Gene markers for lung cancer
A technology for labeling and lung cancer, applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, anti-receptor/cell surface antigen/cell surface determinant immunoglobulin, etc., can solve high medical expenses, adverse Outcomes, lack of lung cancer antibodies, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
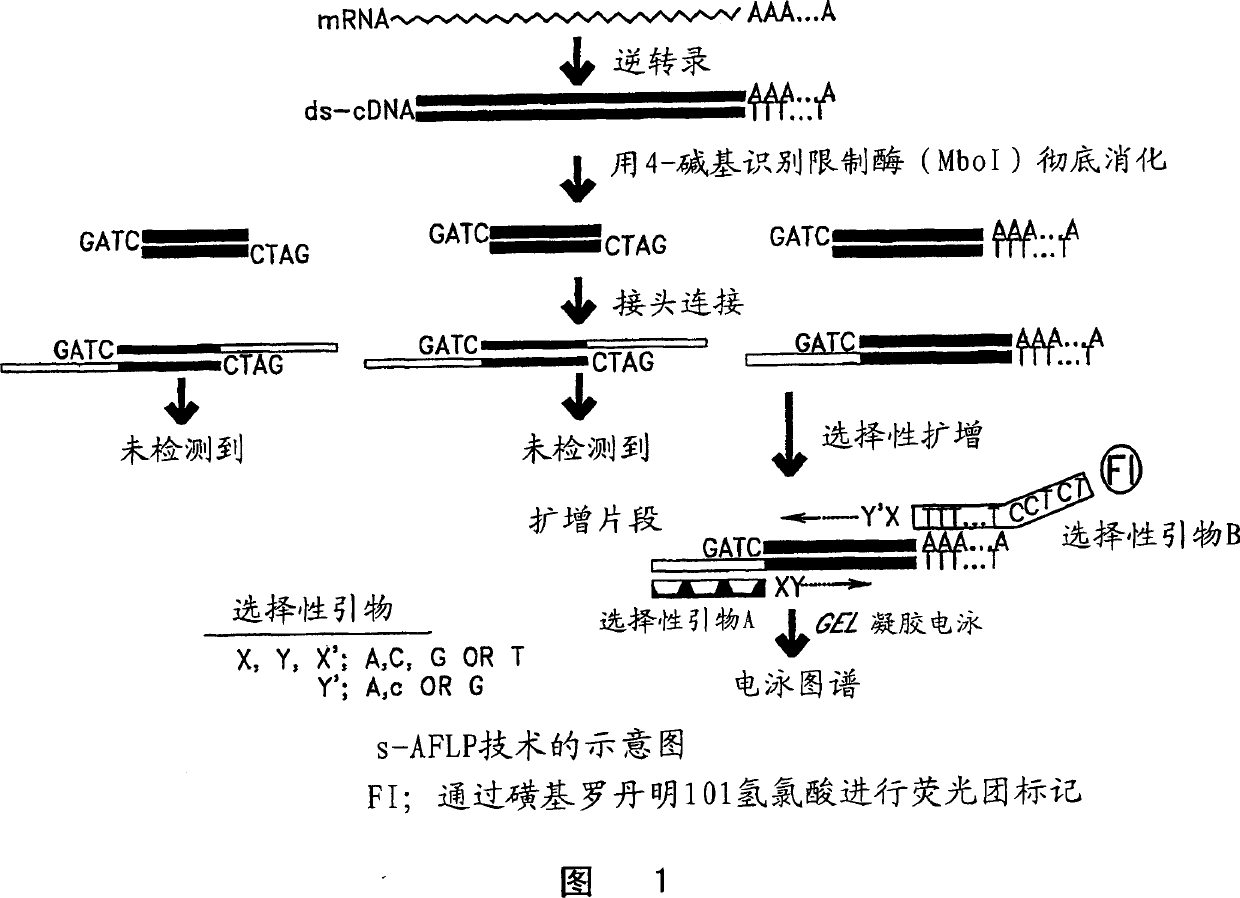
[0038] s-AFLP differential display
[0039] s-AFLP is based on selective PCR amplification of restriction fragments from cDNA libraries. Two sets of selective primers were used. The first set is selective primer A shown in Figure 1, which includes three parts; a core sequence, an enzyme-specific sequence and two selective nucleotides at the 3' end. It can provide 42 = 16 kinds of primers due to the change of selective primers. The second set is the optional primer B shown in Figure 1, which also includes three parts: an anchor sequence, a polyT sequence and two optional nucleotides labeled with fluorophores at the 3' end. It can provide 3 x 4 = 12 primers because there are three selection sequences after polyT (A, G, and C). Therefore, all 3' terminal cDNA restriction fragments including polyA fragments were included in the 192 (16 x 12) types generated by this selective PCR method. Each signal that appeared on the gel display of the amplified fragments represented a non-ove...
