Conductive and resistance material with electrical stability for electronic apparatus
A technology of conductive fillers and inert fillers, which is applied in the direction of conductive materials dispersed in non-conductive inorganic materials, printed circuits assembled with electrical components, conductive adhesives, etc., and can solve problems such as non-disclosure and increased contact resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 Three compositions denoted A-C were prepared from phenolic resin and varying amounts of carbon black. The formulations of these compositions are shown in Table 1:
[0037] Composition A
Filler: 15g carbon black
21g talc
1g silica
Filler: 8g carbon black
21g talc
1g silica
Filler: 2g carbon black
21g talc
1g silica
Resin:
54g phenolic resin
Resin:
54g phenolic resin
Resin:
54g phenolic resin
Thinner:
15-20g butyl carbitol
Thinner:
15-20g butyl carbitol
Thinner:
15-20g butyl carbitol
[0038] The fillers are mixed together by means of a kneader or planetary mixer. The phenolic resin was a xylene-formaldehyde resin from Emerson & Cuming; the resin components were mixed together and added slowly to mix with the filler. The resulting paste was dispersed and mixed...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 This example illustrates the effect of temperature and humidity on the resistivity of compositions A, B and C when in contact with an adjacent metal, referred to as the contact resistivity.
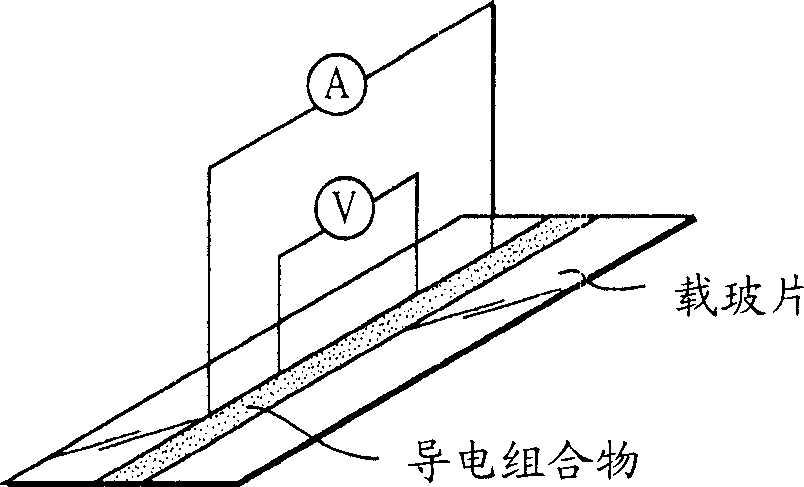
[0042] Contact resistivity test carrier such as Figure 4 As shown, a FR-4 board substrate was included on which was printed an open circuit pattern having 3 mm long metal segments separated by 1 mm horseshoe shaped gaps. The number of connections between the composition and the metal segment is 10. The composition will cure at 175°C for 4 hours.
[0043] By employing multiple metal-adhesive connections in the contact resistance device, the variation in conductivity can be amplified and experimental error minimized. The contact resistance of the entire circuit was measured with a Fluke 45 DualDisplay Multimeter and considered to be the combined resistance obtained by adding the resistivity and the interface resistance between the ends of each metal segment and the test ...
Embodiment 3
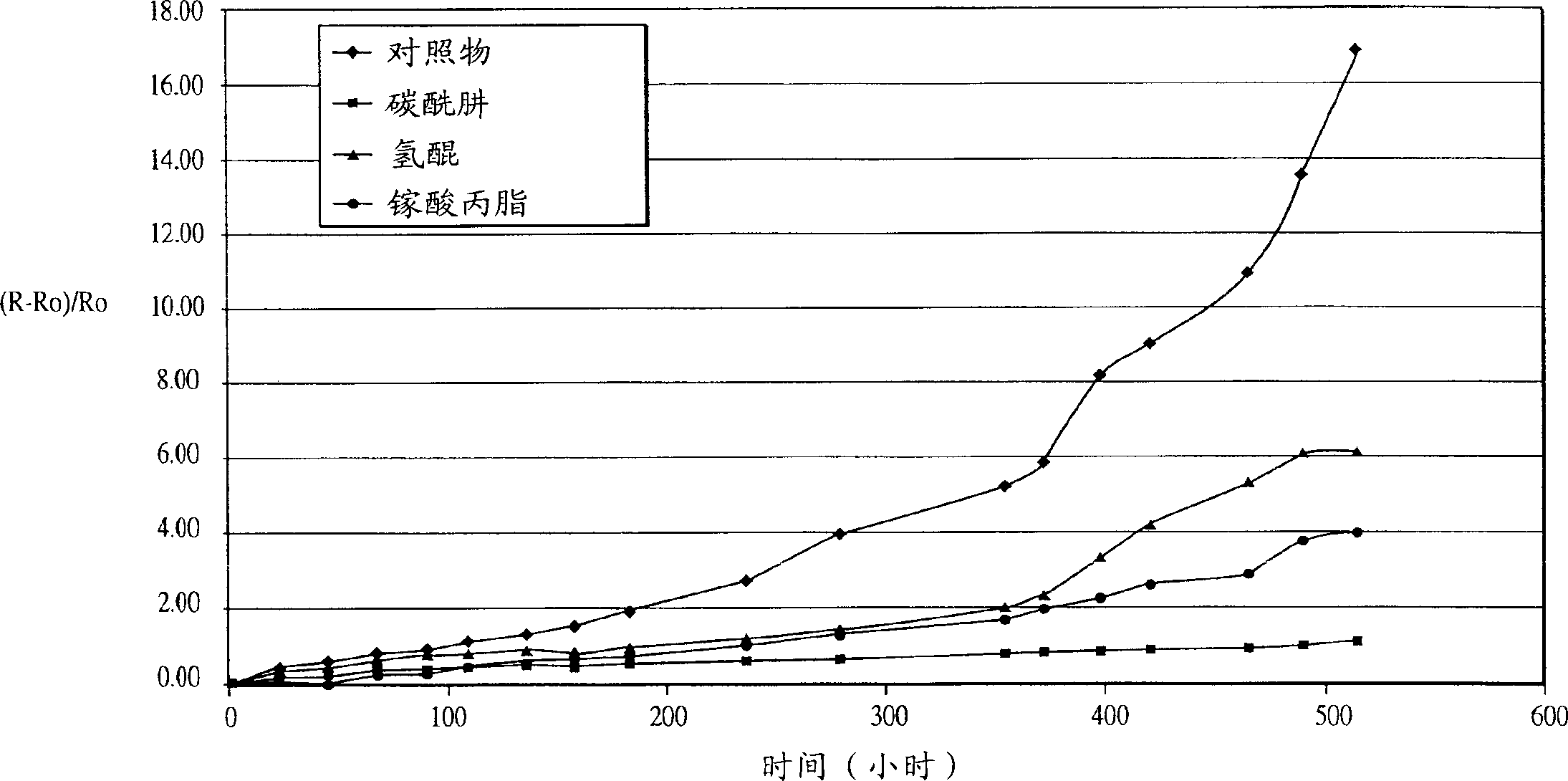
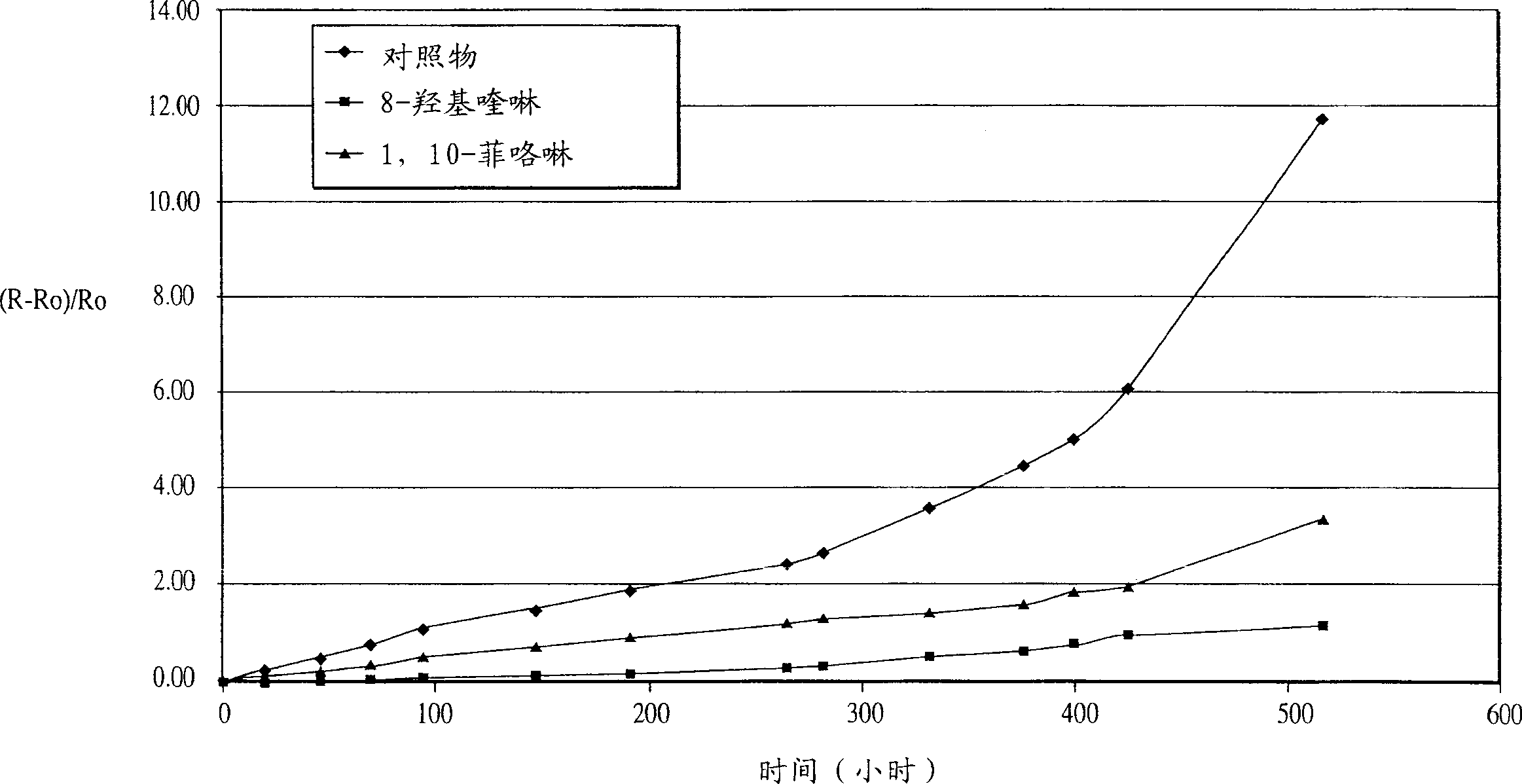
[0049] Example 3: A series of compositions were prepared from composition A in Example 1, doped with different amounts of oxygen scavengers or corrosion inhibitors. As in Example 2, the contact resistivity was measured before and after the treatment under the conditions of 85° C. / 85% relative humidity. The results are shown in Table 4 and show that, except for mercaptobenzothiazole, the presence of oxygen scavengers or corrosion inhibitors are effective in preventing a significant increase in resistivity.
[0050] Composition A
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com