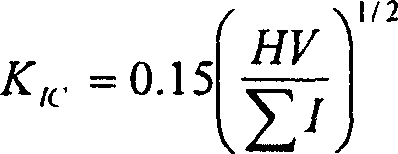Hard alloy sintered by high-entropy alloy binder and compound carbide and preparation method thereof
A composite carbide and high-entropy alloy technology, which is applied in the field of cemented carbide and its production, can solve the problems of failing to change the limitations of a single main element, and achieve the effects of high hardness, good toughness, and excellent temperature resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Take six metal elements such as aluminum, cobalt, chromium, copper, iron and nickel, the molar ratio of which is: 0.5:1:1:1:1:1, and the total weight is about 40 grams. Take 108 grams of titanium carbide and 12 grams of tungsten carbide. Mix metal element powder and two carbide powders in a ball mill, then put the ball mill into a ball mill for 12 hours of high-energy ball milling. Then add 1.5wt% paraffin wax as wetting agent and binder to the ball mill cylinder, and then carry out low-energy ball milling for 6 hours. After unloading and drying, it is pressed into a round embryo of φ12mm×5mm. The last is degreasing and sintering. The deesterification is carried out in a vacuum furnace at 400° C. under a mixed atmosphere of argon and hydrogen. After deesterification treatment, it can be sintered at 1400°C under vacuum. and measure its performance.
Embodiment 2 to 7
[0015] The manufacturing steps of Example 1 were repeated, but the constituent elements of the binder phase and the composition of the composite carbide were changed to the compositions shown in Table 1 for cemented carbide numbers 2 to 7.
[0016] example
[0017] The hardness values of all test pieces of cemented carbide samples No. 1 to 7 were measured by Vickers hardness meter. The load applied during the measurement is 5kgf, and the loading time is 10 seconds. Each test piece measures the hardness values at seven different positions, and takes the average value of the middle five as the hardness of the test piece. The results are shown in Table II.
[0018] Fracture toughness (K IC ) is calculated from the crack length (I) measured by Vickers hardness. Calculated as follows:
[0019] K IC = 0.15 ( HV ΣI ) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com