Zeolite-containing oxidation catalyst and method of use
a technology of oxidation catalyst and zeolite, which is applied in the direction of inorganic chemistry, heating types, domestic heating details, etc., can solve the problems of less effective catalysts used to treat the exhaust of internal combustion engines during periods of relatively low temperature operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example a
Preparation of Fe-Beta Zeolite
[0056] To prepare a sample of iron-exchanged Beta zeolite (Fe-Beta zeolite), 17 grams of iron [II] sulfate was dissolved in 800 ml water. One hundred grams of Beta zeolite was added to the solution which was then stirred for 1 hour at a temperature of 70° C. to 80° C. The resulting slurry was then filtered and washed with 2 liters of water, dried at 120° C. and calcined at 540° C. The resulting material comprised 1.65% by weight iron. This technique was employed to prepare the Fe-Beta zeolite catalysts used in the following Examples.
example b
Preparation of Pt—Fe-Beta Zeolite
[0057] A solution was prepared using 0.54 grams of tetraammine platinum chloride in 500 ml water, to which 100 grams of Beta zeolite was added. The mixture was stirred for 24 hours at room temperature so that platinum ions replaced sodium ions in the zeolite material. The slurry was then filtered and washed with 2 liters water, dried and calcined at 540° C. The resulting calcined, platinum ion-exchanged Beta zeolite was then ion-exchanged with iron [II] sulfate by adding the zeolite to a solution of iron [III] sulfate equivalent to 17 grams of iron [II] sulfate in 800 ml water. The solution was allowed to stand for about 1 hour and was then stirred at 70° C. to 80° C. for 1 hour. The resulting slurry was then filtered, washed with water, dried at 120° C. and calcined at 540° C. On a dry basis, the Beta zeolite comprised 1.6% by weight iron and 0.25% by weight platinum. This technique was employed to prepare the Fe—Pt-Beta zeolite catalyst components...
example 1
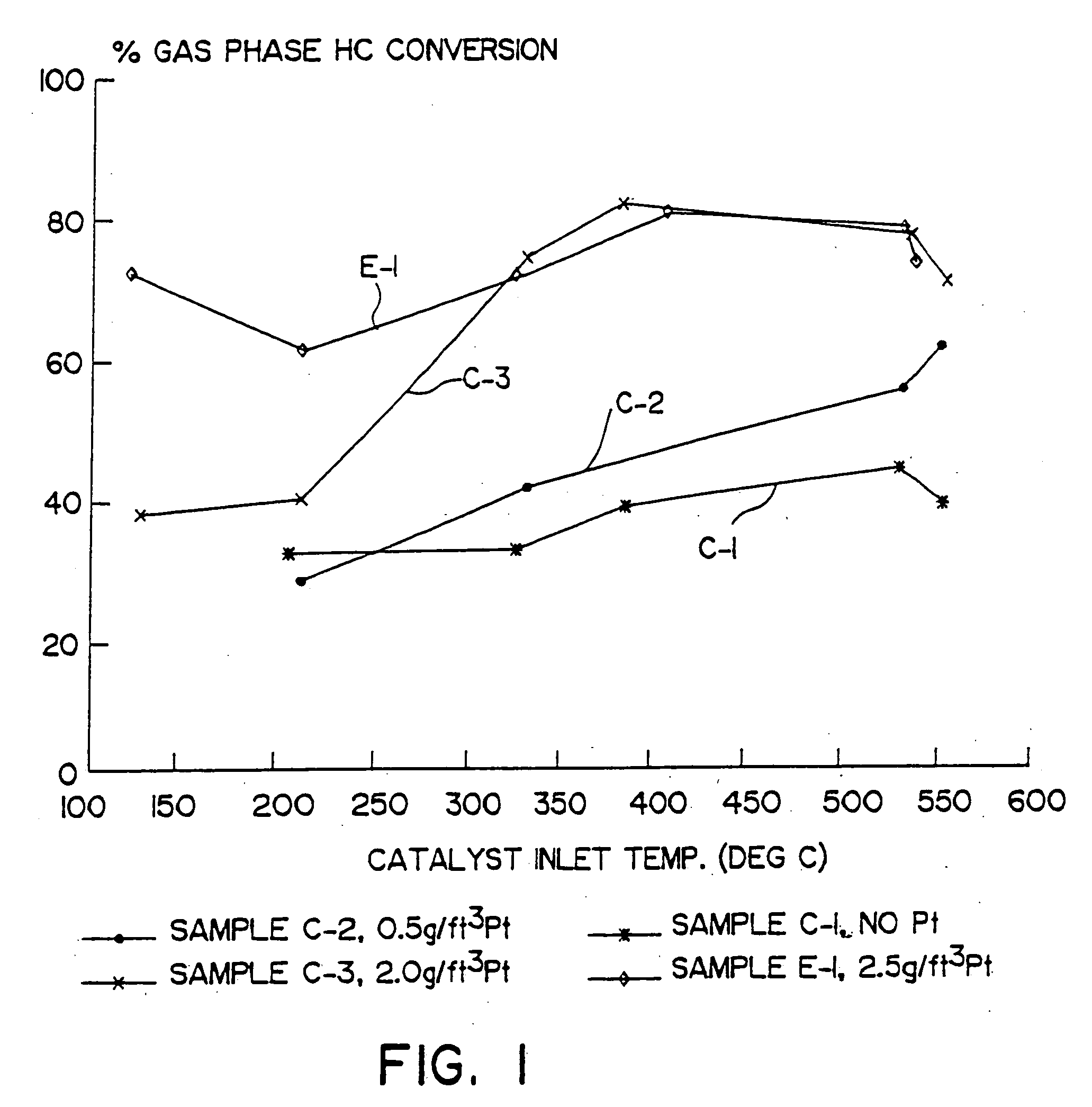
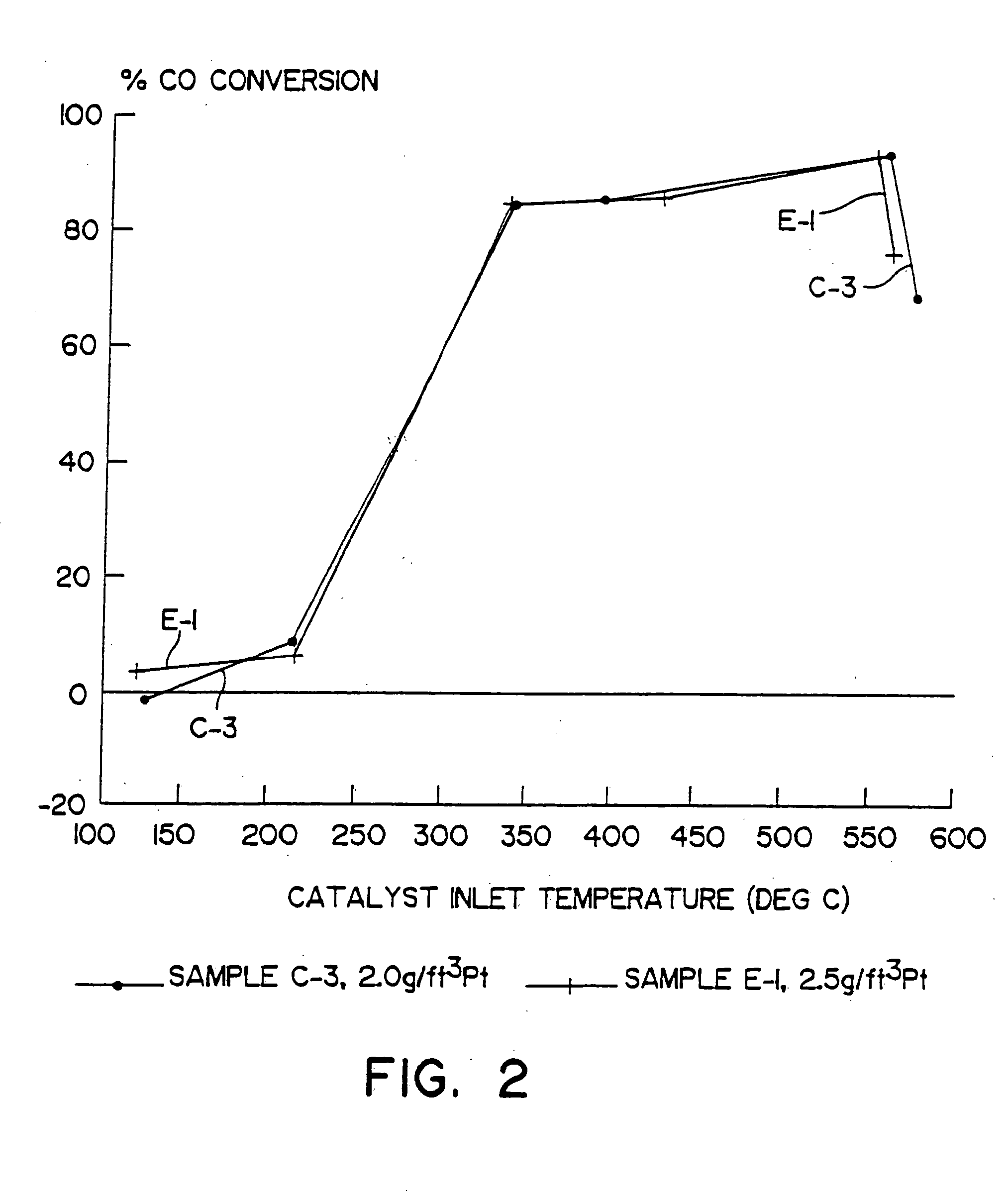
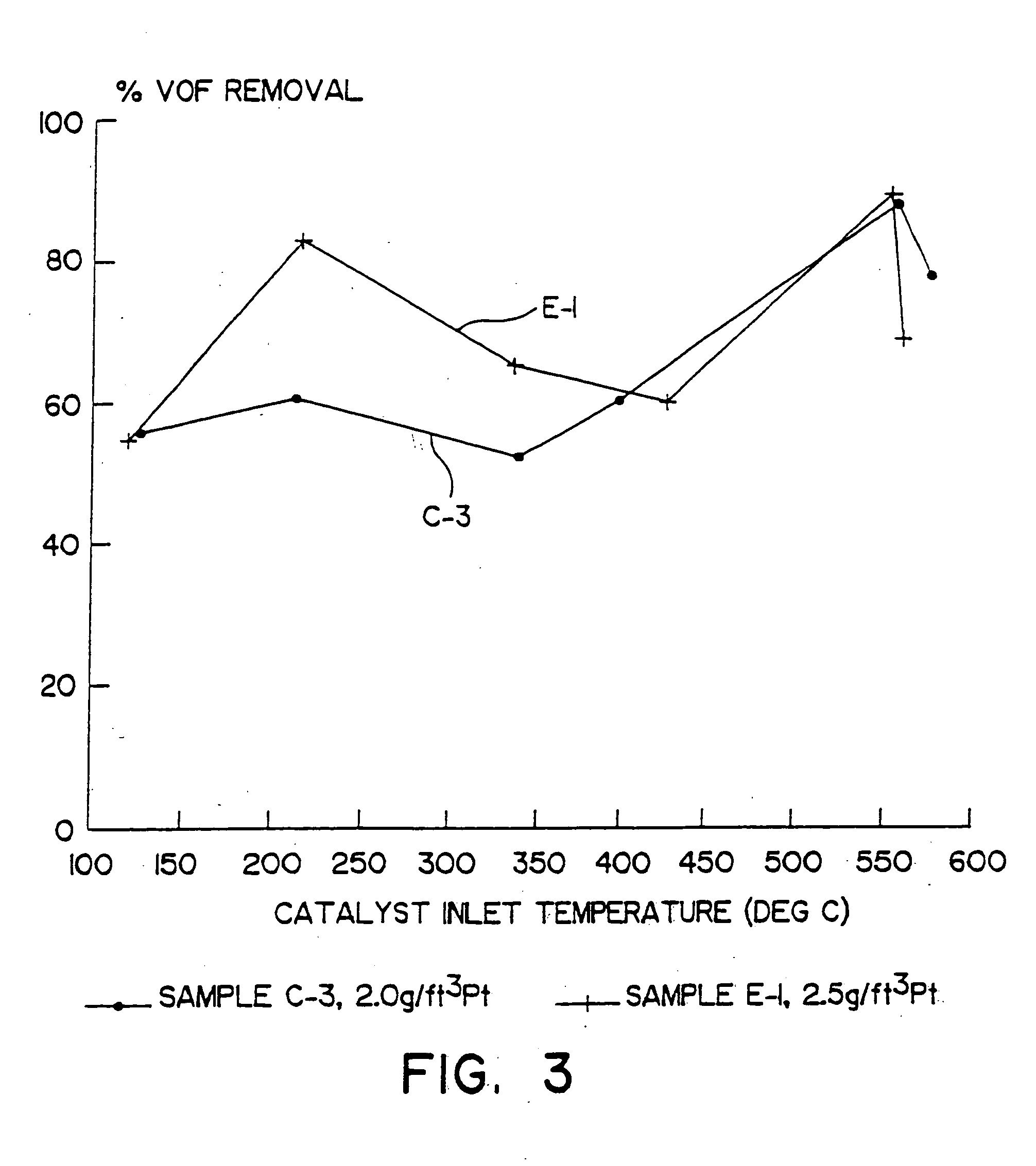
[0058] A. A catalyst according to the present invention was prepared by coating a honeycomb monolith with a catalytic material comprised of a zeolite, bulk ceria and bulk alumina to provide 0.84 g / in3 γ-alumina, 0.83 g / in3 alumina-stabilized ceria and 0.83 g / in3 Fe-Beta zeolite. The honeycomb monolith was a cordierite substrate measuring 9 inches in diameter by 6 inches long and having 4.00 cpsi. The catalyst material also provided 2.5 g / ft3 of platinum, 80 percent by weight of which was dispersed on the alumina, and 20 percent by weight of which was dispersed on the ceria. This catalyst was designated E-1.
[0059] B. For comparison, three other catalysts were prepared to provide a series of three otherwise identical compositions containing a ceria-alumina catalytic material but no zeolite and, in two cases, having platinum dispersed thereon. The platinum loadings of these comparative catalysts were 0.0, 0.5 and 2.0 g / ft3 platinum. Each comparative catalyst comprised a γ-alumina unde...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com