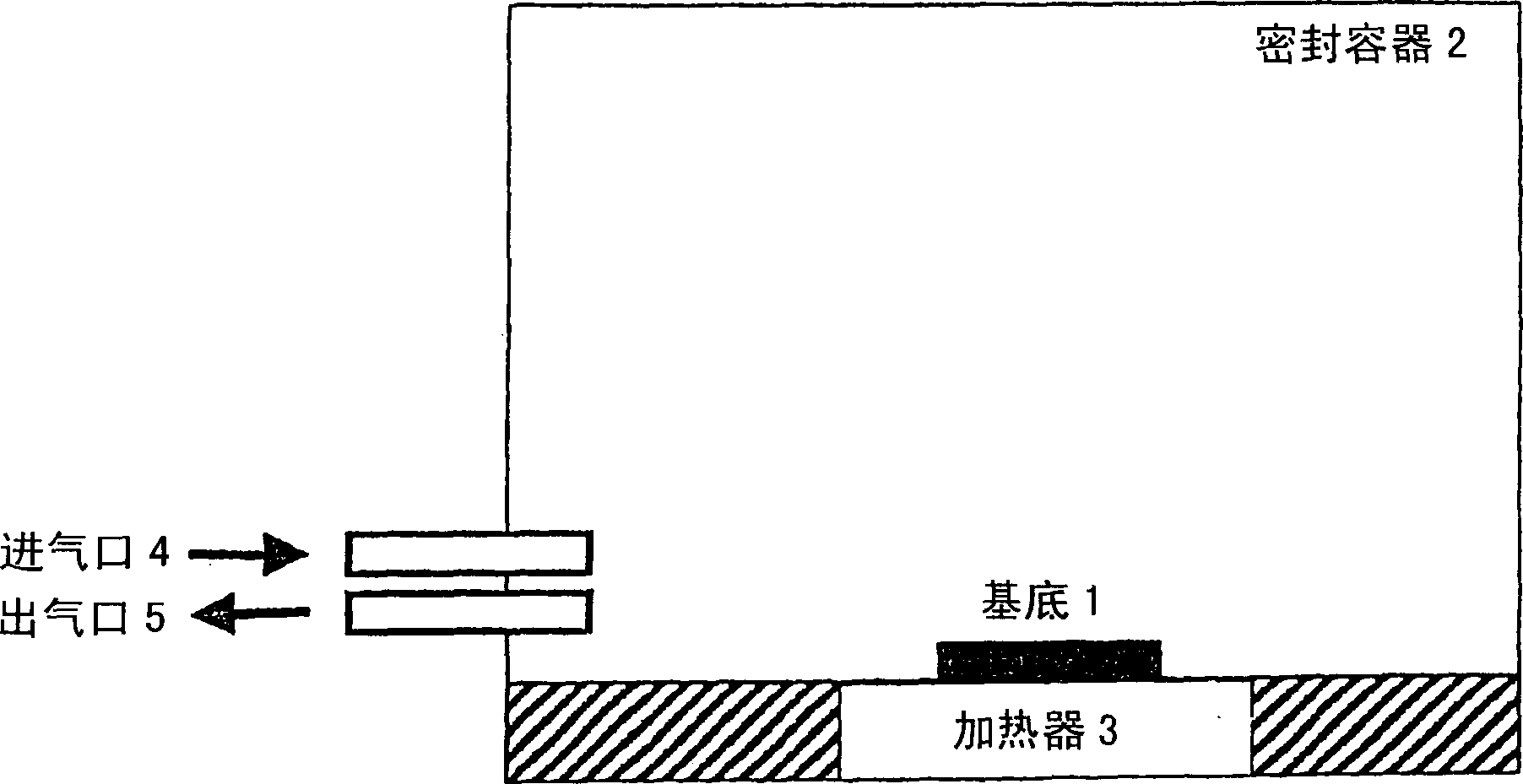
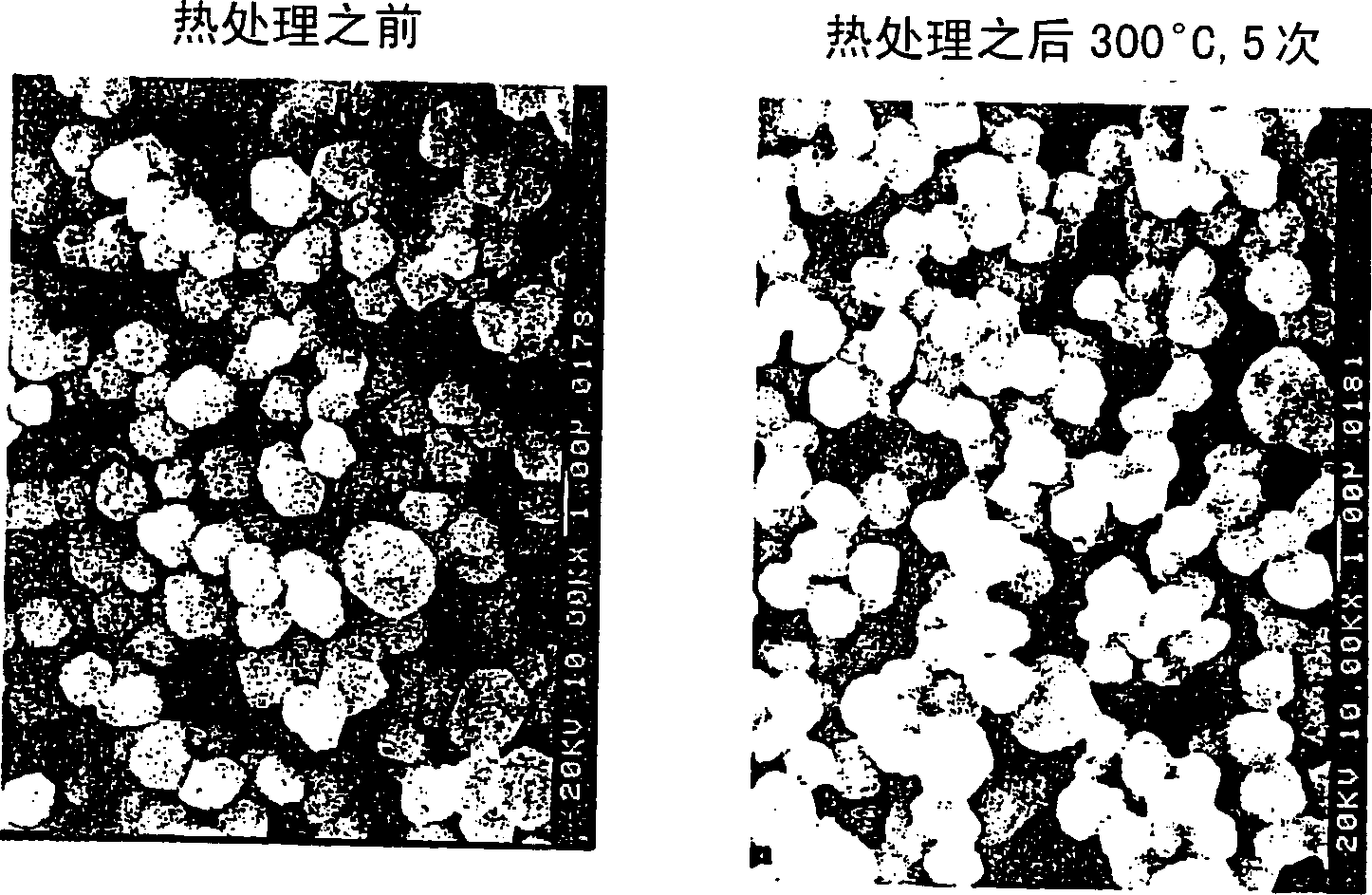
Method for forming fine copper particle sintered product type of electric conductor having fine shape, method for forming fine copper wiring and thin copper film using said method
A technology of copper nanoparticles and particles, which is applied in the formation of conductive patterns, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, circuits, etc., and can solve problems such as high unit cost, broken wires, and narrowed wire intervals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1~1-4 and comparative example 1-1~1-3
[0119] (reduction / roasting treatment in vapor of organic compounds)
[0120] A dispersion of copper ultrafine particles purchased commercially (trade name: independently dispersed ultrafine particles, perfect copper (perfect copper) produced by Ulvac Materials, Inc.), which specifically has an average particle diameter of 5 nm and has The dispersion of the copper nanoparticle of surface oxide film layer, it comprises 100 mass parts copper particles with oxide film layer on the surface, 15 mass parts as the dodecylamine of alkylamine (molecular weight is 185.36, and boiling point is 248 ℃ ), and 75 parts by mass of mineral essential oil as an organic solvent.
[0121] To 100 parts by mass of the copper ultrafine particle dispersion, 5 parts by mass of toluene and then 100 parts by mass of methanol were added to precipitate the contained copper fine particles. With respect to 80 mass parts of copper microparticles, 16 mass parts of bis(2-ethylhexyl)amine was added as an amine c...
Embodiment 1-5 to 1-11 and comparative example 1-4
[0129] (reduction / baking in the presence of organic compounds contained in the coating)
