Method of treating cellulose fibers and products obtained thereby
a technology applied in the field of cellulose fibers and products obtained thereby, can solve the problems of reducing the strength properties of towels and capillaries, loosing wettability properties with time, and reducing wettability properties, so as to prevent/slow down the ageing process of cellulose fibers and increase economic and environmental demands.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Supercritical Fluid (SF) Extraction of Pulp
[0057] This example describes, without limiting the invention, the extraction of pulp with CO.sub.2 as the supercritical fluid.
[0058] Definition
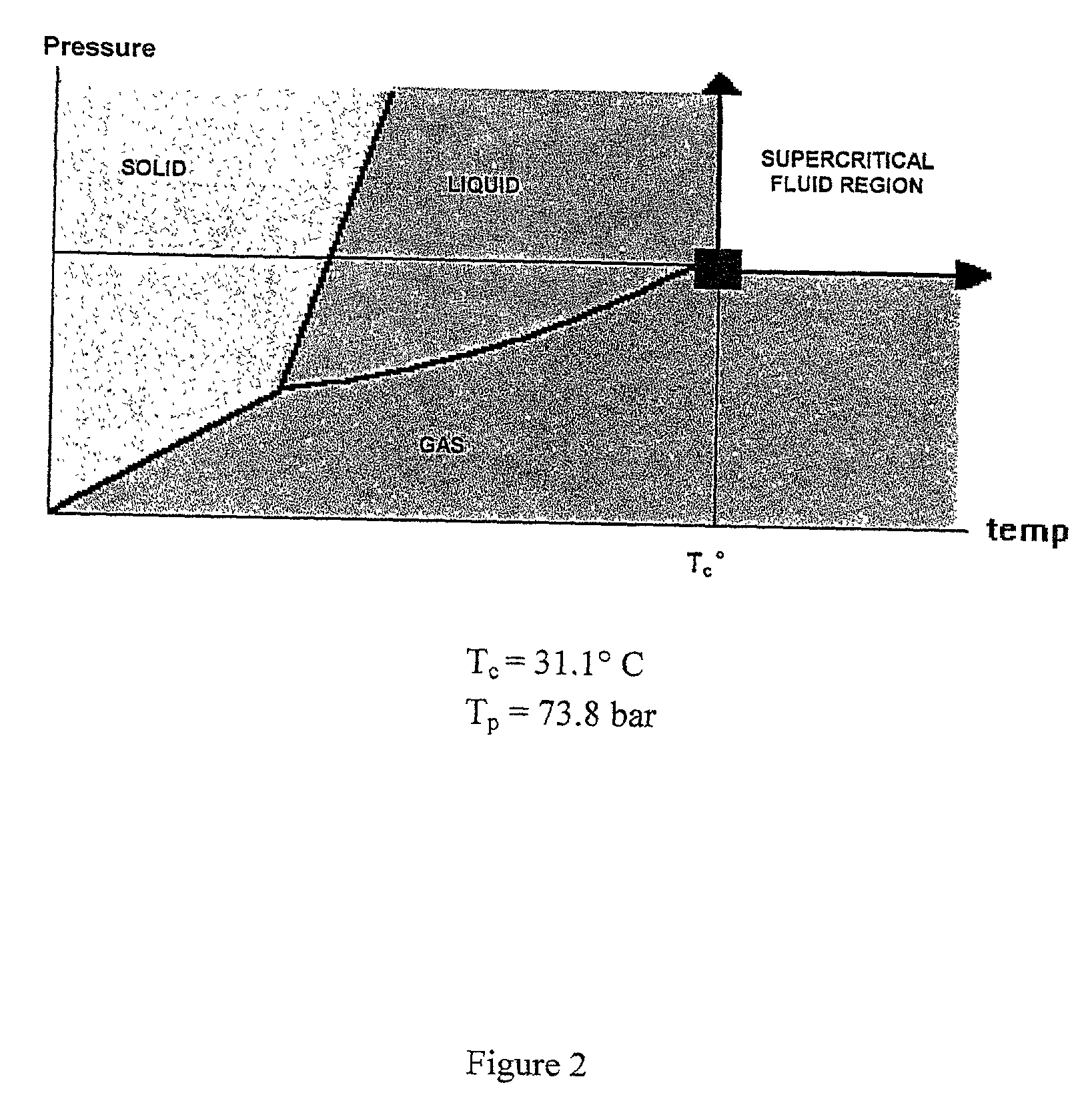
[0059] Wood extractives are defined as the amount of material, which can be extracted from a virgin fiber pulp sample with neutral organic solvents (e.g., hexane, dichloromethane). The method described within this example illustrates a procedure to extract such components by means of supercritical carbon dioxide being as efficient as conventional solvent extraction methods.
