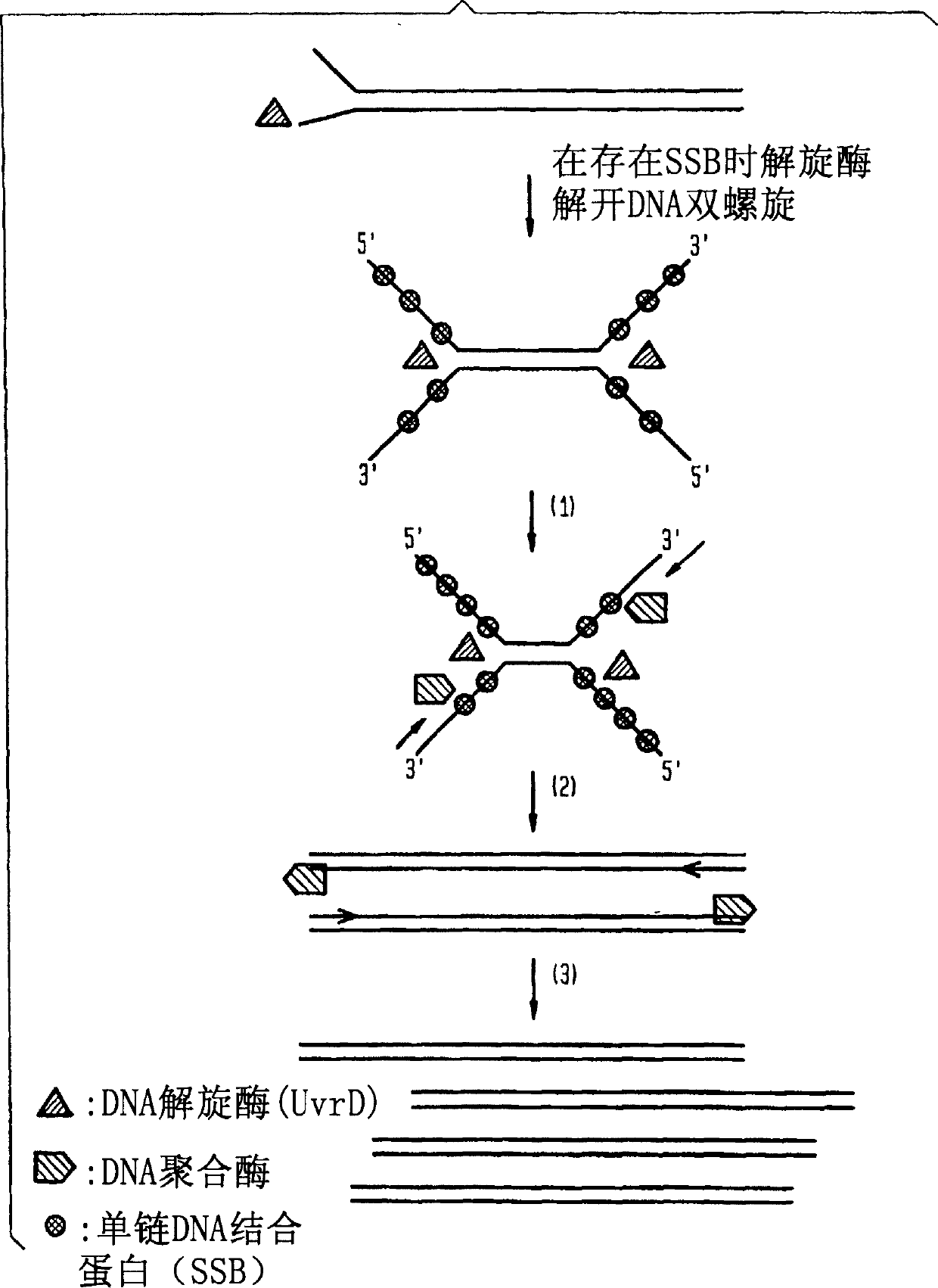
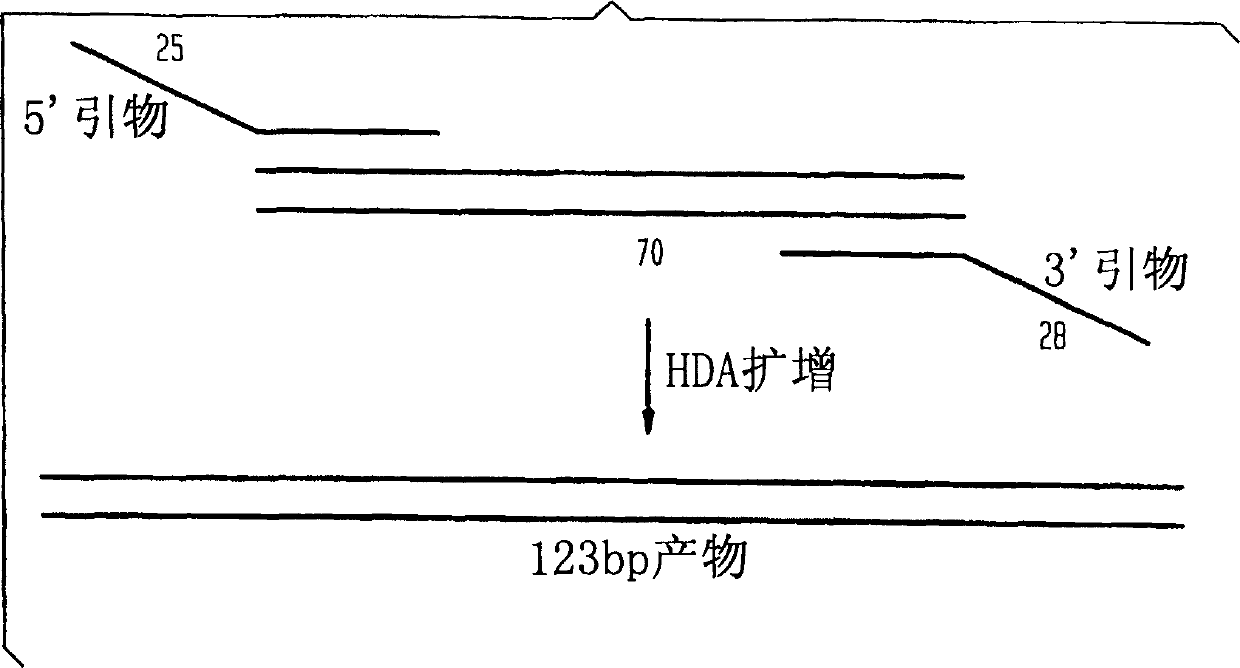
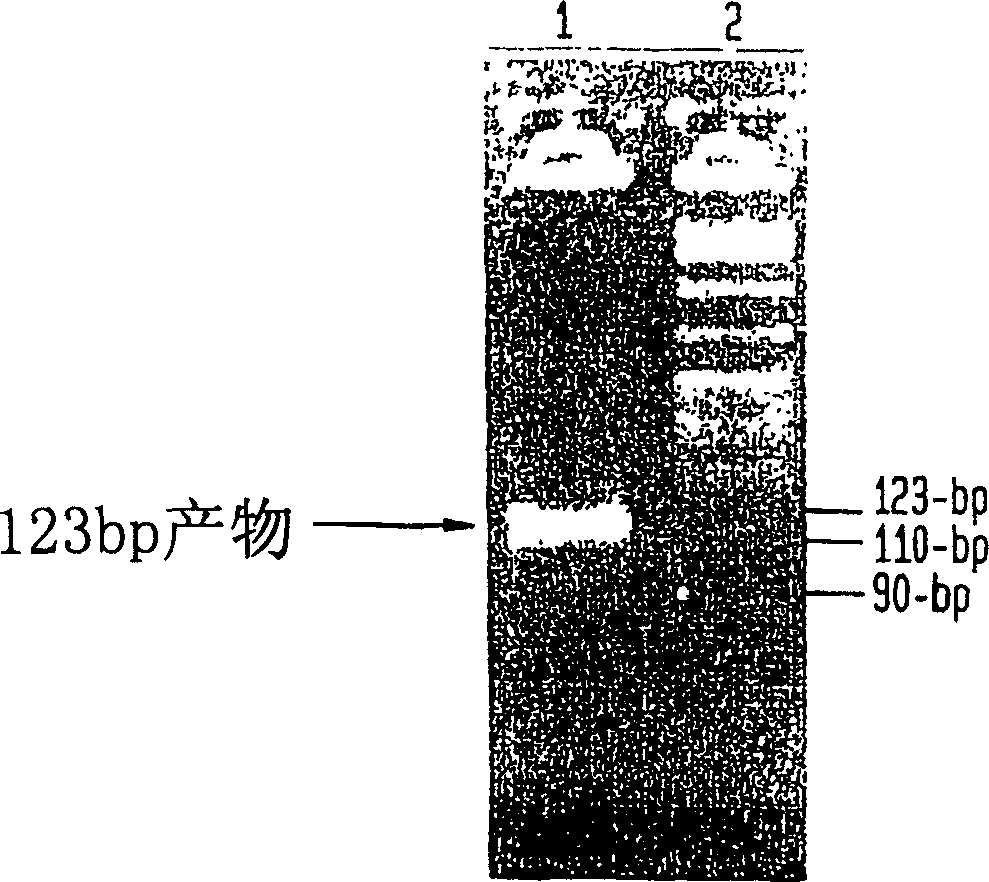
Helicase dependent amplification of nucleic acids
A technology of helicase and nucleic acid, applied in the field of helicase-dependent amplification of nucleic acid, which can solve the problem of extra time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
[0139] Cloning and purification of UVRD helicase and its auxiliary protein MUTL
[0140] 1. Cloning of genes encoding UvrD helicase and MutL proteins.
