Materials and methods for producing geminivirus resistant plants
a technology of geminivirus and material, applied in the direction of viruses/bacteriophages, organic chemistry, peptide sources, etc., can solve the problems of $125 million in tomato production in florida, major limiting factors of transmission geminiviruses, and $125 million in losses, and achieve the effect of providing resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Field Evaluation of Transgenic Resistance to ToMoV
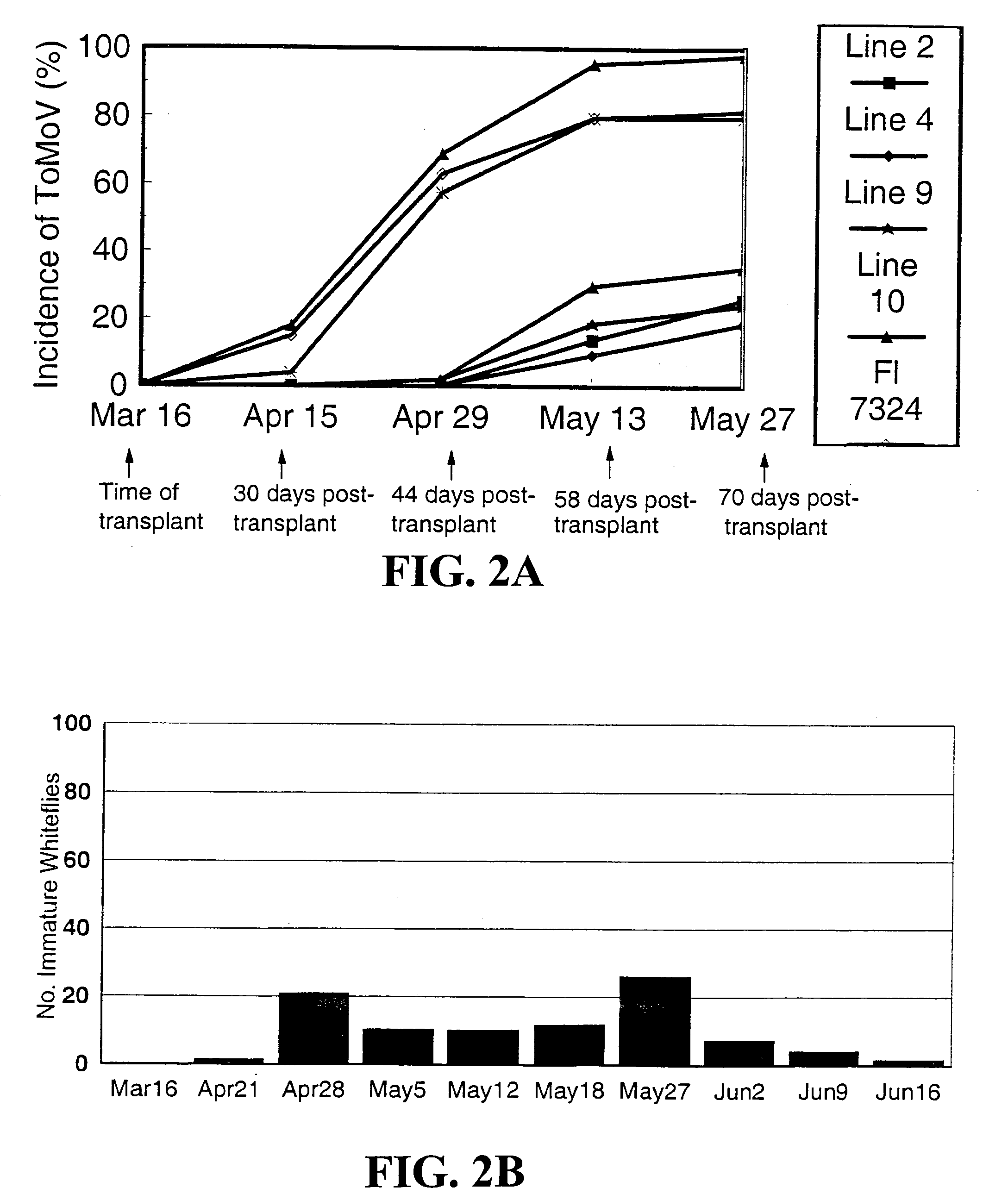
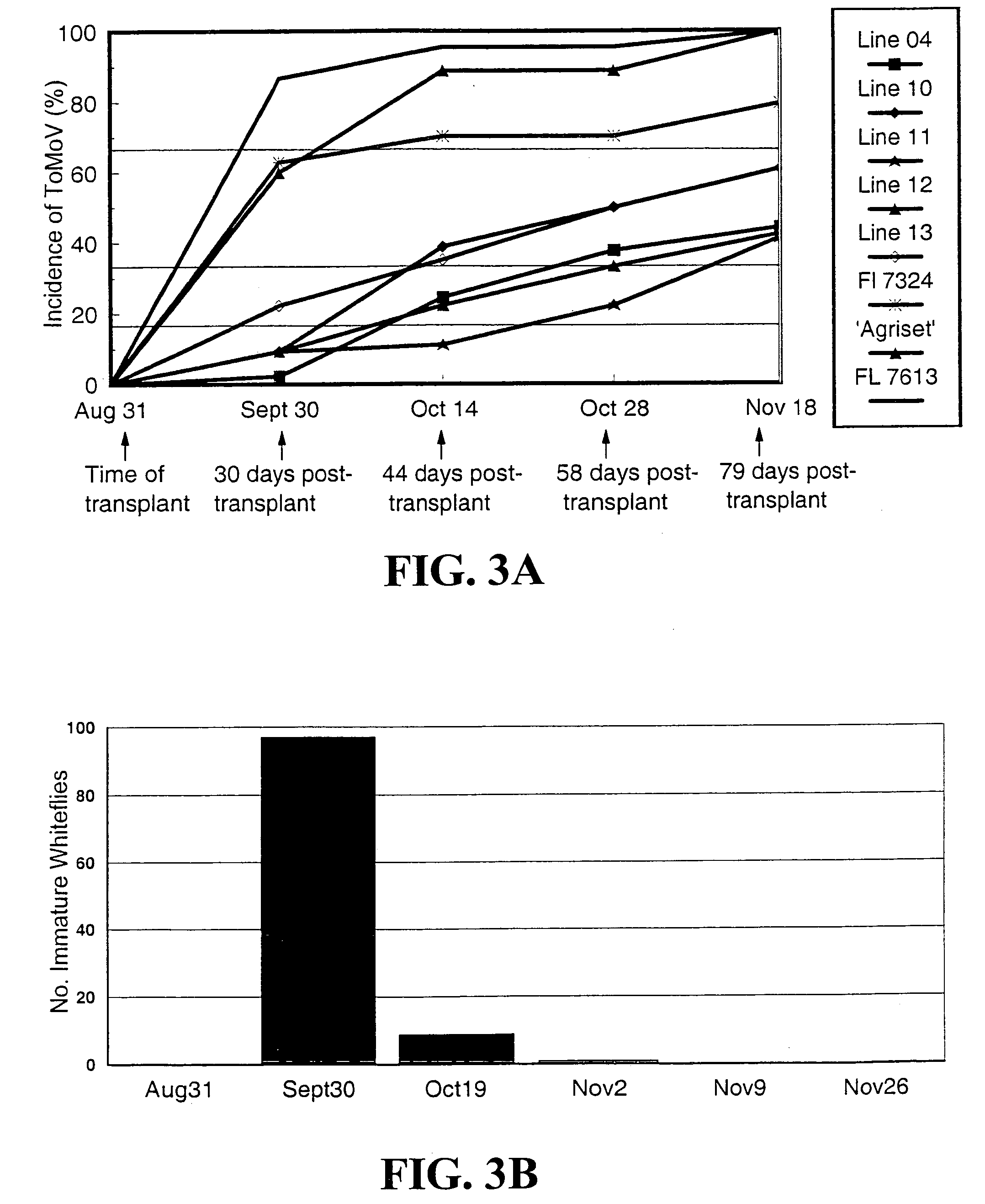
[0028] Advanced breeding lines, FL 7324 and FL 7613 were transformed with ToMoV Rep gene using standard Agrobacterium-mediated transformation techniques. A vector comprising a 35S CaMV (non-enhanced) promoter linked to the Rep gene was used in the transformation. Plant tissue was wounded using tungsten. Plants that contained a Rep transgene were identified using PCR methods. Those plants were then evaluated for resistance to viral infection. Untransformed parents and transformed lines from three different transformation events were evaluated for resistance to ToMoV and for yield, both in the presence and absence of ToMoV. Lines shown in the following tables are four generations past transformation. Lines 02 and 04 are from the same T0 plant in a FL 7613 background, lines 09 and 10 are from a second T0 plant and their background is FL 7324, and lines 11 and 12 are from a third T0 plant, and their background is FL 7613.
