Strengthening and toughening heat treatment process for cold work die steel matrix
A cold work die steel, strengthening and toughening technology, applied in the field of strengthening and toughening heat treatment process, can solve the problems of low impact toughness of steel matrix and insufficient strength and toughness of the matrix, and achieve the effect of improving crack resistance and anti-adhesion performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
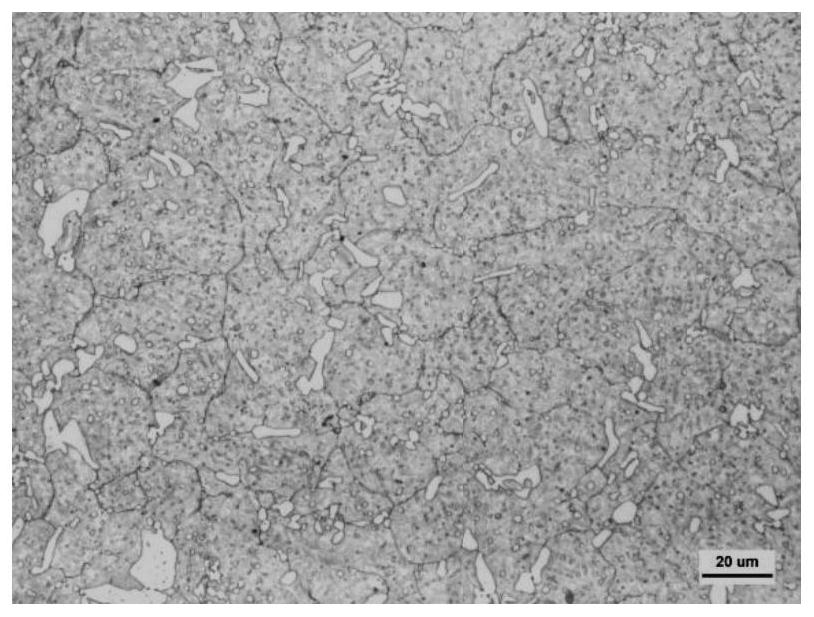
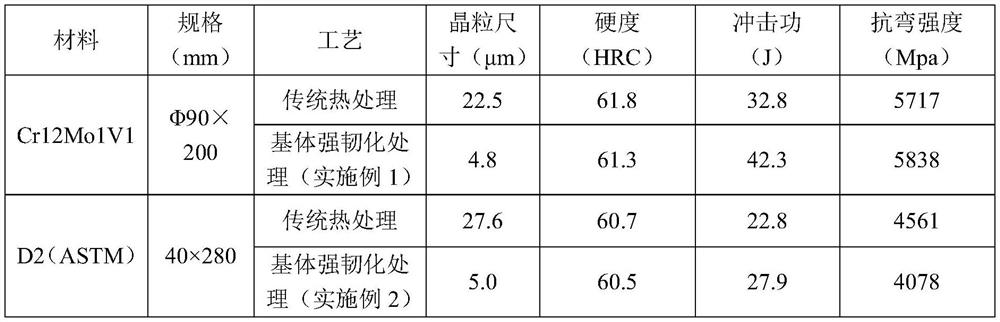
[0031] A heat treatment process for strengthening and toughening a cold work die steel matrix in this embodiment, the heat treatment material is Cr12Mo1V1 cold work die steel with a specification of Φ90mm (meeting the requirements of the GB / T 1299-2014 standard), and Φ90mm×200mm are respectively used for conventional heat treatment (for ratio) and experiments were carried out using the protocol of the invention (Example 1). After heat treatment, the impact, bending and metallographic samples were cut at the radius of 1 / 2 of the steel for microstructure analysis of performance testing. The conventional heat treatment (comparative example) process is: 1030 ℃ quenching + 500 ℃ tempering, its metallographic structure see figure 1 shown.
[0032] A cold work die steel matrix strengthening and toughening heat treatment process provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0033] (1) The first pass of high temperature austenitization: heat the raw material or mold bla...
Embodiment 2
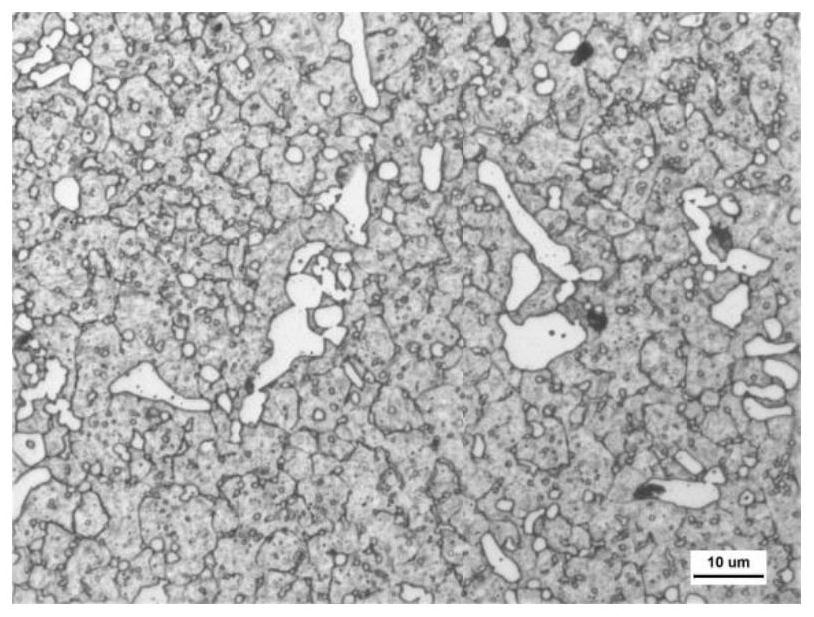
[0040] The invention provides a heat treatment process for strengthening and toughening a cold work die steel matrix. The heat treatment material is Φ90mm specification D2 cold work die steel (meeting the requirements of the GB / T 1299-2014 standard), and 40mm×280mm die blanks are respectively subjected to conventional heat treatment. Compared with the strengthening and toughening heat treatment of the matrix, the two processes are compared. After treatment, the impact, bending and metallographic samples were cut at the longitudinal 1 / 4 of the billet for microstructure analysis of performance testing. The conventional heat treatment process is: quenching at 1030°C + tempering at 540°C.
[0041] A cold work die steel matrix strengthening and toughening heat treatment process provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0042] (1) The first pass of high temperature austenitization: heat the raw material or mold blank to 1160°C at a heating rate of 30°C / h, keep it ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] The invention provides a heat treatment process for strengthening and toughening a cold work die steel matrix. The heat treatment material is Φ90mm specification D2 cold work die steel (meeting the requirements of the GB / T 1299-2014 standard), and 40mm×280mm die blanks are respectively subjected to conventional heat treatment. Compared with the strengthening and toughening heat treatment of the matrix, the two processes are compared. After treatment, the impact, bending and metallographic samples were cut at the longitudinal 1 / 4 of the billet for microstructure analysis of performance testing. The conventional heat treatment process is: quenching at 1030°C + tempering at 540°C.
[0050] A cold work die steel matrix strengthening and toughening heat treatment process provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0051] (1) The first pass of high temperature austenitization: heat the raw material or mold blank to 1180°C at a heating rate of 50°C / h, keep the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com