Process for preparing prion protein gene-free domestic animals
A gene knockout and prion protein technology, applied in the field of bioengineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
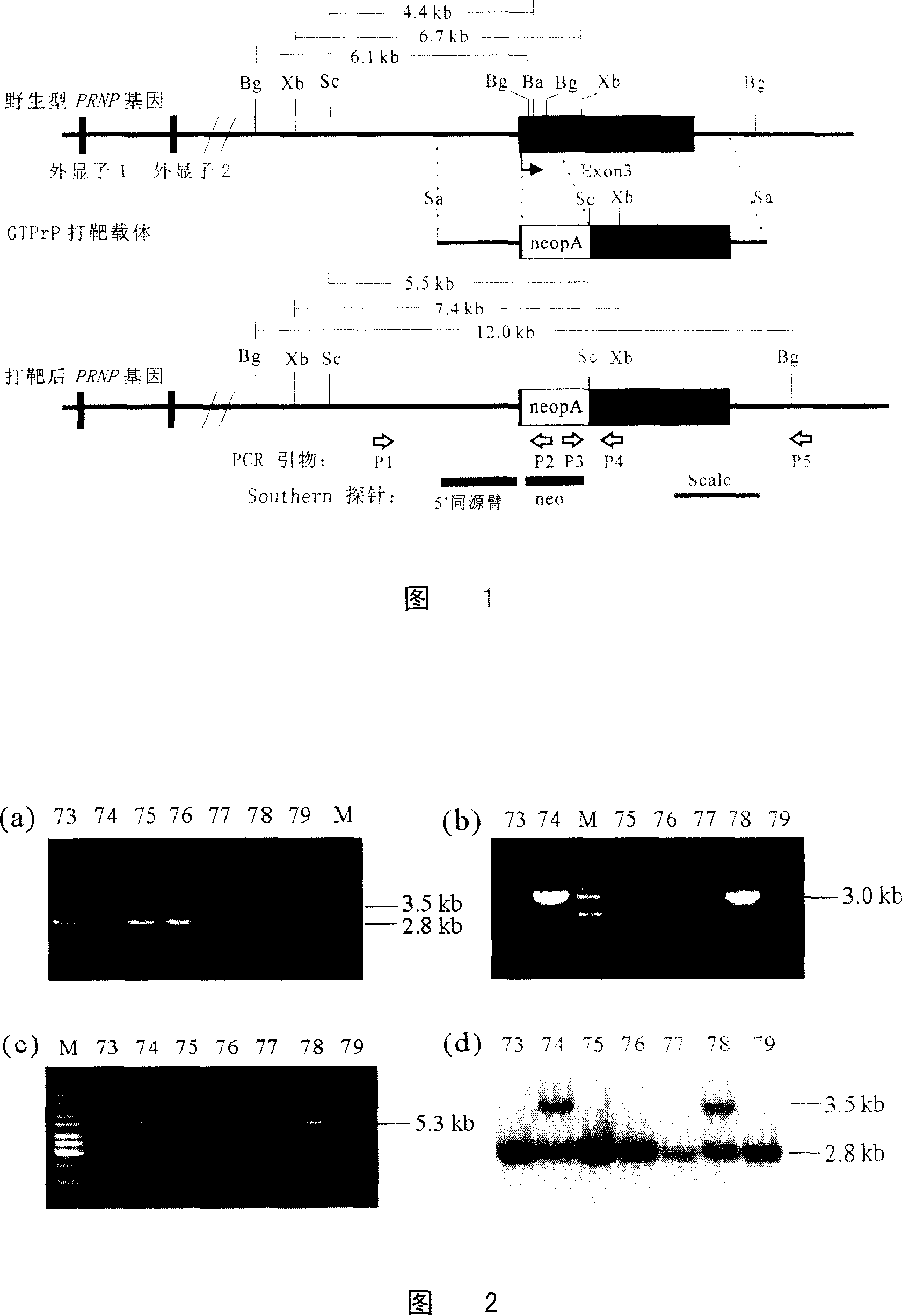
[0054] Cloning of Goat Prion Gene and Construction of Goat Prion Gene Targeting Vector
[0055] 1. Culture and sex identification of primary goat fetal fibroblasts
[0056] Skin or ear tissue of 35-day-old goat fetuses was obtained, and then digested with a digestion solution containing 0.25% trypsin and 1 mM EDTA in a water bath at 37°C for about 15 minutes.
[0057] The digested single cell suspension was centrifuged, the supernatant was removed, and the cell pellet was resuspended in a solution containing 2mM glutamine (GIBCO), 1mM sodium pyruvate (SIGMA), and 1× non-essential amino acids (SIGMA). , 2ng / ml of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF, SIGMA), 10% fetal bovine serum (HyClone), 100units / ml of penicillin, 100μg / ml of streptomycin (SIGMA) in Glasgow minimal medium (GMEM) , SIGMA), the cell suspension was finally divided into culture flasks, cultured in a carbon dioxide incubator for several days, and frozen when the cell density reached about 80%.