[0060] Principle
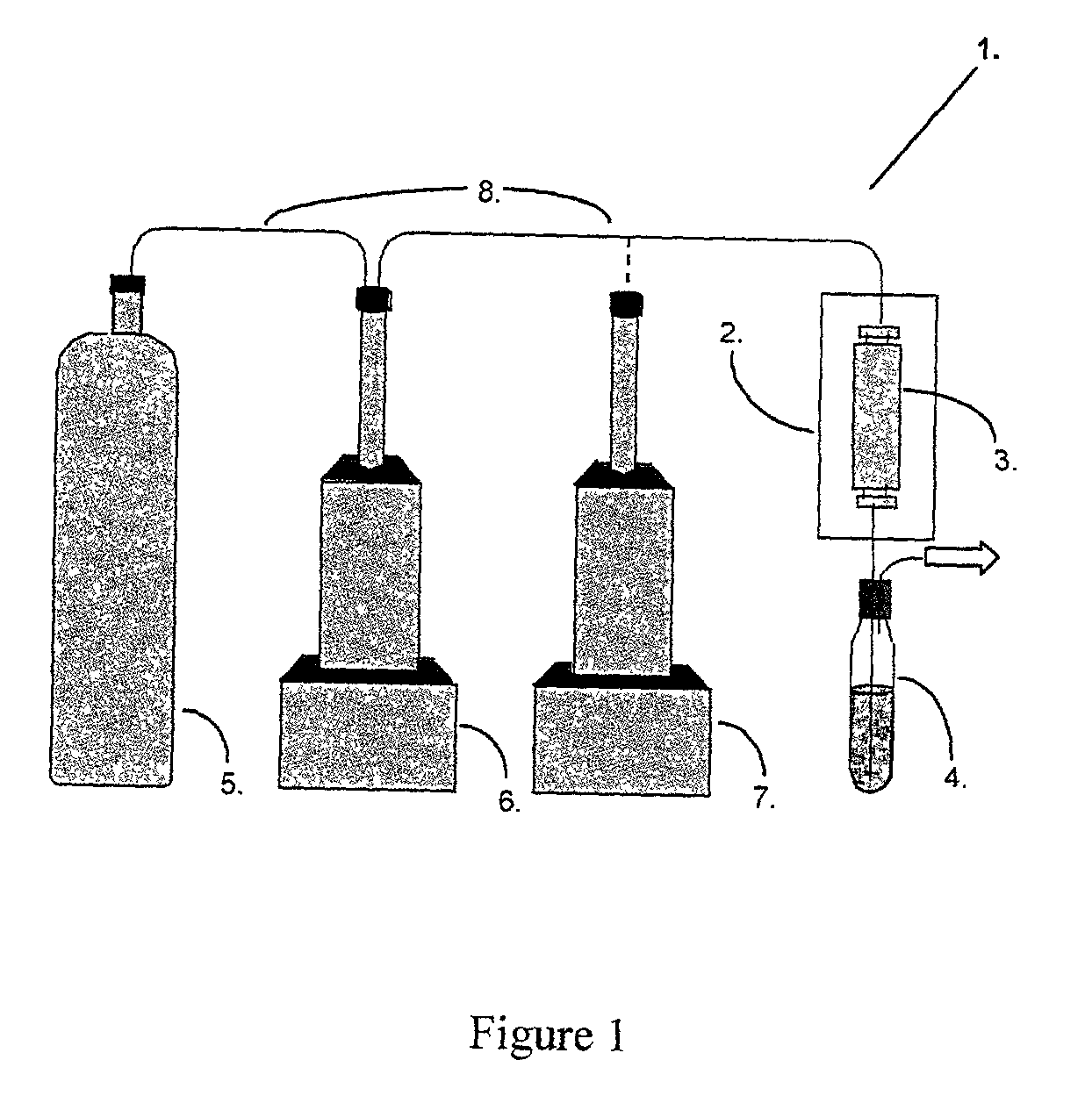
[0061] The pulp sample is homogenized and packed into a sample cartridge. The cartridge is placed in the extractor (1) in the sample cell (2) where it is extracted by carbon dioxide at a specific temperature and pressure. The resulting extract is trapped and collected in a vial (6) filled with dichloromethane (DCM) (FIG. 1).
[0062] Reagents
[0063] Carbon dioxide, CO.sub.2 (Air Liquide, SFC quality) pressurised with 1...
example 2
[0078] Comparison of Supercritical CO.sub.2 Extraction and Solvent Extraction With Dichloromethane.
