Dynamic ice cool storage method and apparatus thereof
A technology of ice storage and equipment, applied in the field of cold storage and refrigeration, can solve the problems of increasing thermal resistance, reducing the cooling coefficient of refrigerators, increasing costs, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
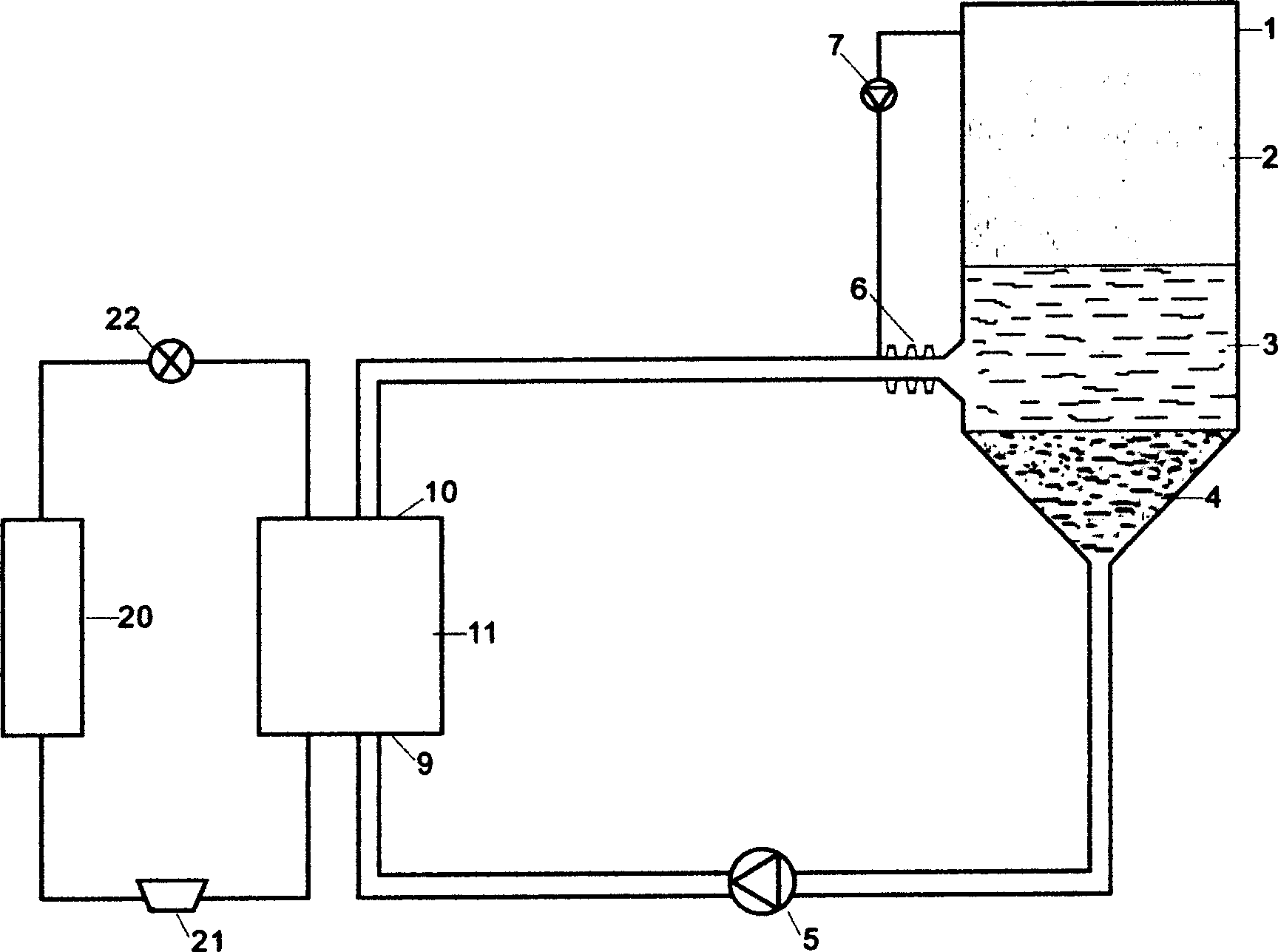
[0021] Fig. 1 is to take cooling through the refrigerant 4, the refrigerant 4 is transported to the heat exchanger 11 by the pump 5 through the transmission pipeline, the temperature of the input end 9 of the heat exchanger 11 is higher than 0°C, and the temperature of the output end 10 is lower than 0°C, due to the refrigerant The melting point of the refrigerant is lower than 0°C, and the refrigerant at the output end 10 is still in a liquid state, and the refrigerant in a liquid state below 0°C is transported back to the energy storage tank 1, and the refrigerant is evenly dispersed in the water layer 3 through the ultrasonic atomizing nozzle 6, The water around the refrigerant quickly absorbs the cooling capacity of the refrigerant, resulting in crystallization. These crystals are called ice crystals 2. The ice crystals float on the water surface due to their small specific gravity, while the refrigerant gradually sinks to the bottom of the tank due to their high specific gr...
