Semiconductor radiation detector, positron emission tomography apparatus, semiconductor radiation detection apparatus, detector unit and nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus
a semiconductor radiation and detector technology, applied in the direction of optical radiation measurement, instruments, x/gamma/cosmic radiation measurement, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the probability of holes being annihilated midway the distance, shortening the distance up to the electrodes, etc., to facilitate maintenance and examination, shorten the time required to mount the semiconductor radiation detectors on the nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus, the effect of shortening the tim
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
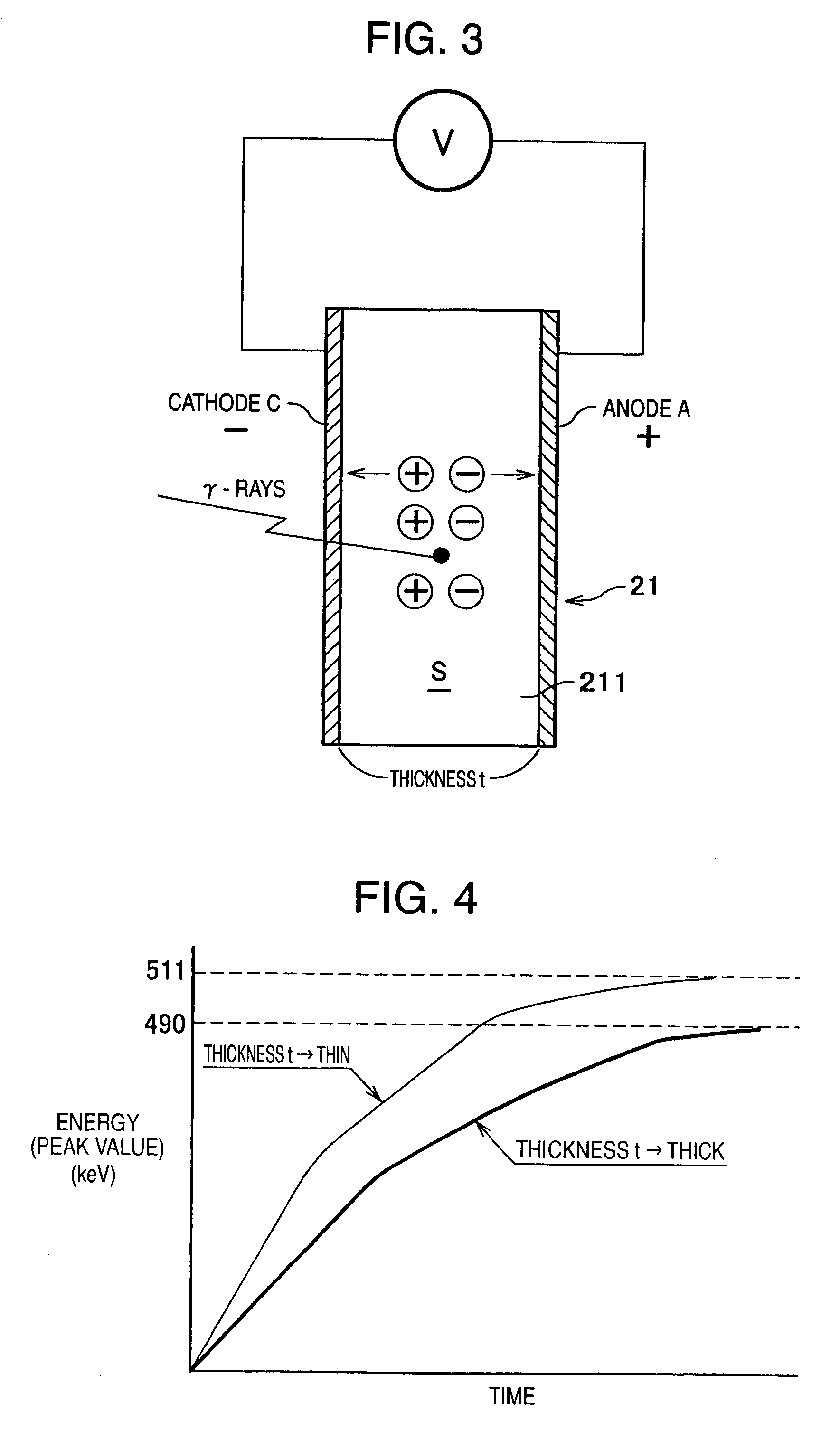
[0036] A nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus which is a preferred embodiment of the present invention will be explained with reference to attached drawings in detail below as appropriate. The following are explanations of the nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus according to this embodiment, distance between electrodes of a semiconductor radiation detector, arrangement (layout) of elements such as analog ASIC on a substrate, and elements applicable to this embodiment for construction of substrate units, etc. Note that an analog ASIC refers to an ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) which is an application-specific IC for processing analog signals and is a kind of LSI.
