Technique for removing and reclaiming phenol from coke-plant waste water
A technology for coking wastewater and wastewater, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of inability to deal with non-volatile phenol, difficulty in desorption, secondary pollution, etc., and achieve the cost of adsorbent. The effect of low cost, simple process operation and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
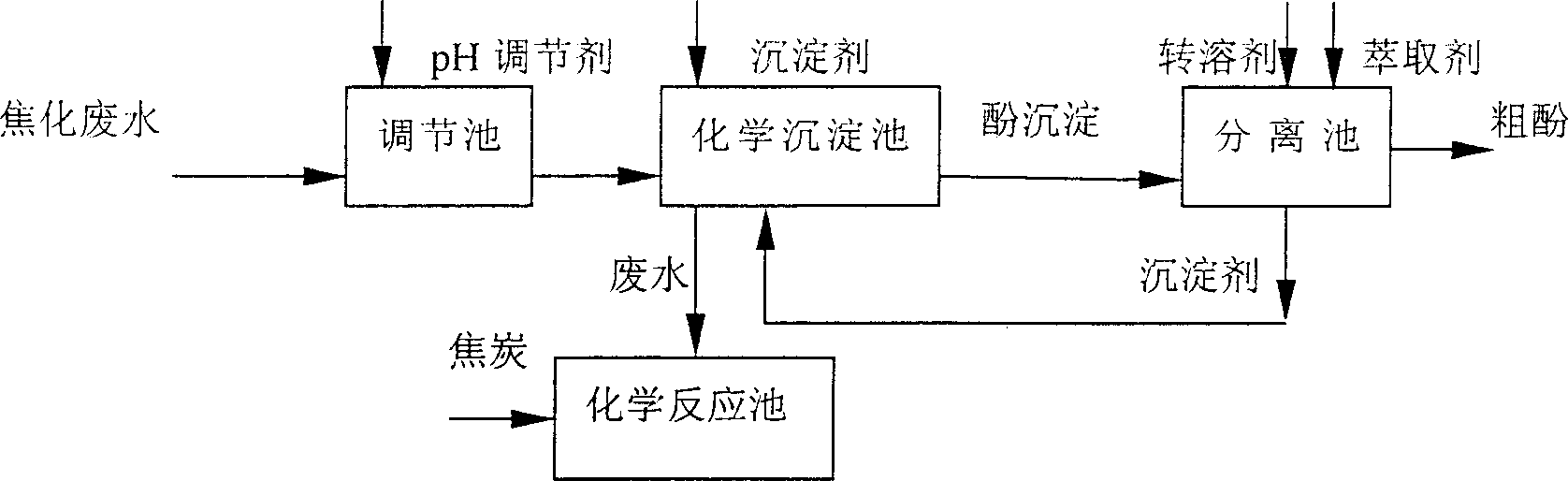
[0018] Take the treatment of coking wastewater with a phenolic content of 1072.79 mg / L in a coking plant as an example:
[0019] 1. At room temperature of 30 °C, the coking wastewater first enters the adjustment tank, and NaOH is added to adjust the pH of the wastewater to 11.03.
[0020] 2. The effluent from the conditioning tank enters the chemical sedimentation tank, where barium ions are added to react with phenolic substances for 15 minutes to form insoluble compounds to precipitate, and the phenolic concentration in the water is detected after filtration. BaCl 2 ·2H 2 The amount of O added was 2 g / L, and the removal rate of phenol was 47.62%. See Table 1 for details.
[0021] 3. The phenol precipitate separated from the chemical sedimentation tank is dissolved with hydrochloric acid, and the precipitant barium ion is reduced for recycling; the phenolate is re-converted into phenol and released, and then benzene is added for extraction and recovery. kg.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Embodiment and reaction conditions are exactly the same as Example 1, BaCl 2 ·2H 2 The amount of O added was increased to 4 g / L, and the removal rate of phenol was 53.25%. See Table 1 for details. The crude phenol was 0.456 kg per ton of coking wastewater treated.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Embodiment and reaction conditions are exactly the same as Example 1, BaCl 2 ·2H 2 The amount of O added was increased to 6g / L, and the removal rate of phenol was 60.53%, as shown in Table 1, and 0.509kg of crude phenol was obtained per ton of coking wastewater treated.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com