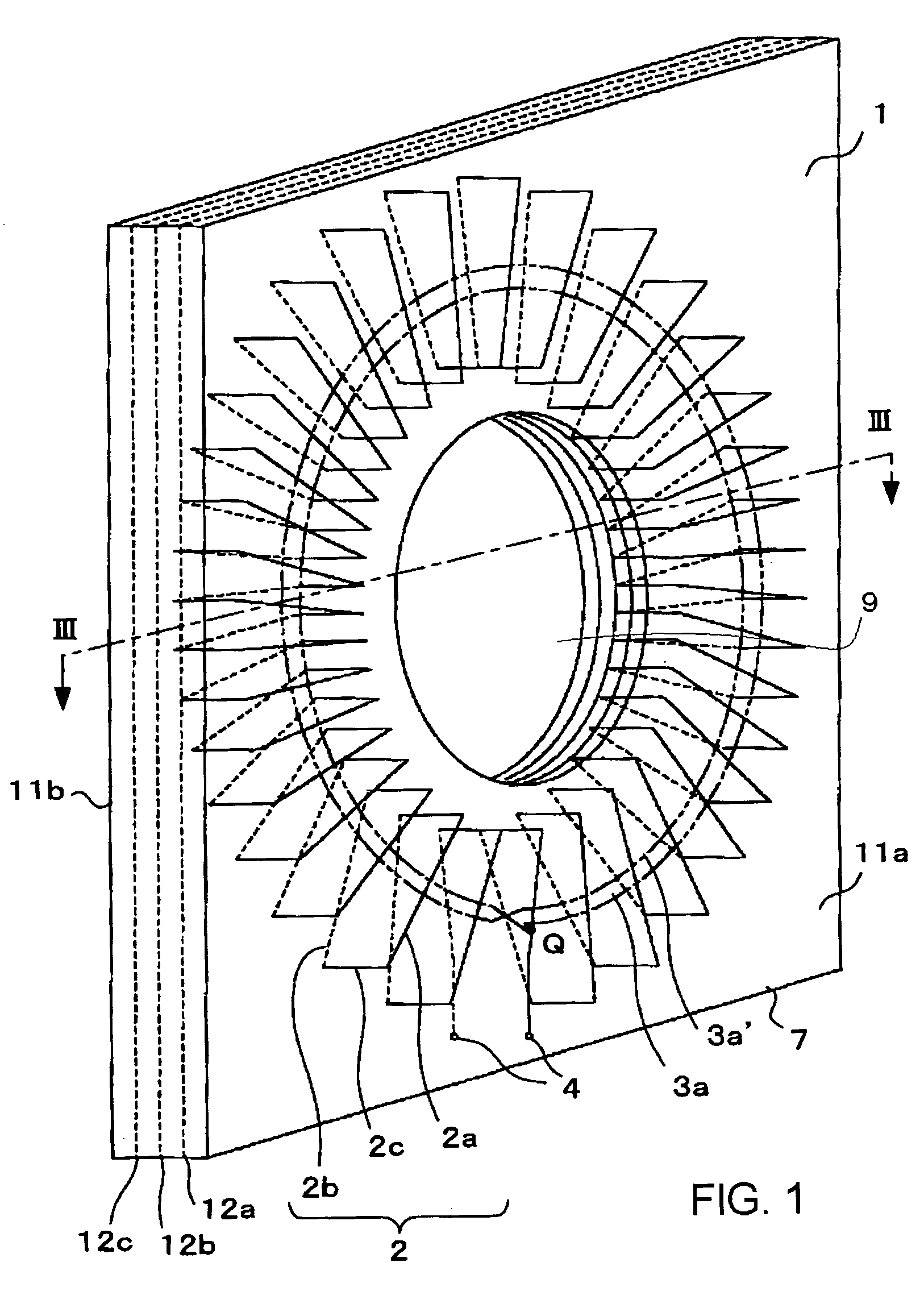
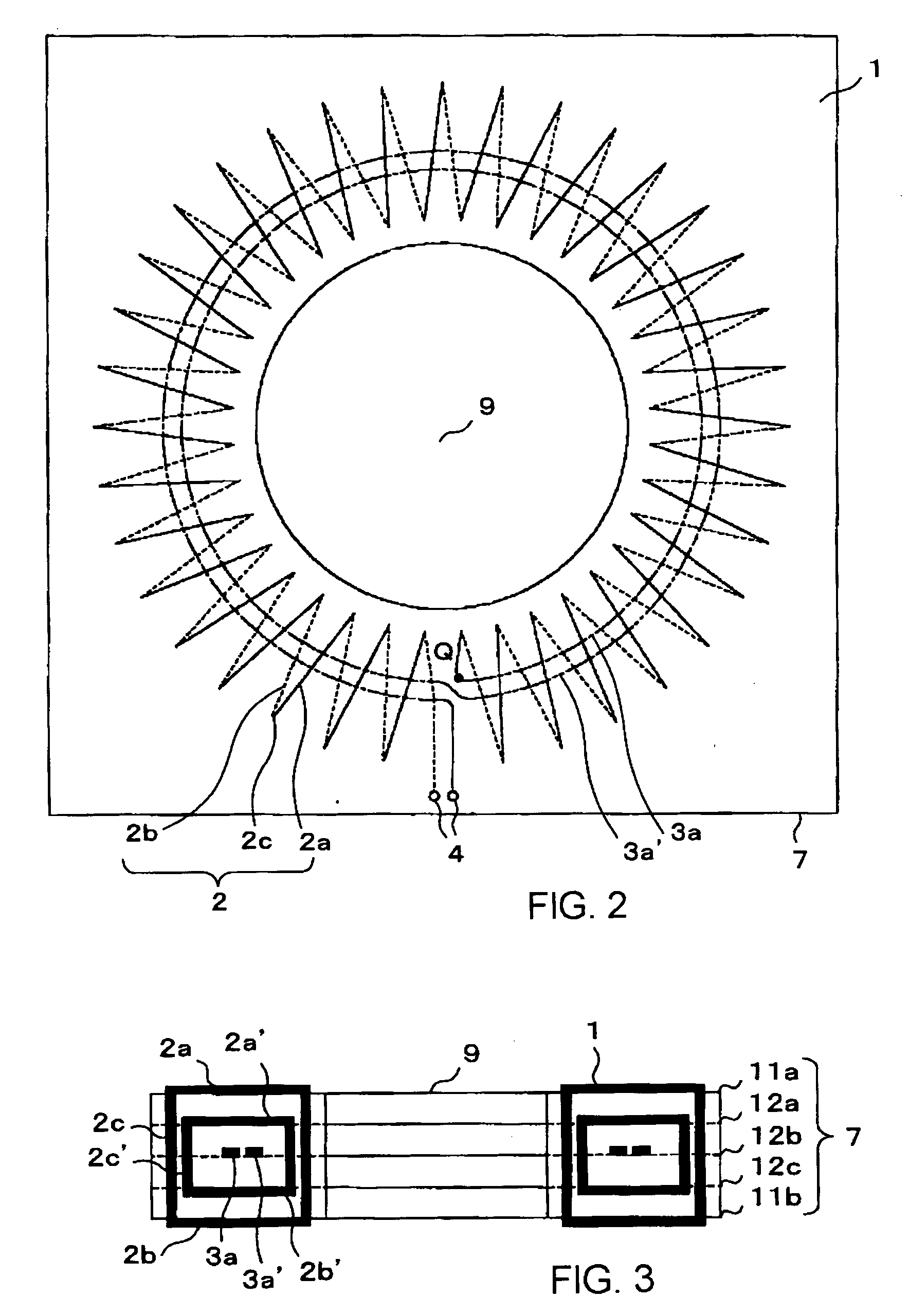
Current transformer
InactiveUS20040178875A1High measure of qualityImprove noiseTransformersCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical conductorMetal foil
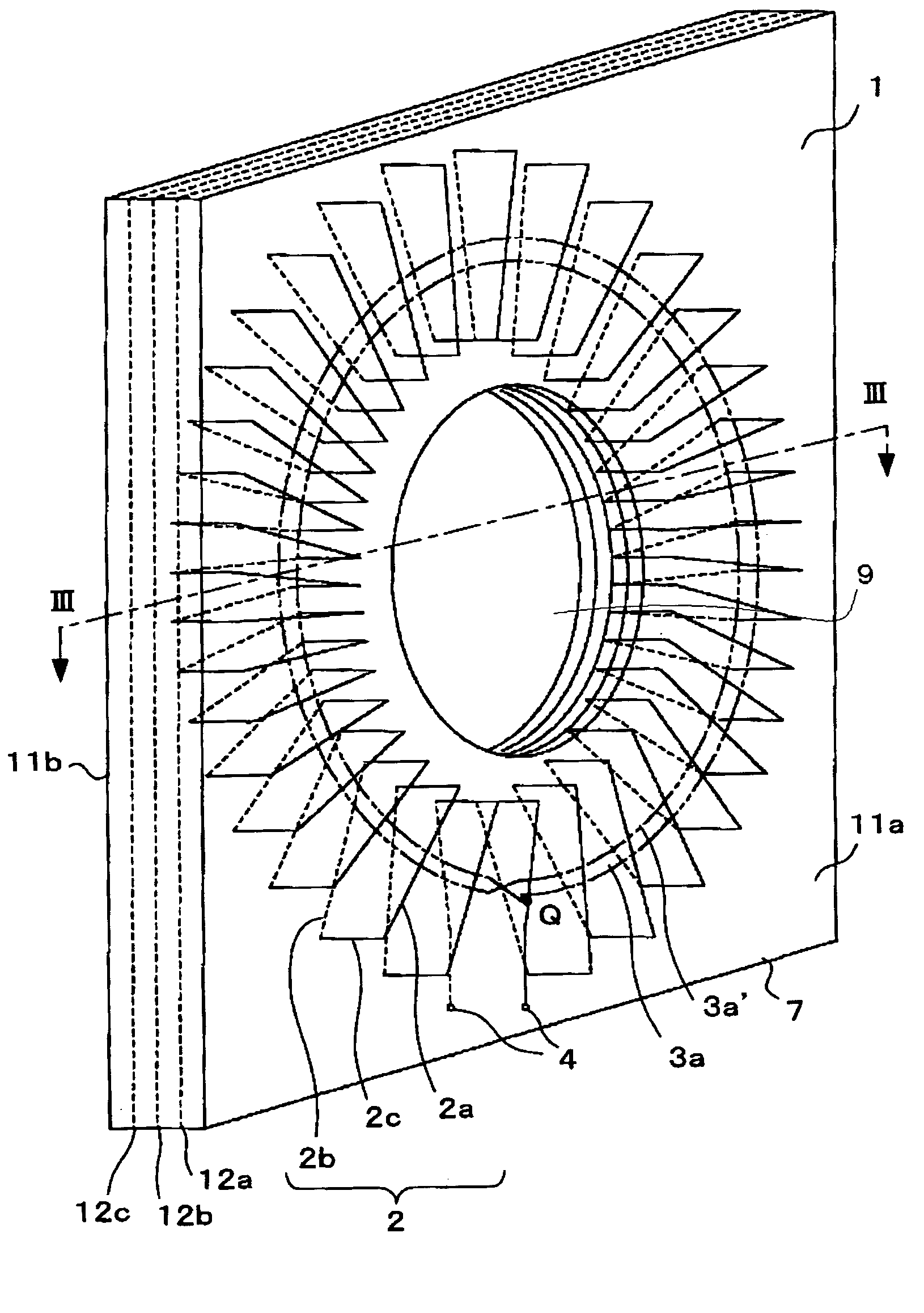
A current transformer includes a Rogowski coil, having an opening at the center in which a conductor penetrates, comprising, a printed circuit board having a plurality of layers forming at least first to fourth circuit board surfaces including a circuit board top surface, a circuit board bottom surface and circuit board conducting internal surfaces between the circuit board top surface and the circuit board bottom surface, a plurality of radial metal foils, each metal foil radiating from a center that is approximately the center of the opening, mounted on the first to fourth circuit board surfaces, a first winding formed by electrically connecting metal foils on the first and second circuit board surfaces with first plated through holes penetrating the first and second circuit board surfaces in a thickness direction of the printed circuit board, a second winding formed by electrically connecting metal foils on the third and fourth circuit board surfaces with second plated through holes penetrating the third and fourth circuit board surfaces in a thickness direction of the printed circuit board, a first return circuit line electrically connected with the first winding in series, a second return circuit line electrically connected with the second winding in series, and a pair of the first winding and the first return circuit line and a pair of the second winding and the second return circuit line being electrically connected in series.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High performance memory based communications interface
ActiveUS7773630B2Quality of serviceProvide qualityTime-division multiplexTransmissionCommunication endpointMultiple frame
Owner:III HLDG 1
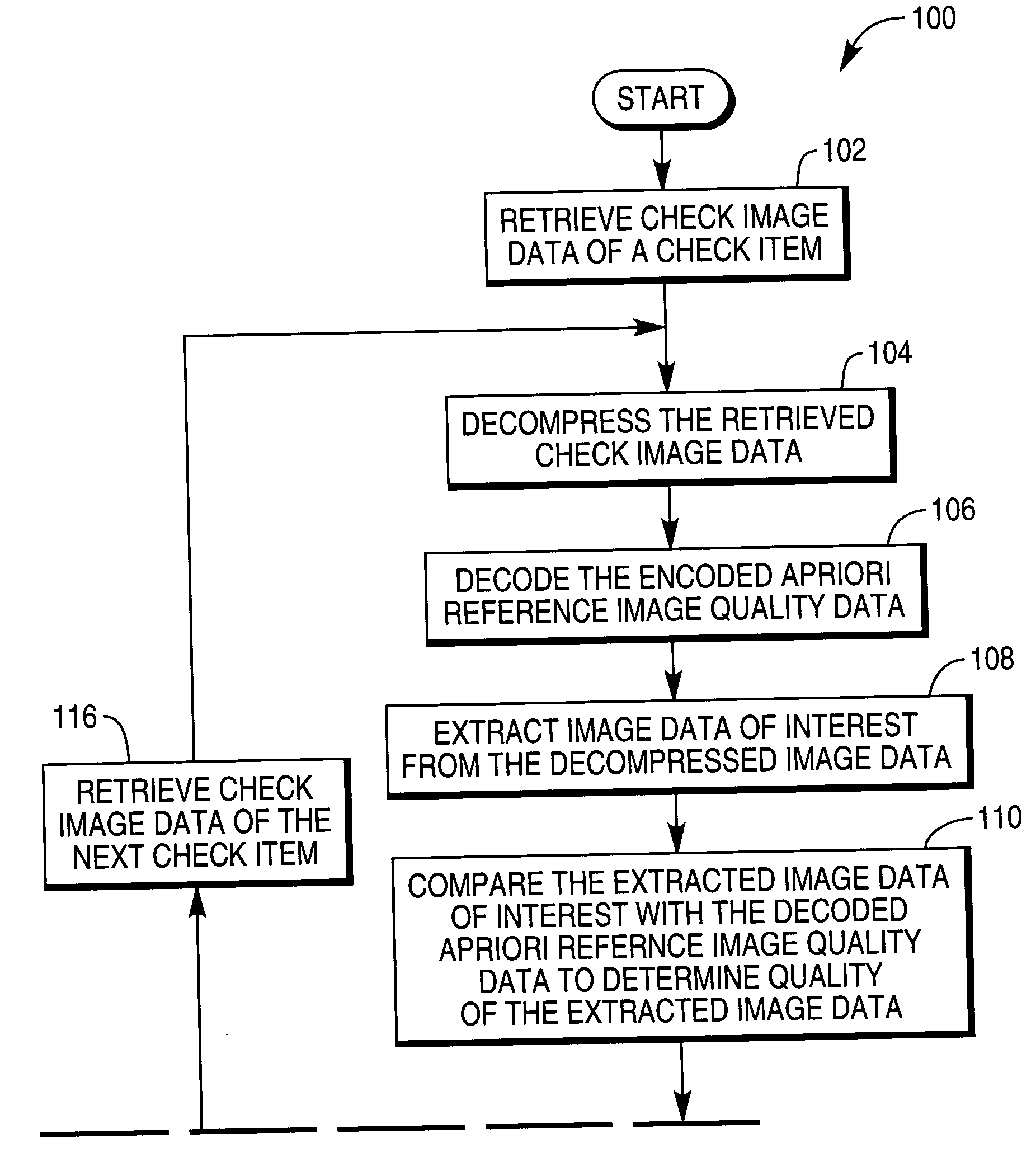
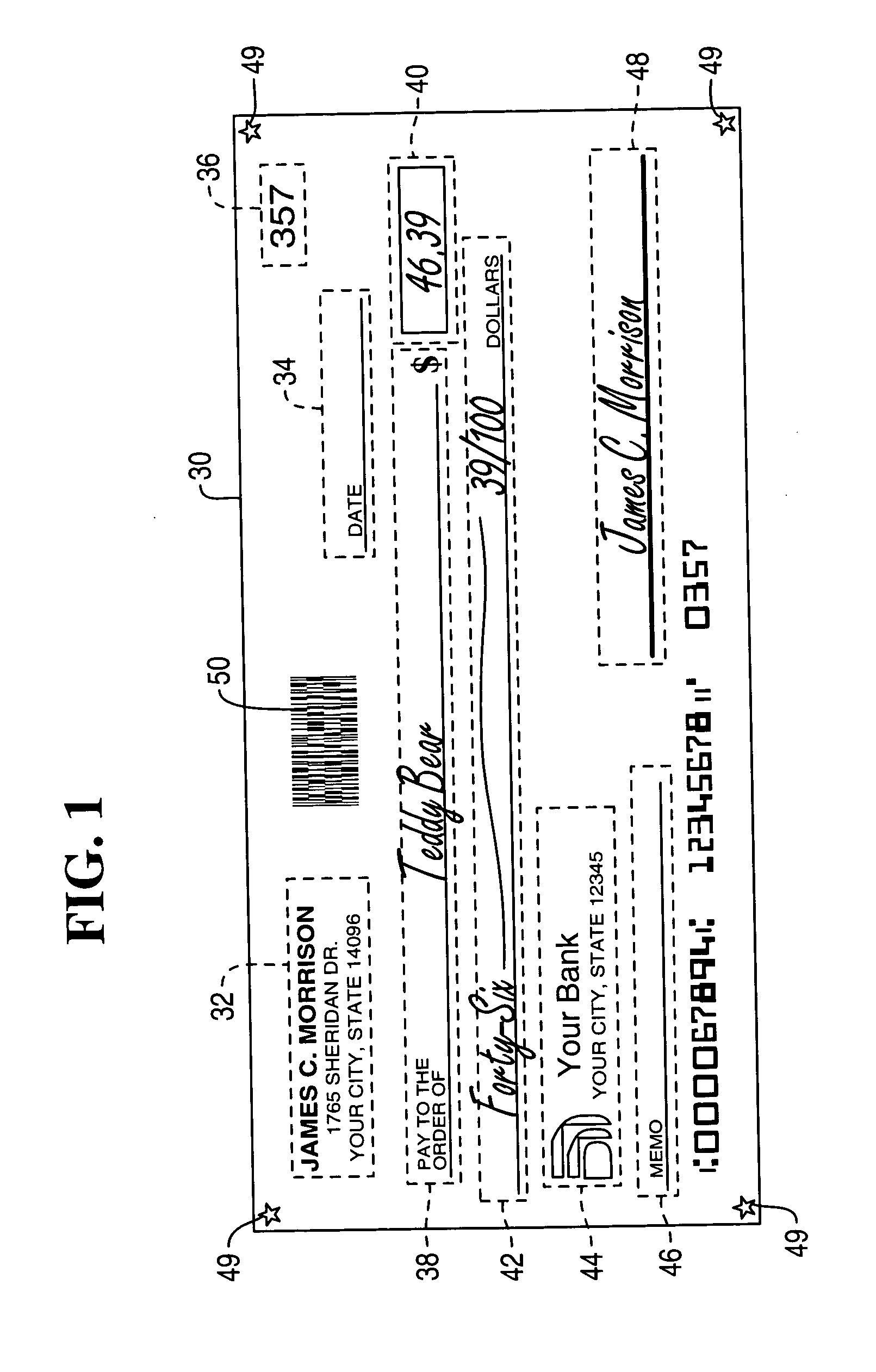
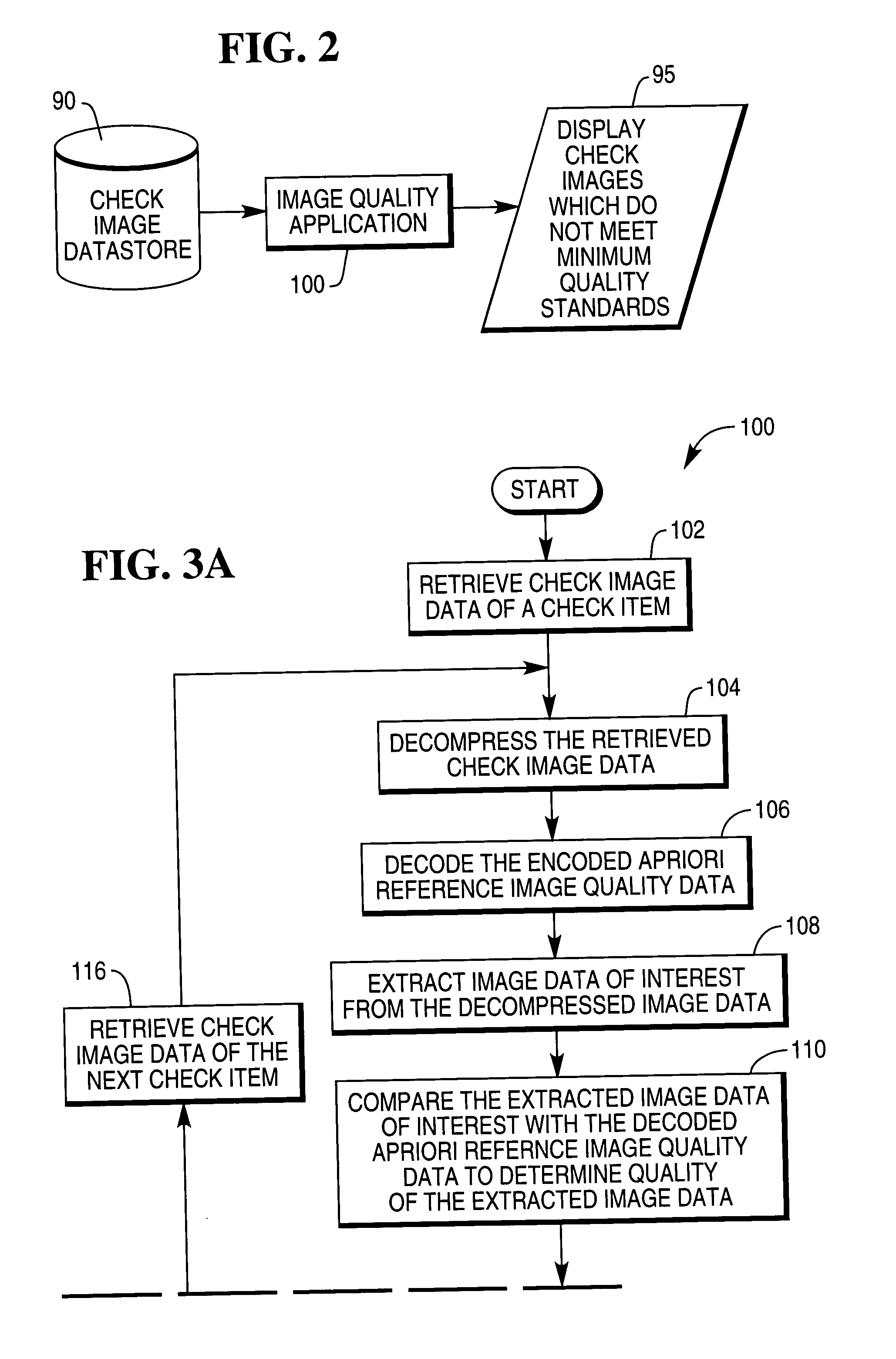
Check and method of providing apriori reference image quality data for use in determining quality of an image of a financial document
A check made of sheet material has at least one field of pre-printed information. Apriori reference image quality data which is representative of at least one characteristic of the pre-printed information contained in the at least one field is stored on the sheet material check. Alternatively, a check made of sheet material has at least one encoded symbol disposed on the sheet material. Apriori reference image quality data which is representative of at least one characteristic of the encoded symbol is stored on the sheet material of the check.
