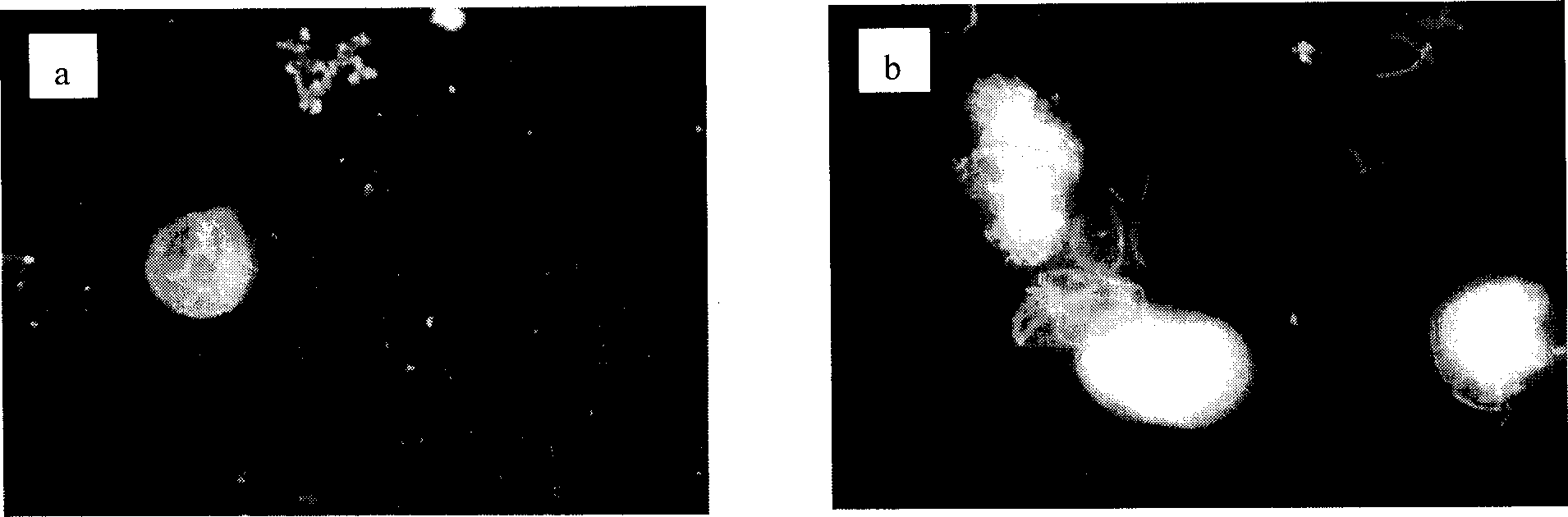
Atexandrium tamarense culture liquid sterilizing process
A technology for culturing liquid and bacteria, which is applied to unicellular algae, sanitary equipment for toilets, water supply devices, etc. It can solve the problems of troublesome operation, high experimental experience in algae separation, and difficulty in balancing, and achieve the effect of short processing time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Use the 2216E solid plate to isolate the bacteria in the algae culture solution, inoculate the isolated strains in 3mL 2216E liquid medium, and culture at 25°C, 180rpm for 20h to the late exponential stage. Take 100 μL of bacterial culture solution and evenly spread it on the 2216E plate, and place it upright to make it completely absorbed. Paste the drug-sensitive paper sheets containing antibiotics (filter paper sheets with a diameter of 6 mm) on the surface of the plate, and each drug-sensitive paper sheet contains 50 μg of gentamicin, 25 μg of neomycin, 25 μg of streptomycin, and 25 μg of kanamycin, Cephalosporin 10 μg and rifampicin 5 μg were incubated on an inverted plate at 25°C until the zone of inhibition was clear and stable, and the diameter of the zone of inhibition was recorded. Filter 250mL algae culture solution in the exponential growth phase with an 8μm filter membrane, and resuspend the algal cells on the filter membrane in 50mL sterile f / 2 culture sol...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Similar to Example 1, the difference is that the isolated strain was inoculated in 4 mL of 2216E liquid medium, and cultured at 30° C., 100 rpm for 24 hours until late exponential. Take 150 μL of bacterial culture solution and evenly spread it on the 2216E plate, and place it upright to make it completely absorbed. Paste the drug-sensitive paper sheet containing antibiotics (filter paper with a diameter of 7mm) on the surface of the plate, invert the plate and incubate at 30°C until the zone of inhibition is clear and stable, and record the diameter of the zone of inhibition. Filter 100 mL of algae culture solution in the exponential growth phase with a 6 μm filter membrane, and resuspend the algal cells on the filter membrane in 20 mL of sterile f / 2 culture solution. Centrifuge at 1000g for 10min, remove the supernatant, and resuspend the algae cells in 50mL sterile f / 2. Repeat centrifugation at 1000g for 10min, remove the supernatant, resuspend the algae cells twice ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Similar to Example 1, the difference is that the isolated strain was inoculated into 5 mL of 2216E liquid medium, and cultured at 20° C. and 250 rpm for 18 hours until late exponential. Take 50 μL of bacterial culture solution and evenly spread it on the 2216E plate, and place it upright to make it completely absorbed. Paste a drug-sensitive paper sheet containing antibiotics (a filter paper sheet with a diameter of 6 mm) on the surface of the plate, invert the plate and incubate at 20°C until the zone of inhibition is clear and stable, and record the diameter of the zone of inhibition. Filter 20 mL of algae culture solution in the exponential growth phase with a 5 μm filter membrane, and resuspend the algal cells on the filter membrane in 80 mL of sterile f / 2 culture solution. Centrifuge at 2000g for 20min, remove the supernatant, and resuspend the algae cells in 20mL sterile f / 2. Repeat centrifugation at 2000g for 20min, remove the supernatant, resuspend the algae ce...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com