Novel metabolic marker for preparing liver cancer detection reagent and application thereof
A technology of metabolic markers and detection reagents, applied in the field of new metabolic markers, can solve the problems of limited accuracy of prediction sensitivity, high mortality rate of HCC, and limited accuracy of prognostic biomarkers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
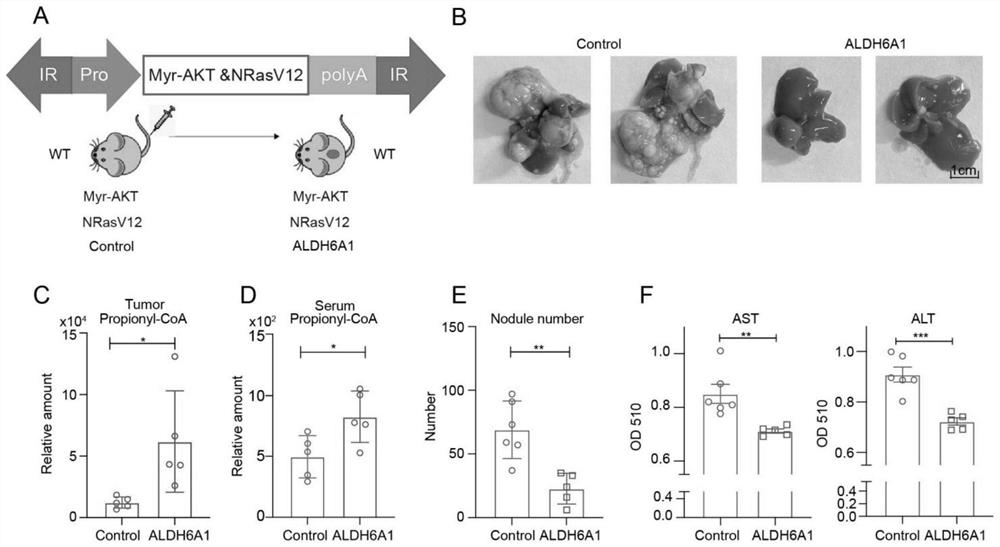
[0039] Example 1: Construction of a mouse liver cancer model by injecting liver-specific AKT / NRAS / ALDH6A1 through high pressure tail vein injection
[0040] 1. Experimental animals and feeding: The experimental animals were C57BL / 6 (WT) mice, and male mice were selected, 8 weeks old.
[0041] 2. Animal feeding and environmental conditions: All experimental mice were kept in the SPF animal room of the School of Life Sciences, Wuhan University. Alternate lighting every 12 hours, temperature 24±2°C, humidity 40-70%, mice were allowed to drink and eat freely.
[0042] 3. Sleep Beauty high-pressure tail vein mouse liver cancer model construction:
[0043] 8-week-old WT male mice were selected. Control group (Control group): pT3-myr-AKT-HA, pT3-vector, pCMV(CAT)T7-SB100 and pT / Caggs-NRASV12 were placed in normal saline and injected into the tail vein of mice under high pressure. Experimental group (ALDH6A1 group): pT3-myr-AKT-HA, pT3-ALDH6A1, pCMV(CAT)T7-SB100 and pT / Caggs-NRASV1...
Embodiment 2
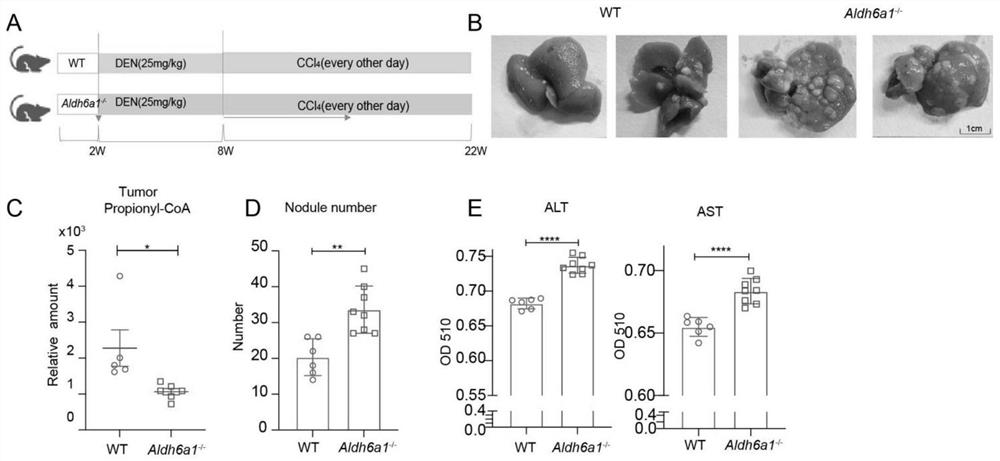
[0048] Example 2: Intraperitoneal injection of DEN / CCl 4 Induced mouse liver cancer model
[0049] 1. Experimental animals and feeding: experimental animals C57BL / 6 background wild type (WT) and Aldh6a1 knockout Aldh6a1 - / - Mice, select male mice, 2 weeks old.
