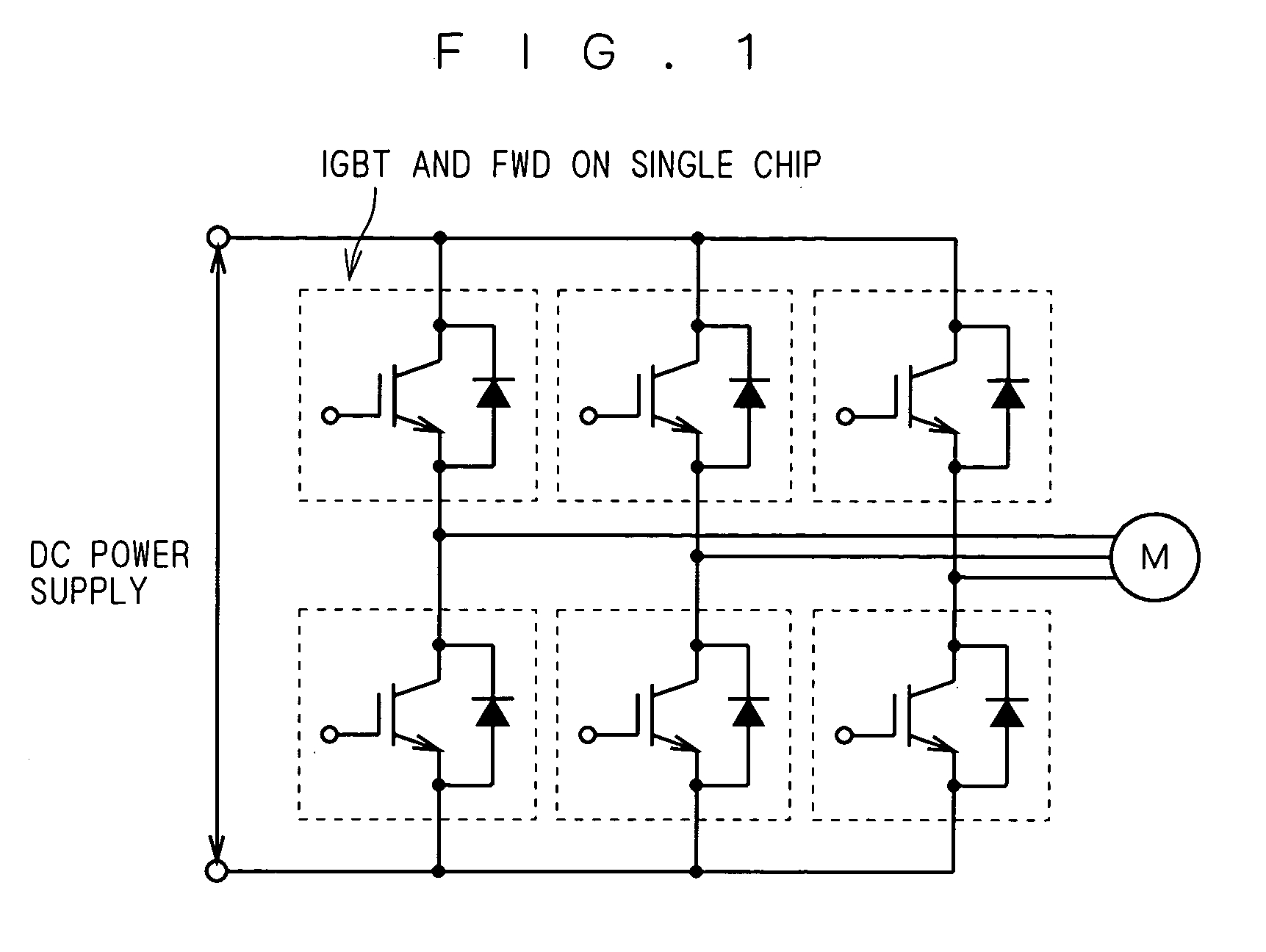
Insulated gate bipolar transistor with built-in freewheeling diode
a bipolar transistor and freewheeling diode technology, applied in the field of bipolar transistors, can solve the problems of significant degradation of igbt, low conductivity of power moseft, and unsuitability of power moseft for high current applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first preferred embodiment
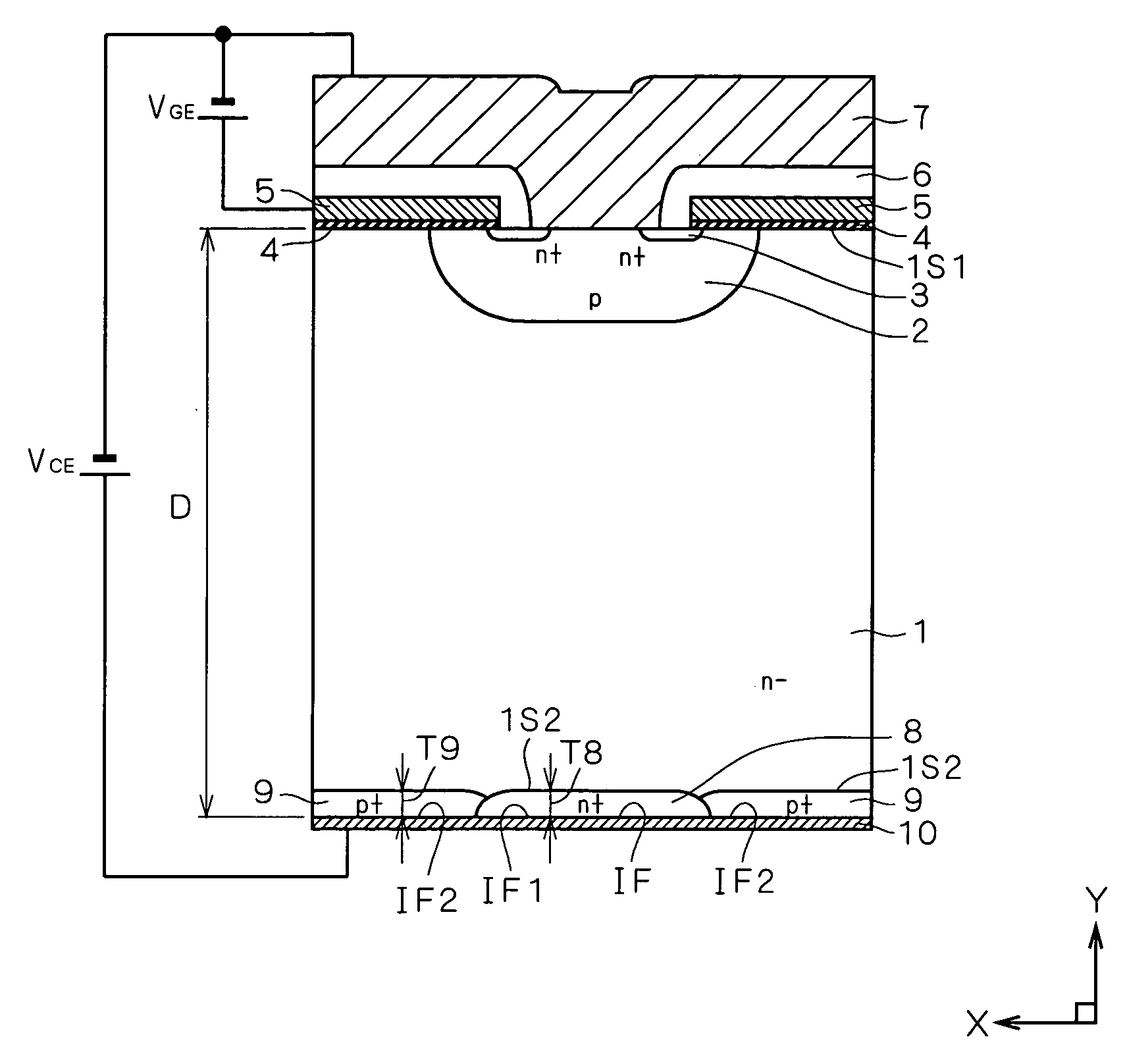
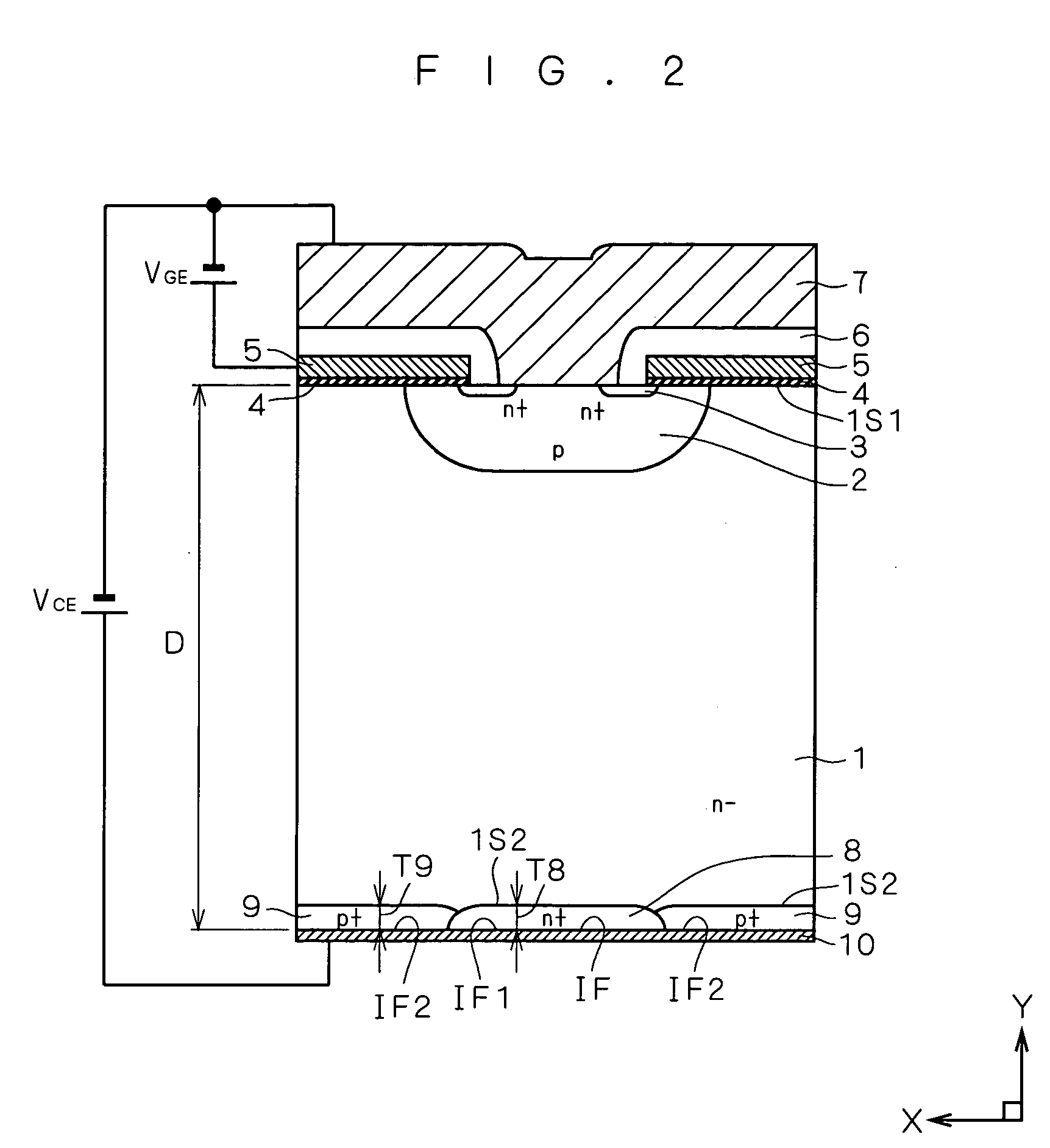
[0041]FIG. 2 is a longitudinal sectional view of a portion of an exemplary structure of an IGBT with a built-in freewheeling diode (semiconductor device) according to a first preferred embodiment. In FIG. 2, a direction “X” is a width direction along a width of a silicon wafer, and a direction “Y” is a thickness direction along a thickness of the silicon wafer. The semiconductor device illustrated in FIG. 2 is achieved by applying the following features of the first preferred embodiment to an IGBT with a built-in freewheeling diode including a MOSFET cell having a DMOS structure.