Nuclear Medicine Diagnostic Apparatus
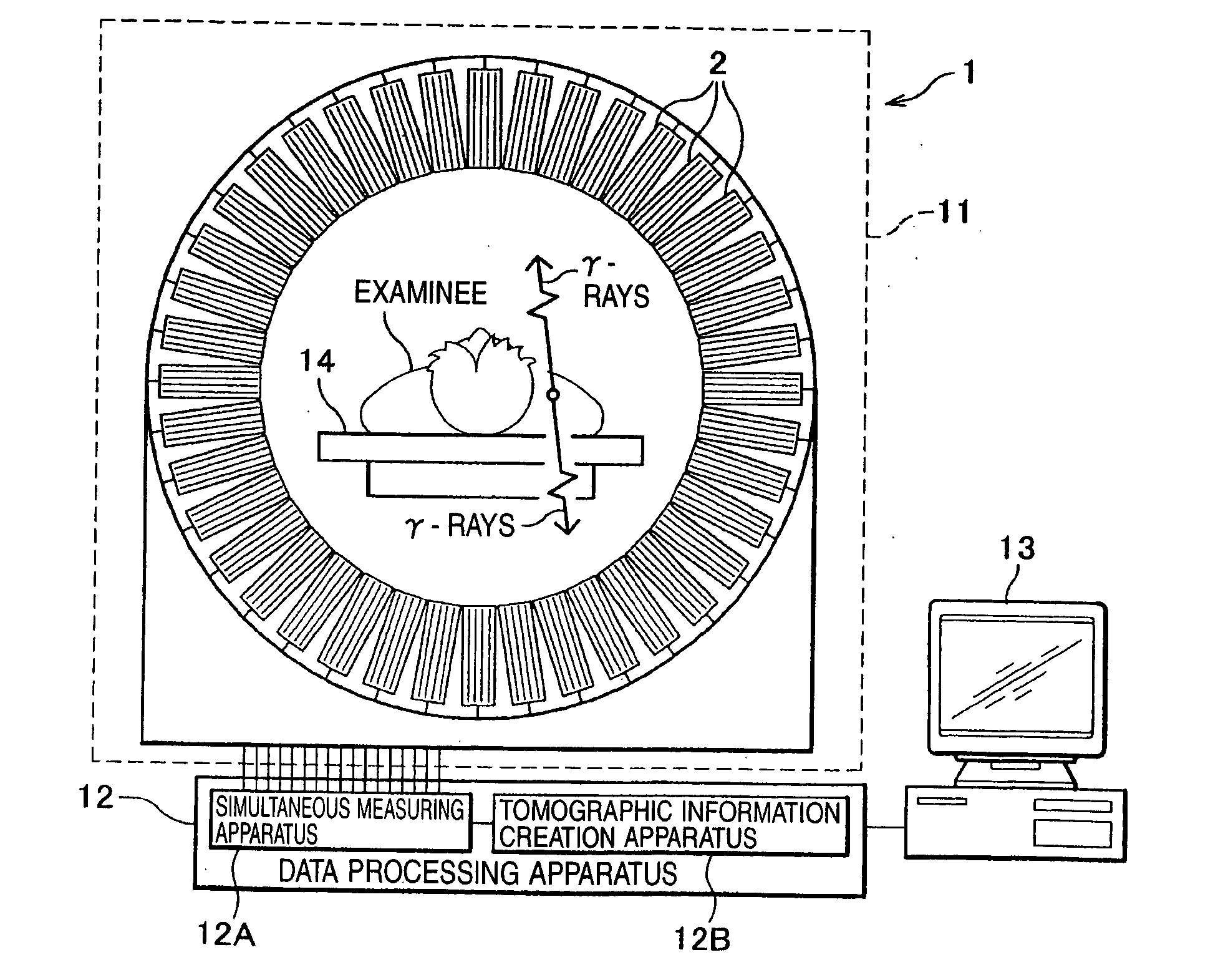
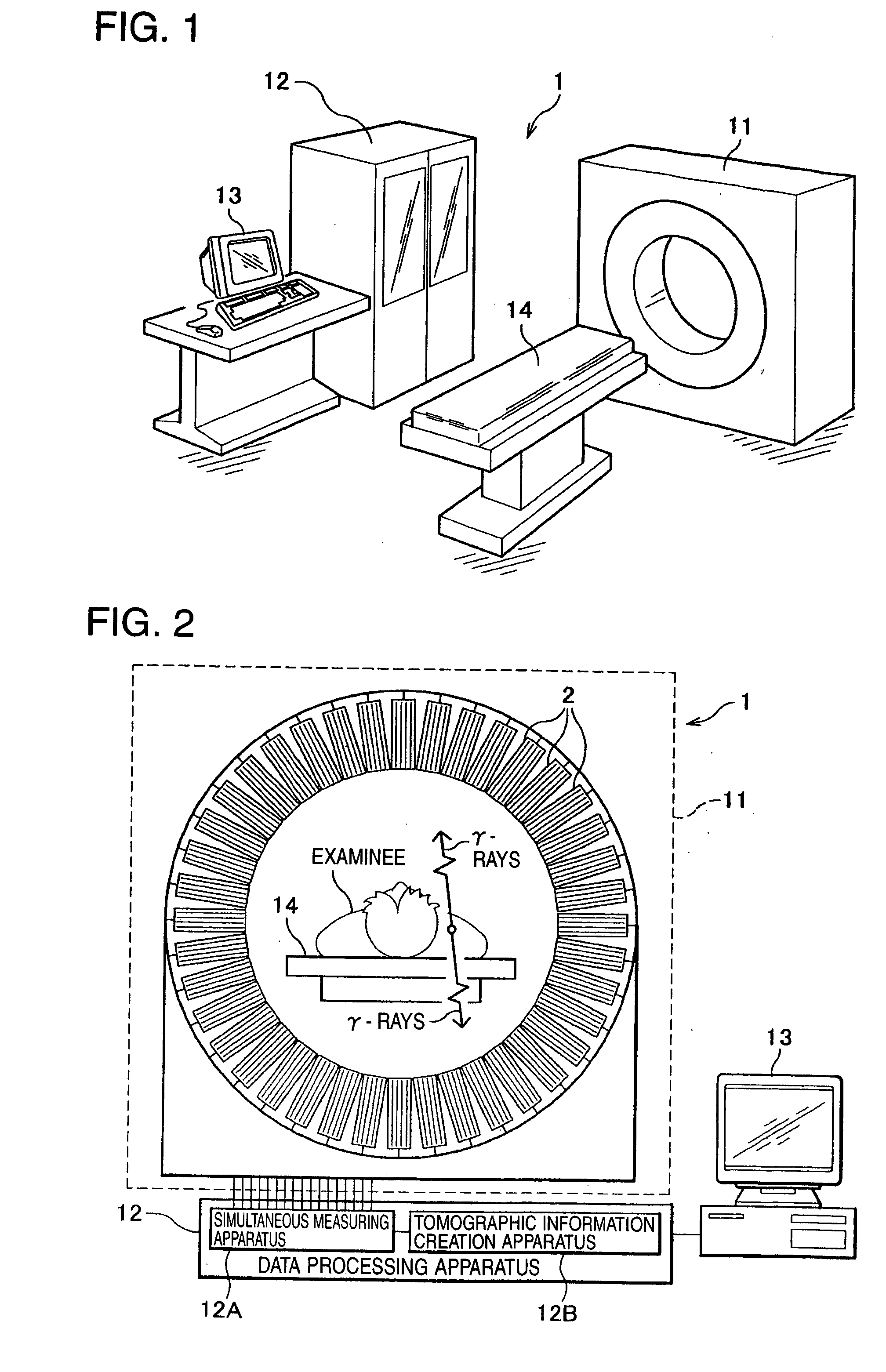
[0037] First, the nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus (radiological diagnostic apparatus) according to this embodiment will be explained. As shown in FIG. 1, a PET apparatus 1 as the nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus is constructed by including a camera (image p...
embodiment 2
[0101] A nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus according to another embodiment will be explained. The nuclear medicine diagnostic apparatus of this embodiment is single photon emission computer tomography (SPECT) apparatus.
[0102] This SPECT apparatus 51 will be explained using FIGS. 13 to 15. The SPECT apparatus 51 is provided with a pair of radiation detection blocks 52, a rotary holder (body of rotation) 57, a data processing apparatus 12A and a display apparatus 13. The radiation detection blocks 52 are disposed at two positions with a 180° difference in the circumferential direction of the rotary holder 57. More specifically, the respective unit support members 56 of the radiation detection blocks 52 are mounted on the rotary holder 57 with a 180° difference in the circumferential direction. A plurality of detector units 2A each including twelve combined substrates 53 are mounted on the respective unit support members 56 in a detachable / attachable manner. Thus, the detectors 21...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com