[0130] First, an aqueous dispersion containing copper ultrafine particles was prepared by a wet reduction reaction. After 30 g of copper sulfate was dissolved in 100 ml of distilled water, 100 g of diethanolamine as a reducing agent was added to the aqueous solution which had been heated to 80°C. Subsequently, while continuing to stir, a wet reduction reaction was performed for 8 hours to obtain a brown aqueous dispersion containing the formed copper microparticles. Acetone was added to the dispersion to remove the diethanolamine and to precipitate copper particles. The cleaning operation with acetone was repeated three times to remove residual raw materials, reaction-induced by-products and impurities. The obtained copper fine particles partially had a surface oxide film layer (oxidized copper) on the surface, and had an average particle diameter of 9 nm.
[0131] 10 parts by mass of ...
Embodiment 1-12
[0139] (reduction / roasting treatment in organic compound vapor)
[0140] A dispersion of commercially purchased copper ultrafine particles (trade name: independently dispersed ultrafine particle refined copper, manufactured by Ulvac Materials, Inc.), which specifically has an average particle diameter of 5 nm and partially has oxidation on the surface, is used. The dispersion of copper nanoparticles in the material film layer, specifically, it contains 100 parts by mass of copper particles, 15 parts by mass of dodecylamine (molecular weight is 185.36, boiling point is 248 °C) for alkylamine, and 75 parts by mass as Mineral essential oils in organic solvents.
[0141] To 100 parts by mass of the copper ultrafine particle dispersion, 5 parts by mass of toluene and then 100 parts by mass of methanol were added to precipitate the contained copper fine particles. 16 parts by mass of bis(2-ethylhexyl)amine as an amine compound, and 4 parts by mass of liquid paraffin as a resin comp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com