[0141] Take advantage of Impact TM Systematic cloning of genes encoding E. coli helicase II or UvrD helicase (Swissprot Accession No.: P03018) and its auxiliary protein E. coli MutL protein (Swissprot Accession No.: P23367), Impact TM The system results in the C-terminal translational fusion of a bifunctional marker consisting of a S. cerevisiae VMA intein and a chitin-binding domain (New England Biolabs, Inc. (Beverly, Mass. ))composition. This protein purification system utilizes the DTT-induced self-cleavage activity of a protein splicing element (called intein) to separate the target protein from the affinity tag (chitin-binding domain). Vent® DNA polymerase was used to amplify the UvrD gene from E. coli K12 genomic DNA using primer 5A (5'GGTGGTACCATGGACGTTTCTTACCTGCTC 3' (SEQ ID NO: 1)) and primer 3A (5'GGTGGT...
Embodiment II
[0148] Method for Amplifying Nucleic Acid Double Helix Targets
[0149] As a model system for helicase-dependent amplification, a synthetic DNA duplex was used as a template for the HDA reaction. This example illustrates the DNA duplex amplification using the UvrD HDA system. Methods for template denaturation, primer annealing and extension are described below.
[0150] Prepare 35 μl of reaction component A by mixing the following: 10 μl of 5×HDA buffer A (175 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 5 mM DTT), 0.5 μl of 70 bp-derived oligodeoxynucleotide (2 μM: 5' TGGCTGGTCACCAGAGGGTGGCGCGGACCGAGTGCGCTCGGCGGCTGCGGAGAGGGGTAGAGCAGGCAGC 3' (SEQ ID NO: 5)) and the DNA template of the bottom oligodeoxynucleotide (2 μ M: 5' GCTGCCTGCTCTACCCCTCTCCGCAGCCGCCGAGCGCACTCGGTCCGCGCCACCCTCTGGTGACCAGCCA 3' (SEQ ID NO: 6)) CATGTTAGGTTCTATGGATCGAGTCTGGCTGGTCACCAGAGGG 3' (SEQ ID NO: 7)), 1 μl of 3' primer (10 μM; 5' TCCCTTAGAGGTCACATTGGATCGAGTCGCTGCCTGCTCTACCCC 3' (SEQ ID NO: 8)), 10 μl of f...
Embodiment III
[0154] HDA amplification of specific sequences from plasmid DNA
[0155] To test whether HDA can be used to amplify specific target sequences in DNA templates, we applied the UvrD HDA system and used two pUC19 / M13 universal primers—primer 1224 and primer 1233—to amplify the 2647bp DNA plasmid pAH1 (Fig. 110 bp sequence in 15 (SEQ ID NO: 9)). Primer 1224 and Primer 1233 are commercially available, and their sequences can be obtained from a company (New England Biolabs, Inc., (Beverly, MA)). The amplification scheme is depicted in Figure 3.
[0156] Prepare two acetate reaction buffers: 10×HDA buffer A, containing 350mM Tris-acetate (pH7.5) and 100mM DTT; 10×HDA buffer B, containing 10mM Tris-acetate (pH7. 5), 1 mg / ml BSA and 90 mM magnesium acetate. Prepare HDA Reaction Component A by combining:
[0157] 5 μl of 10x HDA Buffer A
[0158]1.5 μl of 23 nM AhdI-cut pAH1 plasmid
[0159] 1 μl of 10 μM primer 1224
[0160] 1 μl of 10 μM primer 1233
[0161] 2 μl o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com