Owner:NCR CORP
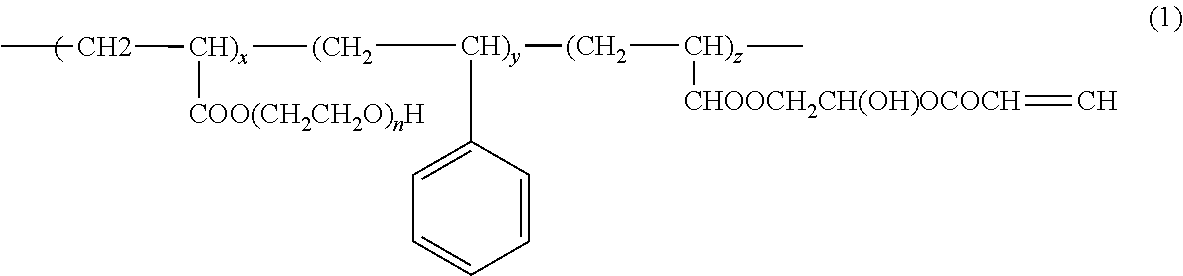
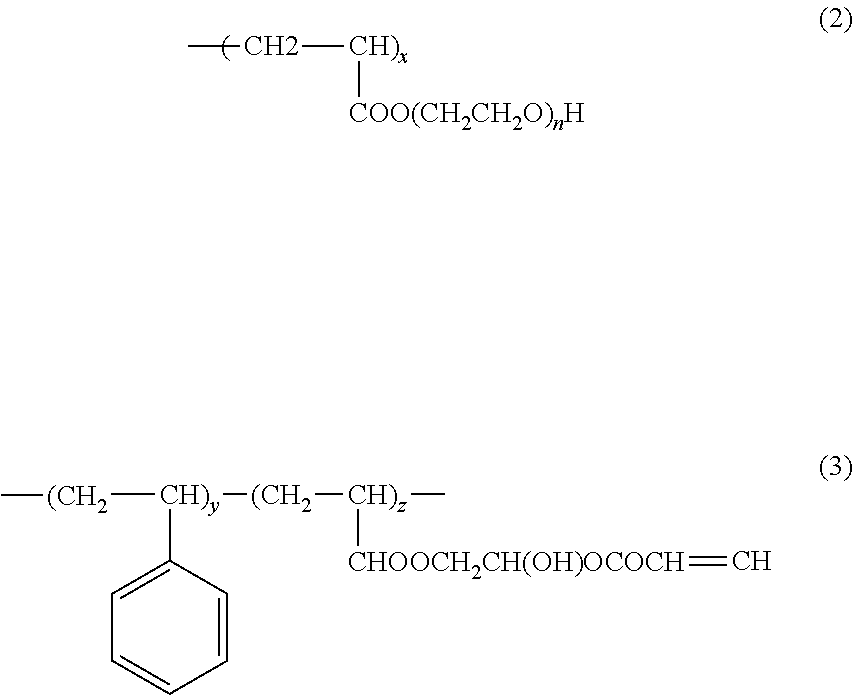
Photopolymerizable polymer micelle, method of producing the same, and ink composition containing photopolymerizable polymer micelle
A photopolymerizable polymer micelle includes a spherical micelle that encapsulates a hydrophobic photopolymerization initiator, the spherical micelle being formed by a block copolymer having a hydrophilic block segment and a hydrophobic block segment, the block copolymer having a number average molecular weight exceeding 10000, and the hydrophobic block segment at least partially having a radically polymerizable group.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
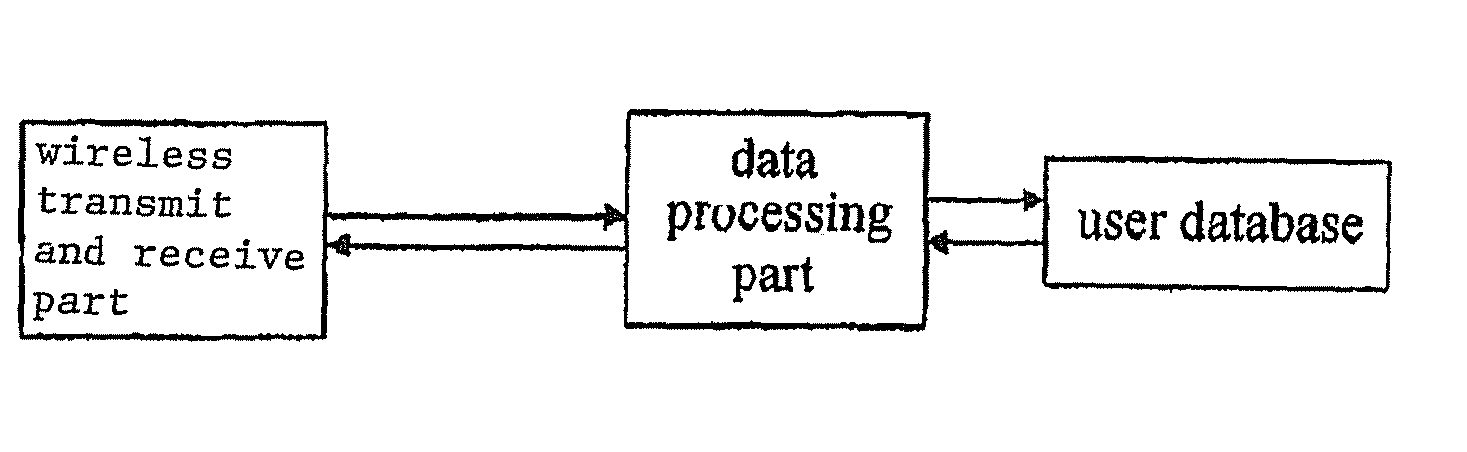
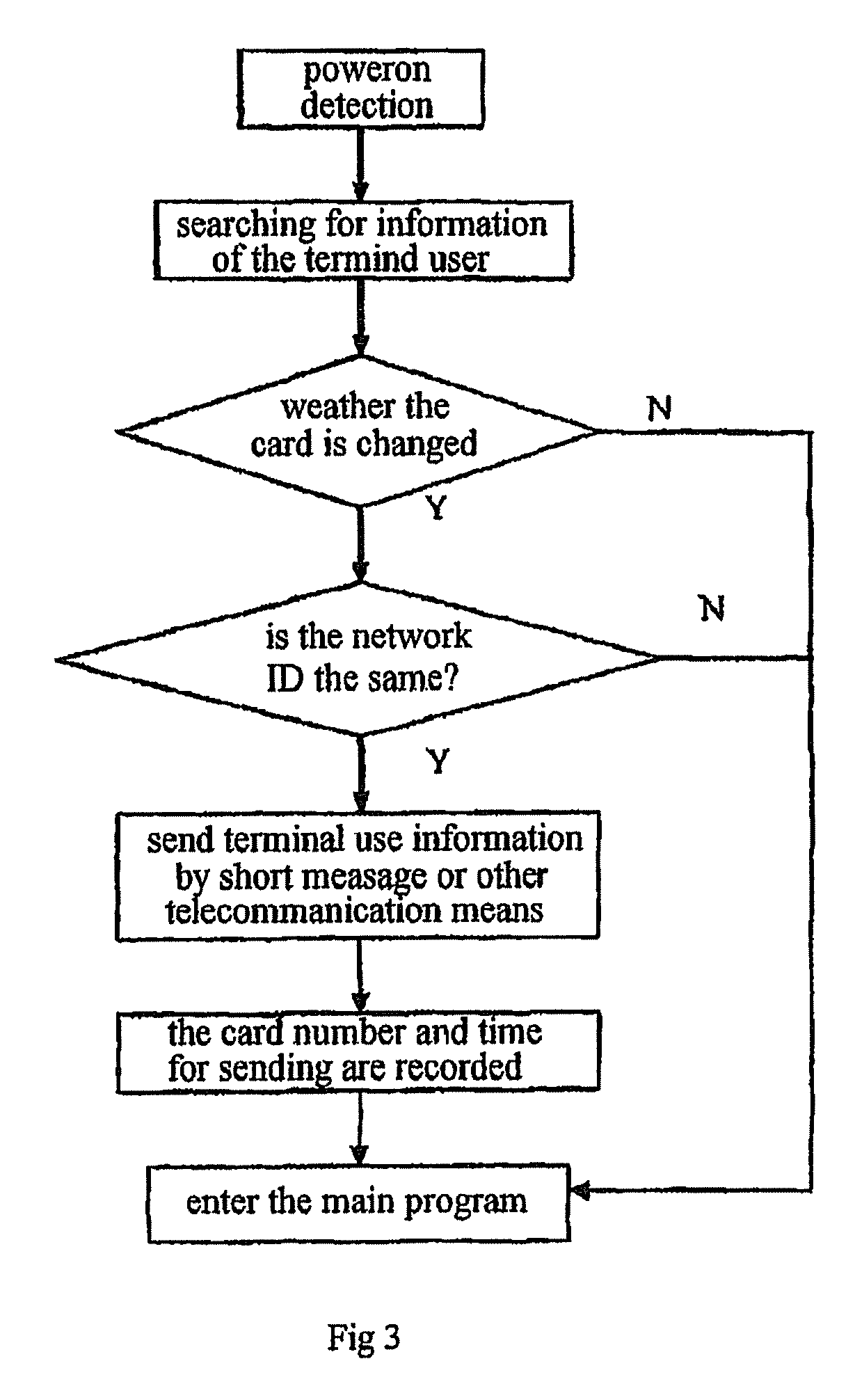
System for identifying mobile terminal device automatically and value added service access
InactiveUS7715824B2Earn incomeWide range of servicesDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationEmail addressNetwork communication
An automatic identification system of mobile terminal equipment, which consists of the mobile terminal equipment, mobile network communication platform and mobile terminal equipment service center. The mobile terminal equipment is provided with subscriber information handling means for transmitting terminal subscribers information to mobile terminal service center through communication channels of the mobile network communication platform. The mobile terminal equipment service center compares the terminal subscriber information with that in its database and then identifies and processes said terminal subscribers information. The terminal subscriber information includes the electronic serial number, terminal subscriber ID identification, terminal software version number and any one or any combination of two or more of the followings: network ID identification, base station number, short message center number Email address, LP internet protocol address and the information of registration place in subscriber identification card.
Owner:HANGZHOU EASYCOMM TECH
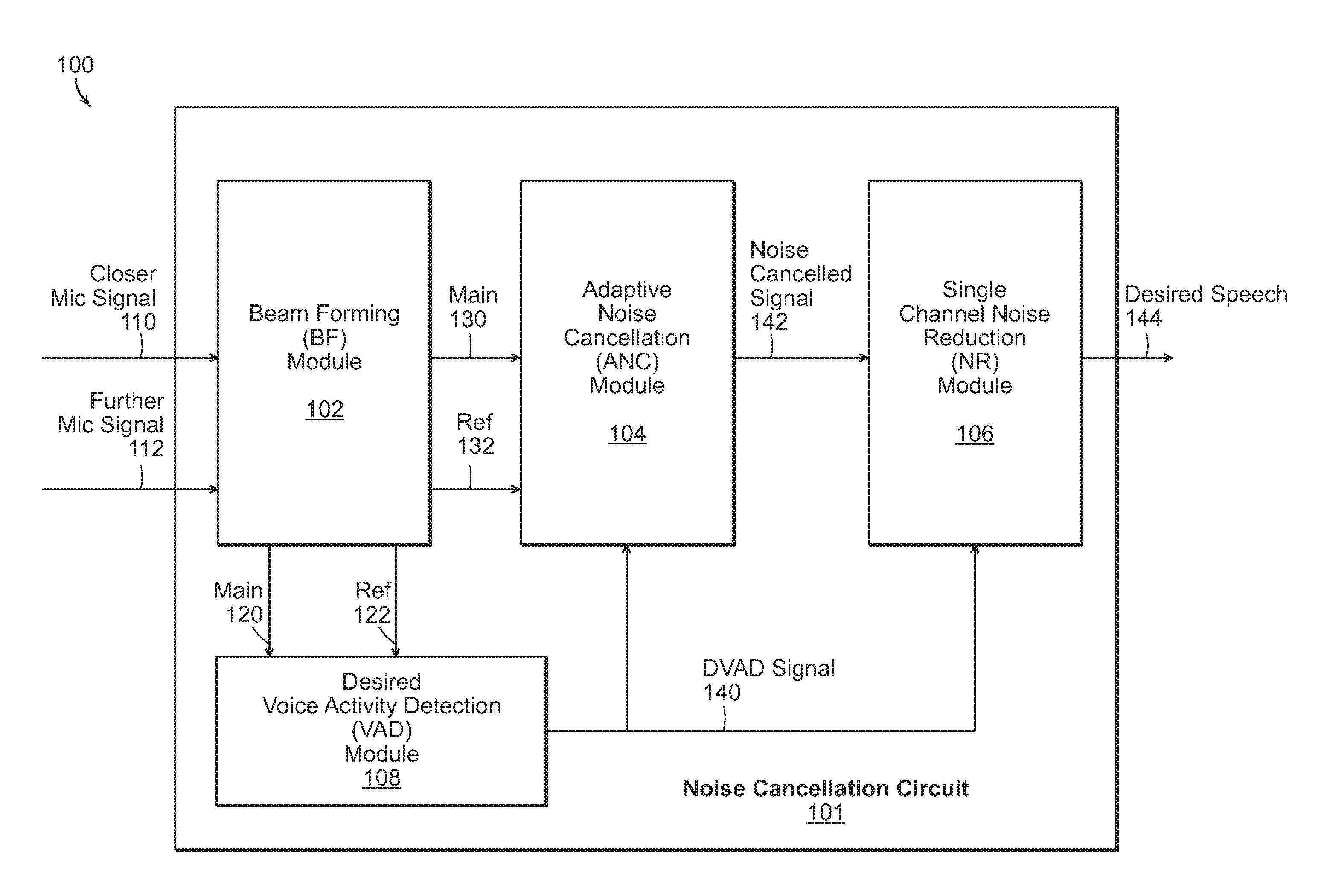
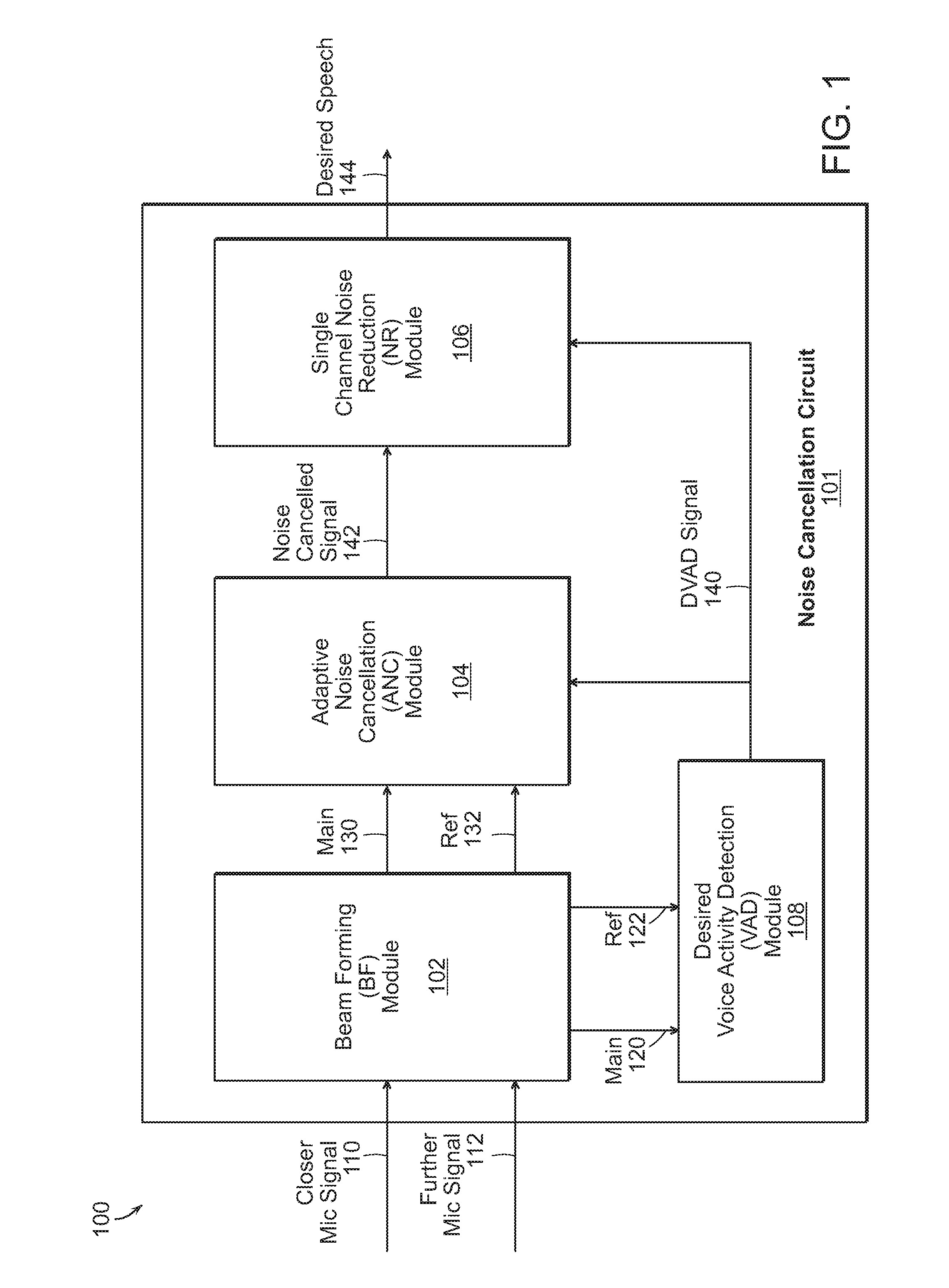
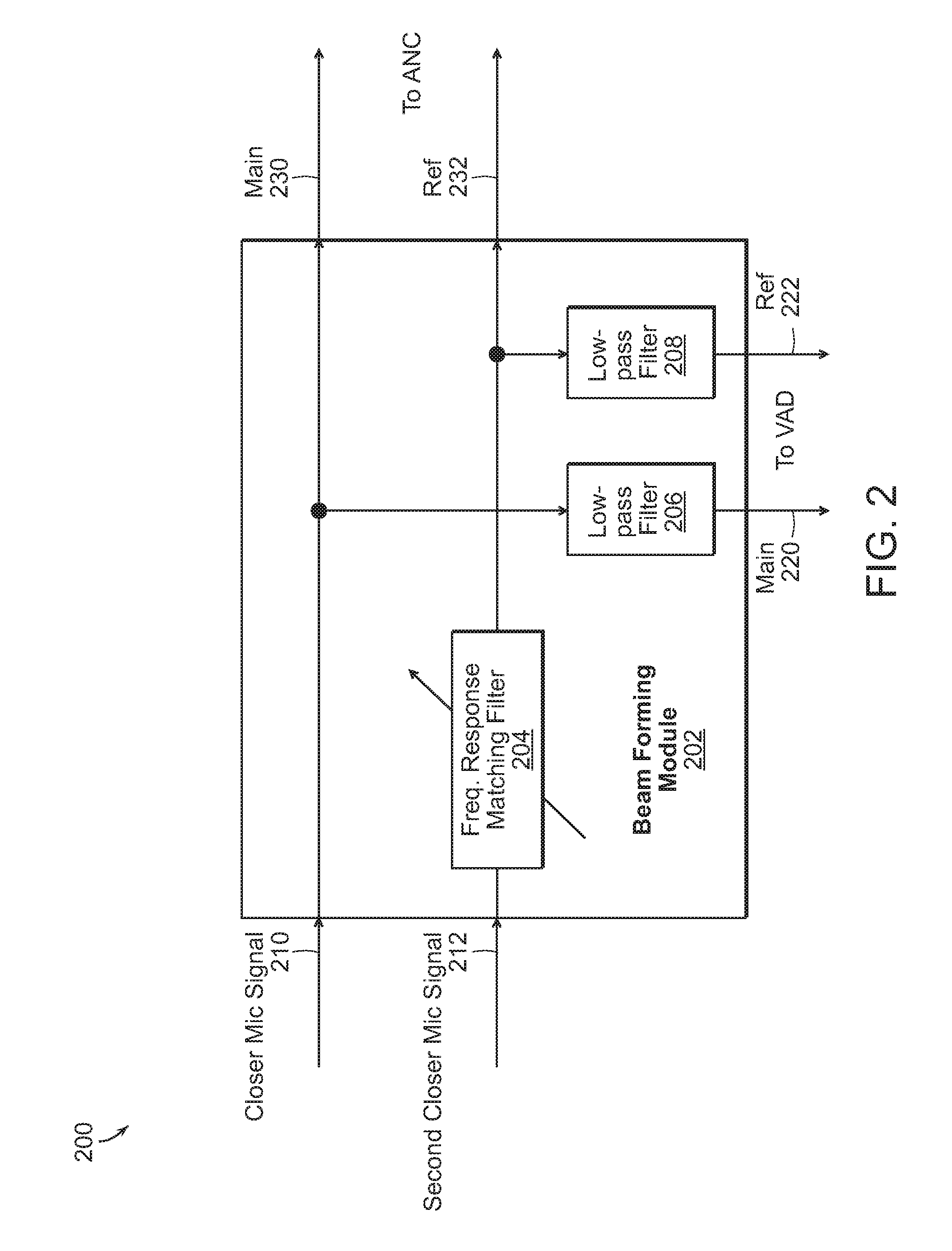
Noise Cancelling Microphone Apparatus
ActiveUS20140278385A1Improves accurate recognition of speechMinimizing unwanted noiseNon-optical adjunctsSpeech analysisReducerEngineering
Example embodiments include a method of reducing noise include forming a main signal and one or more reference signals at a beam-former based on at least two received audio signals, detecting voice activity at a voice activity detector, where the voice activity detector receives the main and reference signals and outputting a desired voice activity signal, adaptively cancelling noise at an adaptive noise canceller, where the adaptive noise canceller receives the main, reference, and desired voice activity signals and outputs an adaptive noise cancellation signal, and reducing noise at a noise reducer receiving the desired voice activity and adaptive noise cancellation signals and outputting a desired speech signal.
Owner:SOLOS TECH LTD
Adaptive ethernet switch system and method
ActiveUS20050063391A1Provide qualityImprove service qualityEnergy efficient ICTError preventionAdaptive servicesQuality of service
The invention relates to switch based aggregation system, method and computer program product for providing Quality of Service (QoS) to a layer 2 configured network comprising a connection oriented switching means connected to a Wide Area Network (WAN). The system comprises an Adaptive Quality of Service (AQS) means connected to said switching means. The Adaptive Quality of Service (AQS) means comprises monitoring means for monitoring the total IP data throughput stream and the RTCP reports in the system, filtering means being capable of filtering the total IP data throughput stream and controlling means for controlling said filtering means depending on the monitoring of the total IP data throughput and adaptable filter criteria.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
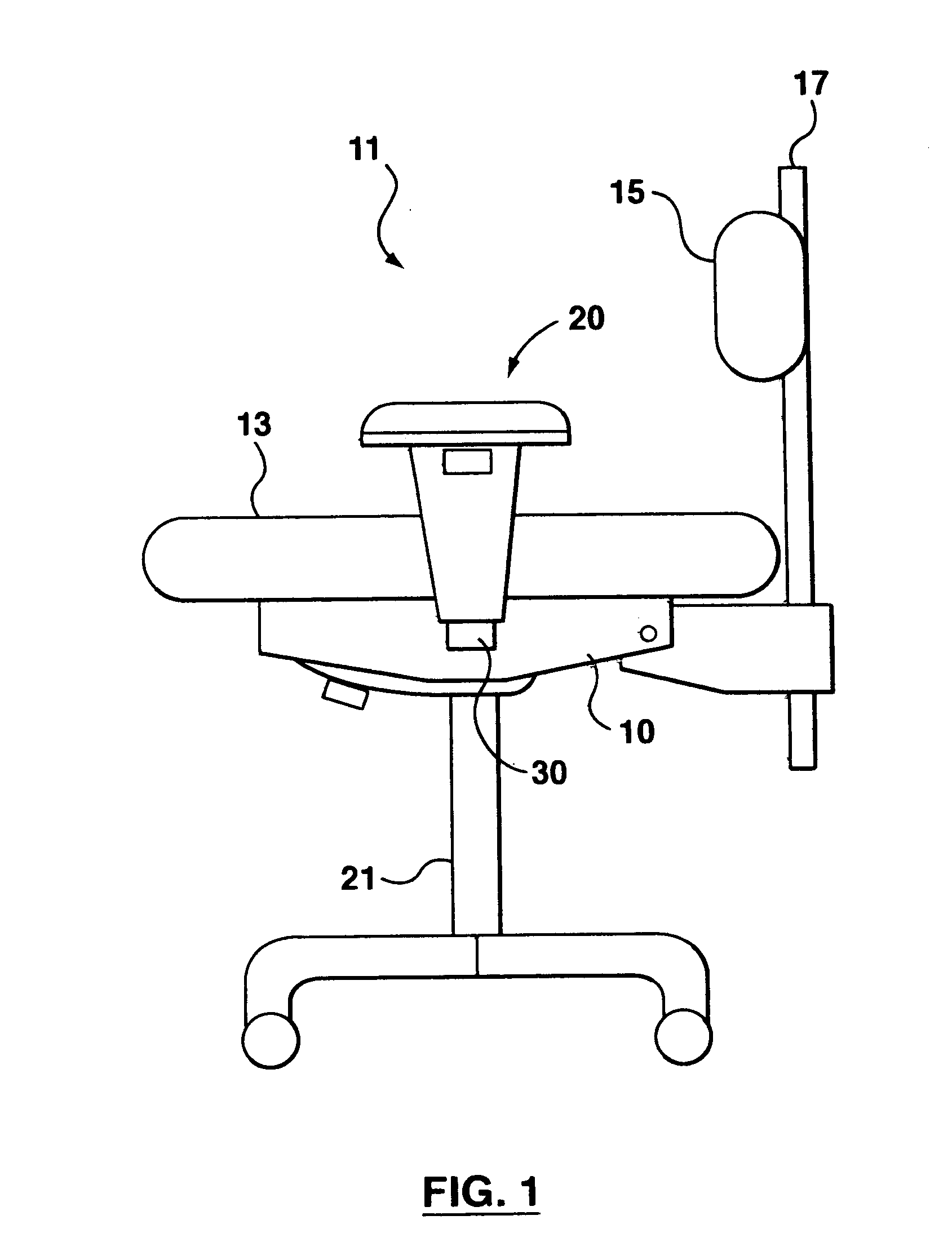
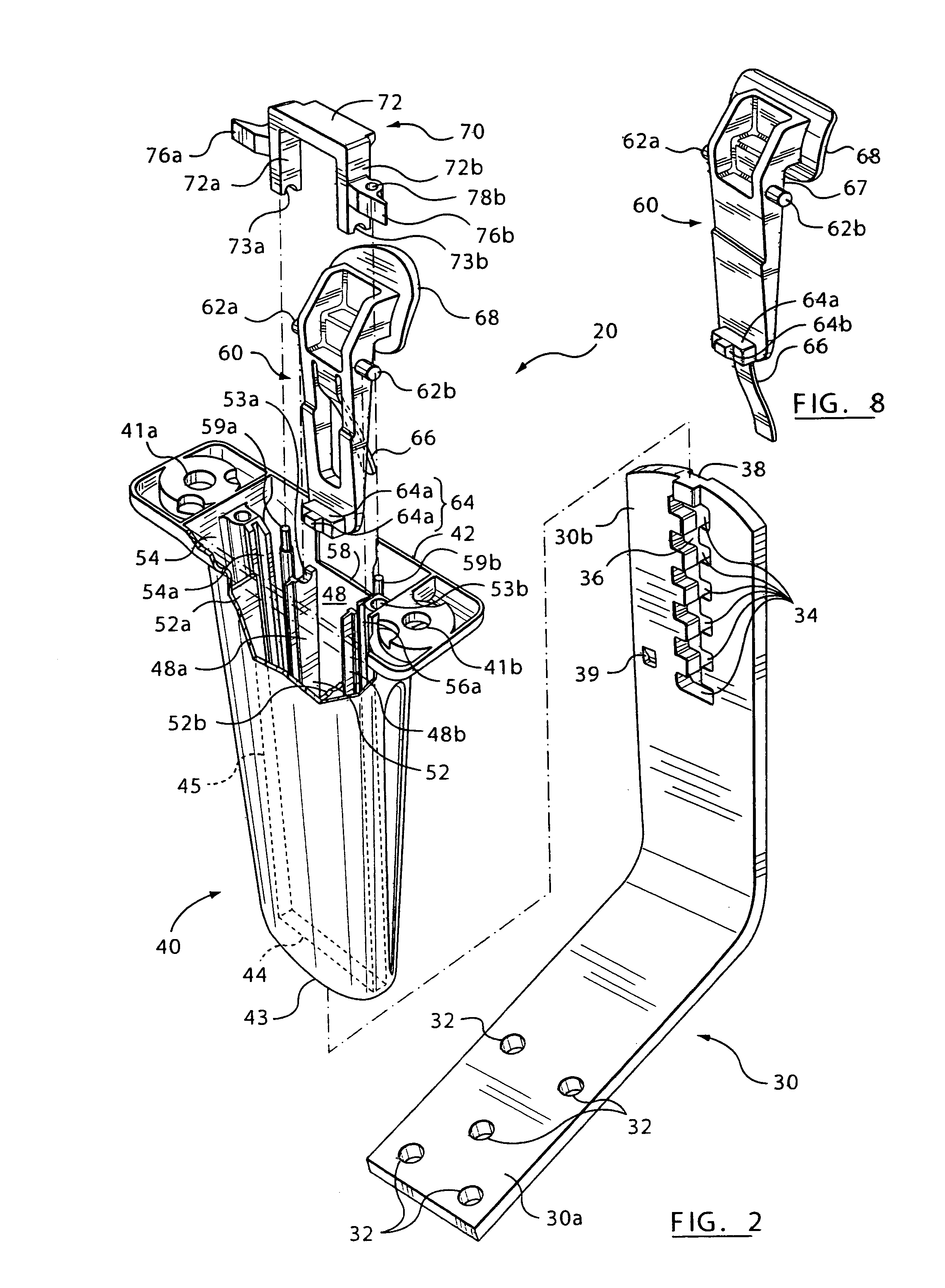
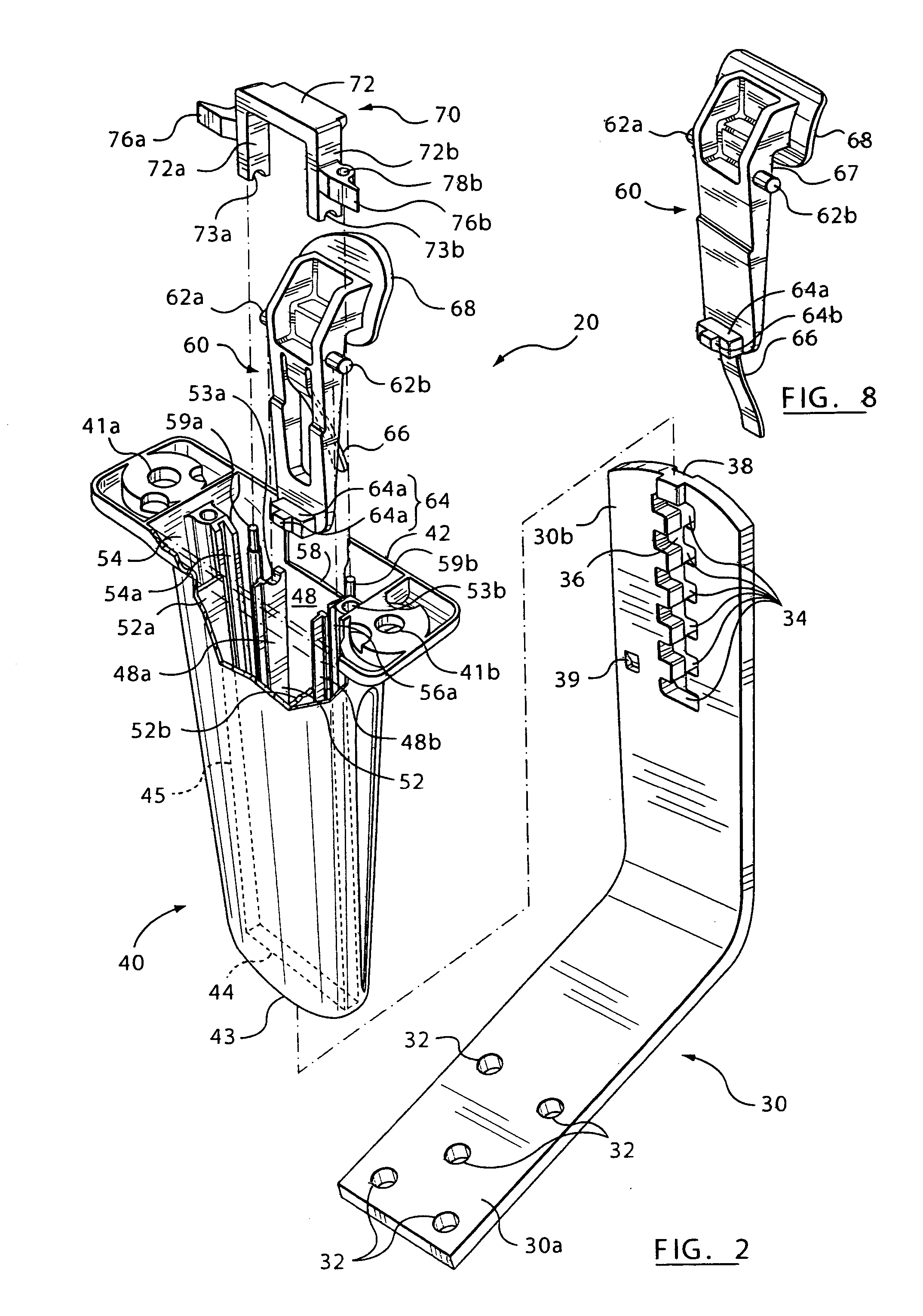
Height-adjustment mechanism for an armrest
A height-adjustment mechanism may include an integral one-piece leverage body; an integral one-piece sleeve; and a locking member. In an embodiment, the integral one-piece leverage body has a handle, a pair of pivot pins projecting from opposed sides, a tongue projecting rearwardly, and a resilient biasing member projecting forwardly. These parts may be made of low cost materials suitable for integrally forming their features in an injection-moulding operation. Various features built in to these parts may provide a user with a sense of quality.
