Method of forming photoresist pattern
A pattern and photoresist technology, applied in the field of forming photoresist patterns, can solve the problems of weakened light source, increased process cost, increased exposure cost, etc., and achieve the effect of small line width
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0029] Figure 1A to Figure 1D It is a schematic flow chart of forming a photoresist pattern according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
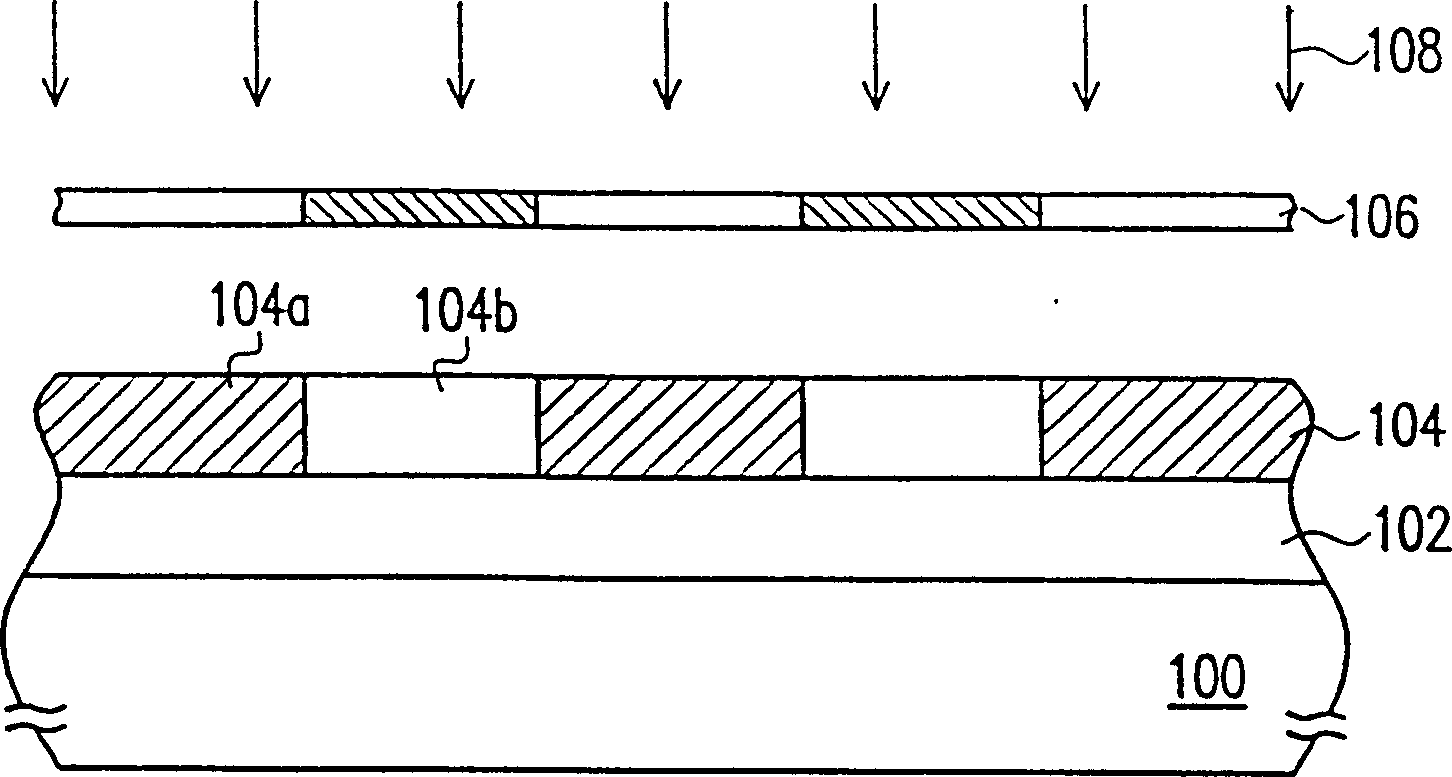
[0030] First, please refer to Figure 1A , a substrate 100 is provided, and a component structure (not shown) is formed in the substrate 100. A material layer 102 to be etched has been formed on the substrate 100. The material layer 102 to be etched is, for example, a metal layer, a polysilicon layer, a silicon nitride layer or silicon oxide layer. And a photoresist layer 104 is formed on the layer to be etched 102 , wherein the material of the photoresist layer 104 is, for example, positive photoresist.
[0031] Please continue to refer to Figure 1A , performing an exposure process 108 on the photoresist layer 104 with a photomask 106, so that the photoresist layer 104 is divided into an exposed area 104a and an unexposed area 104b. The exposed area 104 a is decomposed by light irradiation, and the unexposed area 104 b ...
no. 2 example
[0038] Figure 2A to Figure 2C It is a schematic diagram of the steps of forming a photoresist pattern according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0039] First, please refer to Figure 2A , first provide a substrate 200, in which a component structure (not shown) is formed, and a material layer 202 to be etched has been formed on the substrate 200, and the material layer 202 to be etched is, for example, a metal layer, a polysilicon layer, a silicon nitride layer, etc. layer or silicon oxide layer. And a photoresist layer 204 is formed on the layer to be etched 202 , wherein the material of the photoresist layer 204 is, for example, positive photoresist.