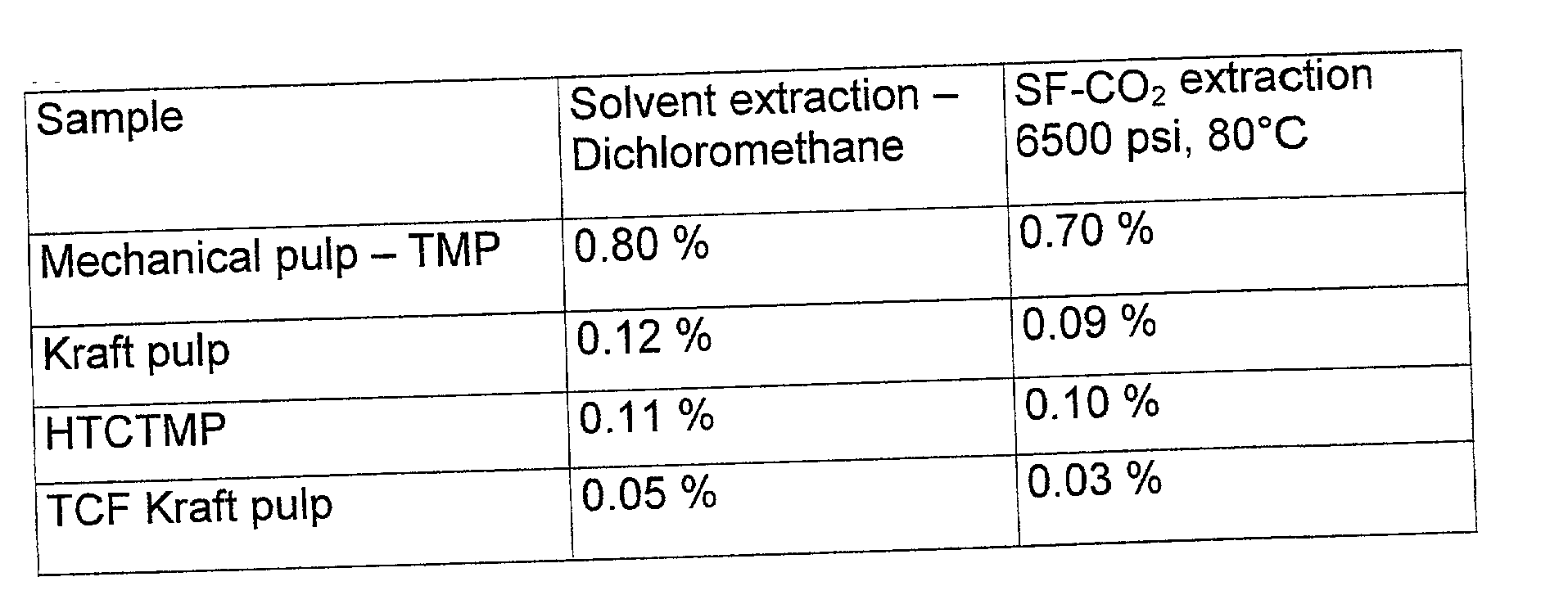
[0079] This example is a comparison between super critical CO.sub.3 extraction and solvent extraction with dichloromethane (DCM) of different pulp materials. For the DCM extraction a standard method (SCAN C 7:62) was used where the pulp is refluxed with DCM in a soxhlet apparatus for six hours followed by a graviometric determination of the extract content.
[0080] The pulp samples are prepared according to the invention with the method described in Example 1. The total extract content and the composition of the extractives in the extracts are shown in FIG. 3.
[0081] From the results shown in FIG. 3a, it appears that the SF-CO.sub.2 extraction is as effective as the solvent extraction with respect to the total extract content. From FIG. 3b it appears that certain compositions are preferably extracted with SF-CO.sub.2 compared to the conventional method using DCM. In particular, the low le...
example 3
[0084] Measurement of Absorption Rate Before and After Extraction With CO.sub.2
[0085] This example describes the absorption rate in sheets prepared from extracted or unextracted sulphite pulp.
[0086] Definition
[0087] Absorption rate is the mean velocity with which a liquid drop of a defined volume is fully absorbed into a paper sheet. The mean velocity is calculated in that the defined volume is divided by the time needed for the liquid drop of the defined volume to be fully absorbed into the paper. The absorption time needed is dependent on both the wettability, i.e., surface chemistry and the basis weight, i.e., network structure of the cellulose fibers used.
[0088] Principle
[0089] A tissue sheet made from a dynamic sheet former called Formette was used in a lab scale equipment for the manufacturing of Formette sheets. The absorption was measured using a high-speed video system.
[0090] Material
[0091] Extraction of sulphite pulp as in Example 1. Fibers were extracted twice, but no sig...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com