Thermoplastic fibers exhibiting durable high color strength characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example # 1
EXAMPLE #1
Polymeric Colorant Fibers
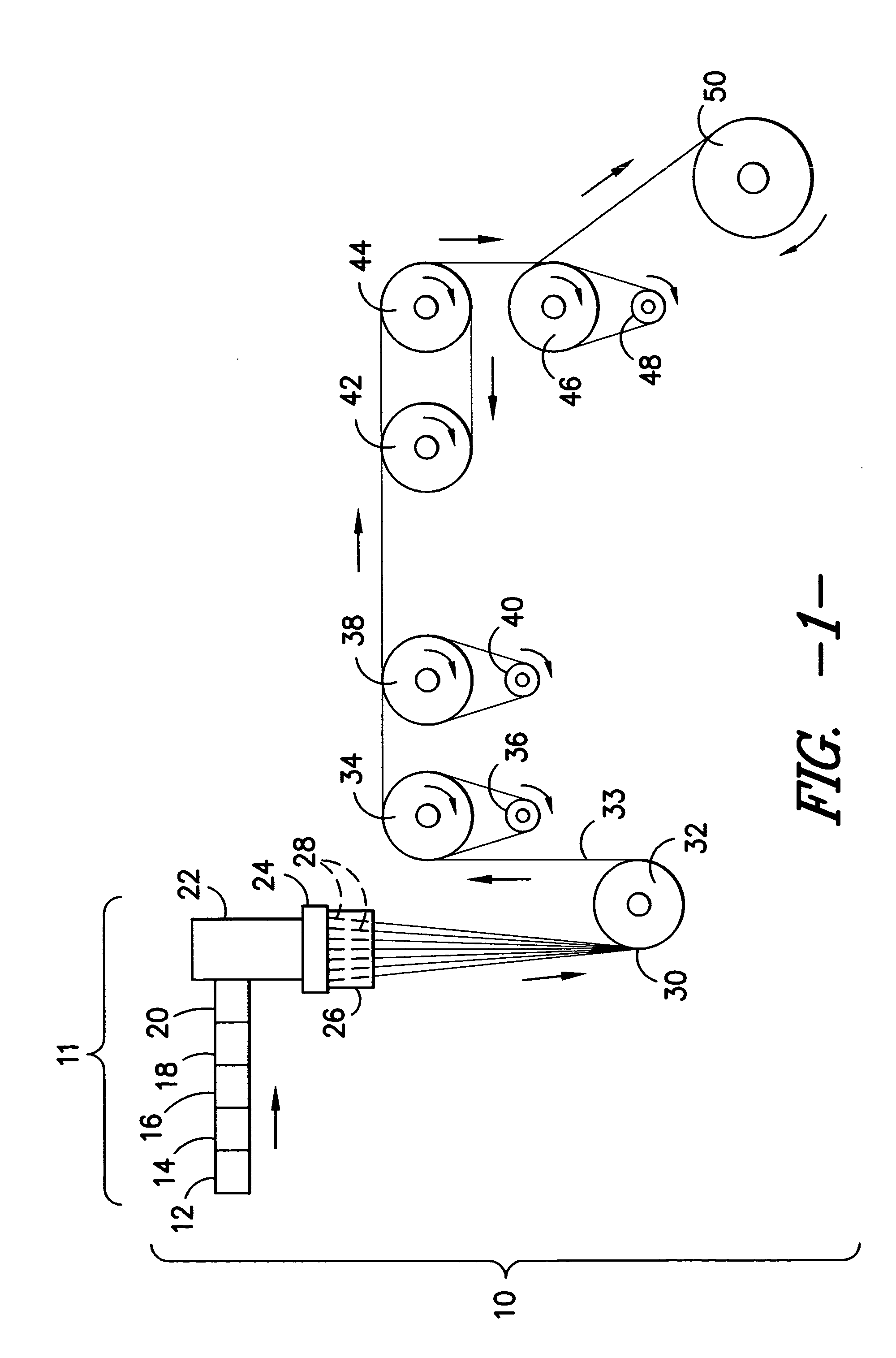
Yarns were made using a commercially available polypropylene fiber grade resin Amoco 7550 (melt flow of 18), using a standard fiber spinning apparatus as described previously. The five colorants from the COLORANT TABLE, above, were formed into 10% concentrates premixed with fiber grade polypropylene resin and fed into the hopper of the extruder during fiber extrusion. In one preferred embodiment, fiber grade resin polypropylene was fed into the extruder on an Alex James & Associates multifilament fiber extrusion line as noted above in FIG. 1 along with a 10% color concentrate including the required liquid polymeric colorants. Yarn was produced with the extrusion line conditions shown in Table 1 using a 68 hole spinneret, giving a yarn of nominally 150 denier. The godet roll temperatures were 67° C. (for 38, 40 in FIG. 1), 85° C. (for 42, 44), and 125° C. (for 46, 48), respectively, with a nominal winder speed of about 1300 m / min. Pigmented fibers...