Owner:LEGGETT & PLATT CANADA
Fire protection cover apparatus for structures
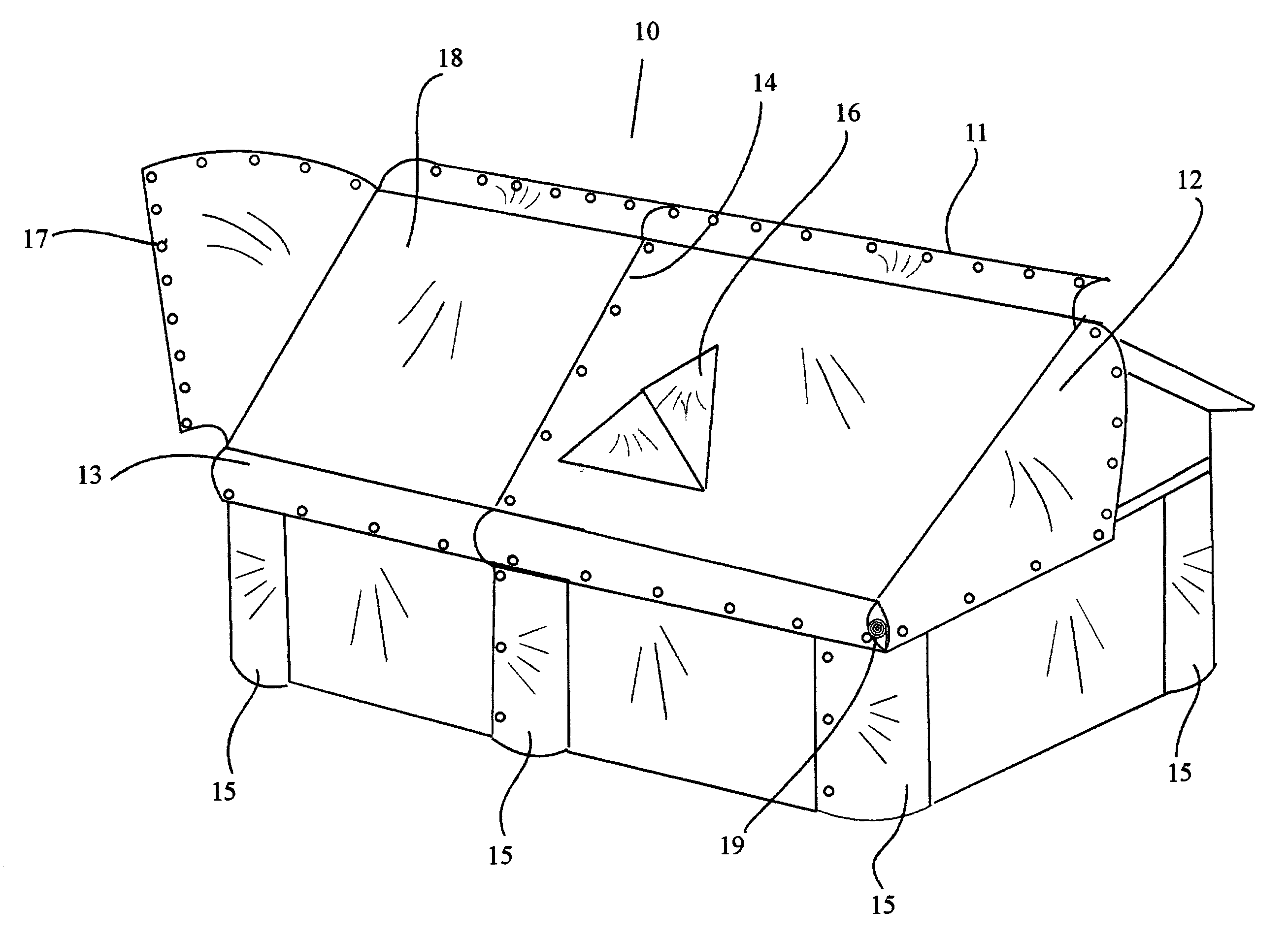
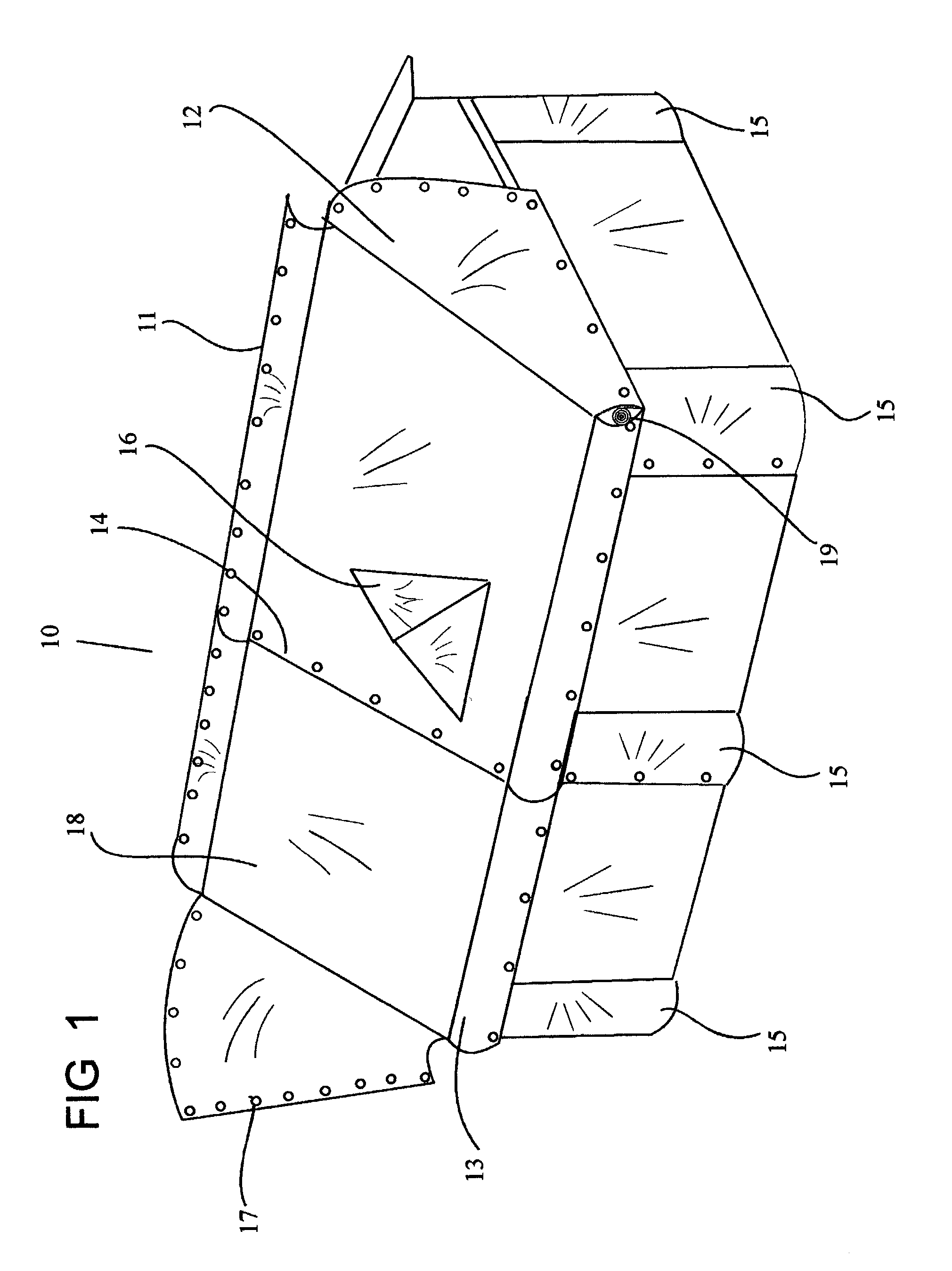
InactiveUS20040074152A1Deployed and retracted with easeAffordable costSunshadesShutters/ movable grillesFastenerFire protection
An apparatus, a wildfire protection method for houses and other structures from the destructive forces of a wildland fire. The current form of the preferred embodiment consists of a highly fireproof material, which is pre-fitted to cover each area of structure including gables or dormers one section at a time. The material is contained on a fireproof deployment apparatus such as a roller means having a retractable mechanism. The deployment apparatus is contained and secured within a housing, this housing being supported by firmly mounting it to strategic areas of the architectural structure. Once installed, deployment of the fireproof covering material is accomplished by unrolling the material from one side of the fireproof deployment apparatus. Each pre-fitted section of fireproof material contains reinforced edges, which are fitted with multiple fasteners by which to attach one section of said fireproof material to another as each is deployed from a series of apparatus. Each section of material is deployed in sequence and fastened to other nearby sections. The fireproof material once deployed by sections and fastened over the entire structure will provide protection from the high heat and burning embers associated with wildfires. Total structure coverage is accomplished very quickly by using several of these apparatus in series, each of which are strategically attached to the structure architecture.
Owner:ROGERS WILLIAM +1
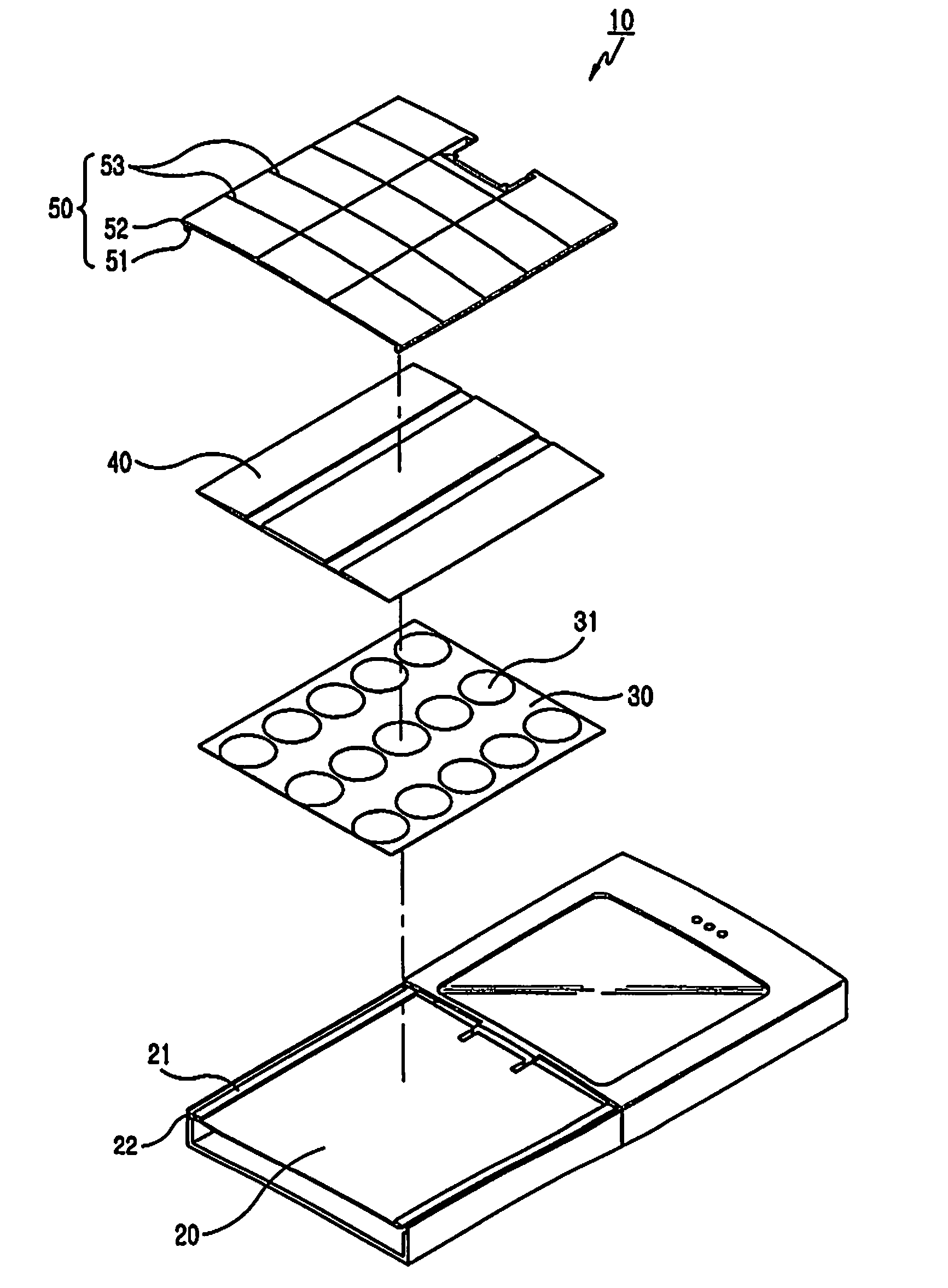
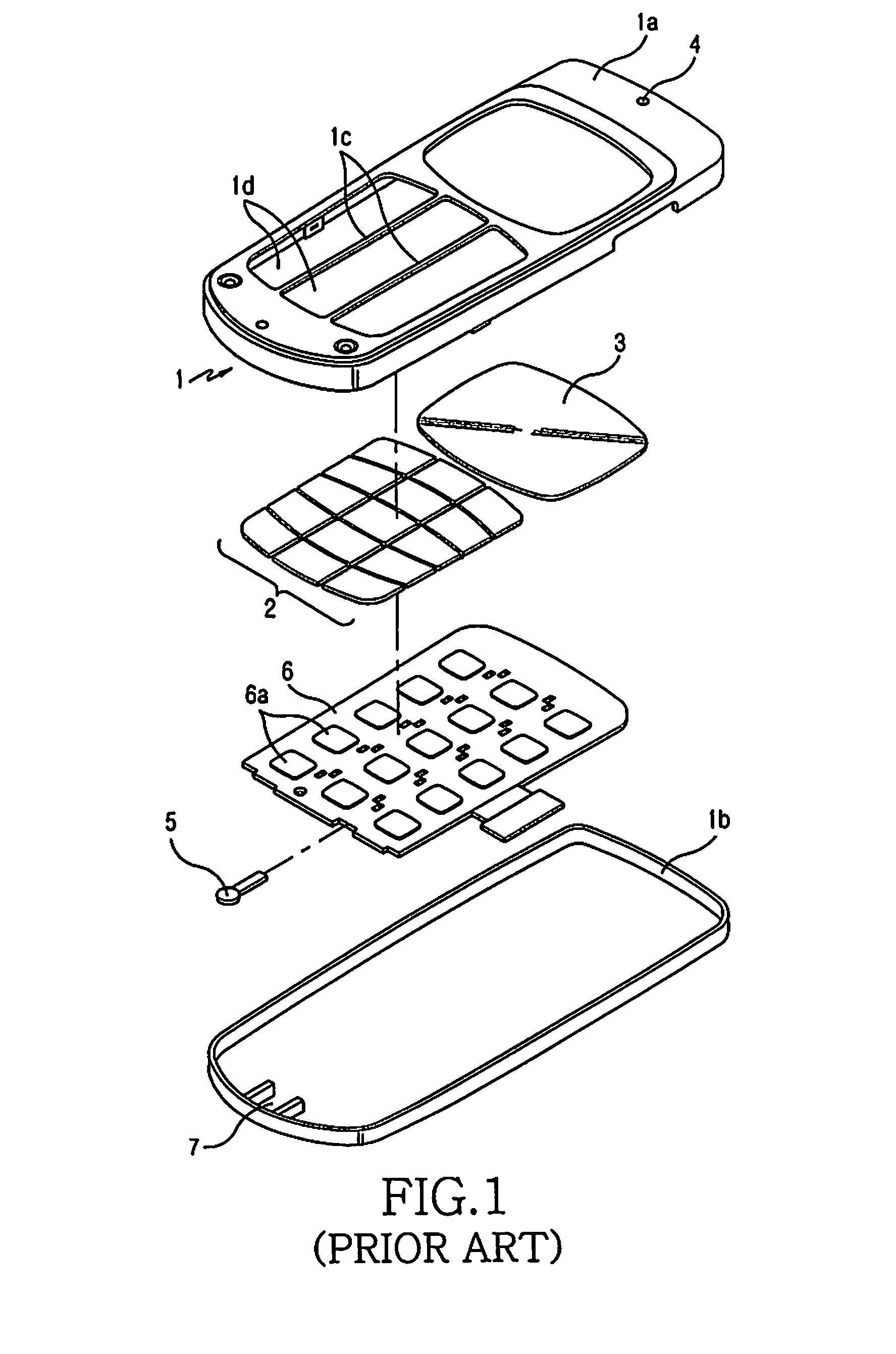
Keypad coupling apparatus for portable terminal
InactiveUS7579561B2Shorten the timeSlimness and miniaturization of the portable terminalInput/output for user-computer interactionEmergency actuatorsFlexible circuitsCoupling
Disclosed is a keypad coupling apparatus for a portable terminal which has a laminated keypad unit arranged on an upper surface of a front case. The keypad coupling apparatus includes a front case provided with a latch; a flexible circuit disposed on the front case and including a plurality of dome switches; a keypad rubber disposed on an upper surface of the flexible circuit; and a keypad provided on an upper surface of the keypad rubber and moving in a pressed direction when the keypad is engaged with the latch and pressed, the keypad rubber making contact with at least one of the dome switches to provide tactile quality of a click.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
