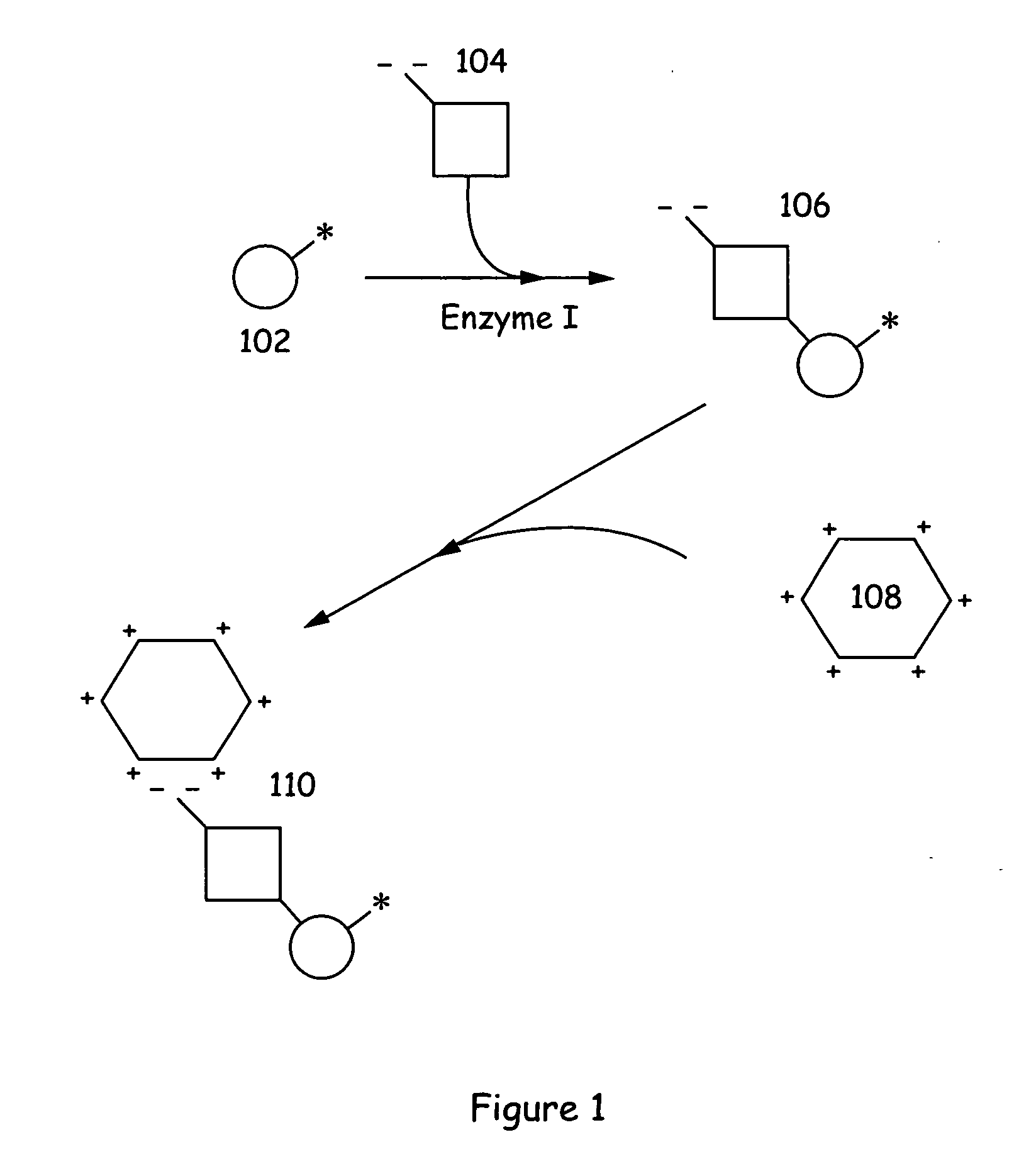
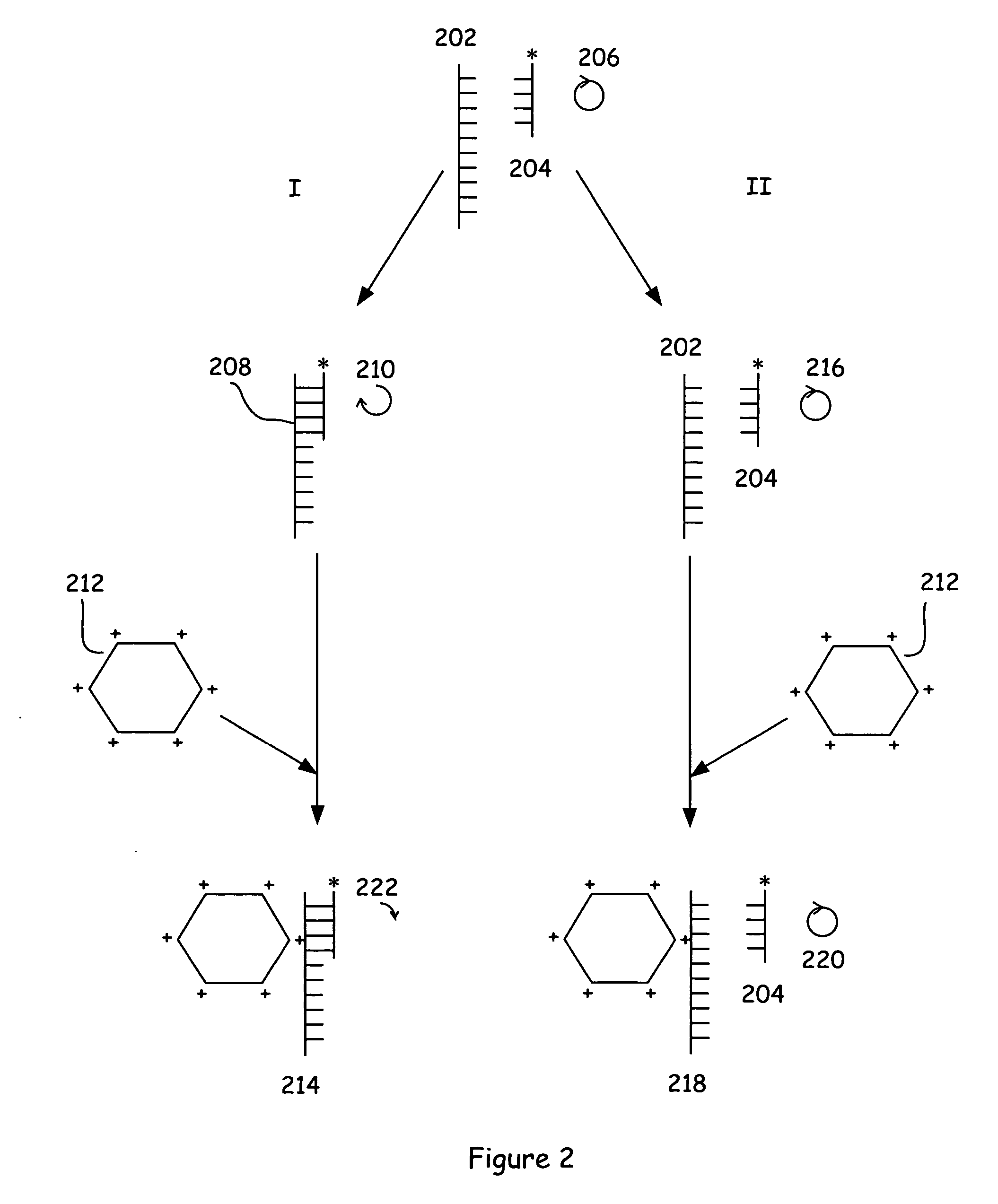
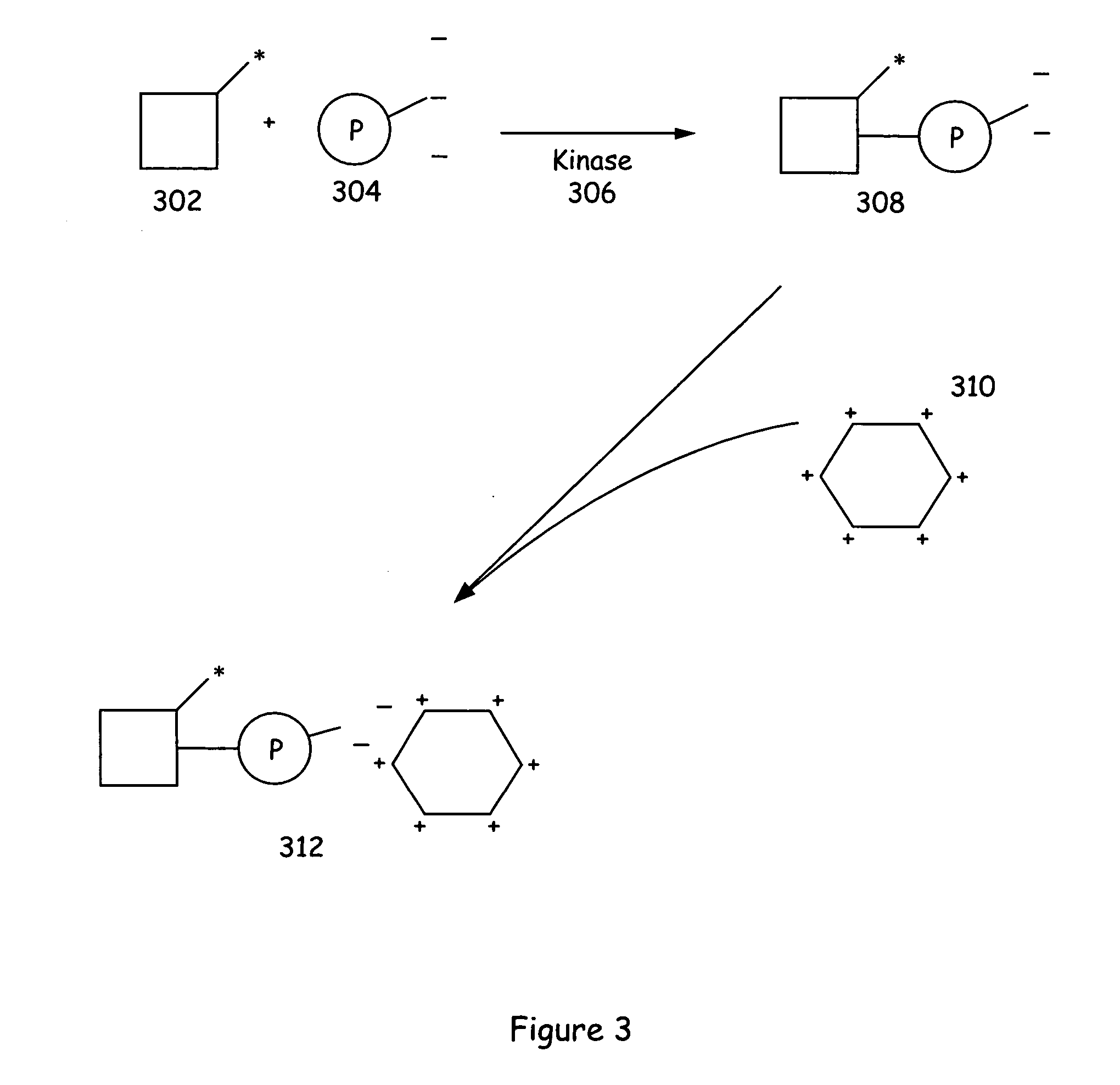
Assay methods and systems
a technology applied in the field of assay methods and systems, can solve the problems of reducing the ability of fluorescent components to emit depolarized fluorescence, and affecting the polarization of fluorescent emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Detection of Phosphorylated Product by Fluorescent Polarization
[0124] An aliquot of a neutrally charged phosphorylatable substrate (Flourescein-QSPKKG-CONH.sub.2) (SEQ. ID NO. 12) was incubated overnight with ATP and CDK2 (cyclin dependent kinase). The mixture was analyzed by standard capillary electrophoresis methods and showed complete conversion of substrate to product. A negative control (no enzyme) was also prepared. The two reaction mixtures were diluted in 50 mM TAPS pH 9.0 buffer (1:40). The fluorescence polarization values were measured by exciting the samples at 490 nm and measuring emitted fluorescence at 520 nm in a cuvette of a fluorimeter equipped to measure fluorescence polarization. Aliquots of a poly-D-Lysine solution and water were added (each added aliquot increased the poly-D-Lysine concentration by 6 .mu.M). The results of the assay are illustrated in FIG. 12A which plots the fluorescent polarization of the sample versus the amount of poly-D-lysine added.
[0125] ...
example 2
Differentiation of Product Concentrations Using Fluorescence Polarization
[0127] Additional experiments were carried out using poly-histidine in place of polylysine. In this case, the buffer used was 50 mM BisTris pH 6.5; the molecular weight of the polyhistidine used was 15800 daltons (available from Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, Mo.).
[0128] Mixtures containing varying ratios of the substrates and products of two serine / threonine kinases were prepared, CDK2 and Protein Kinase A (PKA). The CDK substrate was the same as that described for Example 1, above. The PKA substrate was: Fluor-LRRASLG (SEQ. ID NO. 14) where the C-terminus was either a carboxyl group or a carboxamide group. These mixtures were used as models for kinase reactions at varying degrees of substrate conversion. To these mixtures of substrate and product were added aliquots of a polyhistidine solution and water. The concentration of this aqueous stock was approximately 1.3 mM, and the final concentration was between 10 a...
example 3
Time Course Monitoring of Enzyme Reactions by Fluorescence Polarization
[0132] Another PKA assay was performed with varying concentrations of ATP (0 .mu.M, 0.5 .mu.M, 1 .mu.M, 2 .mu.M, 4 .mu.M, 8 .mu.M, 16 .mu.M and 32 .mu.M) in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 10 mM MgCl.sub.2, 500 nM polyarginine, 184 nM PKA, and 125 nM Kemptide substrate (Fl-LRRASLG-COO.sup.-) (SEQ. ID NO. 14). The resulting assays were monitored over time in order to determine the efficacy of the fluorescence polarization detection methods of the present invention on monitoring reaction time courses. FIG. 16 is a plot of fluorescence polarization vs. reaction time for each different concentration of ATP in the reaction mix. As can be seen, increasing concentrations of ATP generally give faster reaction rates. In all cases except the control, fluorescence polarization measurements increase with time. In particular, as the reactions progress, more of the fluorescent substrate is rendered charged by virtue of the added phosphat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com