[0050] 2. Animal feeding and environmental conditions: All experimental mice were kept in the SPF animal room of the School of Life Sciences, Wuhan University. Alternate lighting every 12 hours, temperature 24±2°C, humidity 40-70%, mice were allowed to drink and eat freely.
[0051] 3. DEN / CCl 4 Construction of mouse liver cancer model:
[0052] Select WT male mice and Aldh6a1 - / - male mice. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with DEN (25 mg / kg) on day 14 of birth; CCl in olive oil at 8 weeks of age 4 (0.5ml / kg) by gavage, once every 2 days, up to 21 weeks. The health of the mice was checked weekly and recorded. At the end of 22 weeks, the whole blood was placed at 4 °C overnight, centrifuged at 2500 rpm, ...
Embodiment 3
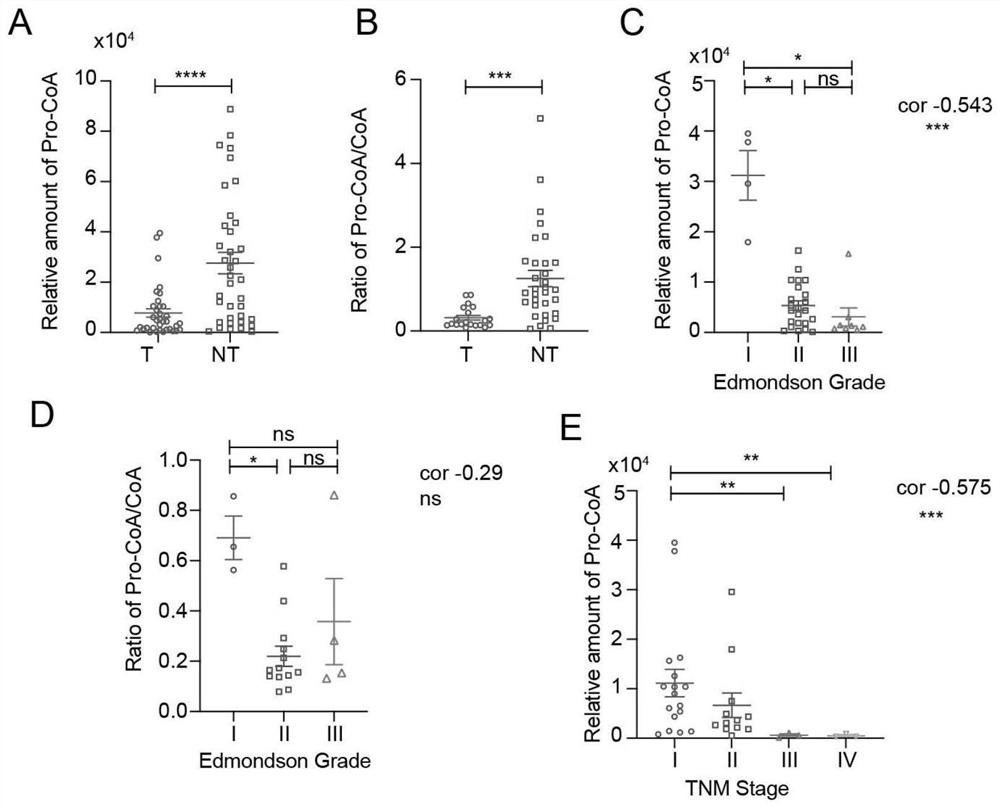
[0056] Example 3: Detection of metabolites in liver tissue of liver cancer patients
[0057] 1. Collection of clinical liver cancer samples: Collect liver tissue samples (cancer tissue and paired paracancerous tissue) of clinical liver cancer patients. The samples are from Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, and signed informed consent by the patients. All procedures comply with the Helsinki Rules. Liver cancer tissue and paired paracancerous tissue were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored in a -80°C refrigerator.
[0058] 2. Detection of tissue metabolite levels: 25 μg of liver cancer tissue and paired adjacent tissue were taken to extract tissue metabolites. The levels of propionyl-CoA and coenzyme A metabolites were detected by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS / MS).
[0059] 3. Correlation analysis of metabolite levels in liver cancer tissue and pathology: The correlation an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com