Embodiment 2
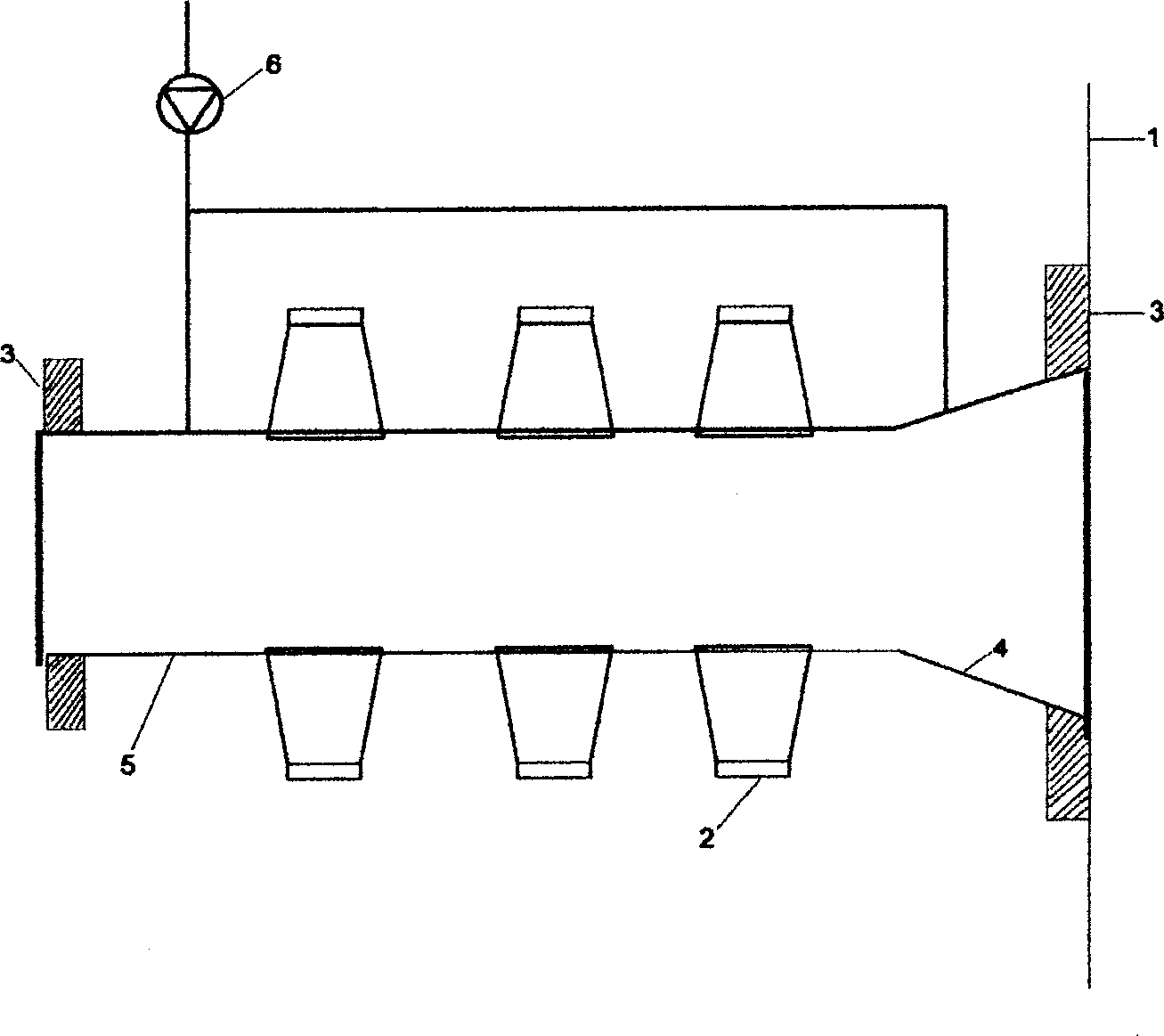
[0027] Figure 2 is the structural diagram of the ultrasonic nozzle, which is installed at the middle and lower entrance of the energy storage tank. The structure of the ultrasonic nozzle is composed of a pipeline 5, a plurality of ultrasonic transducers 2, a flange 3, a conical nozzle 4 and an air pump 6. The transducer 2 is installed on the conical nozzle 4 and the front end pipe wall of the nozzle. The ultrasonic wave emitted by the transducer creates an ultrasonic field in the liquid in the pipe, generating air bubbles to activate the refrigerant flowing through, making the particles smaller, increasing the exchange area between the refrigerant and water, and improving efficiency; and crushing the ice flakes in the refrigerant , to avoid pipeline blockage; at the same time prevent a large number of ice crystals generated by the nozzle from clogging the nozzle; more advantageously, due to the disturbance of the ultrasonic field, the refrigerant is quickly separated from the i...