[0058] The sex...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Knockout of goat PRNP gene using GTPrP targeting vector
[0068] After the vector GTPrP was linearized with SalI, it was transformed into the third passage GFF88 fetal fibroblast cell line by electrotransfection. Approximately 500 million fetal fibroblasts were mixed with 10 μg of linearized GTPRP vector, transferred to a 0.4 cm electroporation cuvette (Bio-Rad), and subjected to 220v, 950 μF by electroporation Gene pulserII (Bio-Rad). Pulsed, cells were then split into several dishes containing GMEM medium. After 48 hours G418 was added to a final concentration of 250 μg / ml.
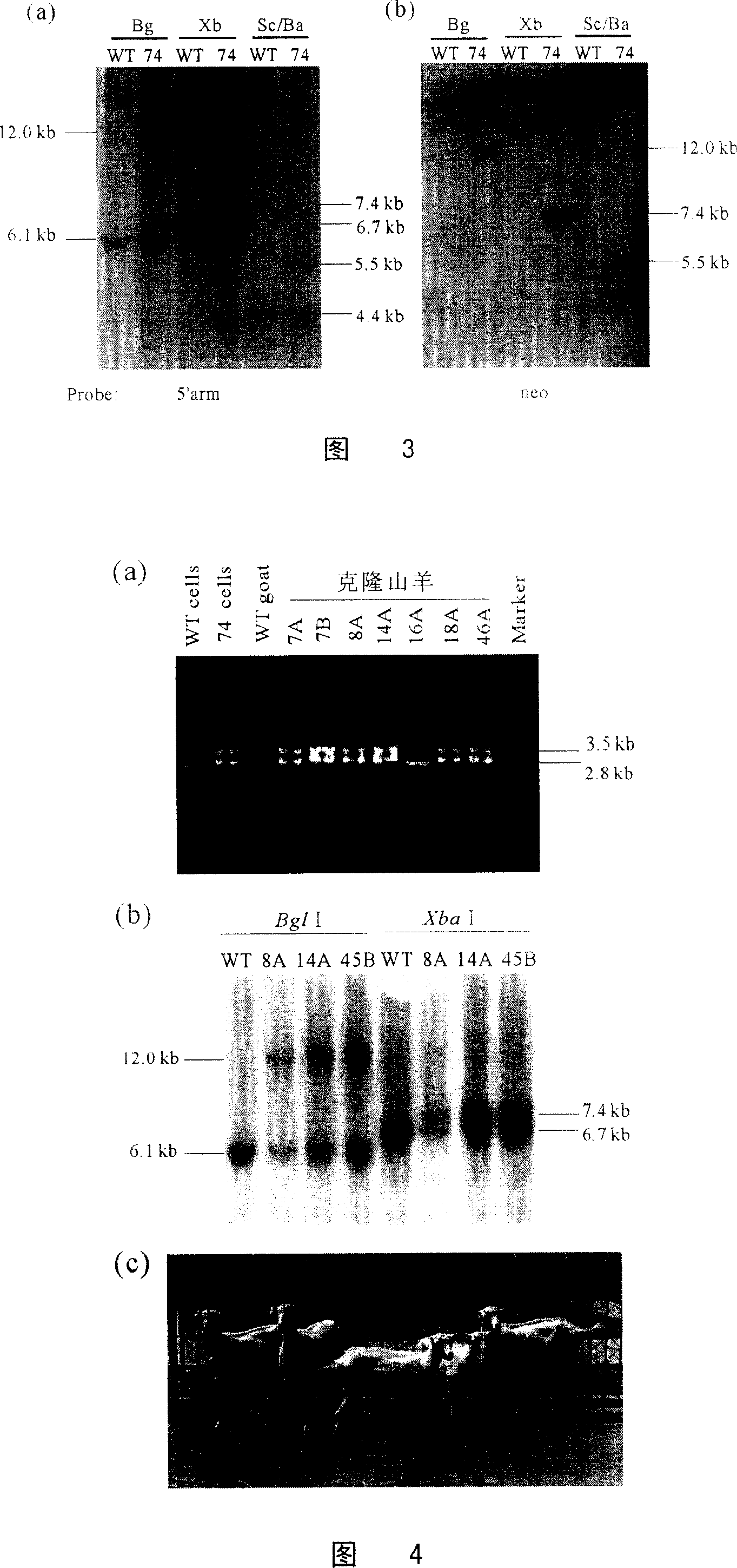
[0069] About 10 days later, cell clones can be seen. The well-grown cell clones were picked out and transferred to the wells of a 96-well plate. When reaching confluence, some cells were isolated for PCR identification, and the remaining cells were further passaged until enough cells were obtained for cryopreservation and extraction of genomic DNA for identification by Southern hybridization, ...