[0042] First, the silicon wafer of the semiconductor device in FIG. 2 includes: 1) as a core portion of the silicon wafer, an N−-type semiconductor substrate (which will be also referred to as an “N−-type layer”) 1 containing an impurity of a first conductivity type (N type in the present example), which includes a first main surface 1S1 and a second main surface 1S2; and 2) a cell of an insulated gate tran...
second preferred embodiment
[0066]FIG. 13 is a longitudinal sectional view of an IGBT with a built-in FWD according to a second preferred embodiment. A device illustrated in FIG. 13 is formed by additionally providing an N-type layer 11 in the device illustrated in FIG. 12 which includes a trench MOSFET cell with a gate electrode buried in each trench formed inside the N−-type layer 1. The N-type layer 11 is horizontally interposed between adjacent trenches and is vertically interposed between the P-type base region 2 and the N−-type layer 1. The device illustrated in FIG. 13 is identical in structure to the device illustrated in FIG. 12 in the other respects.
[0067] Operations of the device illustrated in FIG. 13, when it serves as the IGBT, are basically identical to those illustrated in FIG. 12. However, in the device illustrated in FIG. 13, the N-type layer 11 having a higher impurity concentration than that of the N−-type semiconductor substrate 1 is additionally provided immediately under the P-type base...
third preferred embodiment
[0075] A method of manufacturing an IGBT with a built-in FWD according to a third preferred embodiment essentially includes: 1) forming an MOSFET cell and a first main electrode used for the IGBT in a region on a first main surface side of a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type; 2) polishing the semiconductor substrate provided after formation of the MOSFET cell, from a second main surface thereof (a surface opposite and substantially parallel to the first main surface), to make a thickness of the semiconductor substrate equal to 200 μm or smaller; 3) forming a first semiconductor layer of the first conductivity type and a second semiconductor layer of a second conductivity type adjacent to the first semiconductor layer such that the first and second semiconductor layers extend from a region of the second main surface of the polished semiconductor substrate which faces the MOSFET cell toward an interior of the semiconductor substrate; and 4) forming a second main ele...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com