Embodiment 3
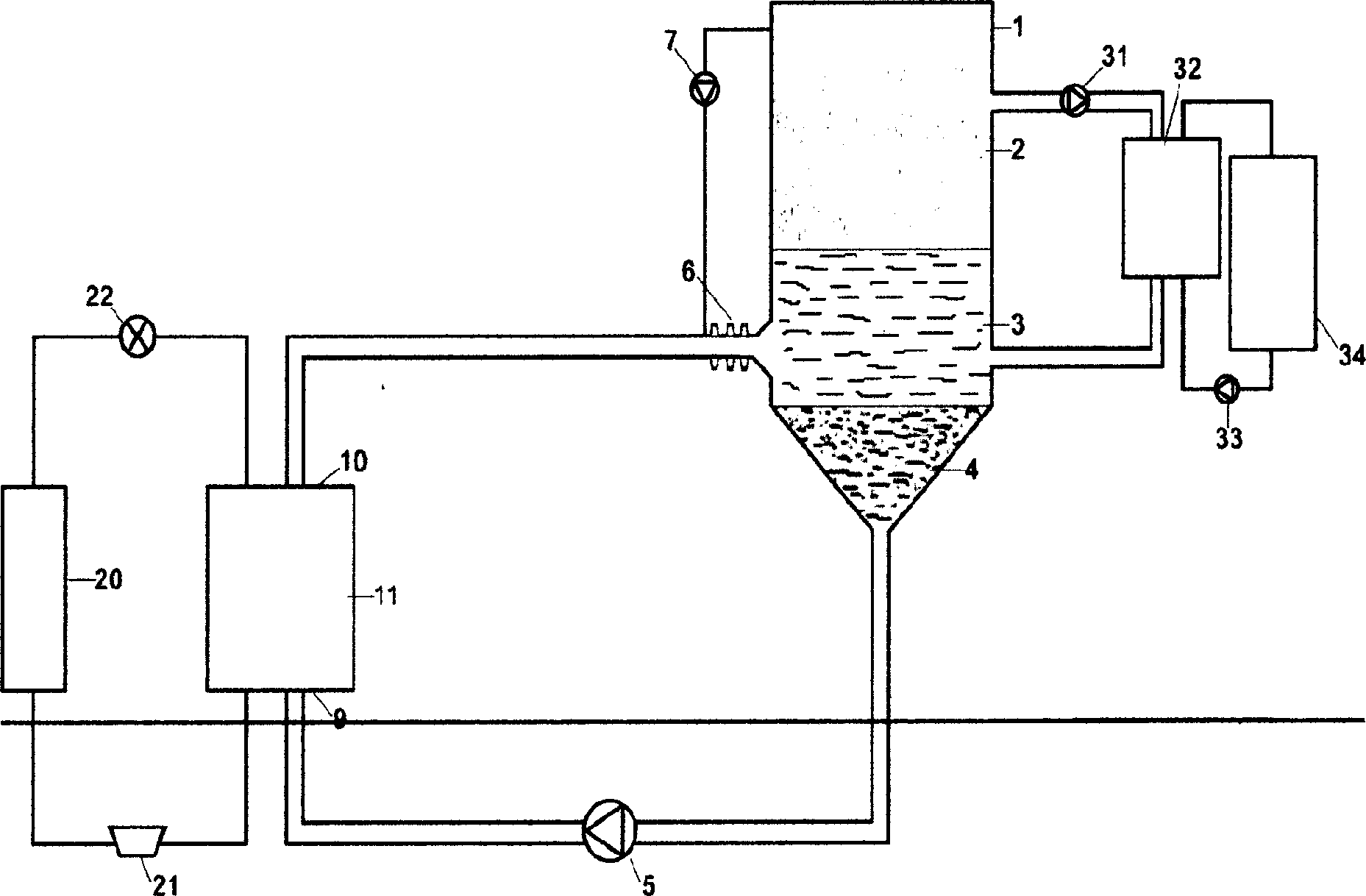
[0029] Figure 3 is a specific application of an ice storage air conditioning system. The refrigeration unit 21, the condenser 20, the expansion valve 22 and the heat exchanger 11 form a refrigeration cycle. Through the heat exchanger 11, the refrigerant absorbs the cooling capacity and becomes a low-temperature refrigerant below 0°C. The water is fully mixed to produce a large number of ice crystals, which float on the water layer of the energy storage tank due to the buoyancy. into the heat exchanger 32 for heat exchange to complete the load refrigeration cycle.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com