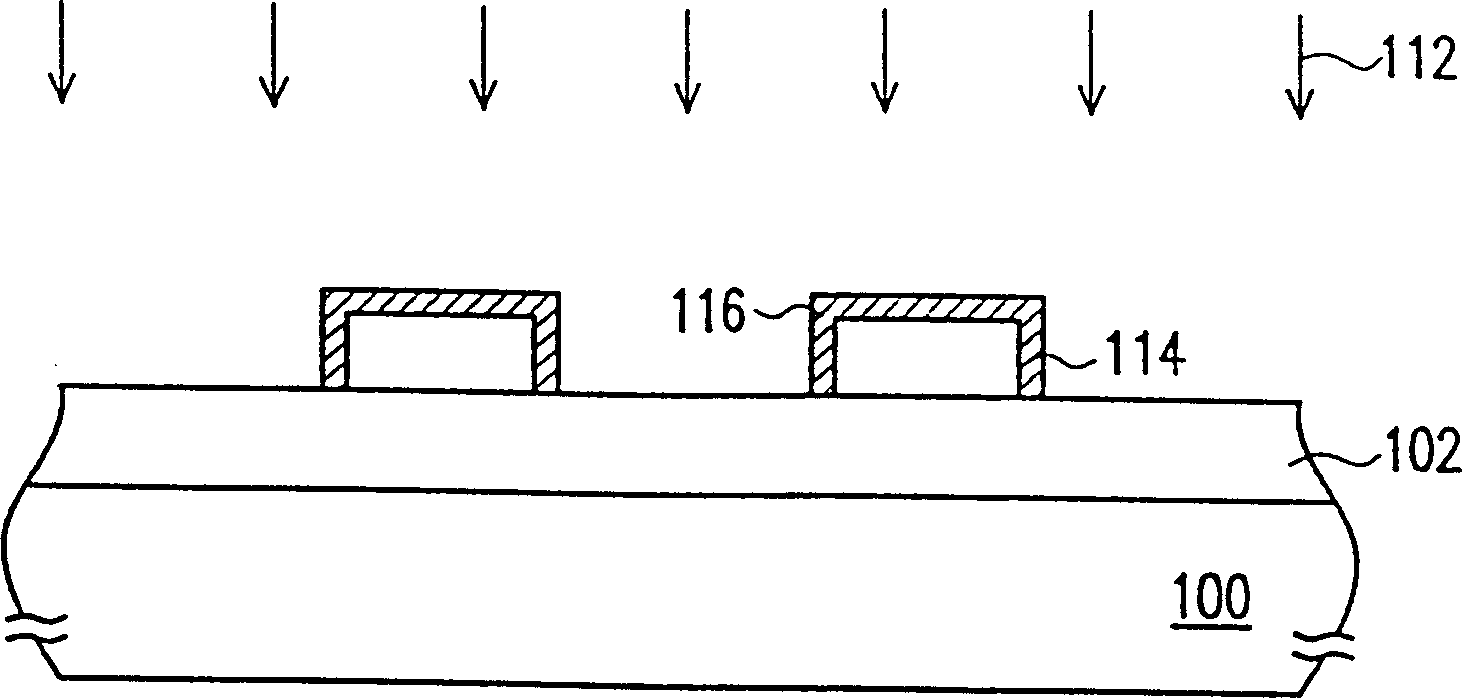
[0040] Please continue to refer to Figure 2A , performing an exposure process 208 on the photoresist layer 204 with a photomask 206, so that the photoresist layer 204 is divided into an exposed area 204a and an unexposed area 204b. The exposed area 204 a is decomposed by being irradiated with light thro...
no. 3 example
[0045] Figure 3A to Figure 3C It is a schematic flow chart of forming a photoresist pattern according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
[0046] First, please refer to Figure 3A , first provide a substrate 300, in which a component structure (not shown) is formed, and a material layer 302 to be etched has been formed on the substrate 300, and the material layer 302 to be etched is, for example, a metal layer, a polysilicon layer, a silicon nitride layer, etc. layer or silicon oxide layer. And a photoresist layer 304 is formed on the layer to be etched 302 , wherein the material of the photoresist layer 304 is, for example, negative photoresist.
[0047] Please continue to refer to Figure 3A , performing an exposure process 308 on the photoresist layer 304 with a photomask 306 , so that the photoresist layer 304 is divided into an exposed area 304 a and an unexposed area 304 b. The exposed area 304 a is irradiated with light through the light-transmitting...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com