example 2
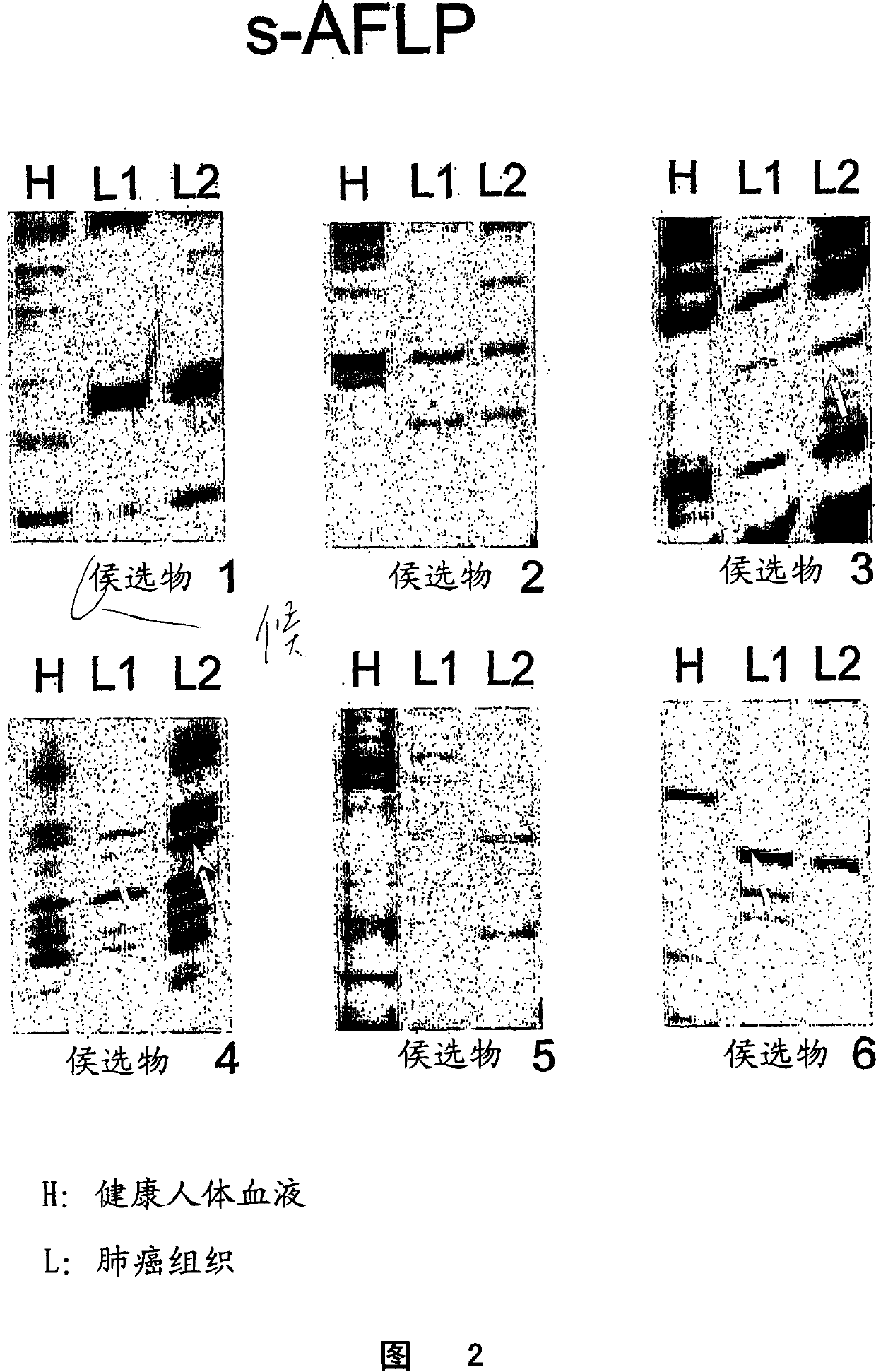
[0055] candidate gene
[0056] Candidate markers are listed in Table 1. The first candidate marker found was identified as the syndecan 1 gene (nucleotide sequence PubMed deposit number BC008765, protein sequence deposit number AAH08765) (SEQ ID NOS: 18 and 19). Figure 6 provides the sequence of the fragment produced by s-AFLP (SEQ ID NO: 22). A blast search of the sequence yielded a paired fragment of exons 2-6 of the syndecan 1 gene (GenBank accession number Z48199). Syndecan 1 is a cell surface transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan from the proteoglycan family that binds the extracellular matrix and growth factors. Loss of regulation of this gene has been identified in several cancers.