Embodiment 3
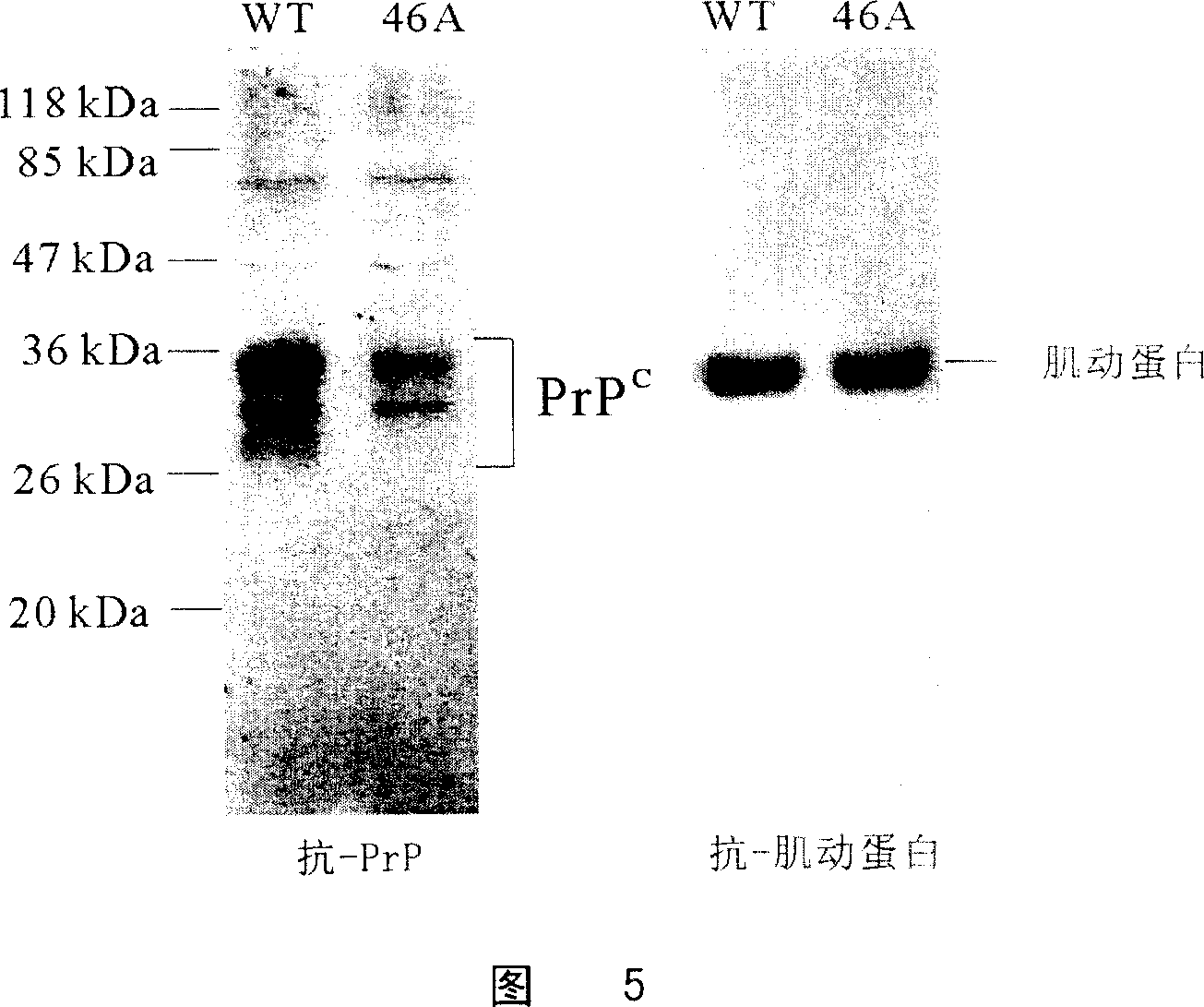
[0087] Preparation of PRNP+ / - goats by nuclear transfer of goat PRNP+ / - cells
[0088] In the research of the present inventors, the donor oocytes, temporary host mothers and recipients for nuclear transfer were all from Saanen dairy goats.
[0089] Simultaneous estrus of goats: female goats were injected with 0.1 mg of prostaglandin-Cl (PG, Shanghai Institute of Family Planning Science), and 25 μg of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) after 24 hours. Simultaneous estrus.
[0090] Superovulation in female goats: intramuscular injection of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) twice a day for 3 consecutive days, the total dose of FSH per goat is 240IU, and PG is injected once on the third day, 24 One LHRH injection hours later.
[0091] Recovery of oocytes: Surgical recovery within 24-30 hours after LRH injection, oocytes were collected after flushing the fallopian tubes with F10 (GIBCO) medium, and 0.2% hyaluronidase was used to remove adhering granulosa cells, and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com