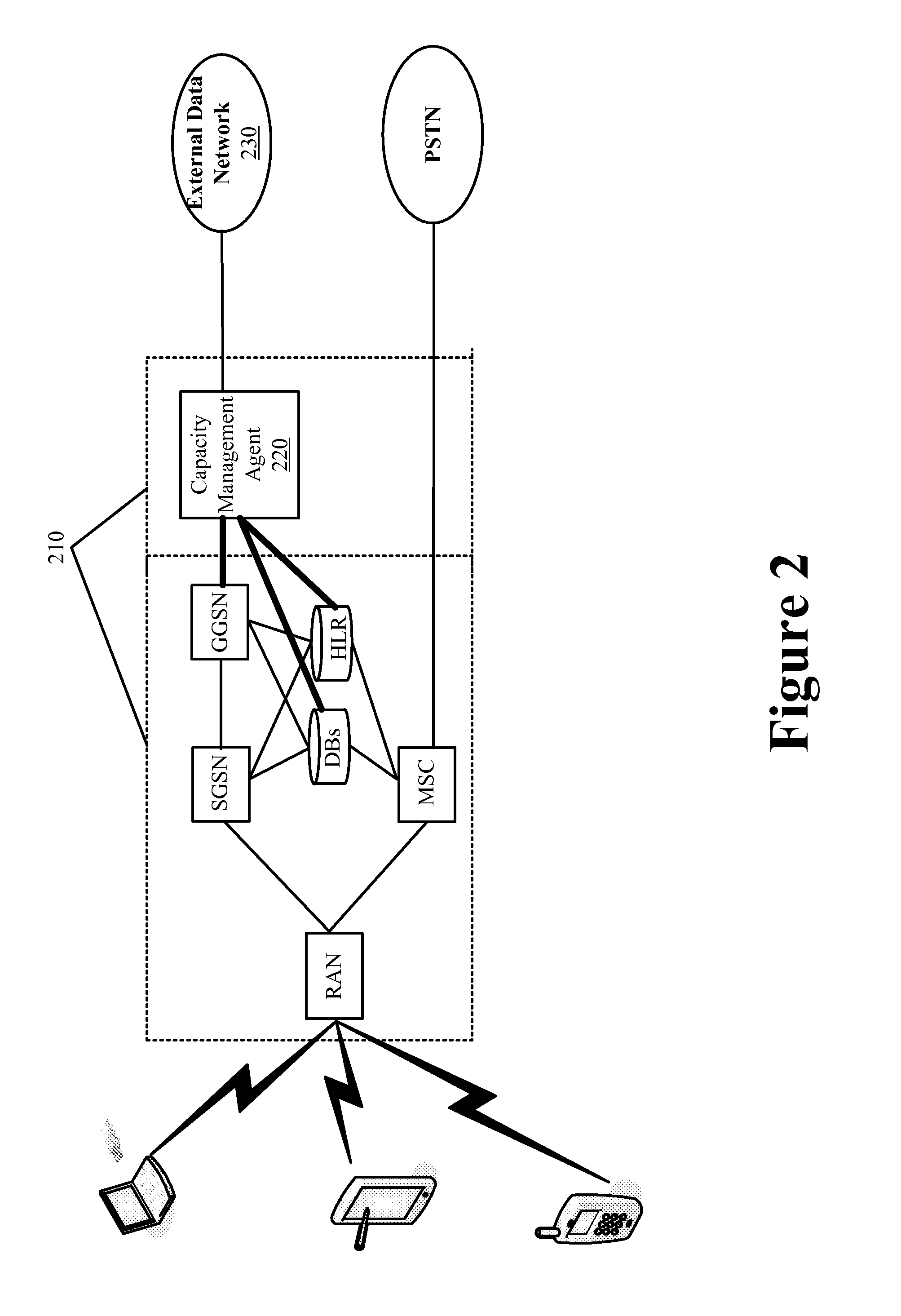
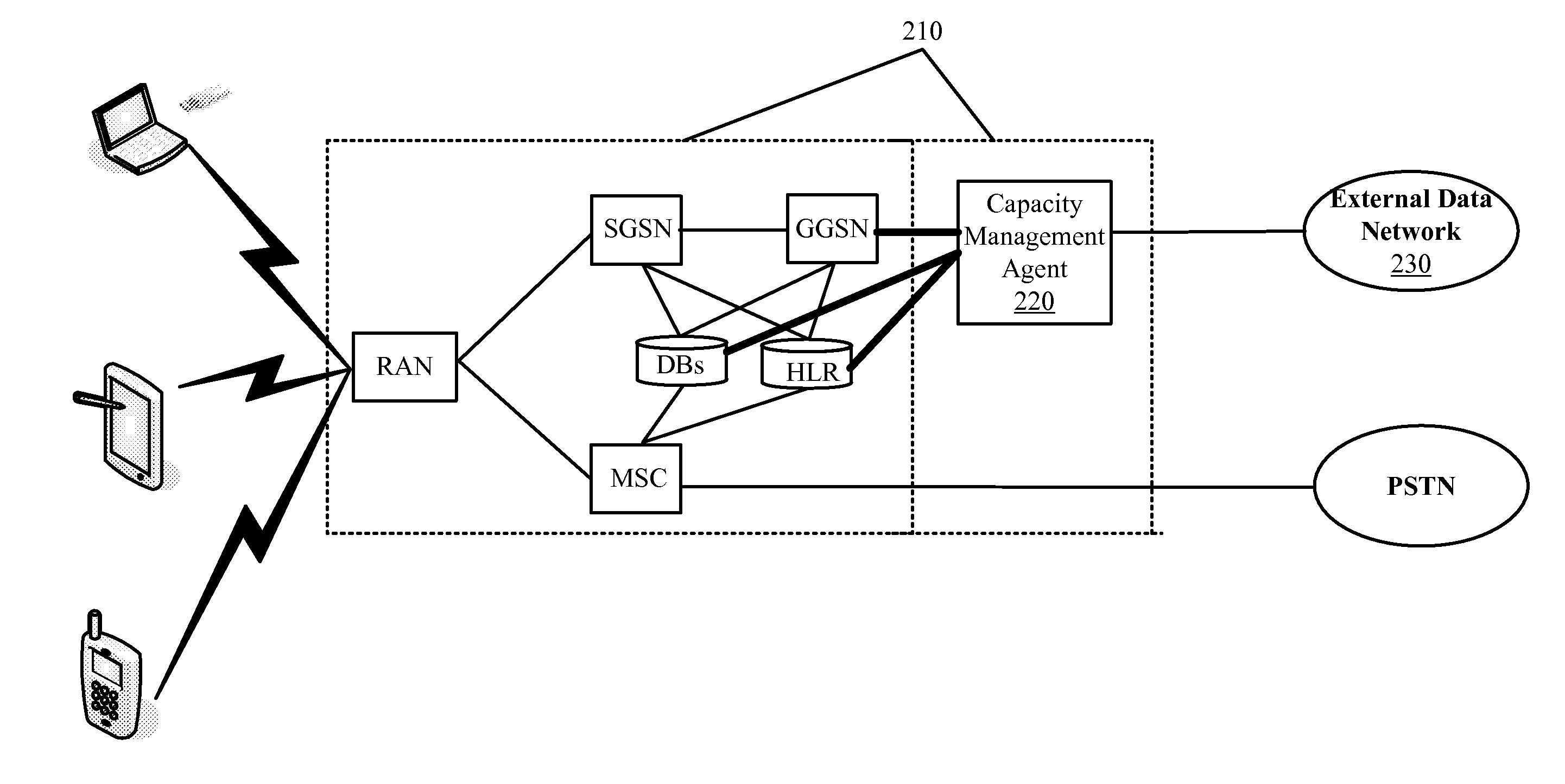
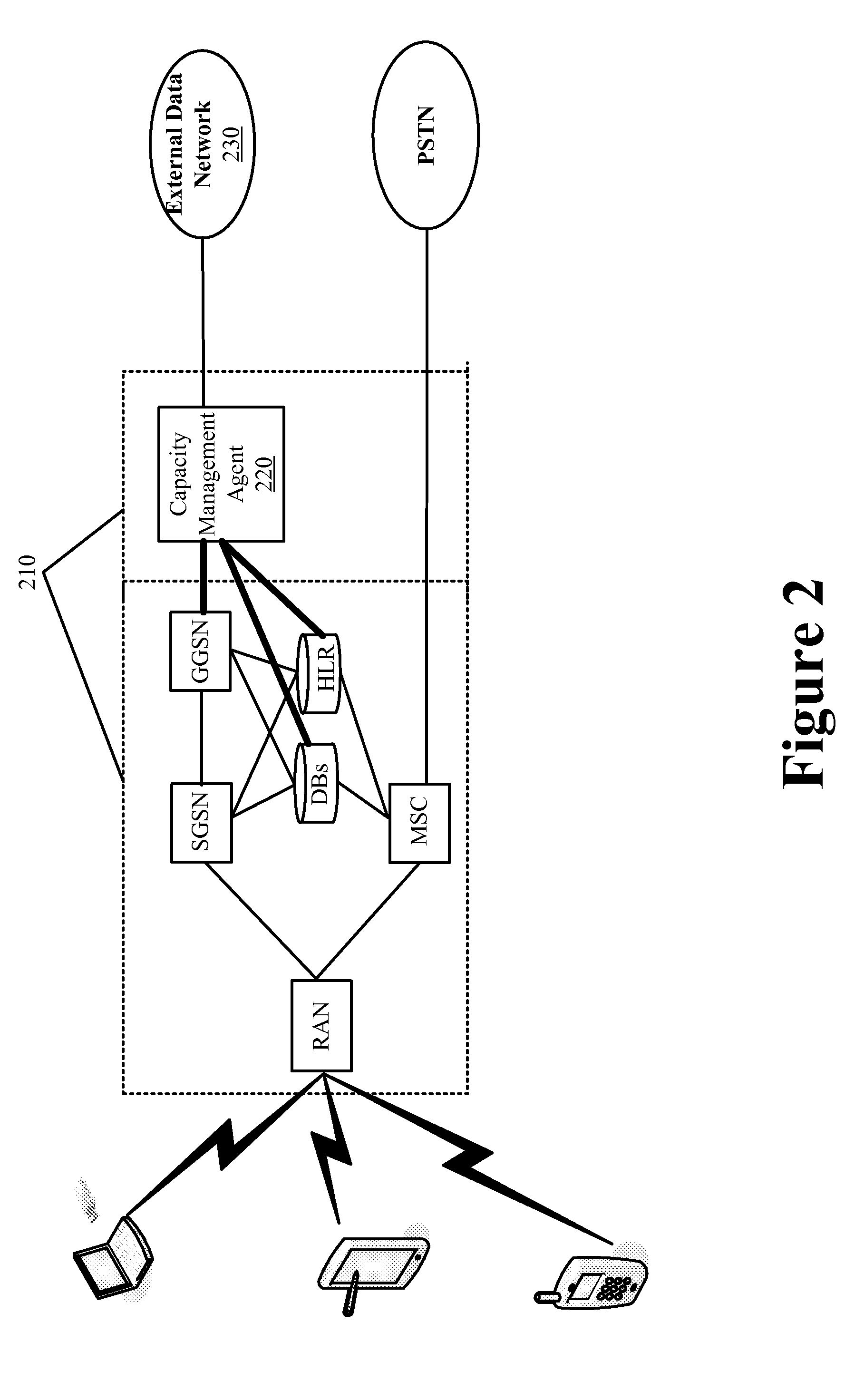
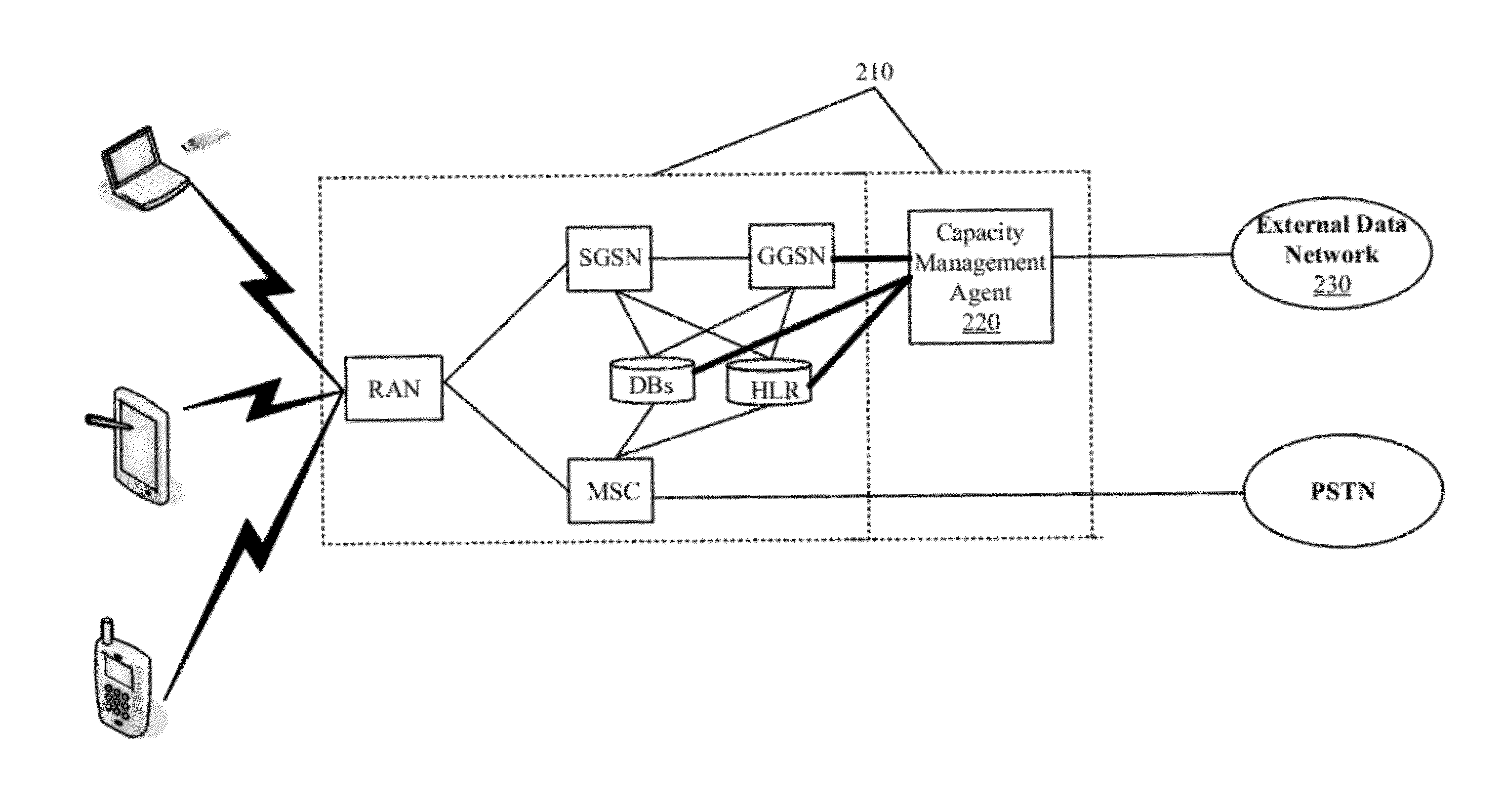
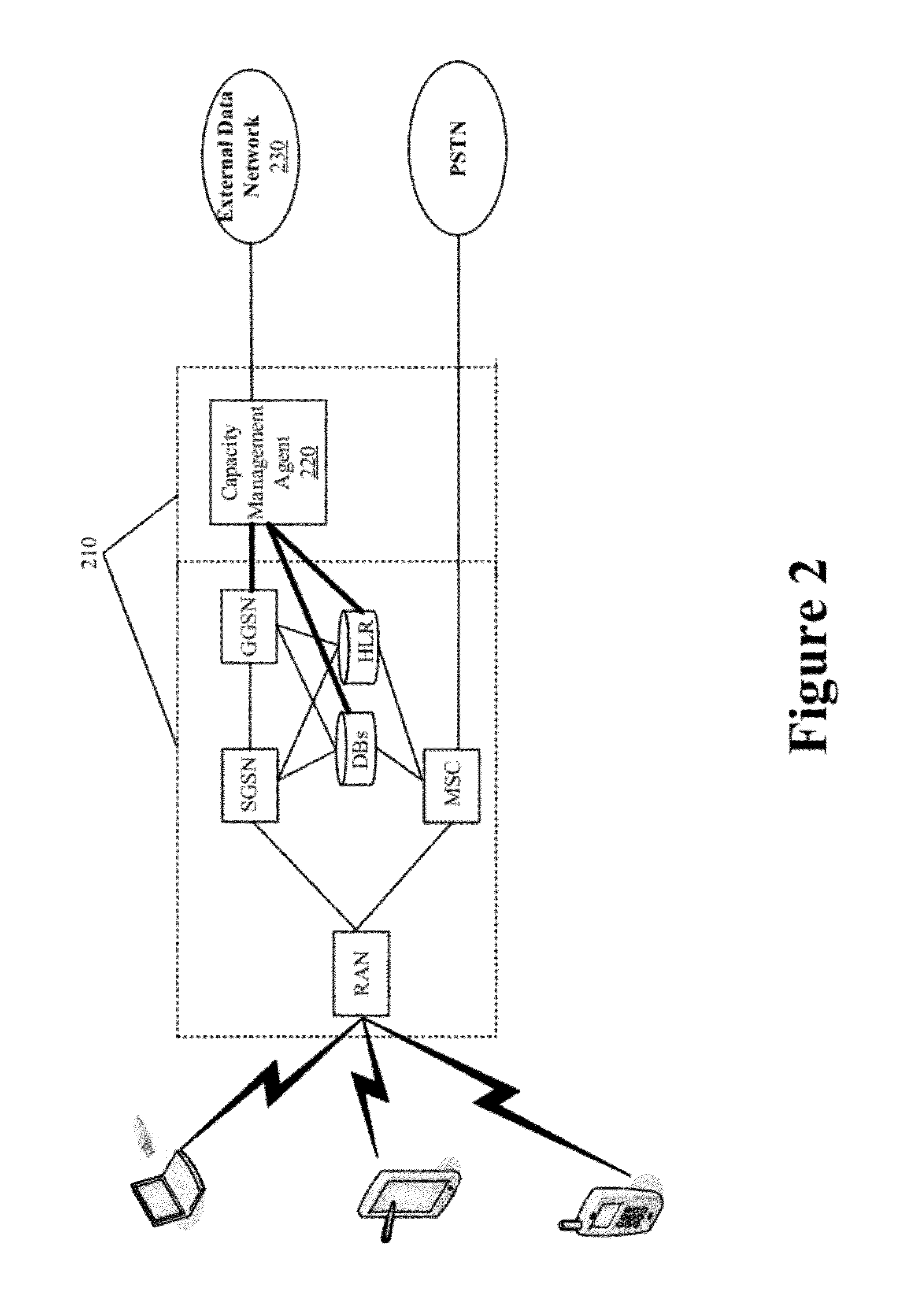
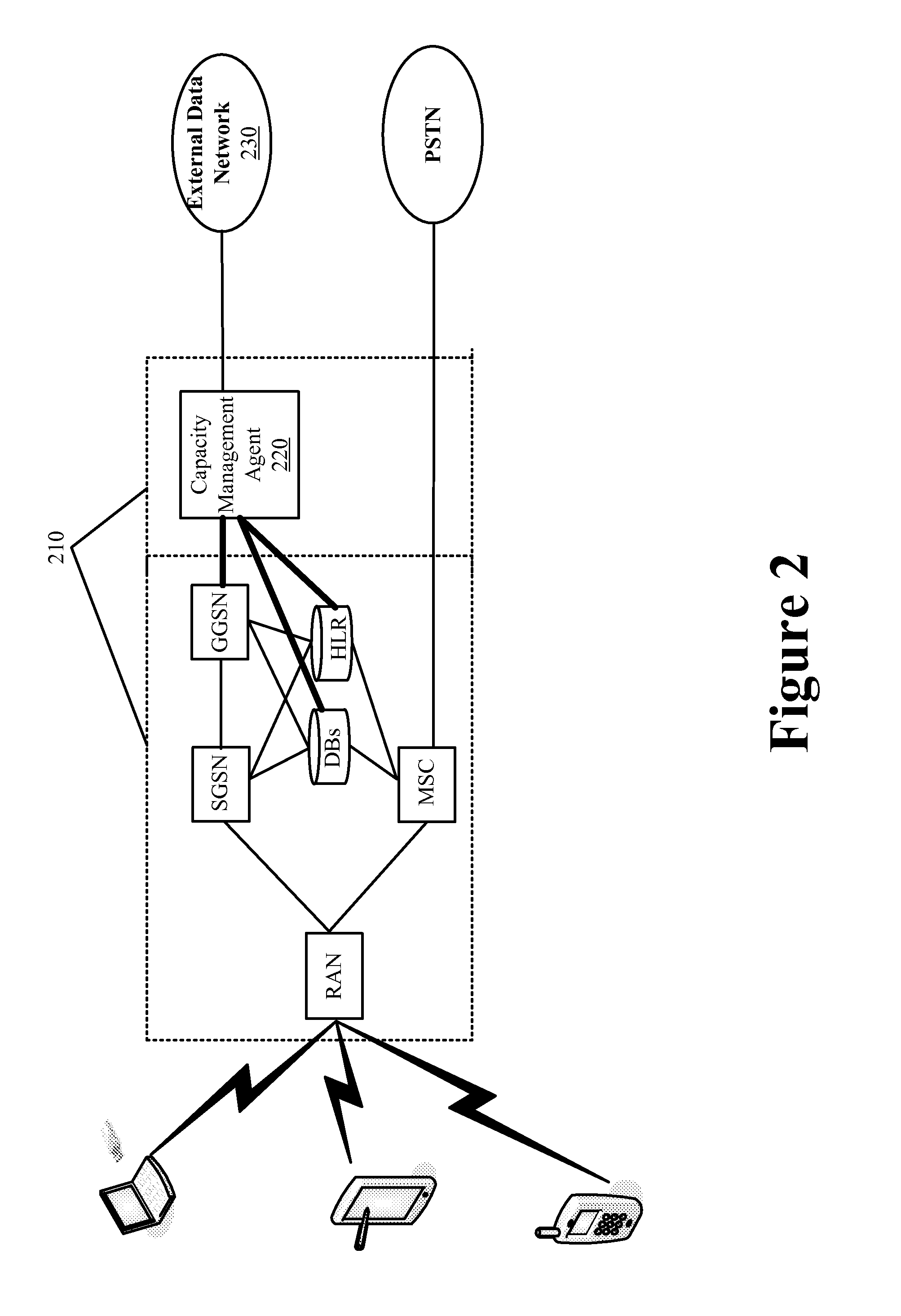
Bandwidth Modification for Transparent Capacity Management in a Carrier Network
ActiveUS20120120818A1Reduce message exchangeImprove abilitiesError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsExternal dataCarrier signal
Some embodiments provide a capacity management agent that modifies bandwidth that is allocated between an end user and a carrier network by caching requested content that is streamed at a first rate and then providing the cached content to the end user through the carrier network at a second rate. The agent performs a process that includes receiving data intended for a service region of the carrier network from an external data network. The process identifies resource availability at the service region. Next, the process passes the data to the service region at the first rate when the resource availability at the service region is not less than a threshold amount and caches the data for passing to the service region at the second rate that consumes fewer carrier network resource than the first rate when the resource availability at the service region is less than the threshold amount.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
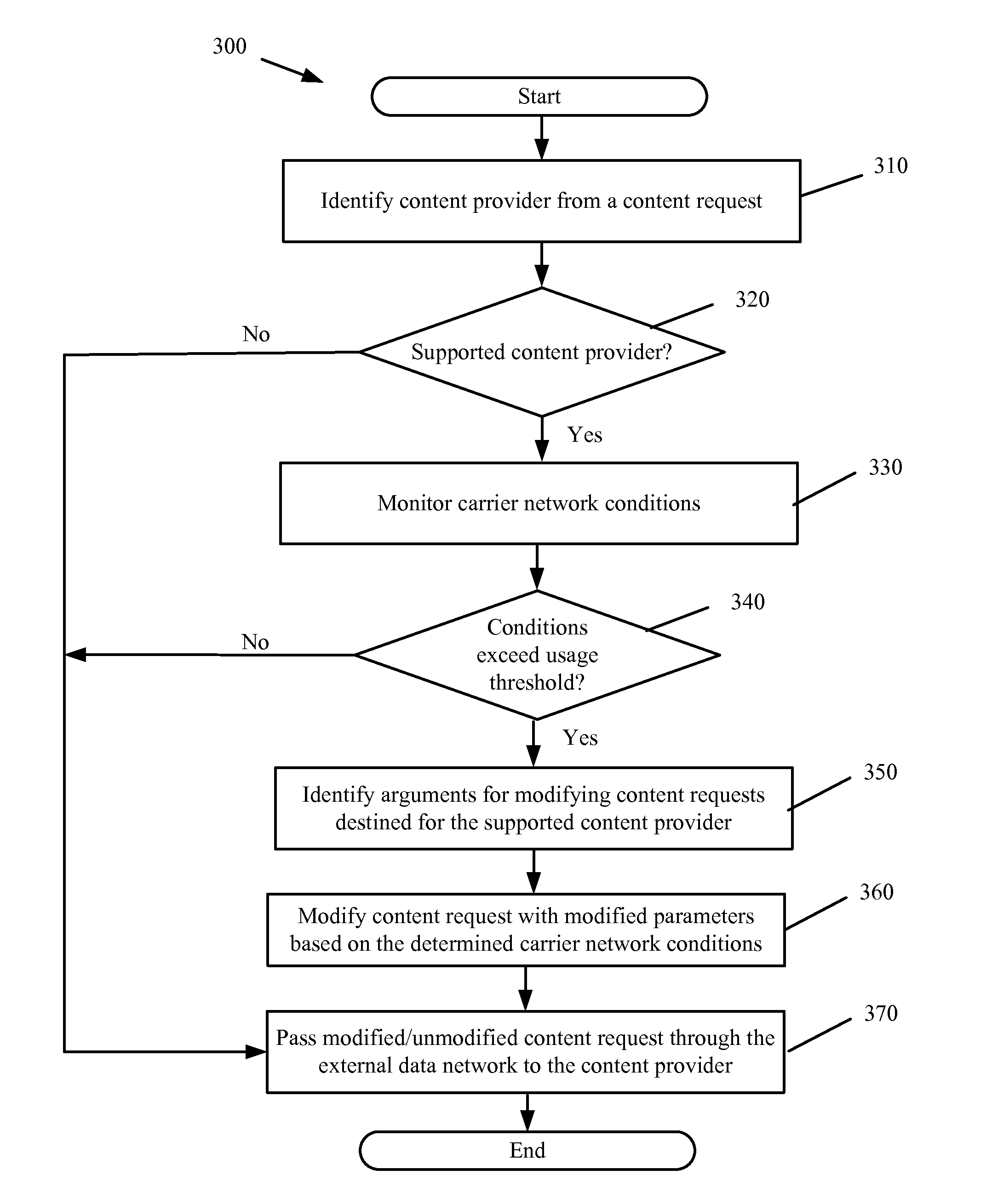
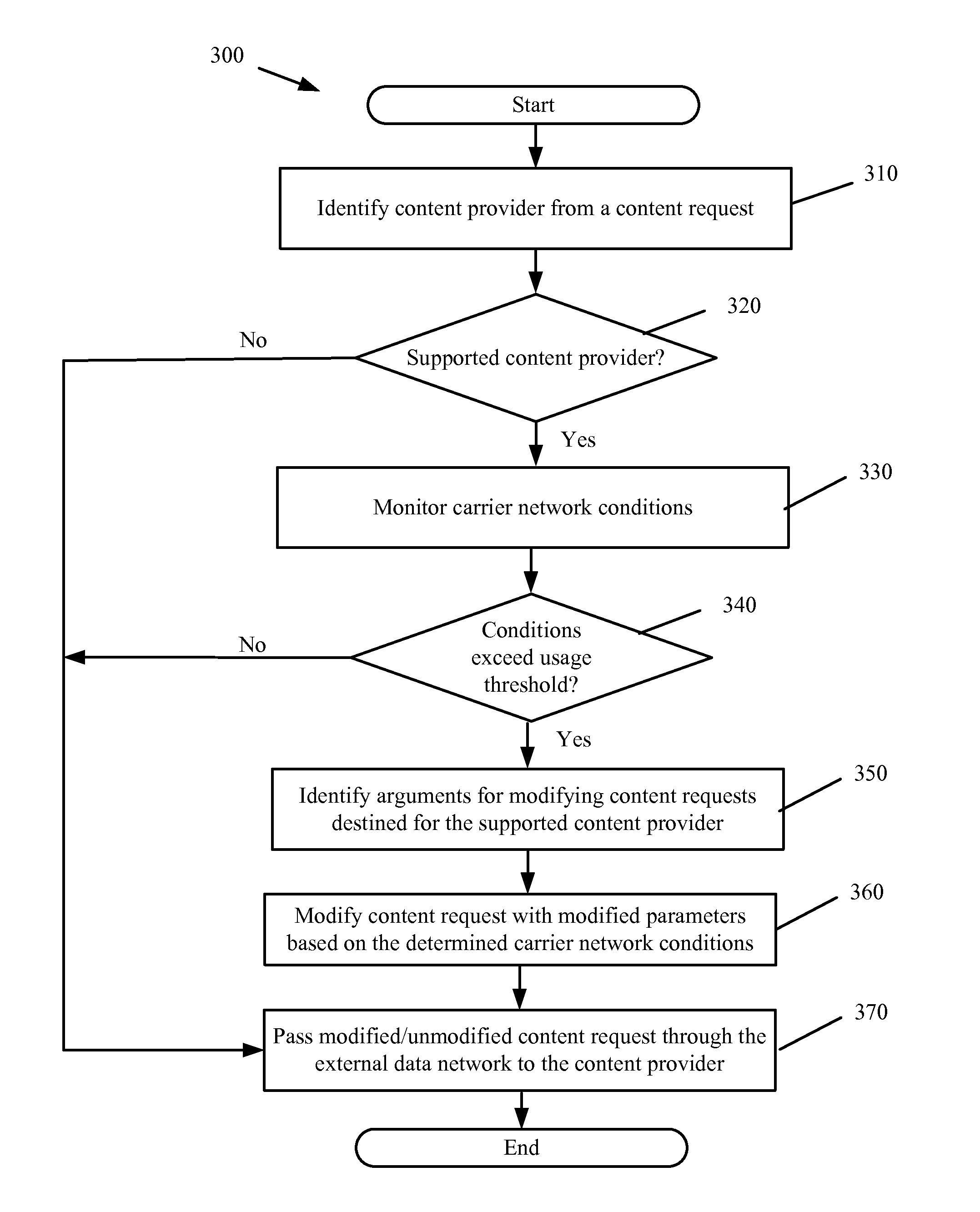
Request Modification for Transparent Capacity Management in a Carrier Network
ActiveUS20120120800A1Reduce message exchangeImprove capacityError preventionTransmission systemsUniform resource locatorCapacity management
Some embodiments provide a capacity management agent that modifies content requests to adjust bandwidth consumption when streaming requested content from a content provider to a requesting user. The modifications include modifying a URL or header information of the request. The agent performs a process that receives a request for content of a content provider. The process identifies a parameter of the carrier network and modifies the