Silicon on insulator read-write non-volatile memory comprising lateral thyristor and trapping layer
A non-volatile, thyristor technology, used in read-only memory, thyristor, static memory, etc., to solve problems such as affecting applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
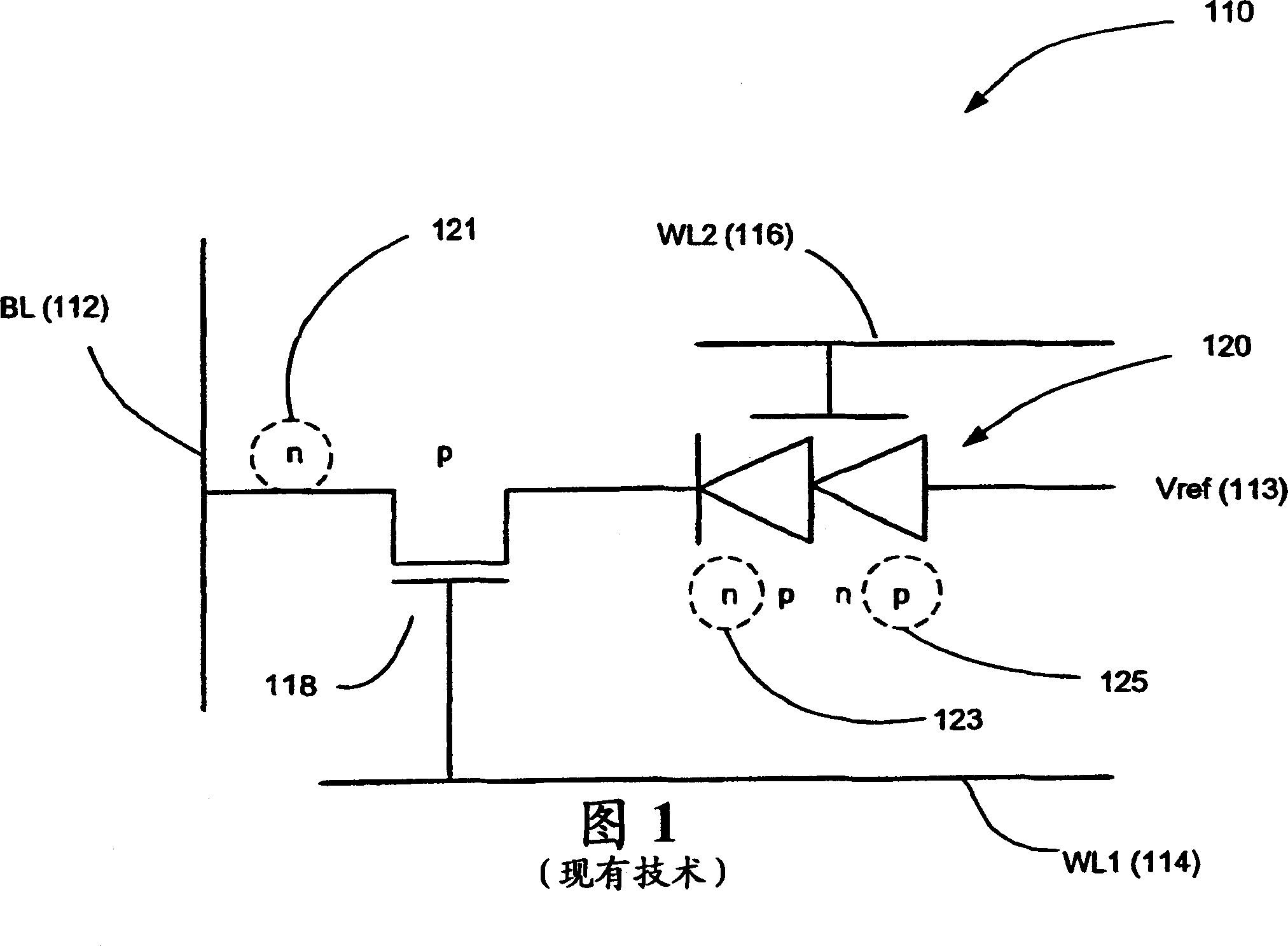
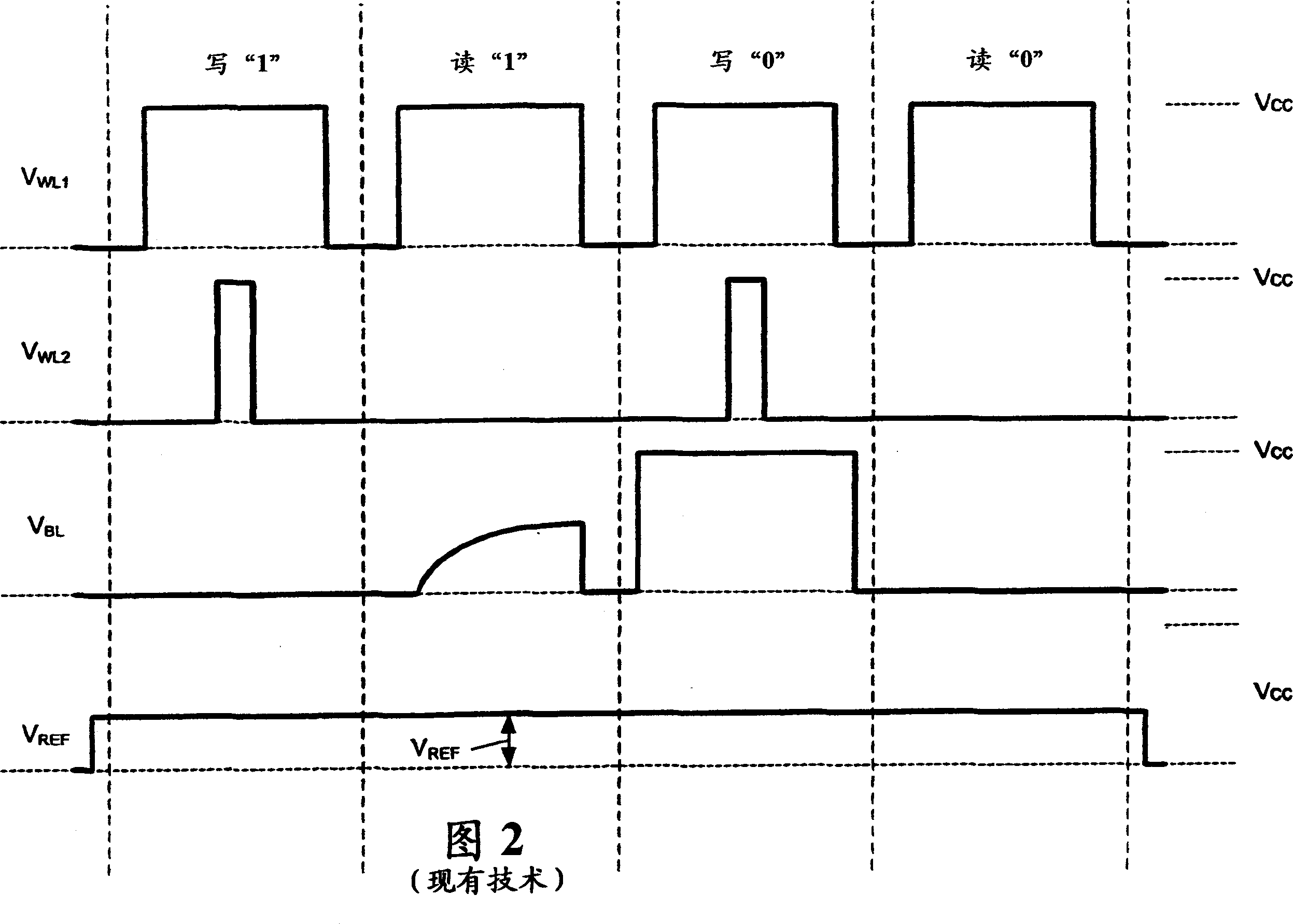
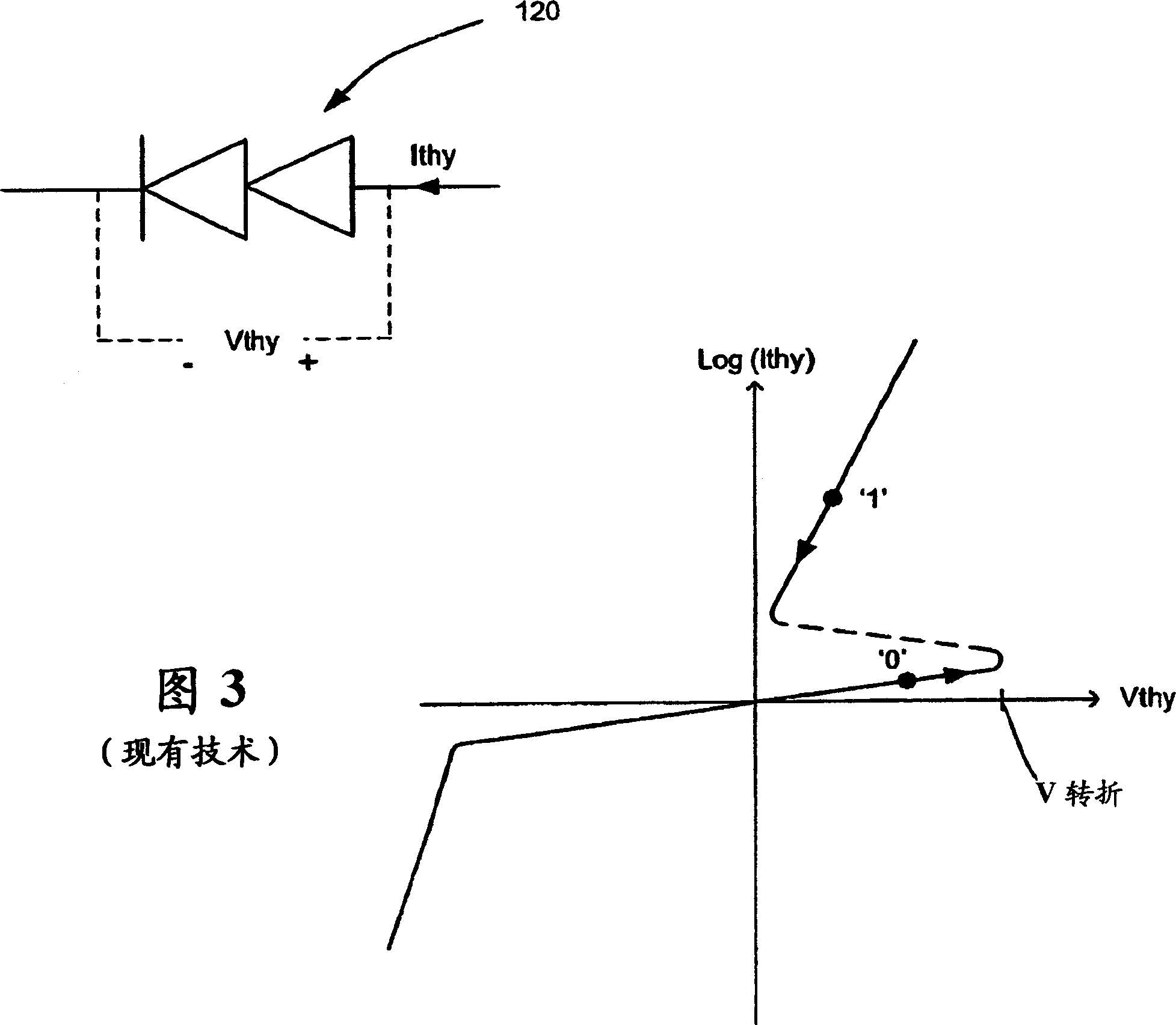
[0025] 4 and 5 show a schematic circuit diagram and a cross-sectional view of an improved thyristor-based cell design 10, respectively. Cell 10 includes elements similar to the thyristor-based cell of FIG. 1 , but differs in several respects. First, the improved cells 10 are preferably, but not necessarily, formed using silicon-on-insulator technology, thereby providing each cell with a floating substrate. As detailed below, this allows the cell to draw lower current and uses the floating body effect to improve the data retention of the cell. Second, the cell design preferably, but not necessarily, incorporates a lateral thyristor formed entirely in the floating silicon substrate. This makes the cell relatively easy to fabricate compared to vertical thyristor-based cells (such as the Nemati reference), or cells that require the thyristor to be at least partially formed on the substrate (such as the '212 application). Also, the insulating floating substrate of each cell prefe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com