Apparatus for treating a substrate with an ozone-solvent solution
a technology apparatus, which is applied in the direction of ozone preparation, disinfection, cleaning using liquids, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient time for the supersaturated solution to return to equilibrium, and the dispense temperature of ozone water solution decreased about 5 degree c, so as to improve the removal rate and reduce the corrosion potential , the effect of reducing the process temperatur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Factors Determining Oxidation Rate or Removal Rate—A Model
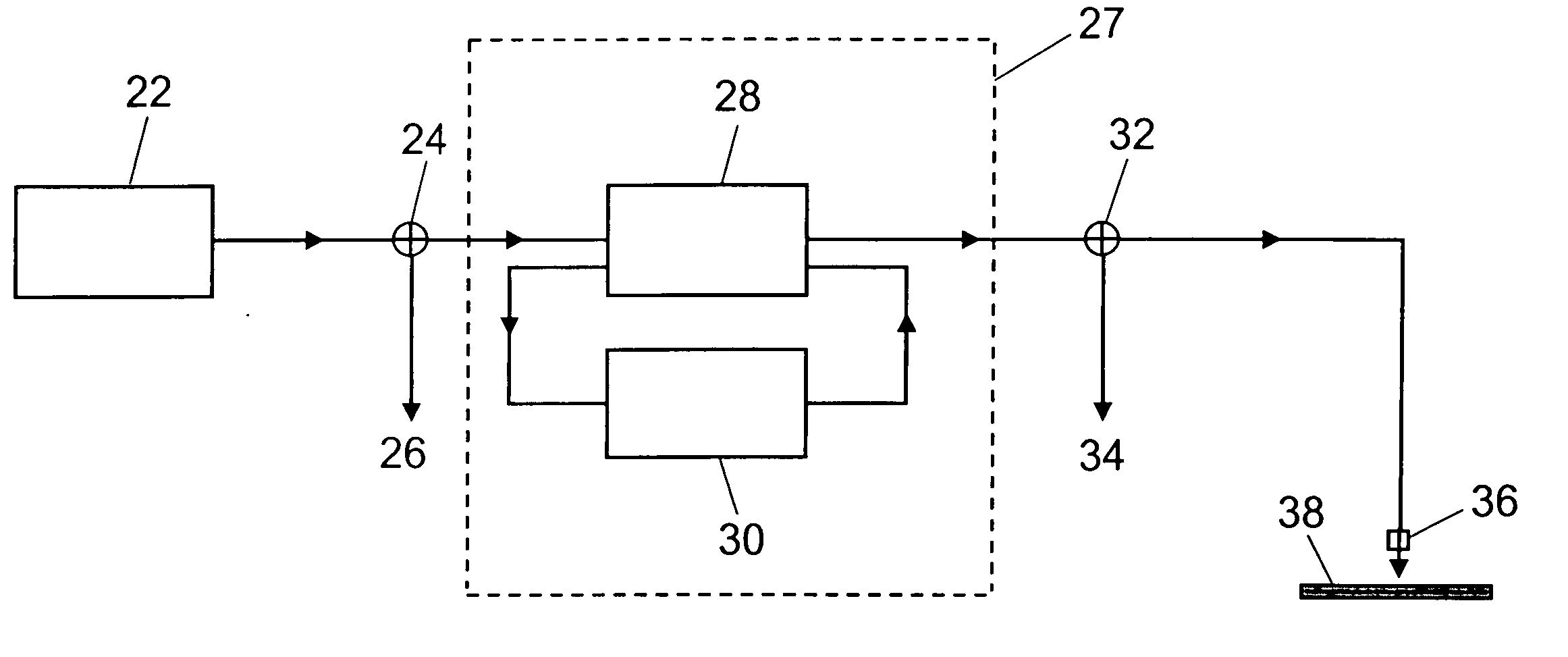
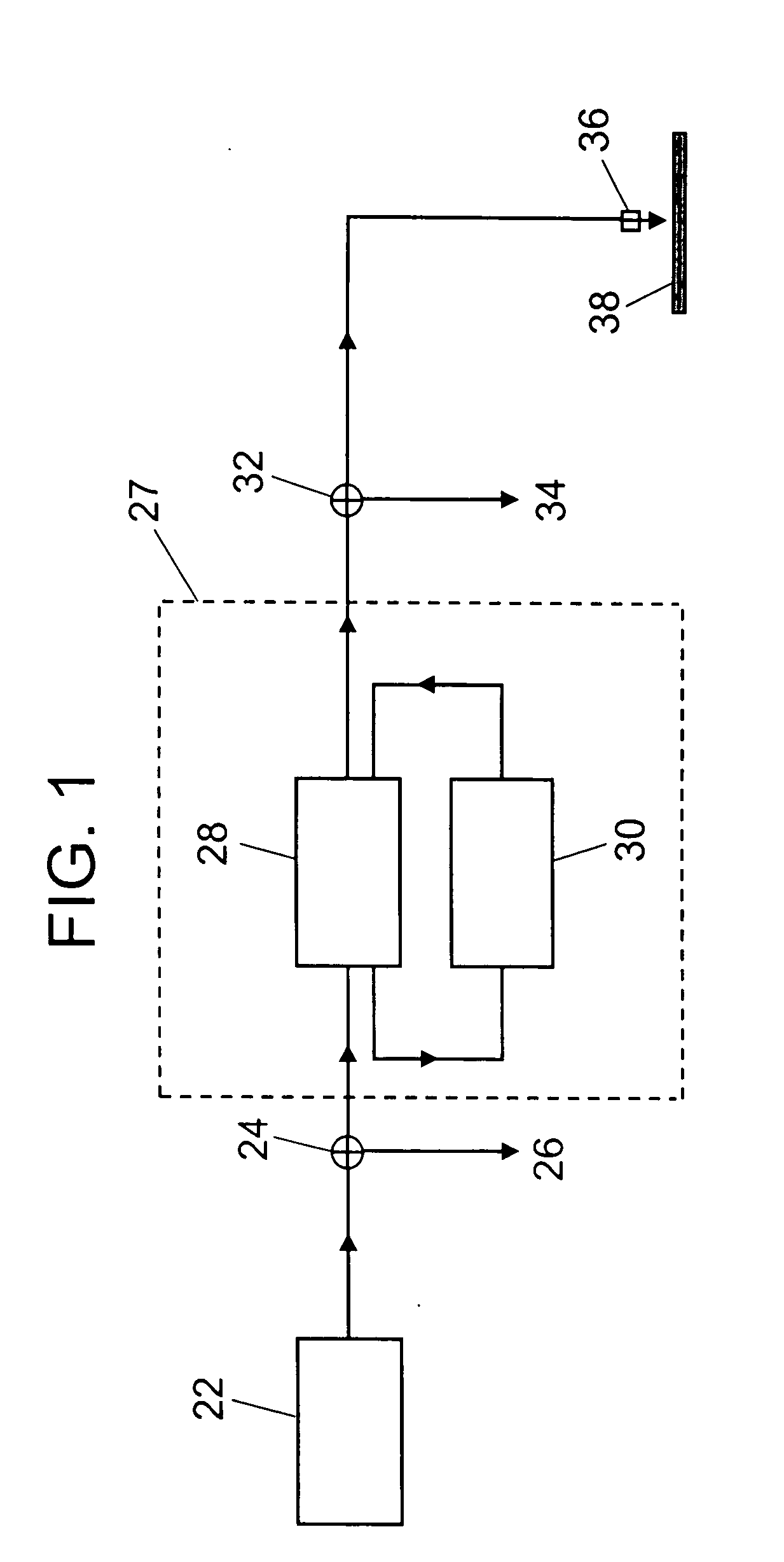
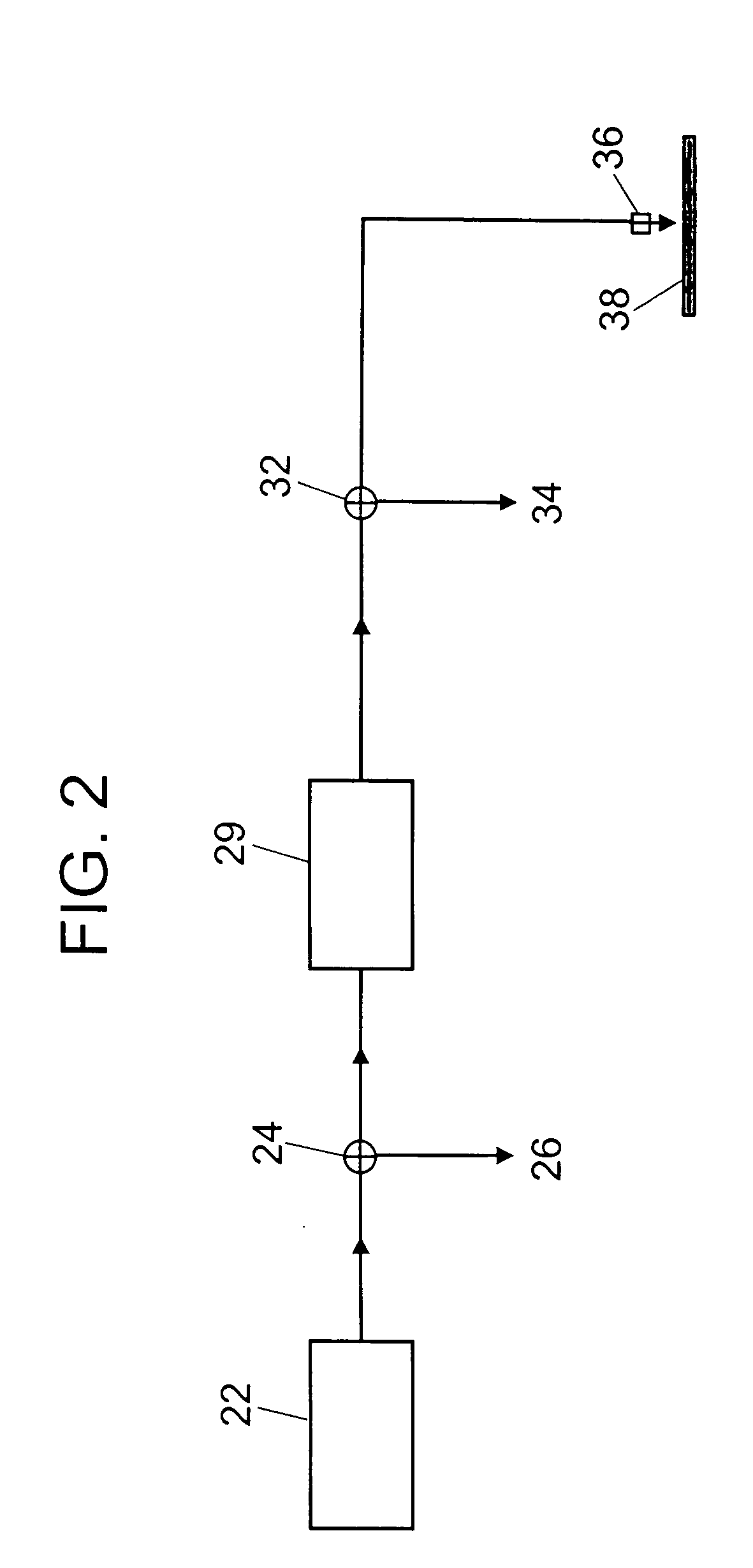
[0056] The inventors have developed a model to help better understand the factors determining oxidation and removal rate of an organic material such as photoresist from a semiconductor wafer using an ozone-solvent solution at concentration C and temperature T. The rate of oxidation and removal of an organic layer from a substrate can be defined in terms of an etch rate. We can write an expression for the etch rate E (cm resist / sec) as E=C*(X / ρ)*(M*S) / (M+S). The parameter C (g ozone / cm3) is the dissolved ozone concentration in the water far from the surface of the organic layer on a semiconductor wafer for example (the bulk concentration). The parameter X (g resist / g Ozone) is the mass of resist removed per mass of ozone consumed at the surface. If we assume that the resist is composed of chains of CH2 units which must be fully oxidized to be removed, then 3 moles of ozone are required to oxide each mole of CH2. This corresp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com