Method for constructing Ustilago esculenta T-DNA mutant library and analyzing insertion sites
A technology for inserting sites and analysis methods, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and can solve problems such as increasing the difficulty of screening mutant libraries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0033] 1 Materials and methods
[0034] 1.1 Materials
[0035] 1.1.1 Test strains
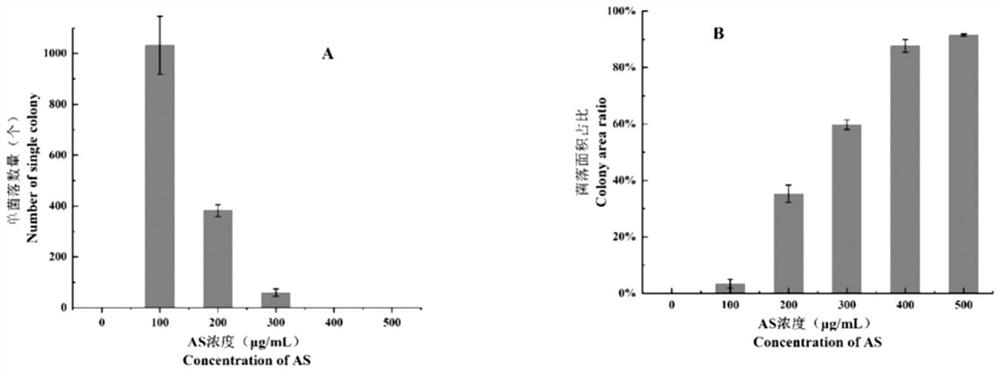
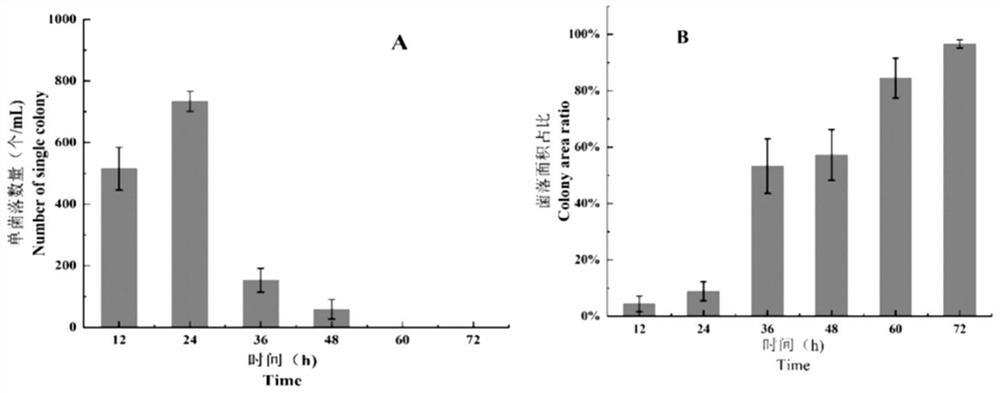
[0036]The self-fusion strain TSP of wild black powder fungus was constructed and preserved by the Key Laboratory of Biometrics and Inspection and Quarantine Technology of China Jiliang University. Agrobacterium strain EHA105 with the binary vector pNeo3300 carrying the Geneticin G418 resistance gene.
[0037] 1.1.2 Chemical reagents
[0038] Acetosy-ringone (AS), 2-(N-morpholine)ethanesulfonic acid (MES), rifampicin, streptomycin sulfate, kanamycin sulfate, cefotaxime sodium, and genetic Mycin (G418) was purchased from Beijing Soleibao Technology Co., Ltd.; Taq enzyme, agarose and other chemical reagents were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.
[0039] 1.1.3 Drugs and culture medium
[0040] 0.1M acetosyringone: AS 196.2g, dilute to 10mL with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); 100mg / mL MES: MES 1.5g, dilute to 15mL with distilled water; 100mg / mL cephalosporin: cephalosporin 1g, di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com