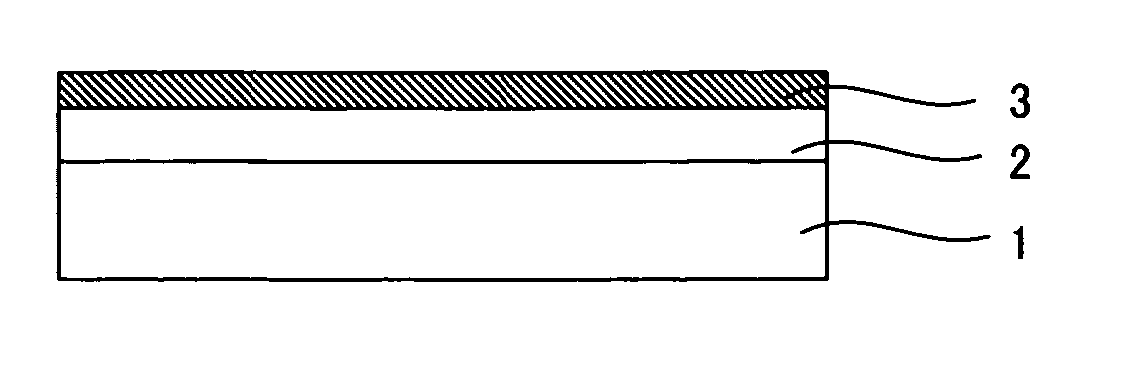
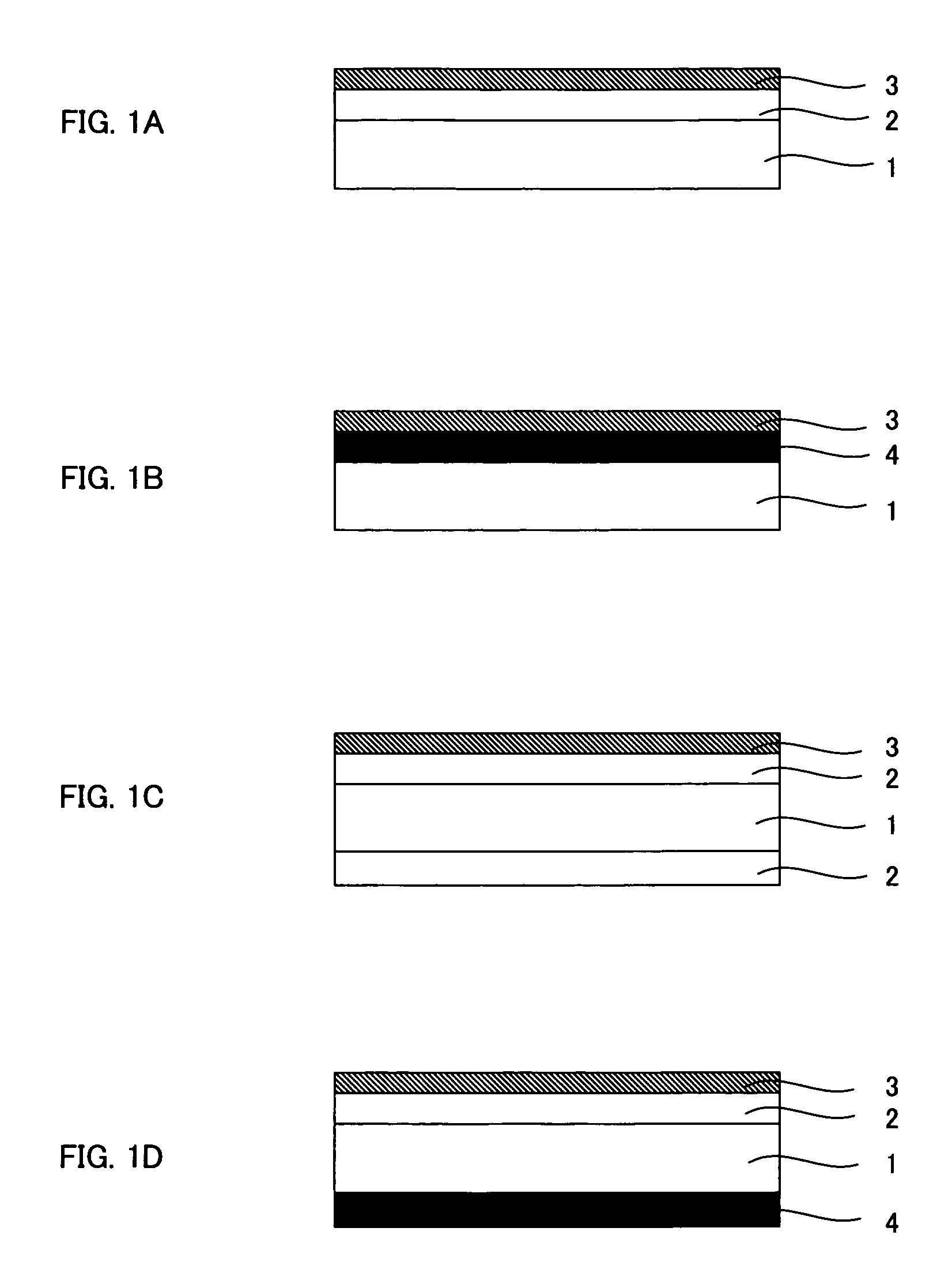
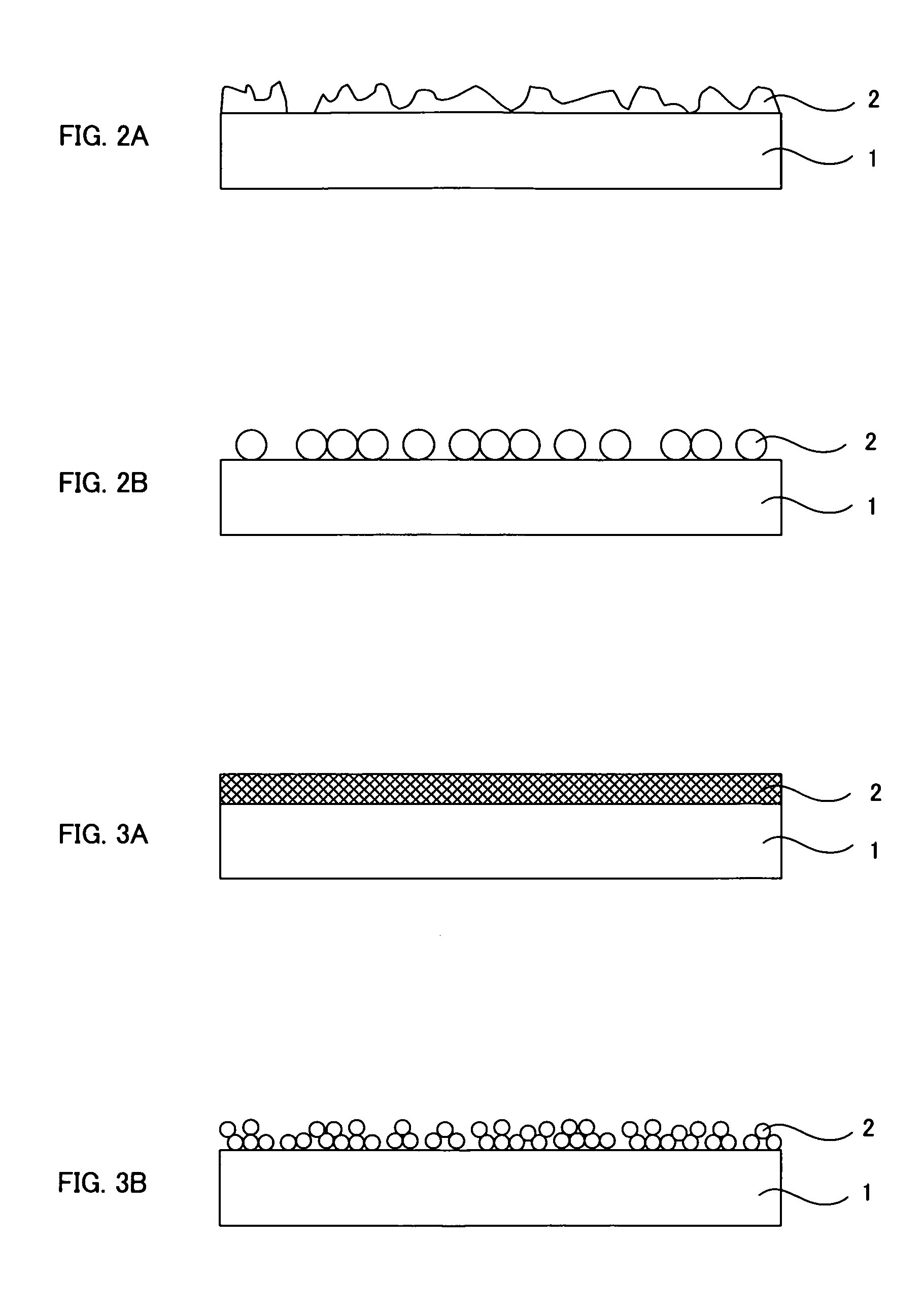
Substrate for bio-microarray and bio-microarray
a bio-microarray and substrate technology, applied in the field of bio-microarrays, can solve the problems of reducing the analysis accuracy of substrates produced without optical processing, reducing the accuracy of substrate analysis based on the intensity of excitation light, etc., to increase the density of probes, suppress reflection, and increase detection accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0102] Forming Anti-Reflection Layer on Substrate
[0103] First, prepared were a solution of 0.4% polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride (PDDA with a molecular weight of 400,000 to 500,000 manufactured by Aldrich Chemical Company), a dispersion of silica particles (MP-1040 manufactured by Nissan Chemical Industries, Ltd.) and ion exchange water. A commercially available slide glass was washed and then immersed in the PDDA solution for two minutes so