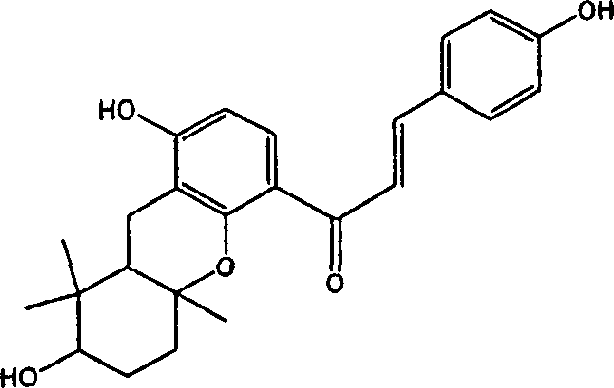
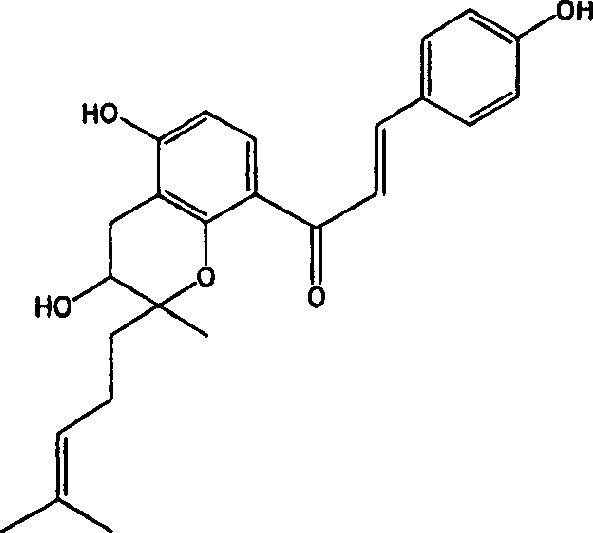
Extract from plant of japanese parsley family and process for producing the same
A technology for extracts and plants, which is applied to the field of extracts of cress family plants and their preparation, and can solve problems such as the inability to show therapeutic effects and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0043] The preparation of the therapeutic or preventive drug of the present invention can usually be carried out by combining the above-mentioned active ingredients with a pharmaceutically acceptable liquid or solid carrier, and if necessary, solvents, dispersants, emulsifiers, buffers, and stabilizers can also be added. , excipients, binders, disintegrants, lubricants, etc., made into solid preparations such as tablets, granules, powders, powders, capsules, and liquid preparations such as conventional liquids, suspensions, and emulsions. In addition, it can also be made into a dry product or other external medicines that can be made into a liquid by adding an appropriate carrier before use.
[0044] The pharmaceutical carrier can be selected according to the administration method and dosage form of the therapeutic drug or preventive drug. When made into an oral preparation containing a solid composition, it can be made into tablets, pills, capsules, powders, fine granules, gr...
Embodiment 1
[0081] 40 mL of extraction solvents (40, 50, 60, 70, 80% ethanol aqueous solution and 100% ethanol) were added to 2 g of the ground freeze-dried product of the stem and leaf part of Angelica sinensis, and extraction was carried out at 25° C. for 30 minutes. The content of chalcones in the centrifuged supernatant was measured by HPLC. As a column, TSK gel ODS-80Ts QA (4.6 mm×25 cm: manufactured by Tosoh Corporation) was used. Solvent A (a mixed solvent of distilled water and acetonitrile at a volume ratio of 4:1, and containing 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid) and solvent B (a mixed solvent of distilled water and acetonitrile at a volume ratio of 1:9, and containing 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid ) linearly varied the ratio of solvent B from 0 to 100% from 0 to 45 minutes, followed by maintaining the ratio of solvent B at 100% for 10 minutes. The elution rate was 1 mL / min, and the detection was carried out at 215 nm and a column temperature of 30°C.
[0082] The results are shown in Tab...
Embodiment 2
[0086] The same extraction as in Example 1 was performed on the pulverized product of the freeze-dried product of the root of Angelica sinensis, and the amount of chalcones in the extract was measured. The results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that when extracting TB1 and TB2 from the roots of Angelica sinensis, the extraction efficiency of aqueous ethanol is better than that of 100% ethanol. In addition, it is also clear that 60%, 70%, and 80% ethanol aqueous solutions are more efficient than 100% ethanol when extracting yellow angelica alcohol and 4-hydroxydrysin from the root of Angelica sinensis.
[0087] extraction solvent
[0088] Express the amount extracted by 100% ethanol extraction as 100%
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com