example 2
Polymeric Colorant Fibers with TiO2 and Pigments
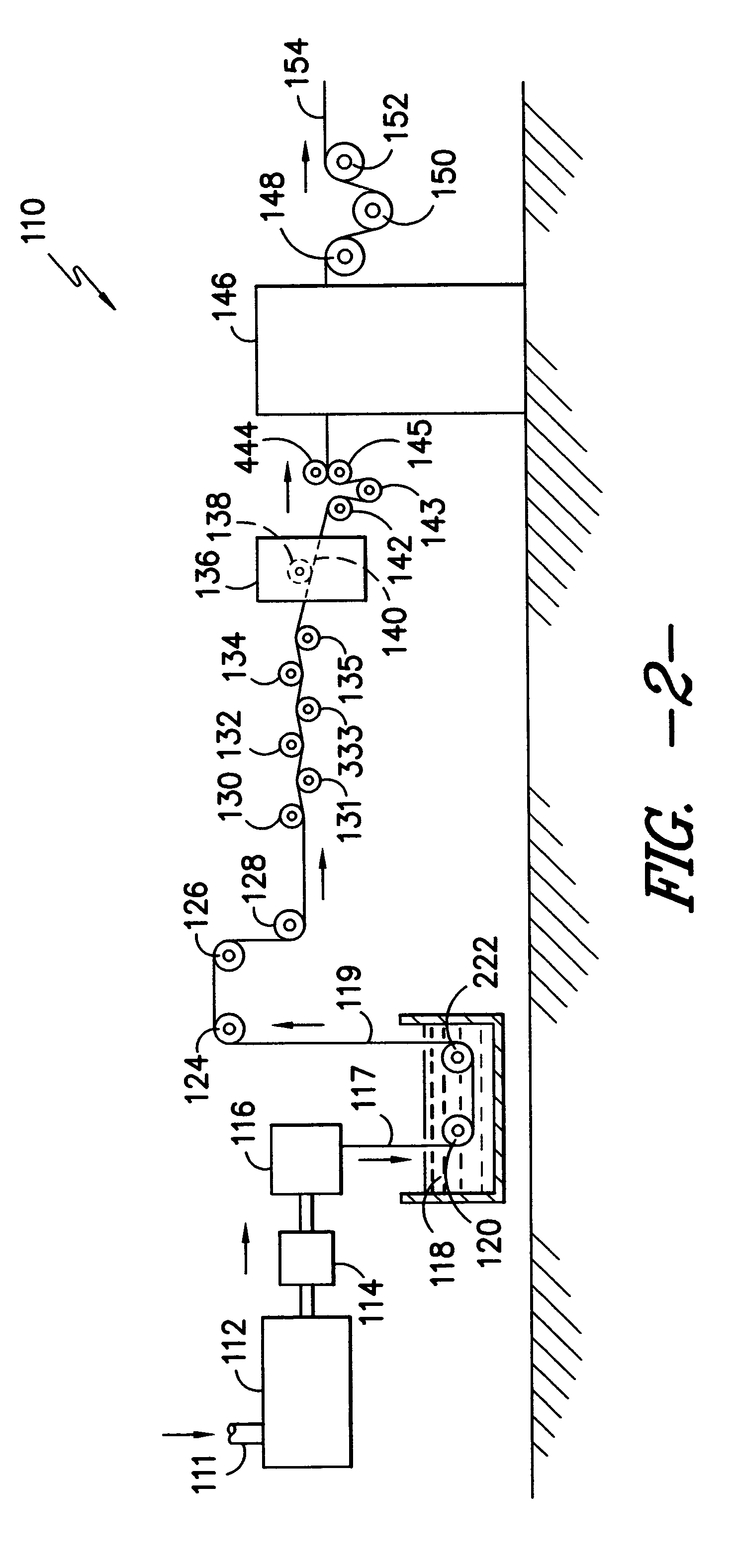
A series of polypropylene samples was produced under the standard fiber spinning conditions described in Example 1 to test the ability to combine both solid pigments and liquid polymeric colorants in the same fibers. The drawing conditions for these example yarns are detailed in the following table.
Procedural ConditionsTable #3Spinning ConditionsRoll SpeedRoll Temperature(m / min)° C.Feed Roll 800Not heatedDraw Roll 1 80555Draw Roll 2145075Draw Roll 3(A + B)2000120 Relax Roll1980Not heated
Using the standard fiber spinning conditions as described above, a series of 10 experiments were performed to produce samples with liquid polymeric colorants labeled by Milliken & Company Product numbers, and TiO2 which is commonly used in the production of thermoplastic fibers to produce dull (9% TiO2) and semi-dull (3% TiO2) appearance. The fibers were successfully produced at all of the conditions tested and the list of colorants, TiO2 levels an...