request when the parameter satisfies a threshold. The process passes the request to the content provider and the content provider provides content that consumes a first set of resources in response to an unmodified request and a second set of resources in response to a modified request. When the parameter identifies congestion, the first set of resources is greater than the second set of resources. When the condition parameter identifies underutilization, the first set of resources is less than the second set of resources.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
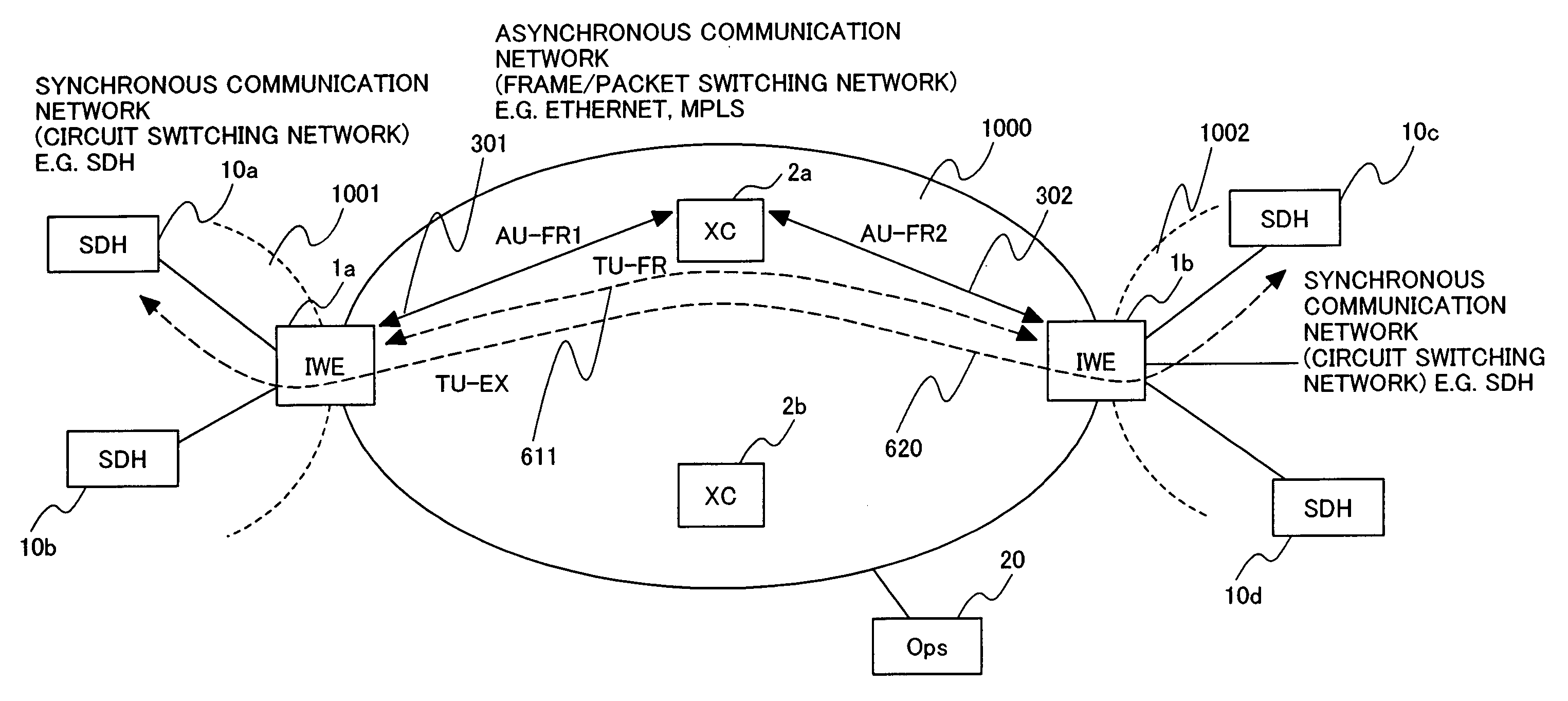
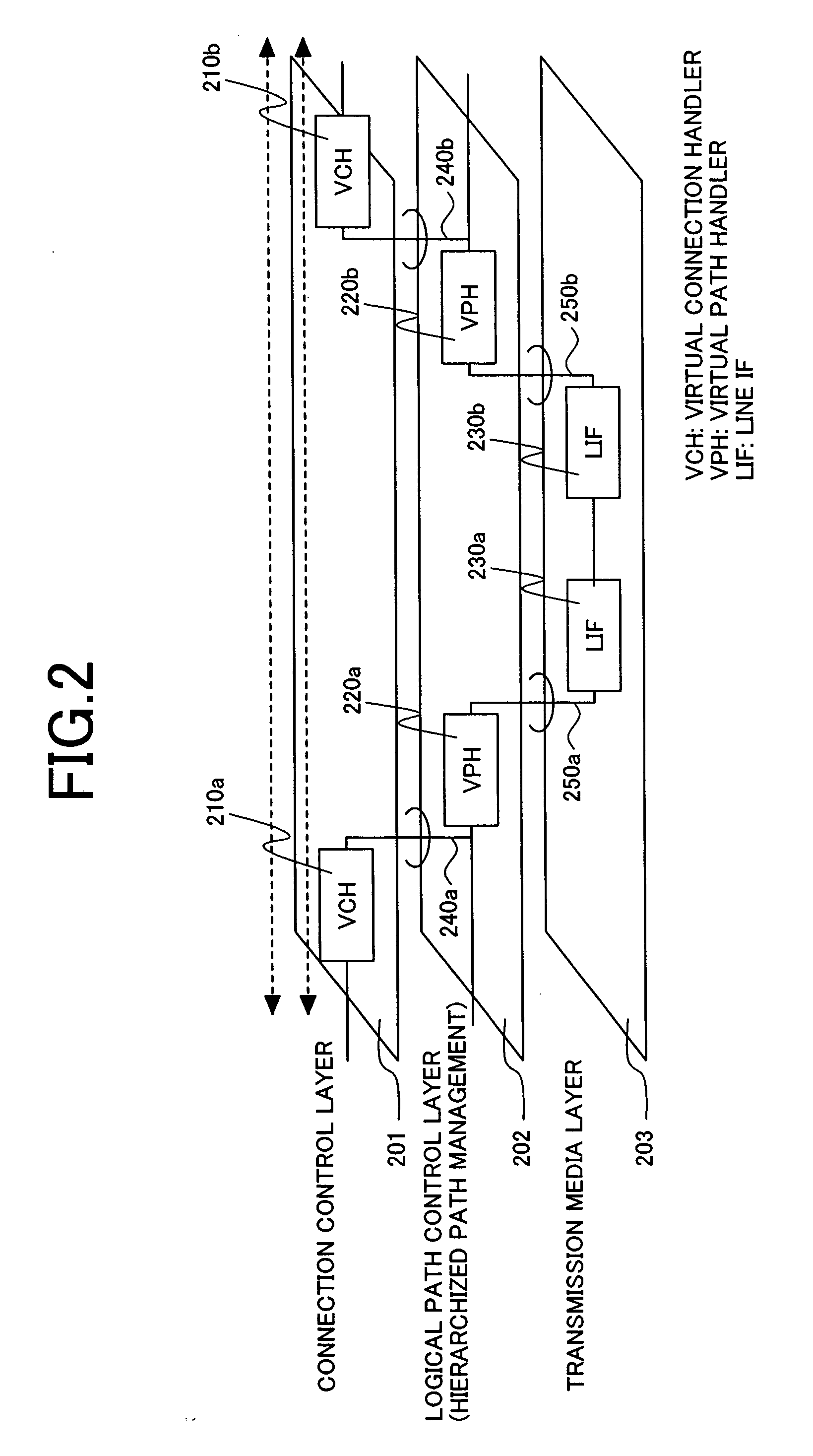
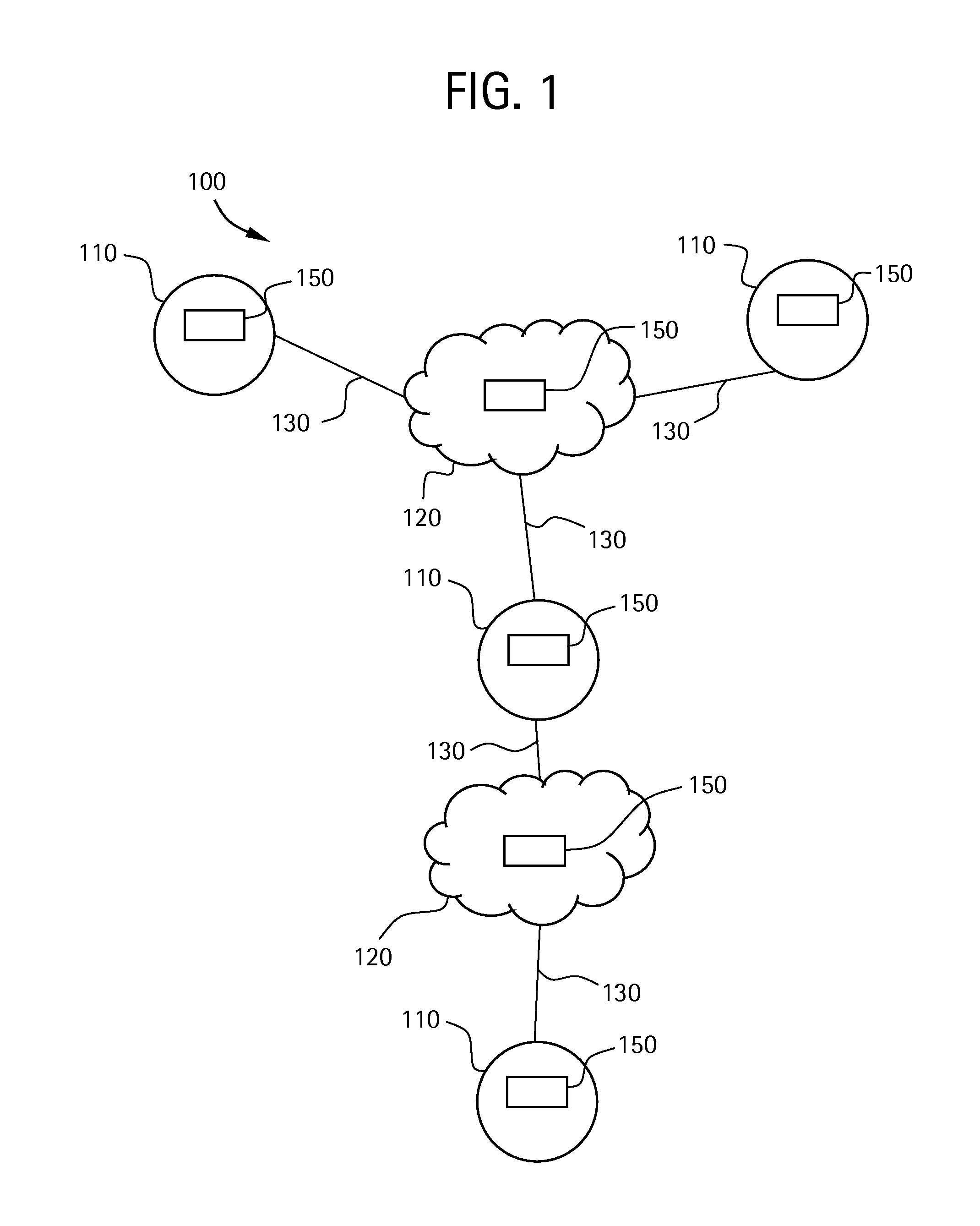
System apparatus and method for interconnecting TDM and frame/packet communication networks
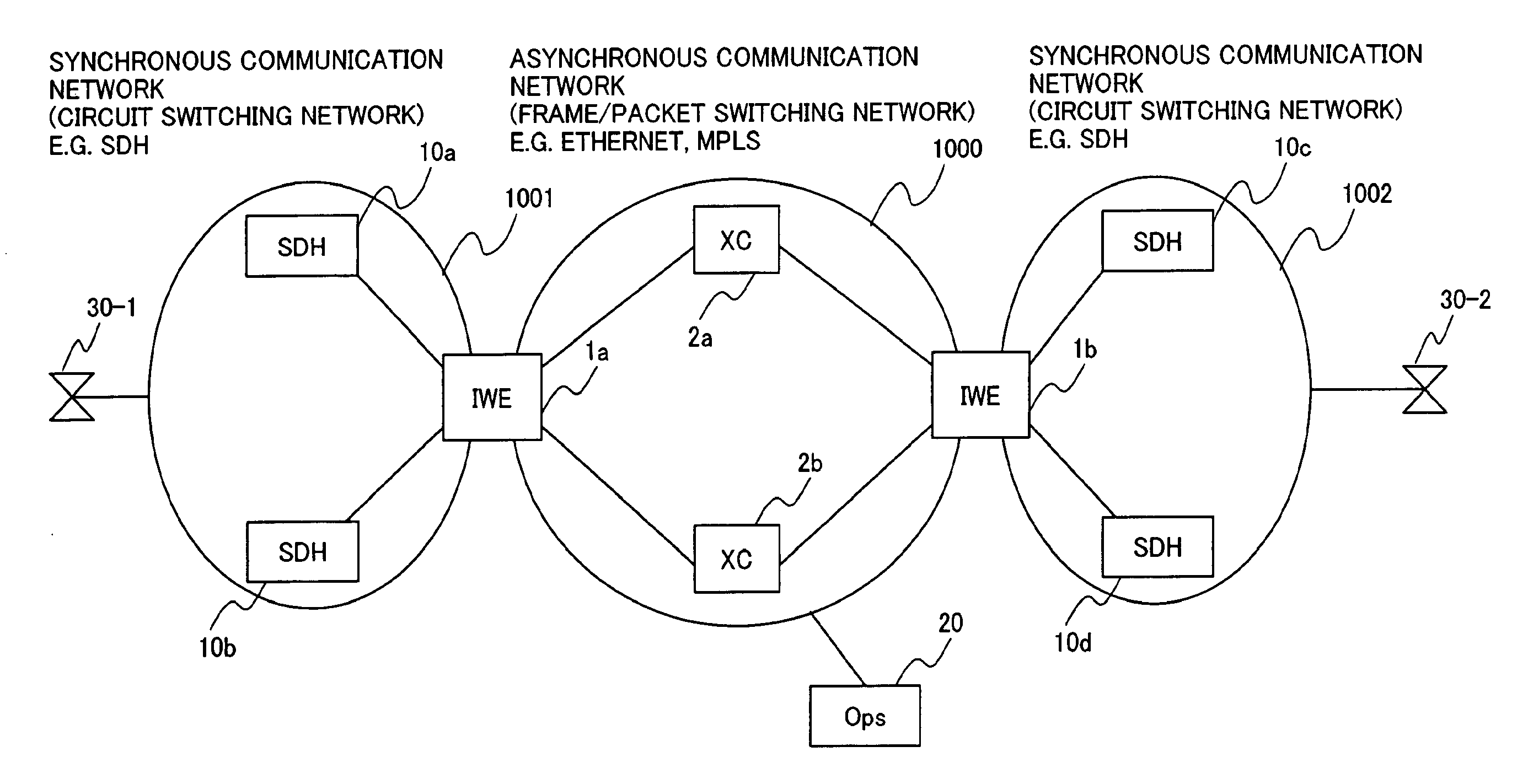
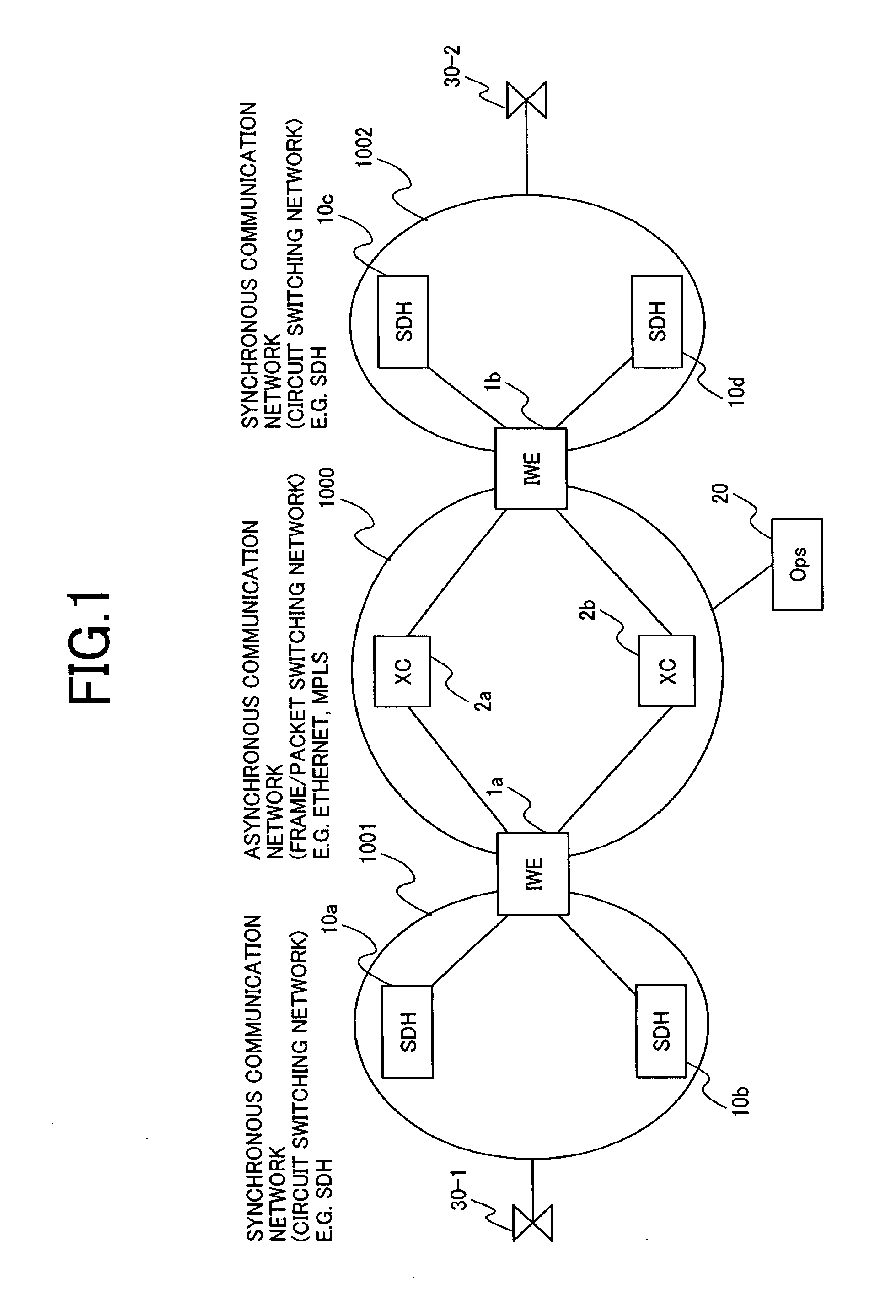
InactiveUS20070053369A1Improve communication qualityAdd supportTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPacket communicationSynchronous network
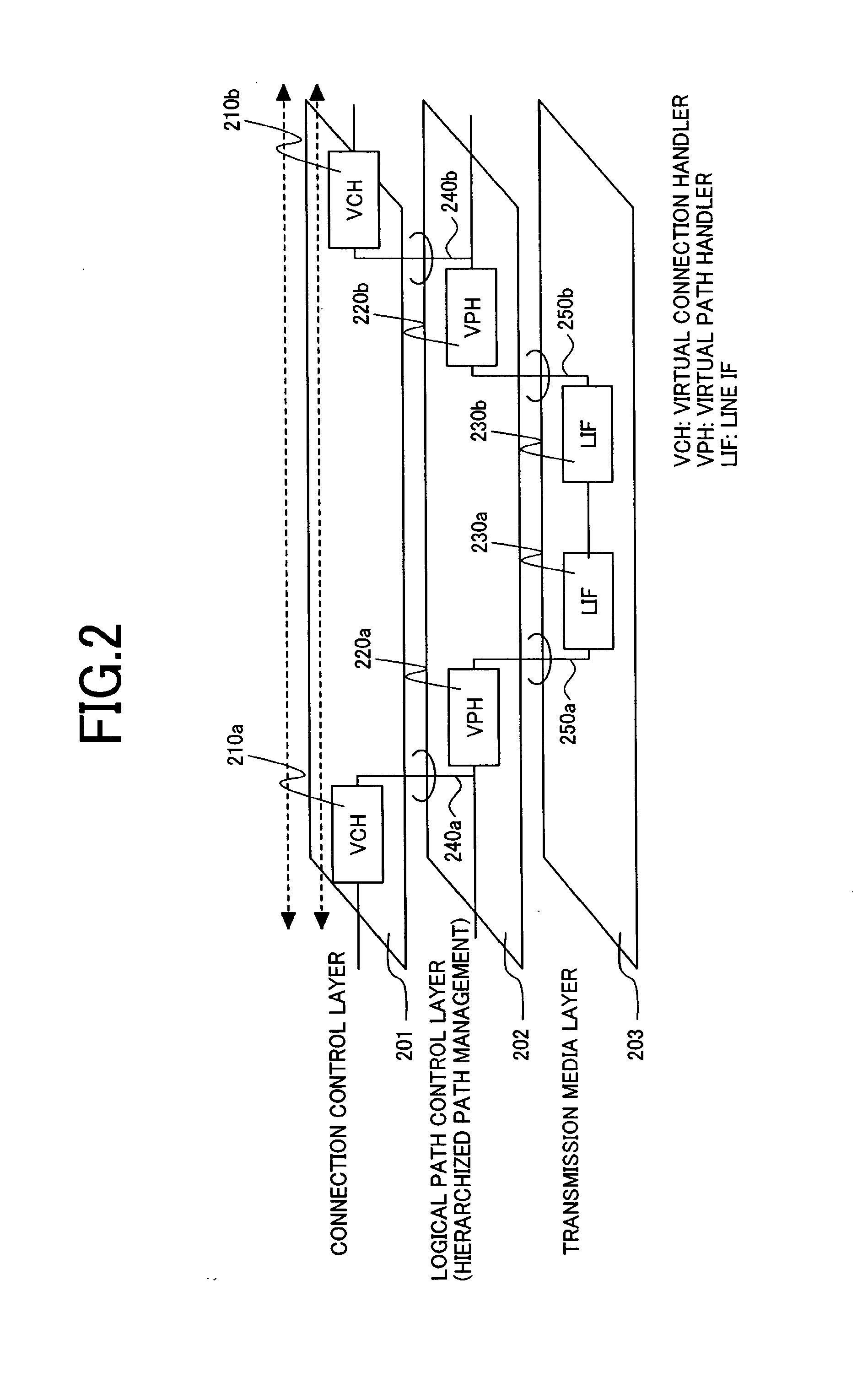
An interconnection between fully synchronous networks of the prior art and next generation frame communications networks, which is required for the shift to next-generation packet networks and a broader-based connection service, is realized. Here, the first point is that a means of bidirectional frame format conversion between a synchronous multiplexing system and a logical multiplexing system is provided, and a method of transmitting data between different networks on a path as if it was being transmitted in the same network. The second point is that when converting network control information in an STM network into data suitable for a packet network, even across the boundary of a synchronous multiplexing system and a logical multiplexing system, a unified communication management means is provided over the whole path. For this purpose, a hierarchized logical path control method is used wherein, in a network comprising two or more information relay devices having one or more line interfaces, this network performs communication between information relay devices using data packets, and has a means, when performing communication between any two points in the network, to control the path via which the packets pass between arbitrary end points, and the communication control means has a first communication path management function which performs communication