that PDDA was allowed to adsorb onto the slide glass. Washing with the ion exchange water was then performed for two minutes for the purpose of removing unnecessary PDDA. The PDDA-adsorbing slide glass was then immersed in MP-1040 for one minute for the purpose of forming an anti-reflection layer. After the silica particles were allowed to adsorb, washing with ion exchange water whose pH was adjusted to 10 was performed for four minutes. After the process, an anti-reflection layer comprising fine particles and having unevenness was formed o...
example 2
[0106] Forming Anti-Reflection Layer on Substrate
[0107] Prepared were a solution of 0.4% polyallyamine hydrochloride (PAH manufactured by Aldrich Chemical Company), a solution of 0.4% polyacrylic acid (PAA manufactured by Aldrich Chemical Company), and ion exchange water. The PAH solution and the PAA solution were prepared so as to have a pH of 7.8 to 8.5 and a pH of 3.5, respectively. A commercially available slide glass was washed and then subjected to 10 cycles of PAH / PAA alternate adsorption (10 cycles of PAH adsorption and 10 cycles of PAA adsorption) so that a layer-by-layer self-assembled film was prepared. The film was then treated with acid so as to have a porous structure / uneven structure for providing an anti-reflection performance. Heat treatment was then performed to crosslink PAH and PAA by amide bond so that the anti-reflection structure was fixed. A series of these processes were according to Hiller et al., Nature Materials, Vol. 1, page 59, 2002.
[0108] (Forming Im...
example 3
[0110] Forming Anti-Reflection Layer on Substrate
[0111] The process of Example 1 was used.
[0112] (Forming Immobilization Layer on the Substrate Having Anti-Reflection Layer)
[0113] Chemical vapor deposition using 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (manufactured by Across Chemical Co.) was performed to form an amino group-containing layer on the surfaces of the silica particles used in the anti-reflection layer. A microarray substrate was prepared by a series of these processes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com