Method for producing lactic acid bacteria formulation and lactic acid bacteria bacteriocin using ethanol draff liquid
A technology of lactic acid bacteria bacteriocin and waste liquid, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria and other directions, can solve problems such as waste of resources, and achieve the effects of increasing utilization value, extending industrial chain and reducing production costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
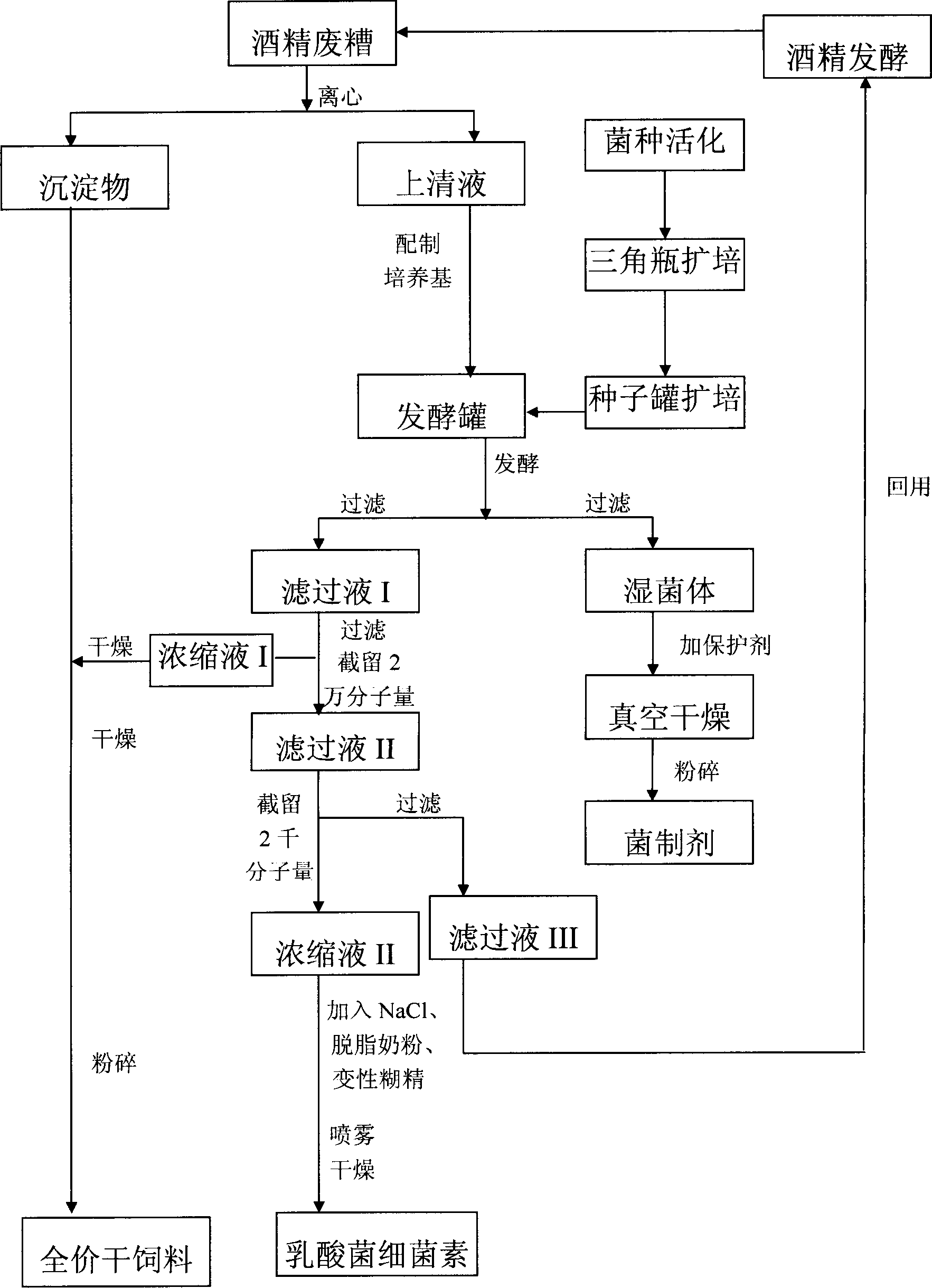
[0050] Example 1 Production of Lactic Acid Bacteria Preparations by Submerged Fermentation of Corn Alcohol Waste Grains
[0051] 1. Preparation of corn alcohol waste residue filtrate
[0052] Collect fresh alcohol waste liquid, centrifuge through a horizontal centrifuge (WL450 produced by Sichuan Jiangbei Machinery Factory), separate solid and liquid, take the separated liquid and filter it through a plate and frame filter, and collect the filtrate, which is the alcohol waste liquid filtrate.
[0053] Second, the process conditions of lactic acid bacteria fermentation
[0054] 1. Lactic acid bacteria strain expansion process:
[0055] (1) Production strain:
[0056] Lactobacillus gasseri 1-7;
[0057] Lactobacillus crispatus 23-5;
[0058] Enterococcus faecalis 23-7;
[0059] Freeze-dried and preserved strains were provided by the Institute of Industrial Microbiology, Liaoning Normal University.
[0060] The ratio of the liquid strain expansion culture medium: add 0.5% y...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2 Production of Lactic Acid Bacteria Bacteriocins by Submerged Fermentation of Corn Alcohol Waste Grains
[0071] 1. Preparation of corn alcohol waste residue filtrate
[0072] Collect fresh alcohol waste liquid, centrifuge through a horizontal centrifuge (WL450 produced by Sichuan Jiangbei Machinery Factory), separate solid and liquid, take the separated liquid and filter it through a plate and frame filter, and collect the filtrate, which is the alcohol waste liquid filtrate.
[0073] Second, the process conditions of lactic acid bacteria fermentation
[0074] 1. Lactic acid bacteria strain expansion process:
[0075] (1) Production strain:
[0076] Lactococcus lactis (Lactococcus lactis.LN992);
[0077] Lactobacillus brevis;
[0078] Freeze-dried and preserved strains were provided by the Institute of Industrial Microbiology, Liaoning Normal University.
[0079] (2) Liquid strain expansion culture medium:
[0080] Add 0.5% yeast extract to the filtrate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com