management at the connection level which is terminated at the end point of a communication section, and a second communication path management function which performs communication management for each section of a physical circuit or logical circuit which is terminated at each communication section between any adjacent information relay devices in the communication section.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
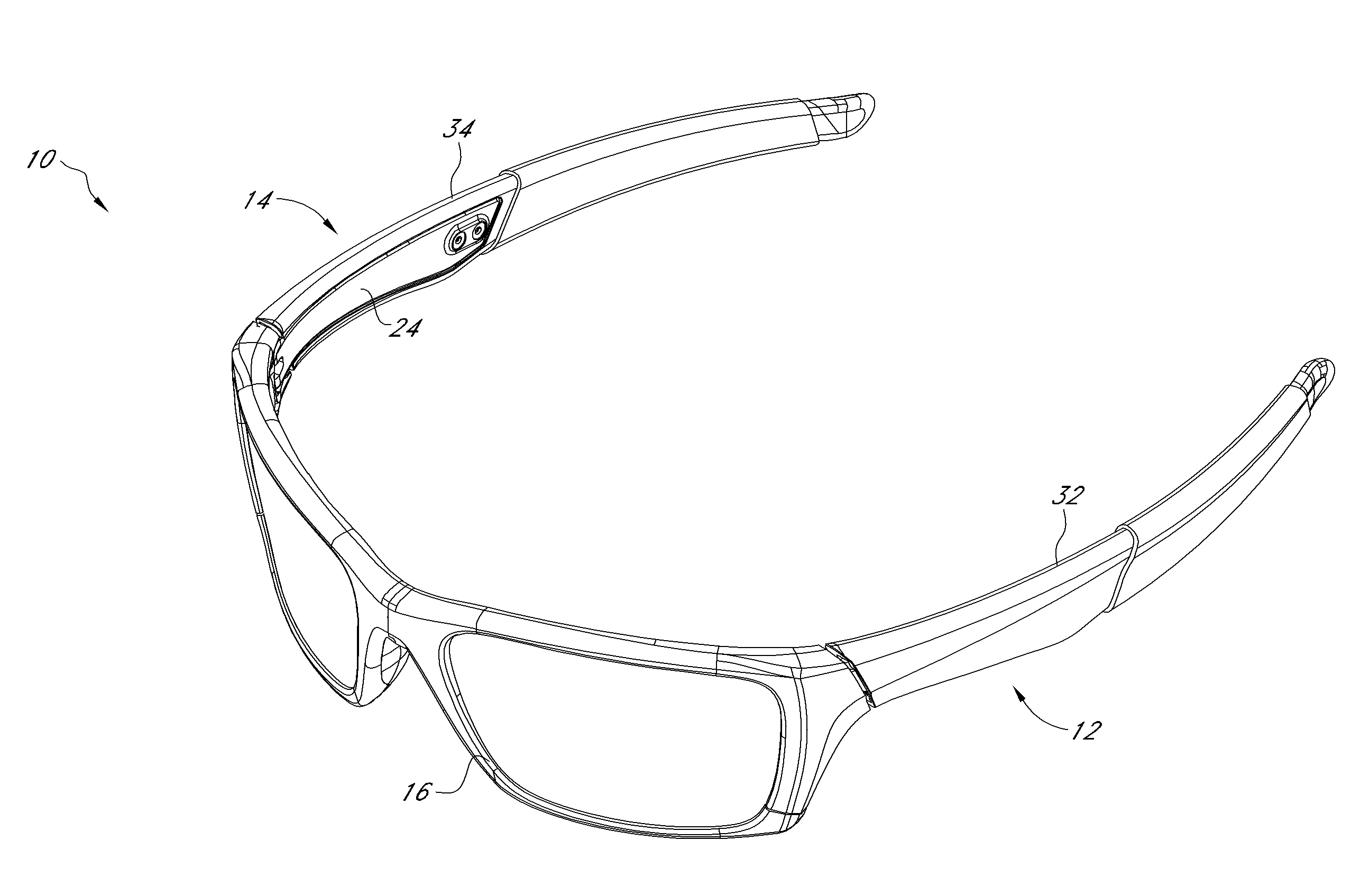
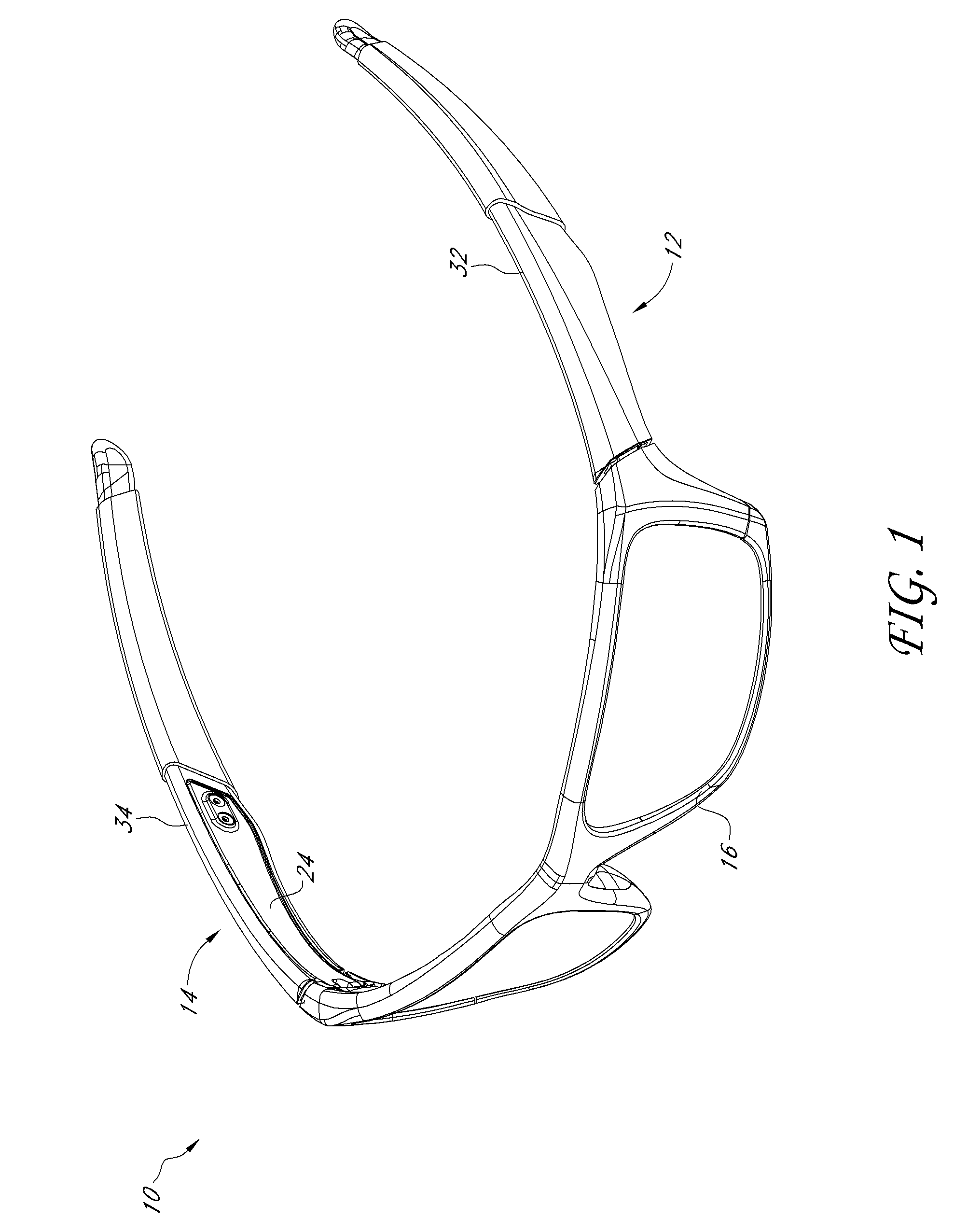
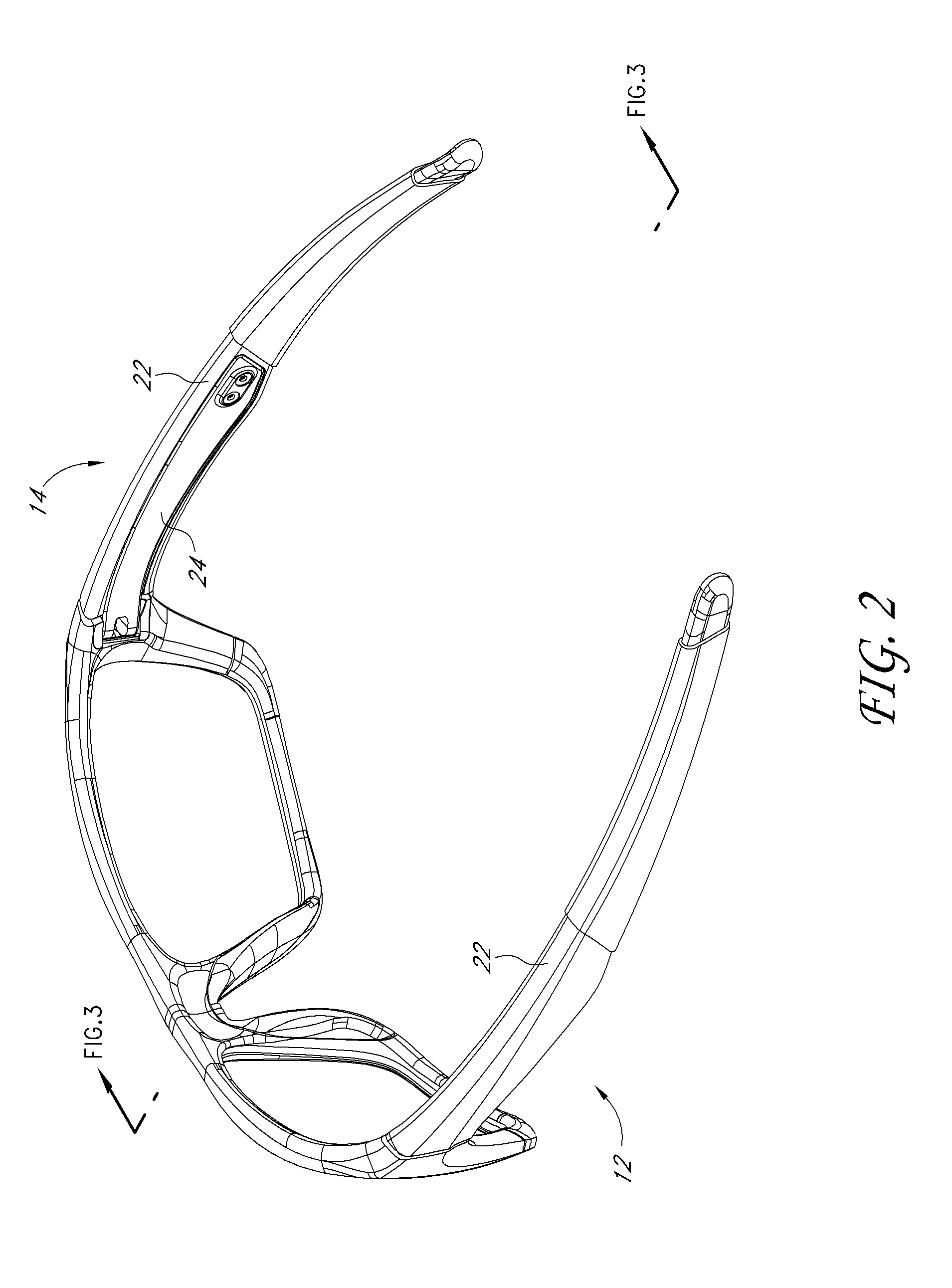
Eyeglass earstem with enhanced performance
ActiveUS20110109873A1Improve fitImprove comfortNon-optical partsMulti-purpose toolsClassical mechanicsEyewear
Owner:OAKLEY INC
Adaptive ethernet switch system and method
ActiveUS7529250B2Provide qualityImprove service qualityEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceAdaptive services
The invention relates to switch based aggregation system, method and computer program product for providing Quality of Service (QoS) to a layer 2 configured network comprising a connection oriented switching means connected to a Wide Area Network (WAN). The system comprises an Adaptive Quality of Service (AQS) means connected to said switching means. The Adaptive Quality of Service (AQS) means comprises monitoring means for monitoring the total IP data throughput stream and the RTCP reports in the system, filtering means being capable of filtering the total IP data throughput stream and controlling means for controlling said filtering means depending on the monitoring of the total IP data throughput stream and adaptable filter criteria.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
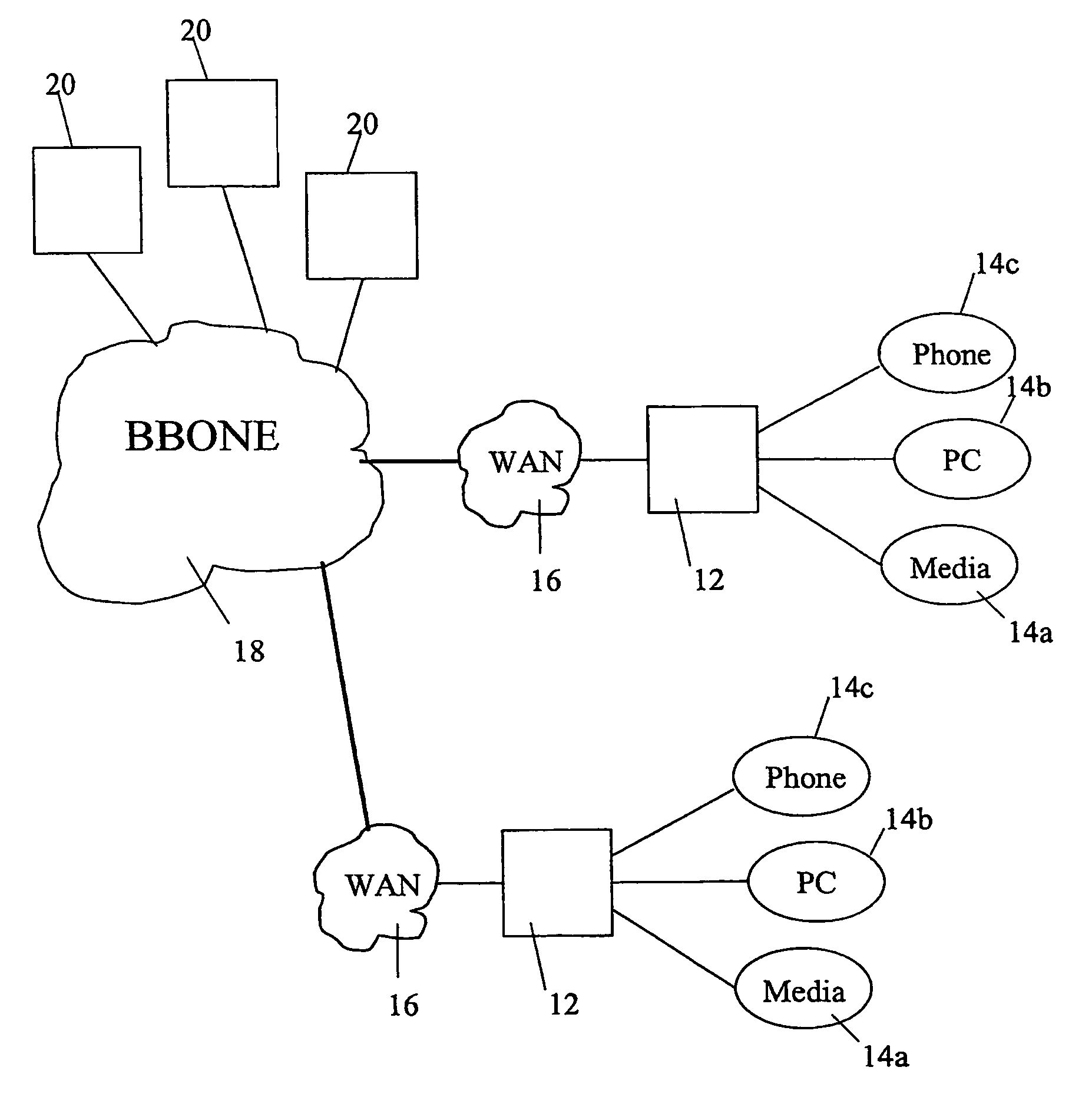
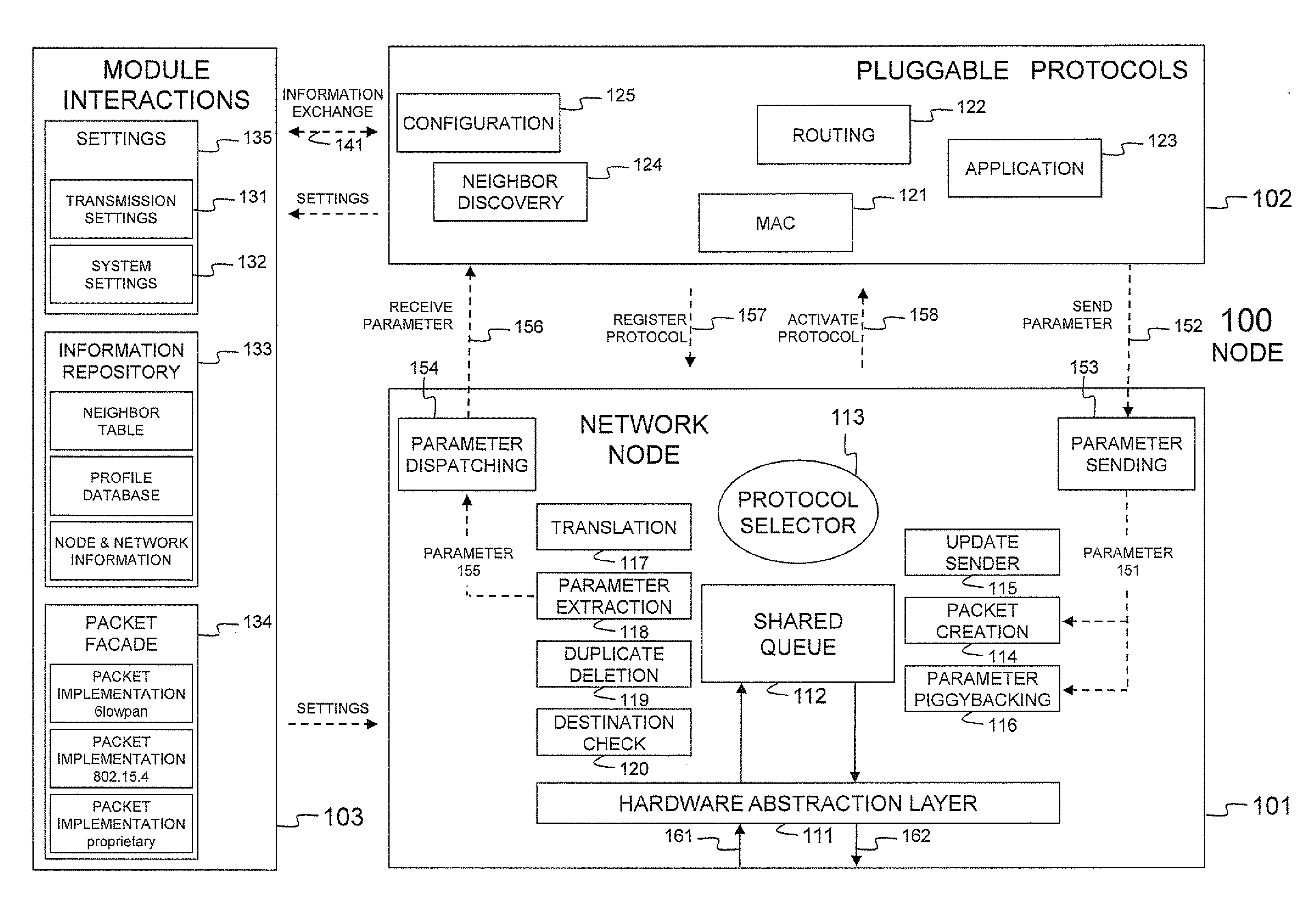
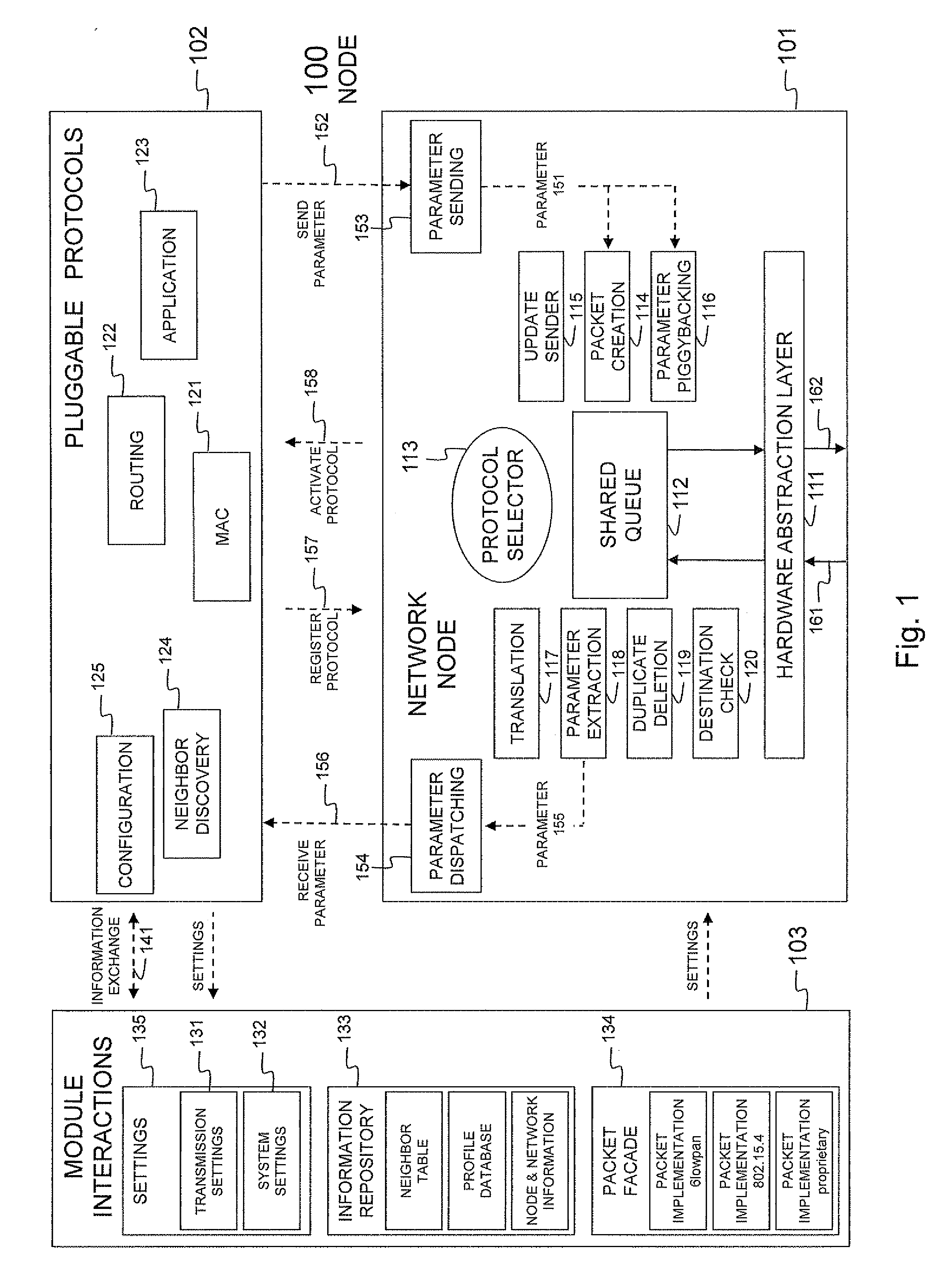
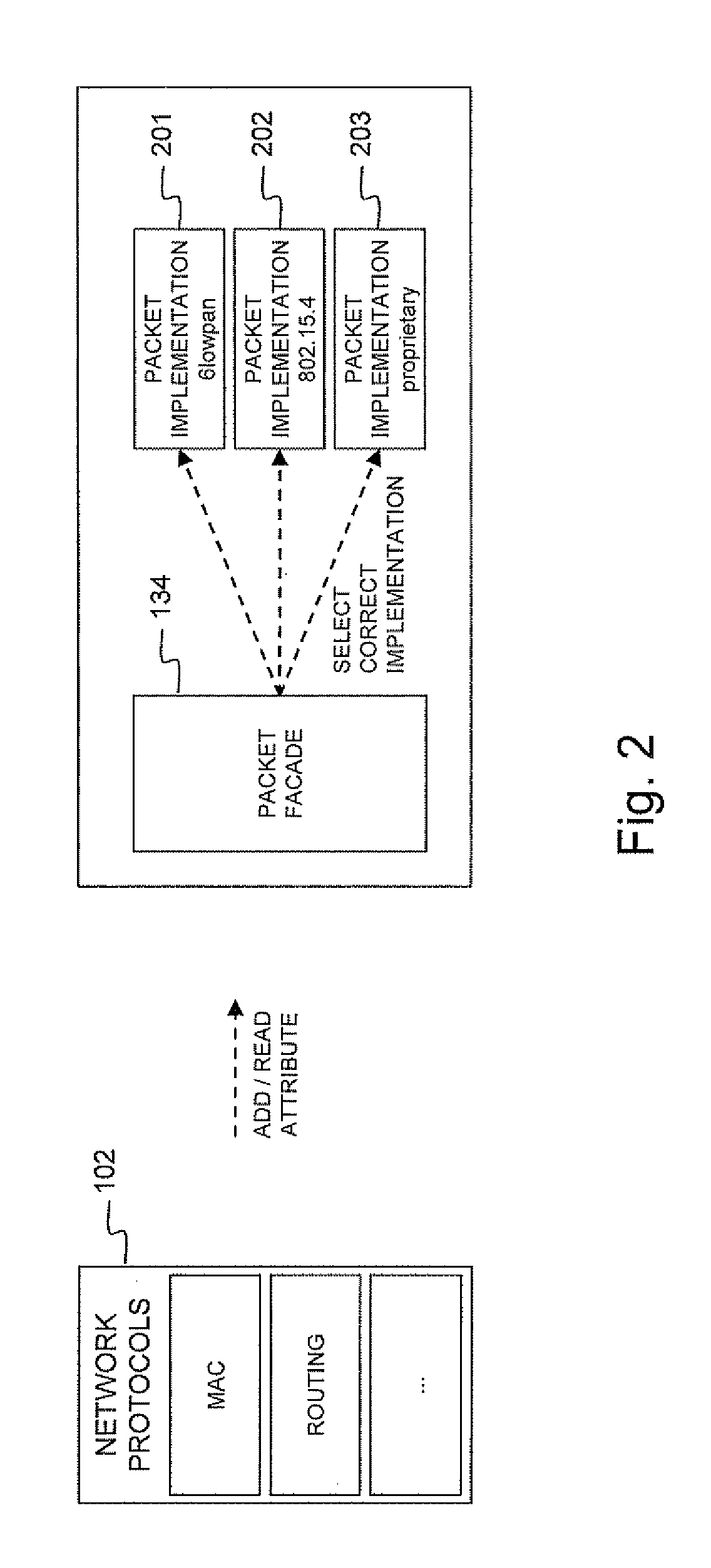
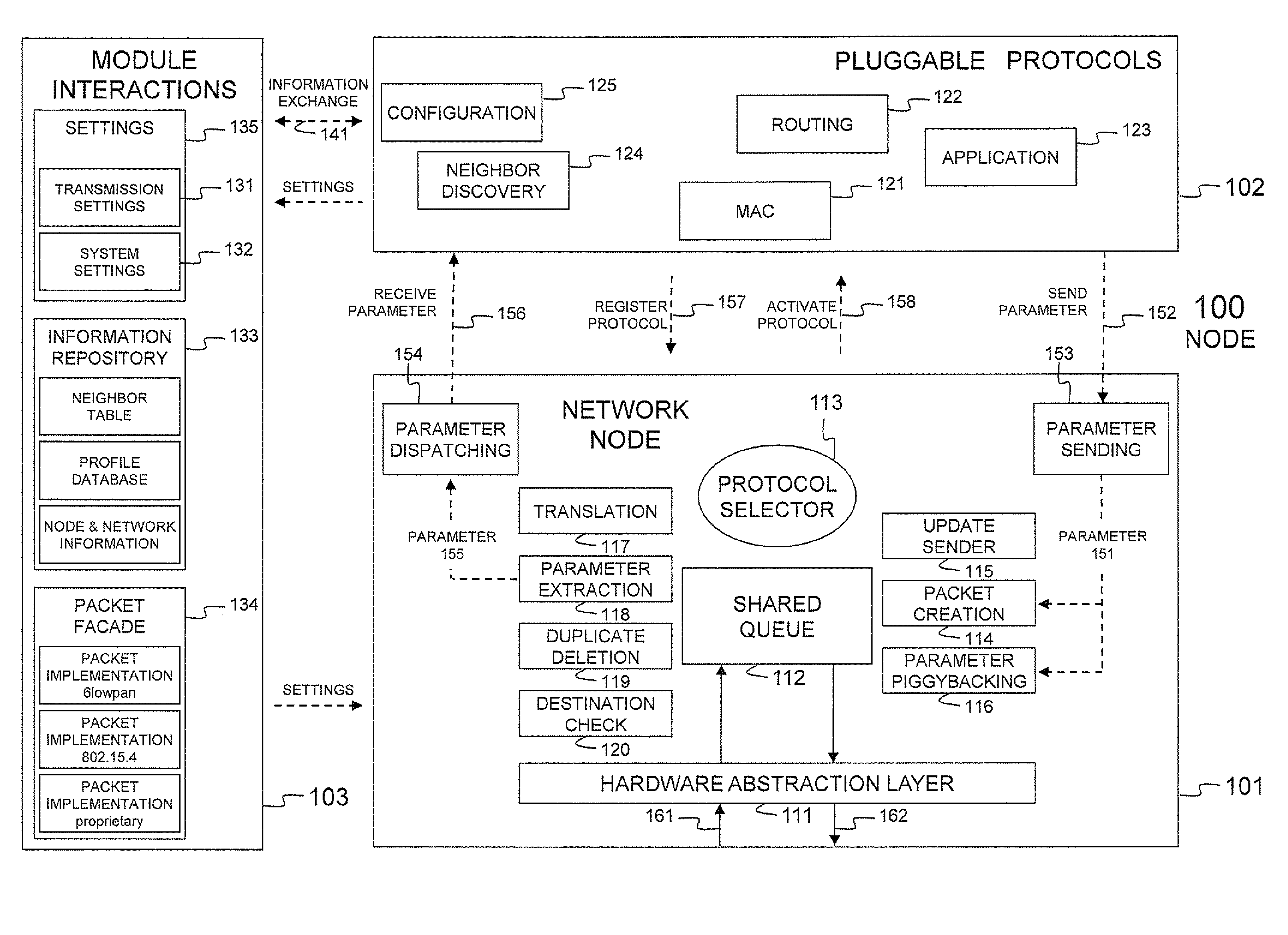
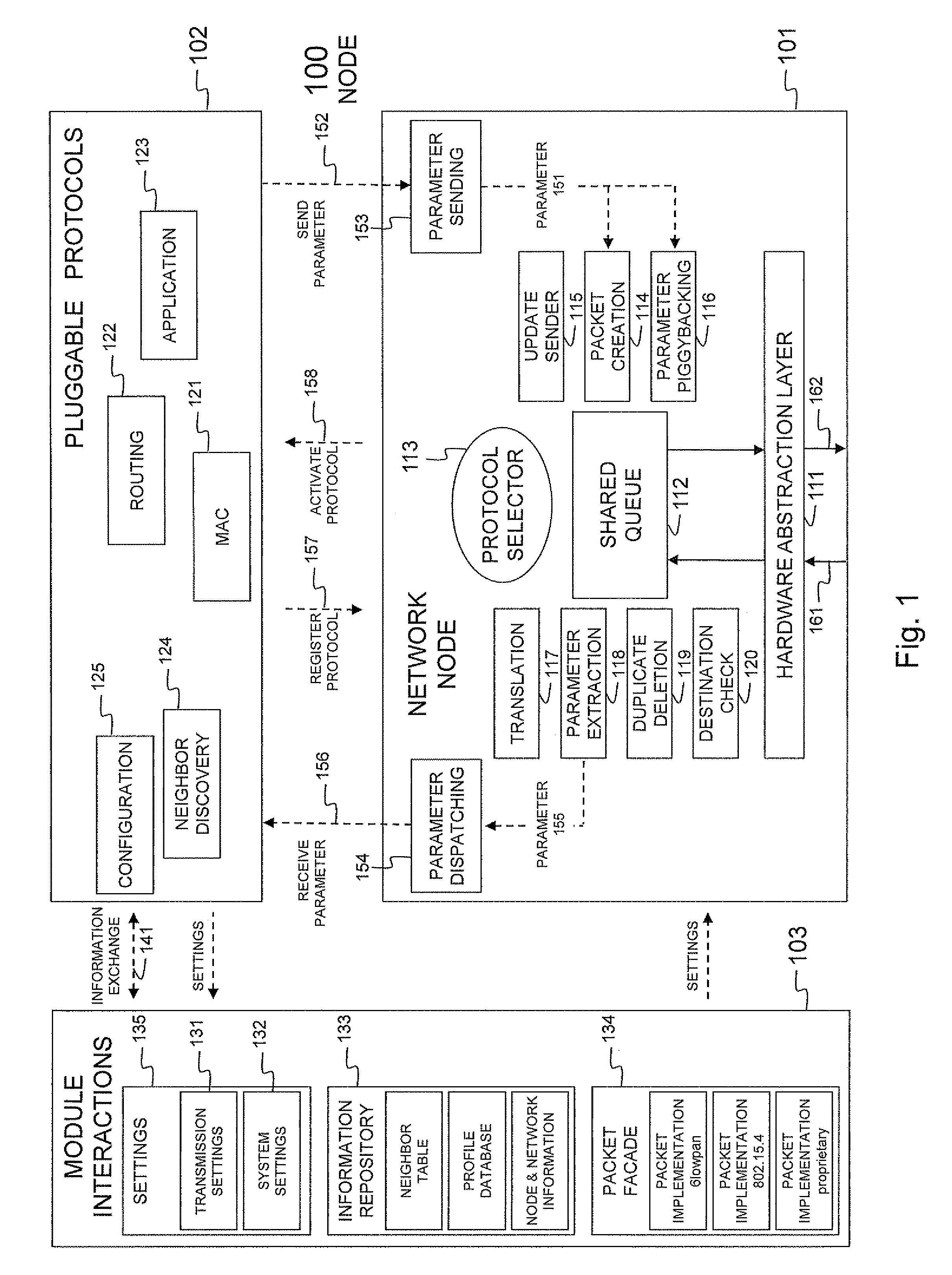
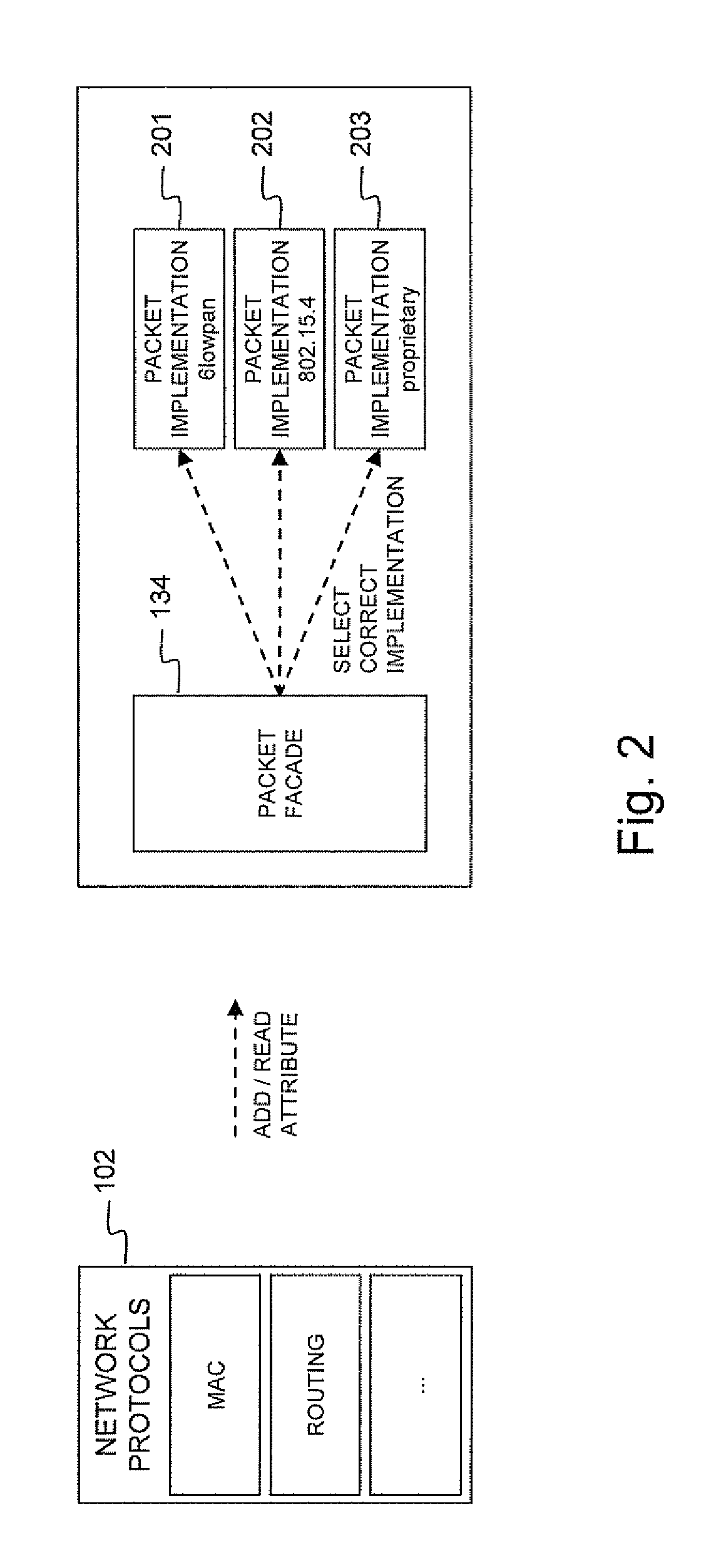
Node and wireless sensor network comprising the node
InactiveUS20110310779A1Remove overheadFacilitate communicationNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexWireless sensor networkingWireless sensor network
A node (100) according to the invention is able to generate or receive, process and transmit information (161). At runtime, the node (100) dynamically determines and activates the protocols for processing the generated or received information (161).