example 3
Polymeric Colorant Fibers with Nucleators
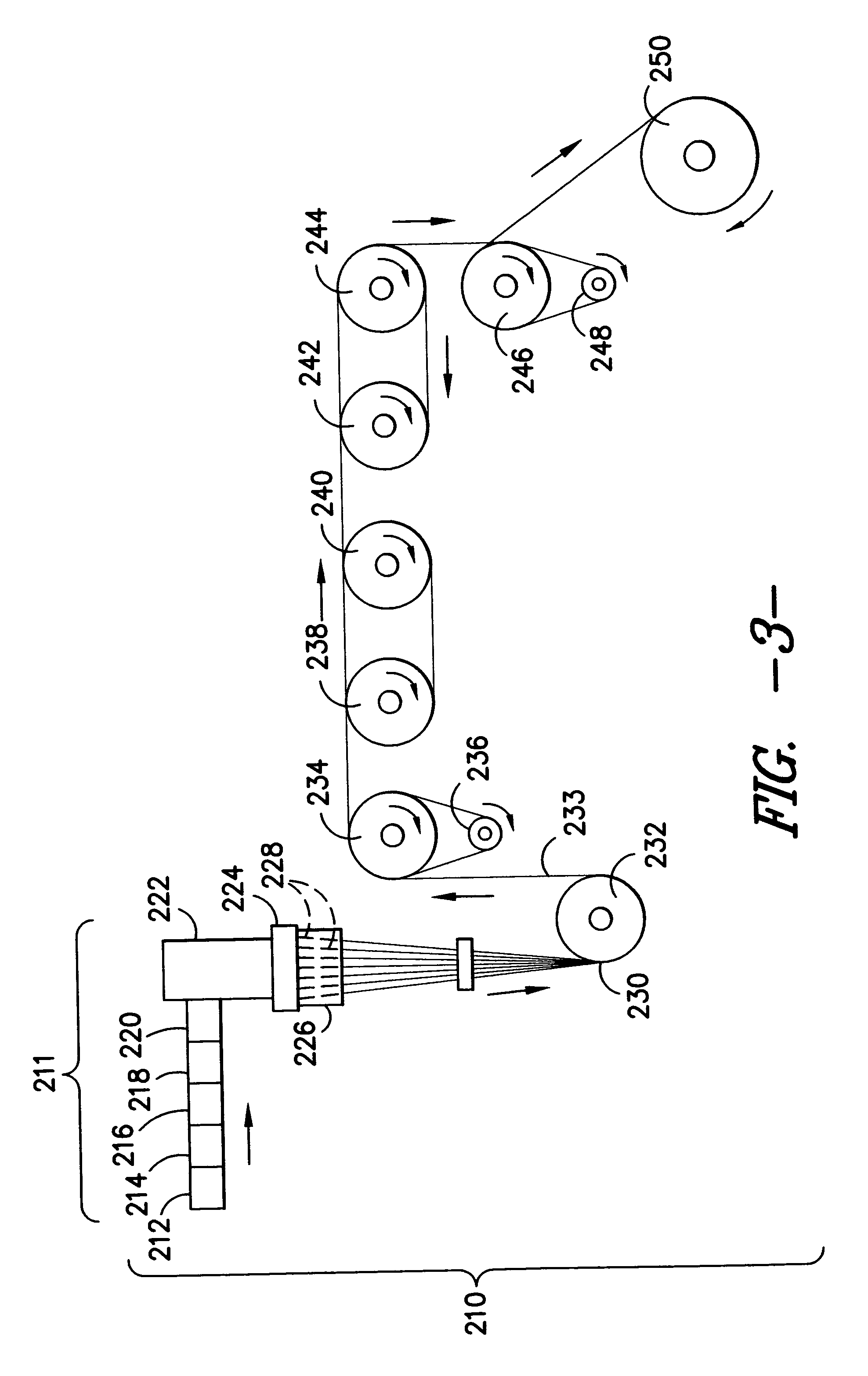
A series of experiments were conducted using commercially available nucleators in combination with the liquid polymeric colorants (from the COLORANT TABLE, above) to produce continuous filament fibers. Using the same conditions as described in Example 1 above, 13 samples were produced using a commercially available polypropylene nucleator, Millad 3940 (MDBS). Fiber compositions for the 13 experimental samples are found in Fiber Additives Table #3 below and the physical properties of the final fibers are found in Fiber Properties Table #4.
Fiber Additives Table #3Nucleated Fiber ConditionsAdditiveColorHeatLevelLevelSetDrawSample IDPolymerAdditive(ppm)Color(%)(C.)RatioAAmoco 7550M3940275010% Colorant #30.51254.0BAmoco 7550M3940275010% Colorant #30.51255.1CAmoco 7550M3940275010% Colorant #30.51253.4DAmoco 7550M3940275010% Colorant #50.51253.4EAmoco 7550M3940275010% Colorant #20.51254.0FAmoco 7550M3940275010% Colorant #20.51253.4GAmoco 7550M39...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com