[0029] Souther...
example 2
Performance in the Presence of ToMoV and Whiteflies
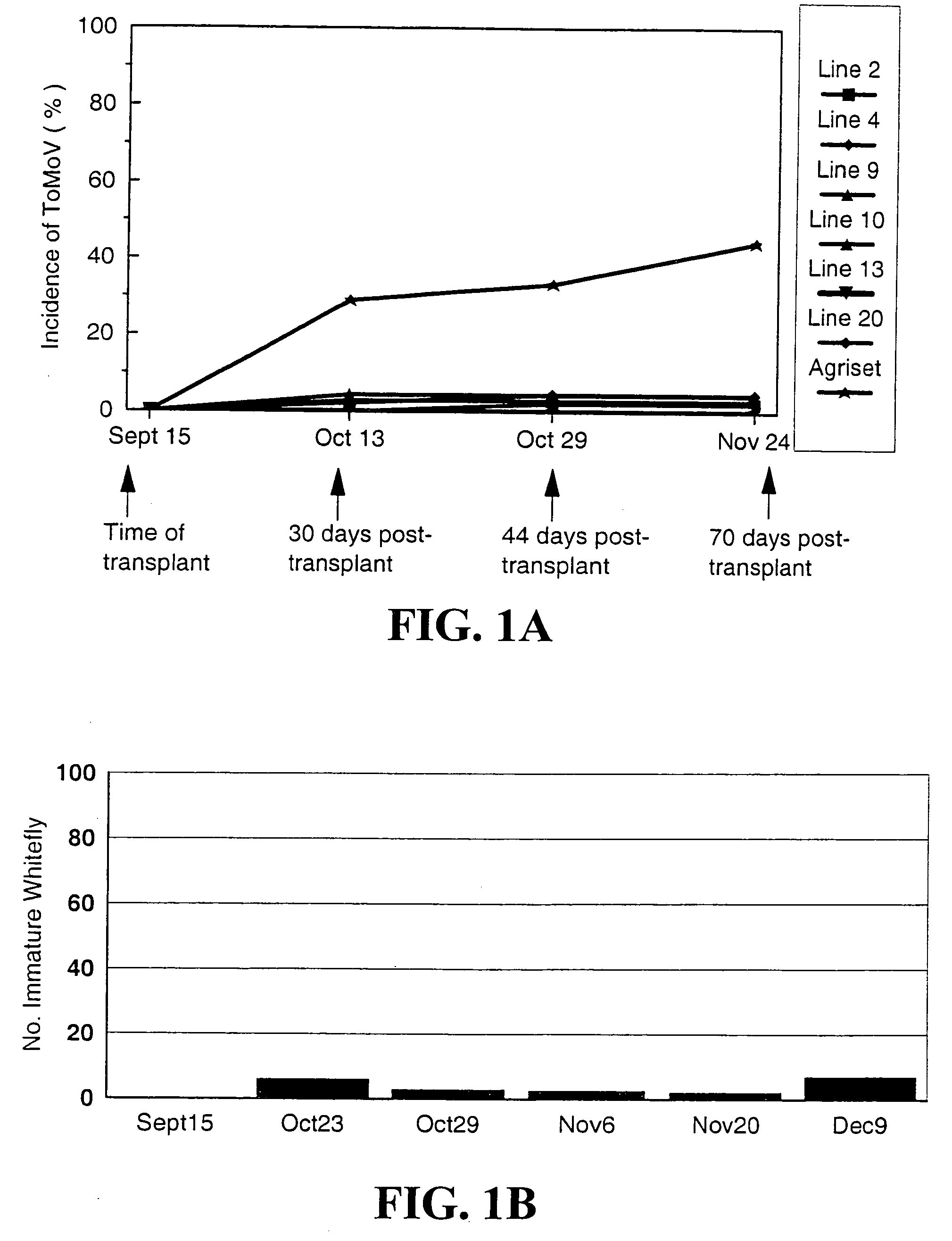
[0030] For three seasons, Fall 1997, Spring 1998, and Fall 1998, tomato transplants to be evaluated were set into a field which was within 20 feet of a large block of tomatoes which was a continuous source of viruliferous whiteflies throughout the season. No imidacloprid was applied to the plants being evaluated but attempts were made to keep whitefly populations below a threshold which would result in irregular ripening of the fruit (20 immature whitefly / 10 terminal leaflets). Whitefly populations were evaluated approximately every 2 week beginning about 4 week after transplanting. Whitefly populations varied each season, with the highest populations occurring in the Fall 1998 trial. The trials consisted of 15 plants per block, with three replications, in a randomized complete block design. Plants were evaluated every other week for the presence of whiteflies and virus. Plants displaying virus-like symptoms were assayed by nucleic...
example 3
Yields
[0031] Results are shown in Tables 1, 2 and 3. The transformed lines yielded as much or more than the untransformed parents and the commercial hybrid ‘Agriset’ in all three trials. The best transformed lines, 02, 04, 11 and 12 yielded approximately 50%-100% more marketable fruit than the untransformed lines. Yields of these transformed lines in the presence of ToMoV and whiteflies were comparable to yields of the untransformed lines in the absence of virus and whiteflies. In addition, transformed plants yielded well in both fall and spring production seasons.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pathogen-derived resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com