Owner:UNIV GENT +1
Height-adjustment mechanism for an armrest
A height-adjustment mechanism may include an integral one-piece leverage body; an integral one-piece sleeve; and a locking member. In an embodiment, the integral one-piece leverage body has a handle, a pair of pivot pins projecting from opposed sides, a tongue projecting rearwardly, and a resilient biasing member projecting forwardly. These parts may be made of low cost materials suitable for integrally forming their features in an injection-moulding operation. Various features built in to these parts may provide a user with a sense of quality.
Owner:LEGGETT & PLATT CANADA
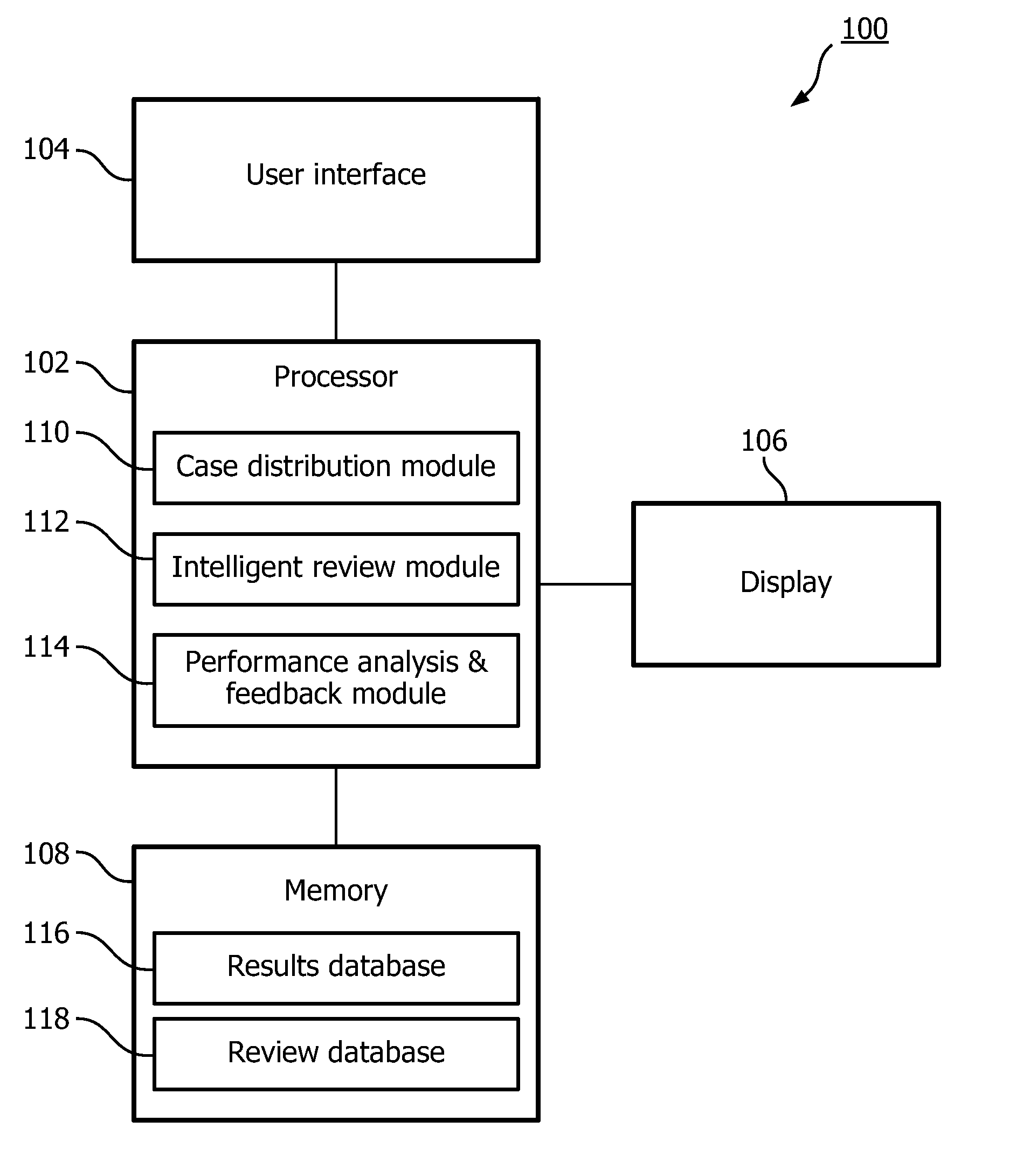
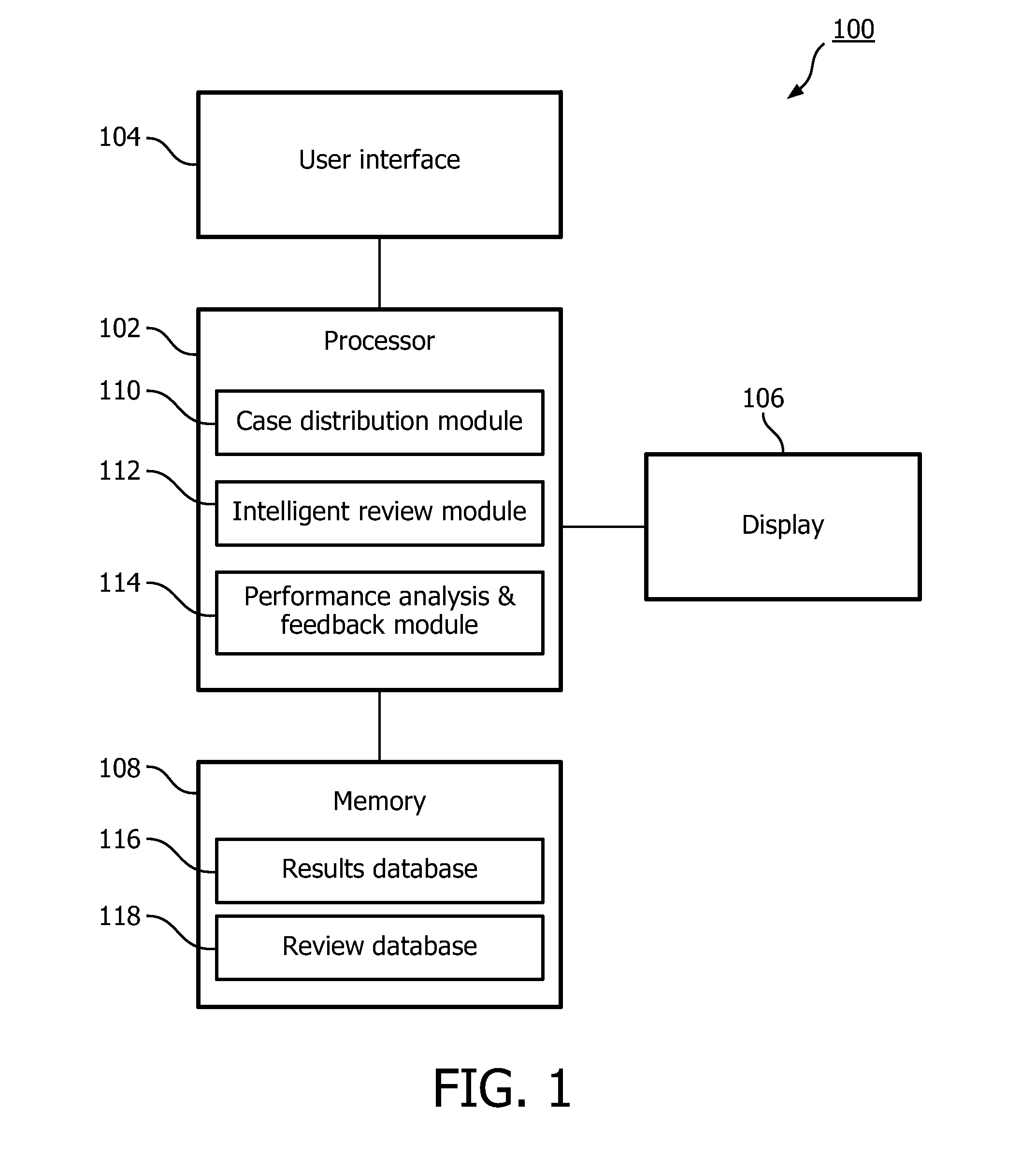
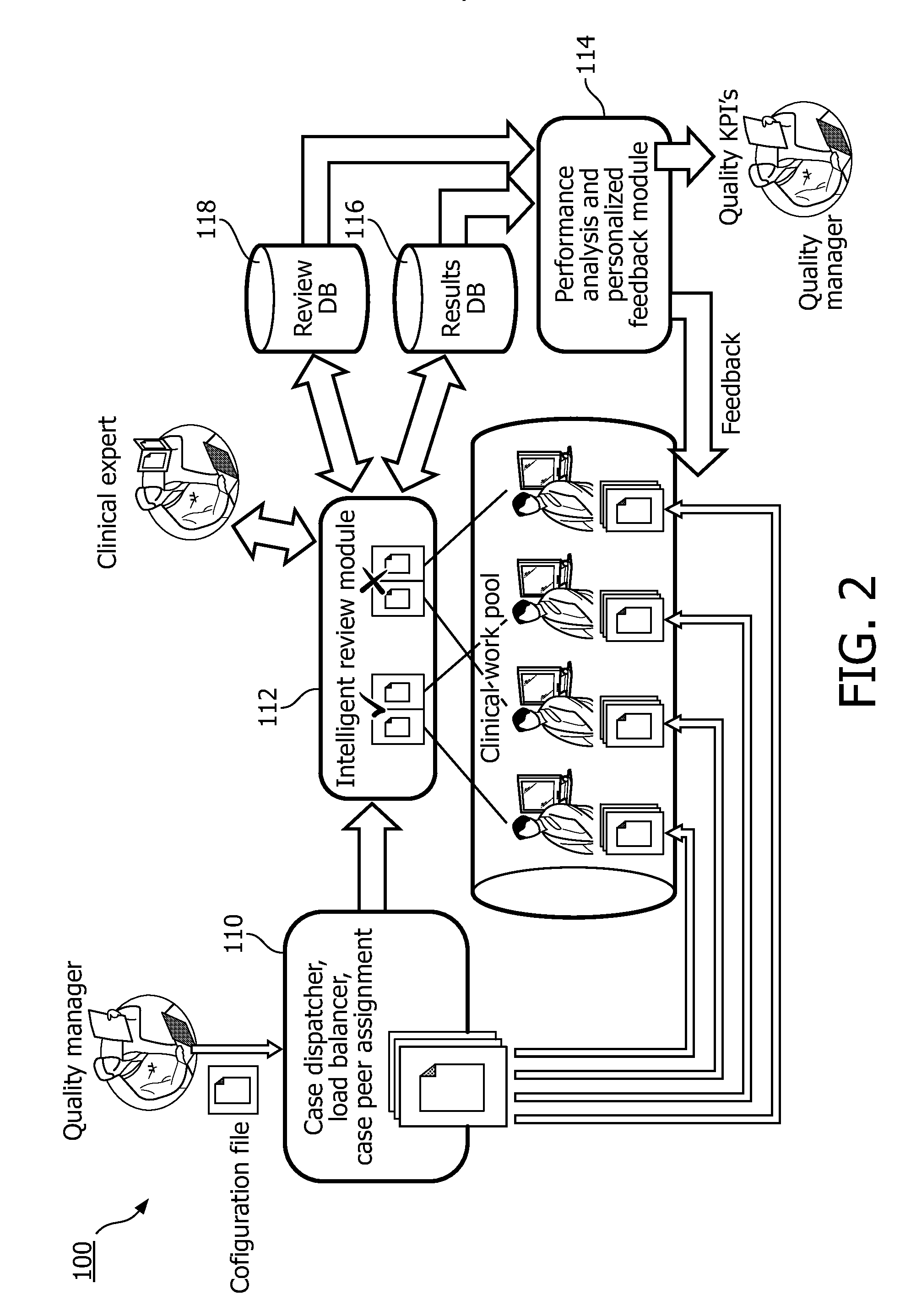
System and method for quality review of healthcare reporting and feedback
InactiveUS20150134349A1Provide qualityQuality improvementHealthcare resources and facilitiesResourcesEngineeringQuality assessment
A system and method for providing quality review of healthcare reporting and supporting quality improvement. The system and method performing the steps of multiplying a select number of cases of a plurality of cases to be analyzed using a processor, assigning the plurality of cases and multiplied cases to members of a work pool using the processor, retrieving case reports created by members of the work pool for the multiplied cases and analyzing case reports for one of the multiplied cases in a first review using the processor.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Contact lens with multi-layered pattern
ActiveUS20160306189A1Highlight and enhance and define limbal regionMore depthSpectales/gogglesOptical partsEngineeringGraphics
Contact lenses that comprise a multi-layer design may be utilized to enhance and / or highlight the appearance of the eyes upon which the contact lenses are positioned while maintaining a natural look. These exemplary designs each comprise three layers; namely, a unique limbal design graphic, a unique inner effect graphic and a unique outer effect graphic. The layers may be formed utilizing any number of design elements and design principles. The limbal design graphic is the portion of the overall pattern that surrounds the outer diameter of the iris and is closest to the sclera and is meant to highlight, enhance and / or define the limbal region of the eye; however, it also comprises elements that extend into the iris. The inner effect graphic layer is the portion of the overall pattern that is meant to enhance the iris; however, it may comprise a portion that also contributes to highlighting, enhancing and / or defining the limbal region of the eye. The outer effect graphic layer is the portion of the overall pattern that is meant to enhance the iris; however, it may comprise a portion that also contributes to highlighting, enhancing and / or defining the limbal region of the eye.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Systems and methods for applying back-pressure for sequencing in quality of service
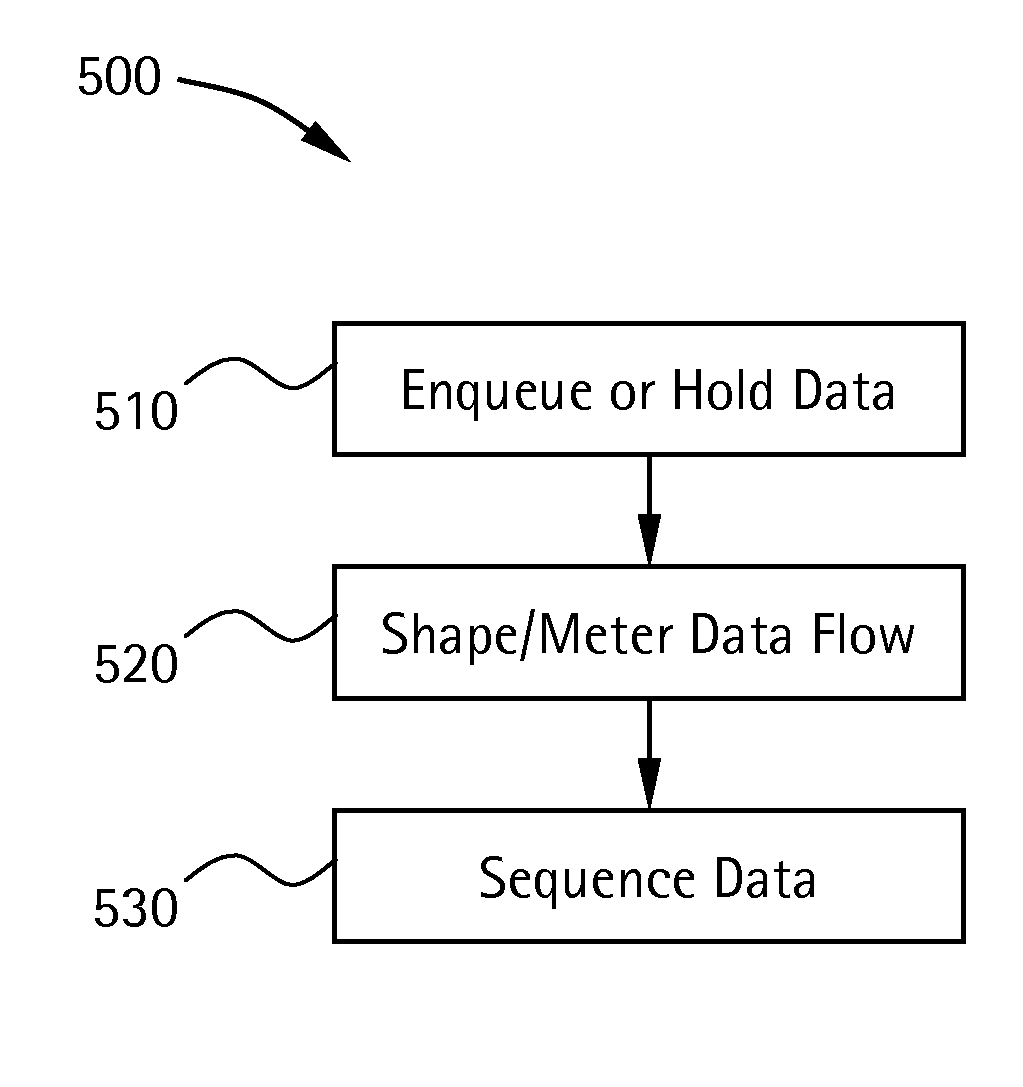
InactiveUS20080013559A1Level of qualityProvides level of QualityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsQuality of serviceData stream
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for data communication. Certain embodiments provide a method including temporarily holding data being transmitted, determining a sequence of the data based at least on data priority and metering transmission of the data based on at least one user-specified metering criterion to provide a level of quality of service in transmitting the data. Certain embodiments provide a computer-readable medium having a set of instructions for execution on a processing device. The set of instructions includes a holding routine for temporarily holding data being transmitted, a sequencing routine for determining a sequence of the data based on at least one sequencing criterion, and a metering routine for metering a flow of the data based on at least one metering criterion to provide a level of quality of service in transmitting the data.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Keypad coupling apparatus for portable terminal
InactiveUS20080105526A1Shorten the timeSlimness and miniaturization of the portable terminalInput/output for user-computer interactionEmergency actuatorsFlexible circuitsCoupling
Disclosed is a keypad coupling apparatus for a portable terminal which has a laminated keypad unit arranged on an upper surface of a front case. The keypad coupling apparatus includes a front case provided with a latch; a flexible circuit disposed on the front case and including a plurality of dome switches; a keypad rubber disposed on an upper surface of the flexible circuit; and a keypad provided on an upper surface of the keypad rubber and moving in a pressed direction when the keypad is engaged with the latch and pressed, the keypad rubber making contact with at least one of the dome switches to provide tactile quality of a click.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Geolocation information storage system for mobile communications data
A system (200) and method (500) are provided for storing communication session data and geolocation information derived from a wireless mobile communications system (210). A record of data for each communication session taking place in at least one geographical region of the mobile radio communications network (210) is stored (510) in a first storage area (220). Each record of data is accessed (520), and a subset of the data for each communication session is stored (530) in a second storage area (250). Geo-location information is derived (540) for each communication session, and stored in the second storage area (250) The method and system may allow much more rapid access to subsets of data, and if necessary to the original records.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS UK
Request modification for transparent capacity management in a carrier network
ActiveUS8457010B2Increase capacityMonetizeError preventionTransmission systemsCapacity managementUniform resource locator
Some embodiments provide a capacity management agent that modifies content requests to adjust bandwidth consumption when streaming requested content from a content provider to a requesting user. The modifications include modifying a URL or header information of the request. The agent performs a process that receives a request for content of a content provider. The process identifies a parameter of the carrier network and modifies the request when the parameter satisfies a threshold. The process passes the request to the content provider and the content provider provides content that consumes a first set of resources in response to an unmodified request and a second set of resources in response to a modified request. When the parameter identifies congestion, the first set of resources is greater than the second set of resources. When the condition parameter identifies underutilization, the first set of resources is less than the second set of resources.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
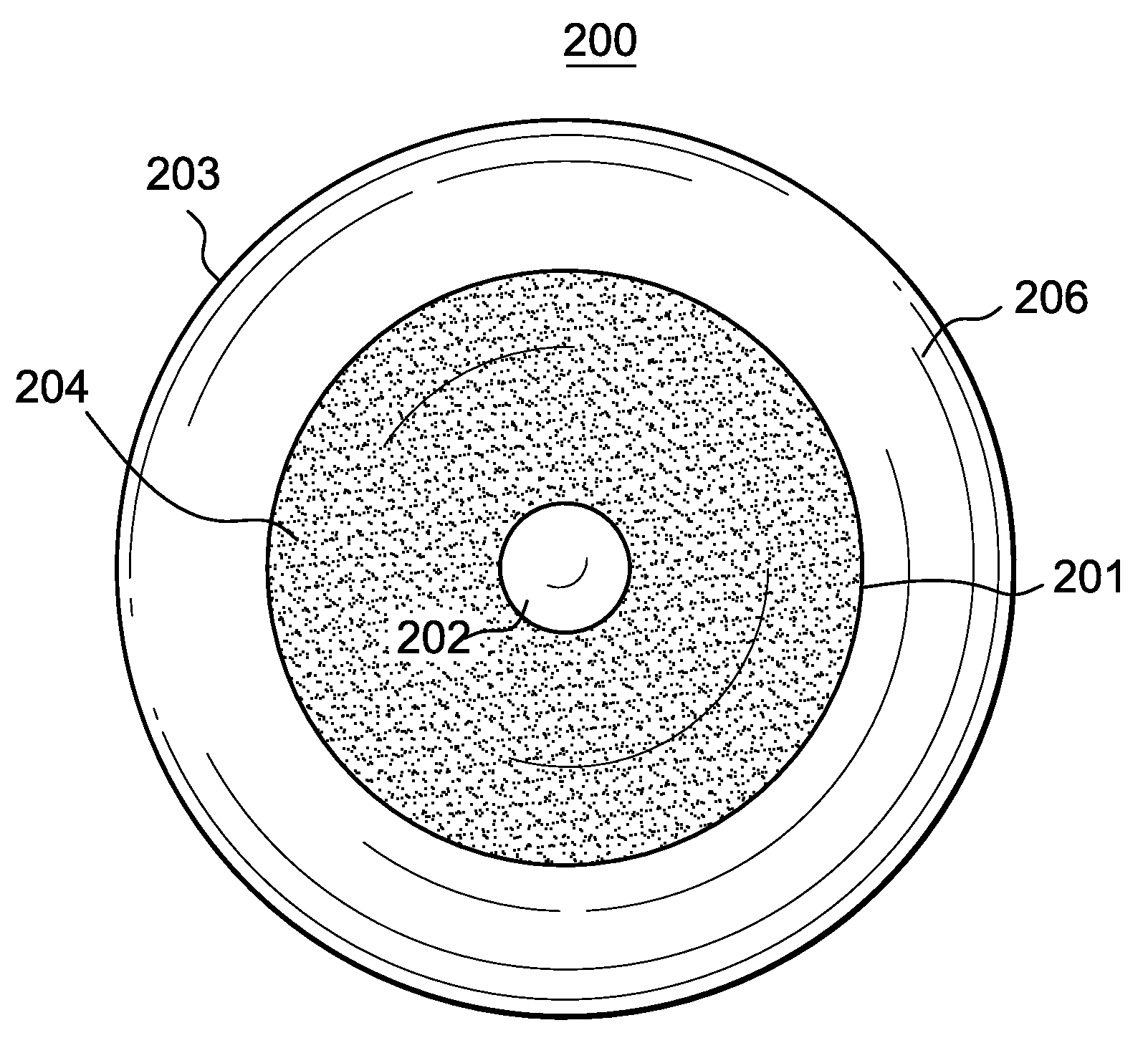
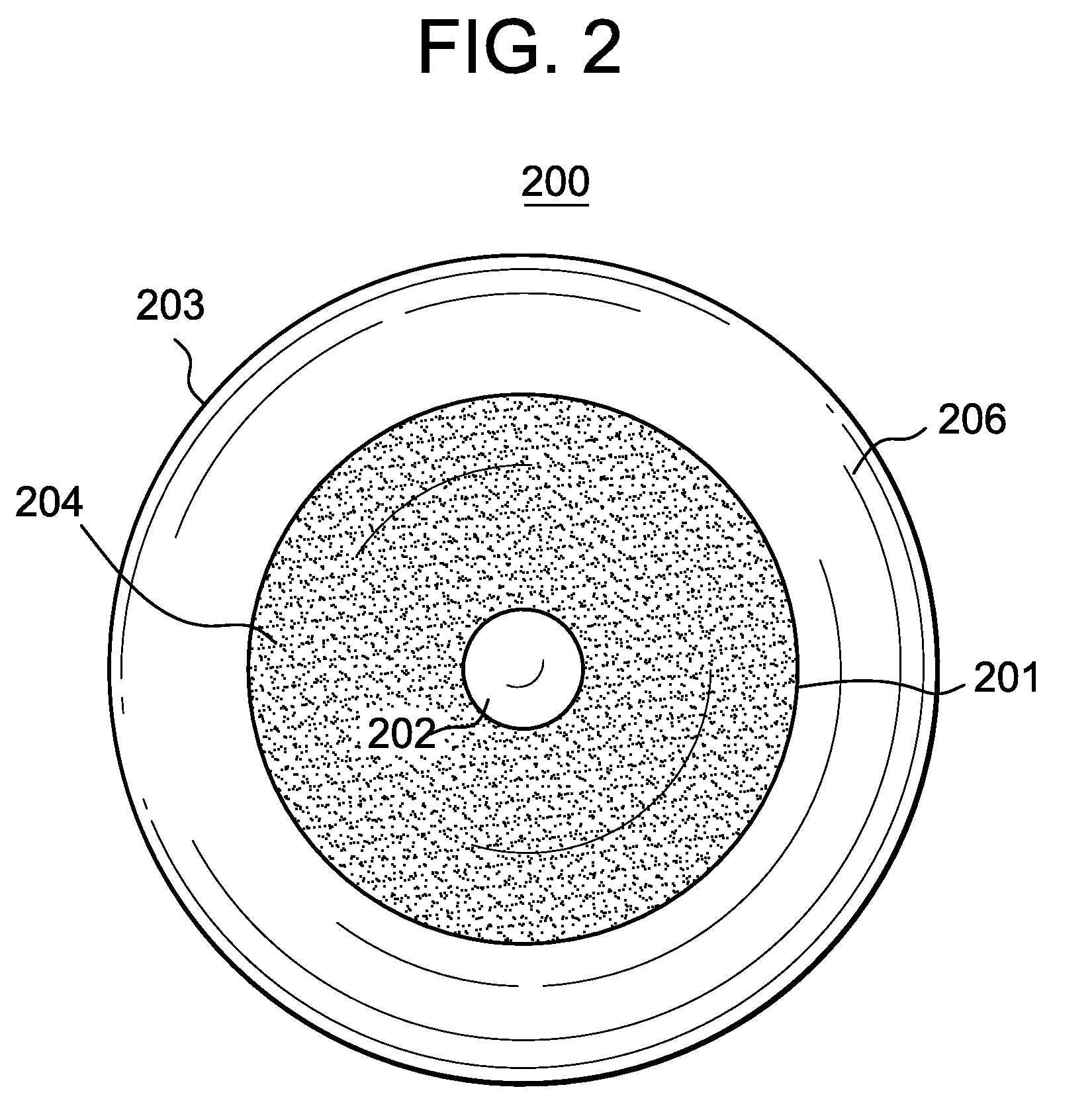
Annular shaped clear layer in cosmetic contact lenses
ActiveUS20160266403A1Enhance visual appearanceImprove visual effectsSpectales/gogglesOptical partsClear LayerEngineering
Contact lenses comprising designs / colorants may be utilized to enhance and / or highlight the appearance of the eyes upon which the contact lenses are positioned. These contact lenses comprise a substantially annular shaped clear layer on the front curve surface to completely encapsulate the designs / colorants within the contact lens. The annular shape provides no clear coat over the optic region thereby ensuring high optical quality.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Bandwidth modification for transparent capacity management in a carrier network
ActiveUS8559326B2Increase capacityMonetizeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsExternal dataCarrier signal
Some embodiments provide a capacity management agent that modifies bandwidth that is allocated between an end user and a carrier network by caching requested content that is streamed at a first rate and then providing the cached content to the end user through the carrier network at a second rate. The agent performs a process that includes receiving data intended for a service region of the carrier network from an external data network. The process identifies resource availability at the service region. Next, the process passes the data to the service region at the first rate when the resource availability at the service region is not less than a threshold amount and caches the data for passing to the service region at the second rate that consumes fewer carrier network resource than the first rate when the resource availability at the service region is less than the threshold amount.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Node and wireless sensor network comprising the node
InactiveUS8711743B2Facilitate communicationProvide qualityNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexWireless sensor networkingComputer science
A node (100) according to the invention is able to generate or receive, process and transmit information (161). At runtime, the node (100) dynamically determines and activates the protocols for processing the generated or received information (161).