[0057]Another candidate marker was identified as collagen 1α2 (nucleotide sequence PubMed accession number J00114, protein sequence accession number AAA51996) (SEQ ID NO: 20 and 21). Figure 7 provides the sequences of the old fragment (SEQ ID NO: 24) and the new fragment (SEQ ID NO...
example 3
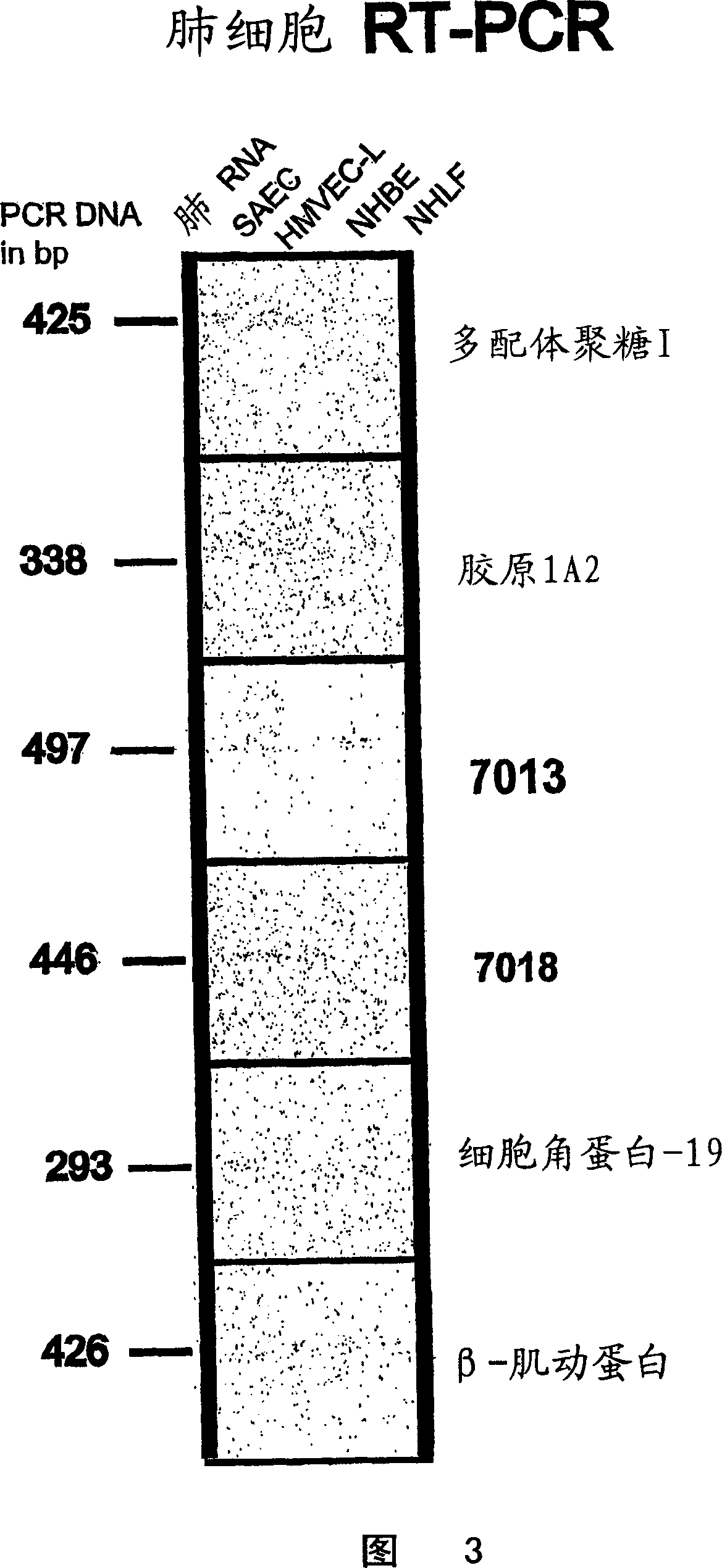
[0062] Expression of said markers in normal lung cells and lung cell lines
[0063] To determine whether the markers are expressed in normal human lung cells, RT-PCR was performed on normal human lung RNA using small air vent epithelial cells from human lung, small vessel epithelial cells from lung, bronchial epithelial cells and normal human lung adult cells. Equivalent RNA from fibroblasts.
[0064] Preparation of total RNA from normal lung or lung cancer cell lines
[0065] Total RNA was isolated from cells by acid-guanidine thiocyanate / phenol / chloroform extraction using the TRI REAGENT(R) method (Molecular Research Center, Inc., Cincinnati, OH, USA). Exhaustive purification of RNA is not necessary, and in fact, some DNA contamination is acceptable if primers are designed to span introns.
[0066] RT-PCR
[0067] All RNA samples were treated with DNaseI prior to reverse transcription to ensure no genomic DNA contamination. 1 unit of DNaseI (Life Technologies) was used p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com