Owner:UNIV GENT +1
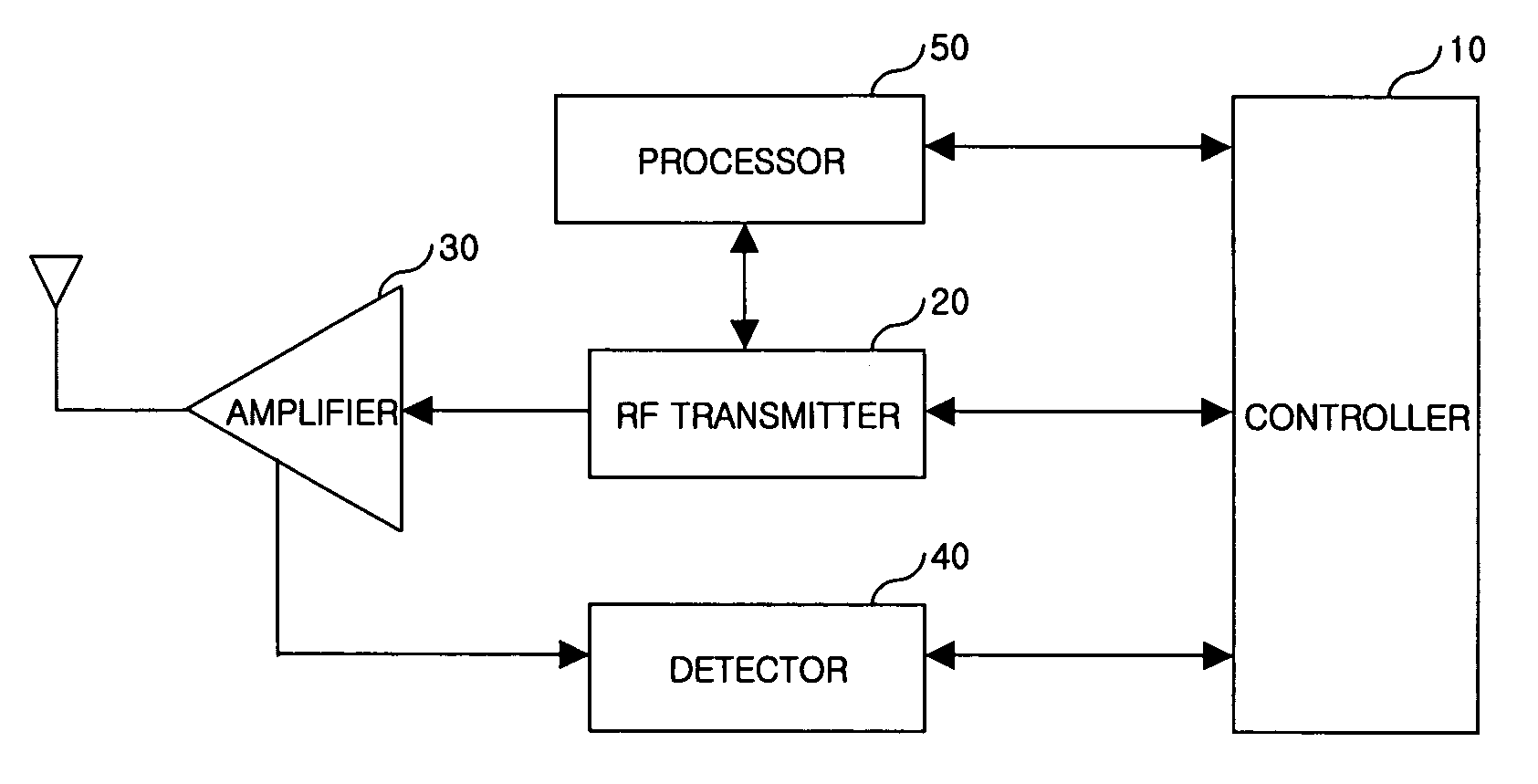
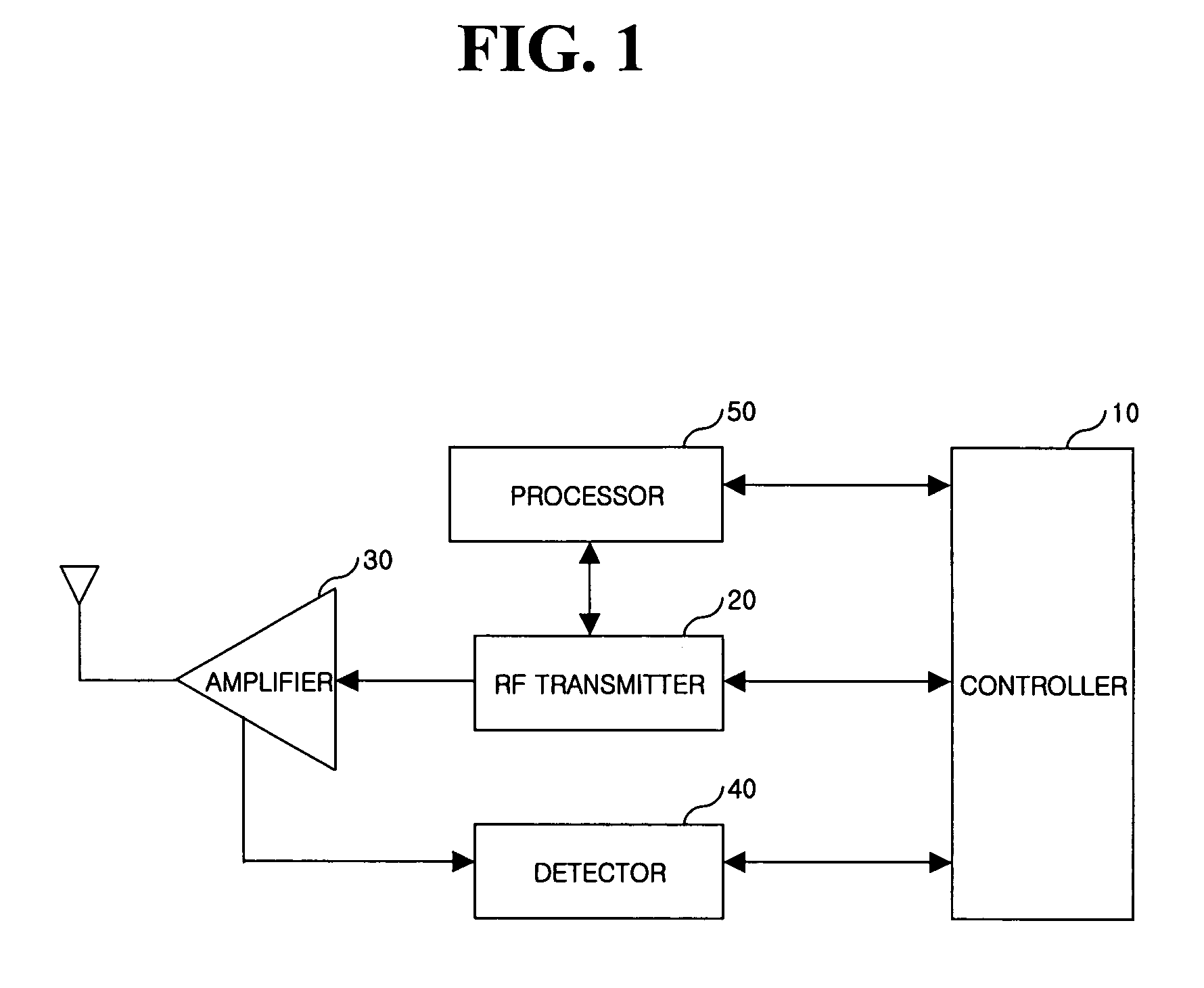
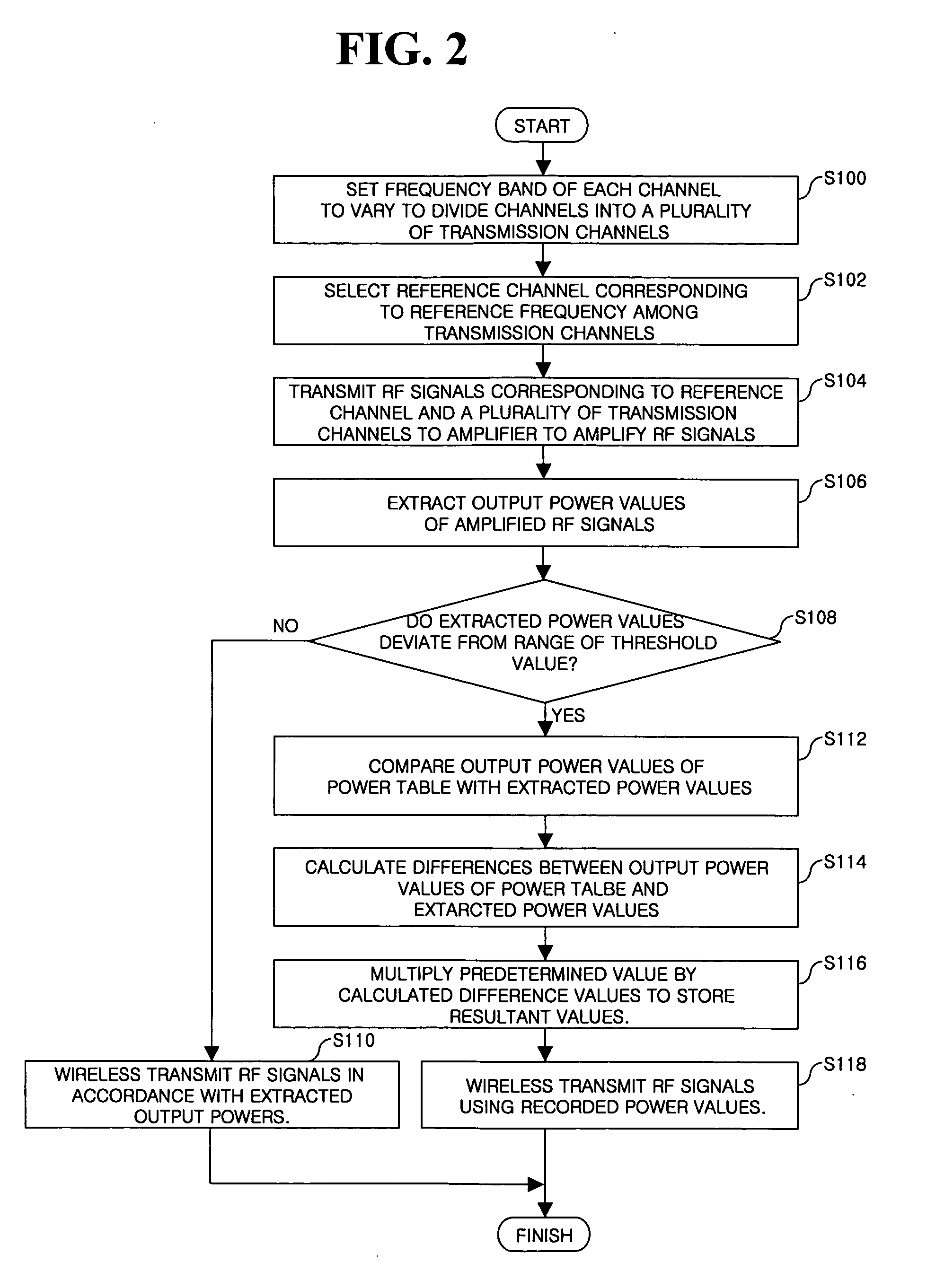
Apparatus for limiting maximum output of each transmission channel of mobile communication terminal and method thereof
InactiveUS20060132058A1Provide communication qualityProvide qualityPower managementElectric light circuit arrangementCommunication qualityTransmission channel
An apparatus for limiting the maximum output of each transmission channel of a mobile communication terminal and a method thereof are provided. The method includes detecting output powers of signals, calculating differences between the detected output powers and output powers previously stored in a terminal when the detected output powers deviate from the range of a threshold value, multiplying a predetermined number by the calculated difference values to store the resultant values, and transmitting signals using the stored power values. Therefore, output power of each transmission channel is controlled so that it is possible to provide improved communication quality without interference.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for controlling quality of service in mobile communication system
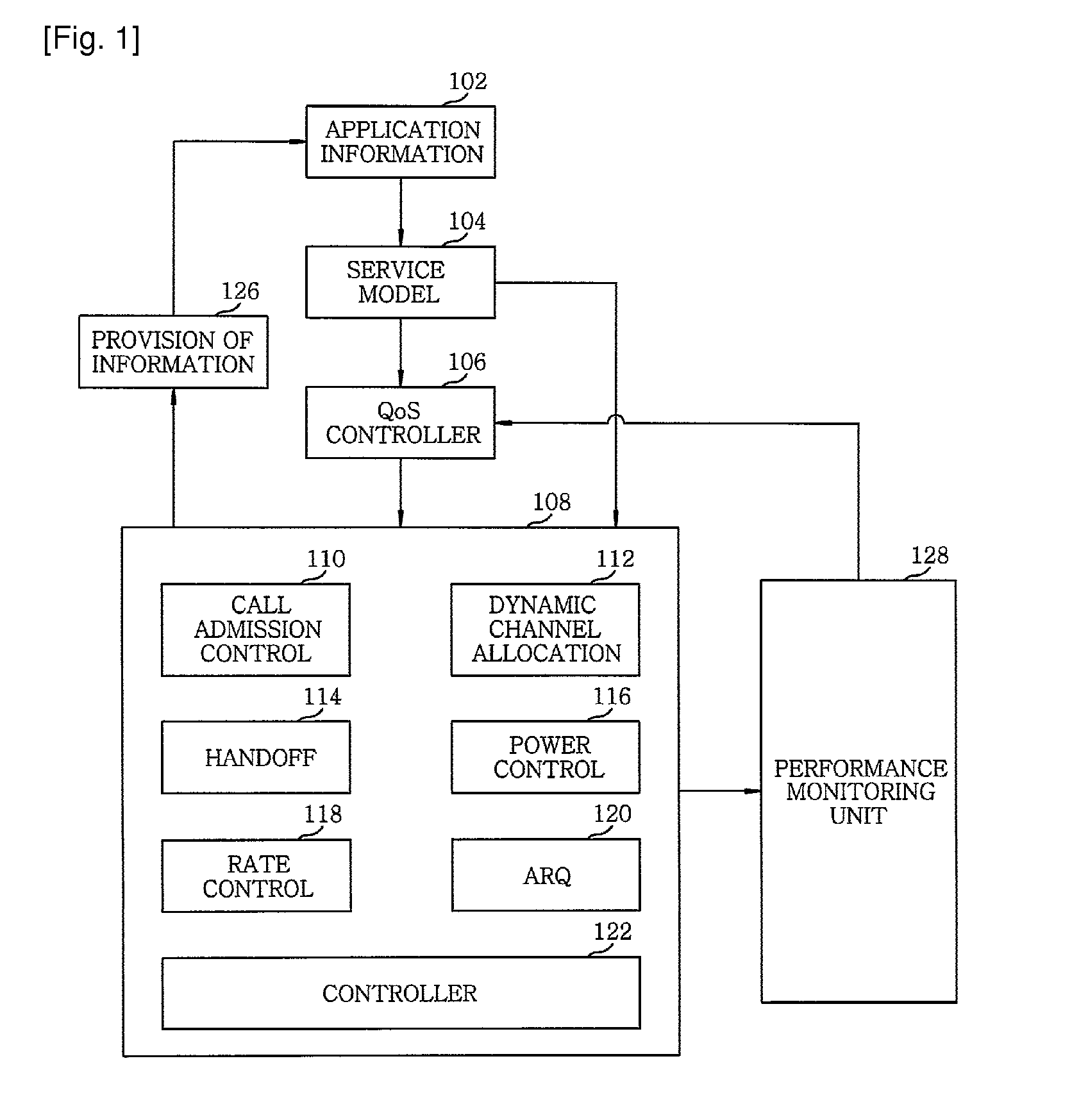
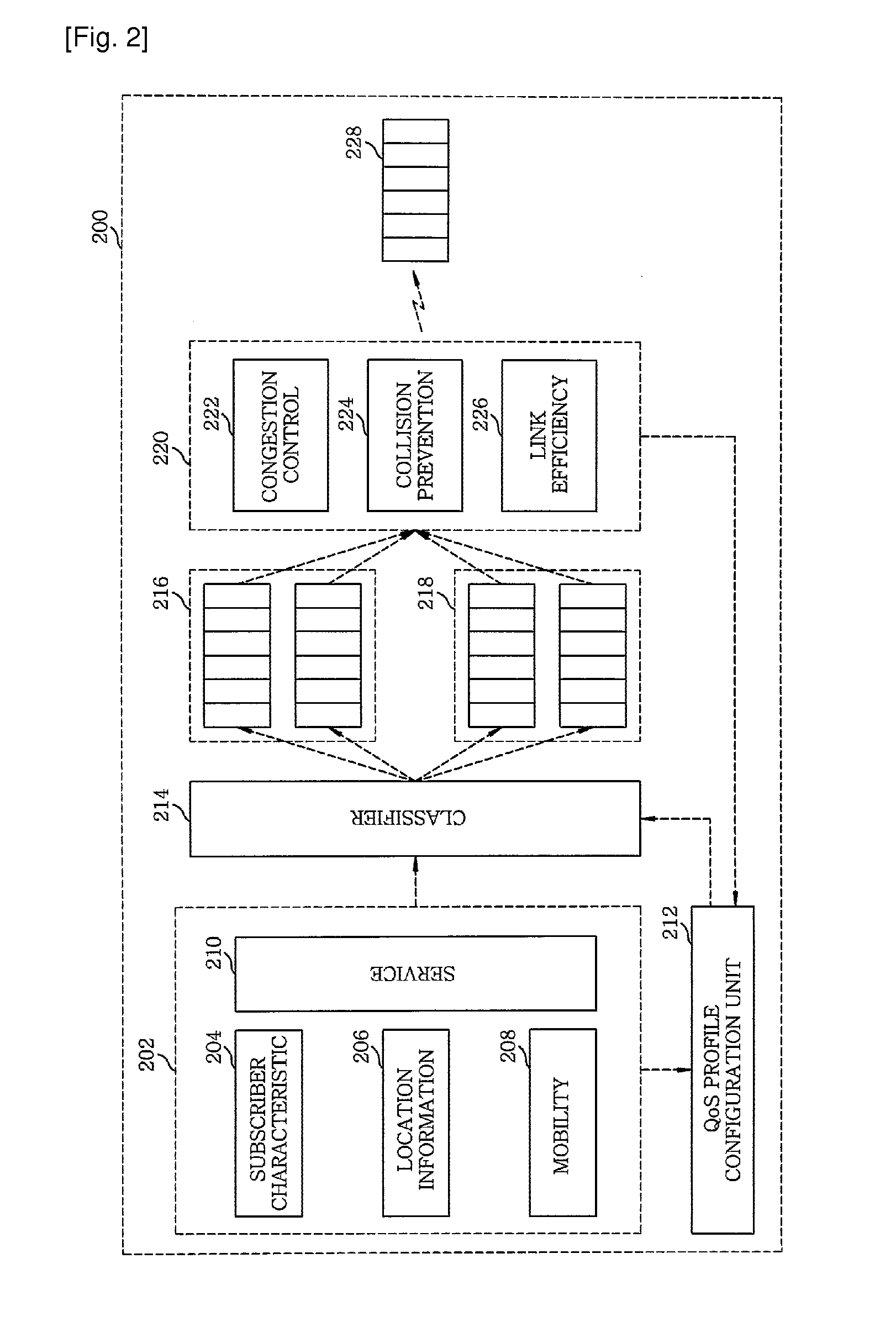
InactiveUS20100035623A1Provide qualityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceDistributed computing
A method for controlling quality of service (QoS) in a mobile communication system includes configuring a service model to operate radio resources, based on an application to provide a requested service from a subscriber terminal; forming a QoS profile using the service model; allocating the radio resources for each requested services in accordance with the QoS; providing information on the allocated radio resources to the application; monitoring a condition of the allocated radio resource; and controlling the QoS by reflecting information obtained from the monitored condition.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
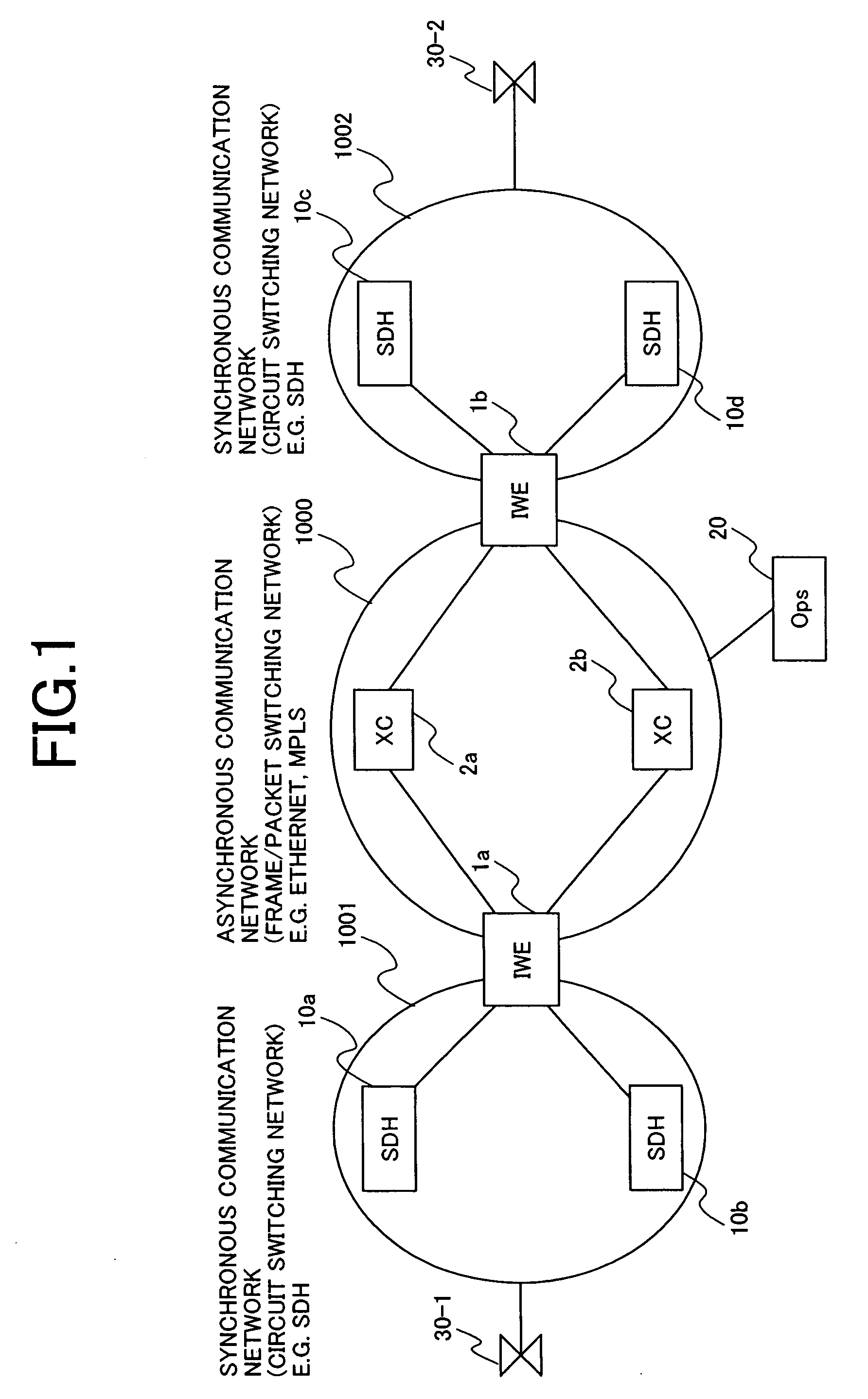
System Apparatus and Method for Interconnecting TDM and Frame/Packet Communication Networks
InactiveUS20120219006A1Impairing maintenanceImpairing operabilityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPacket communicationMultiplexing
An interconnection between fully synchronous networks and next-generation frame communications networks is disclosed. A means of bidirectional frame format conversion between a synchronous multiplexing system and a logical multiplexing system is provided, along with a method of transmitting data between different networks on a path as if it were being transmitted in the same network. Further, when converting network control information in an STM network into data suitable for a packet network, even across the boundary of a synchronous multiplexing system and a logical multiplexing system, a unified communication management means is provided over the whole path.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com