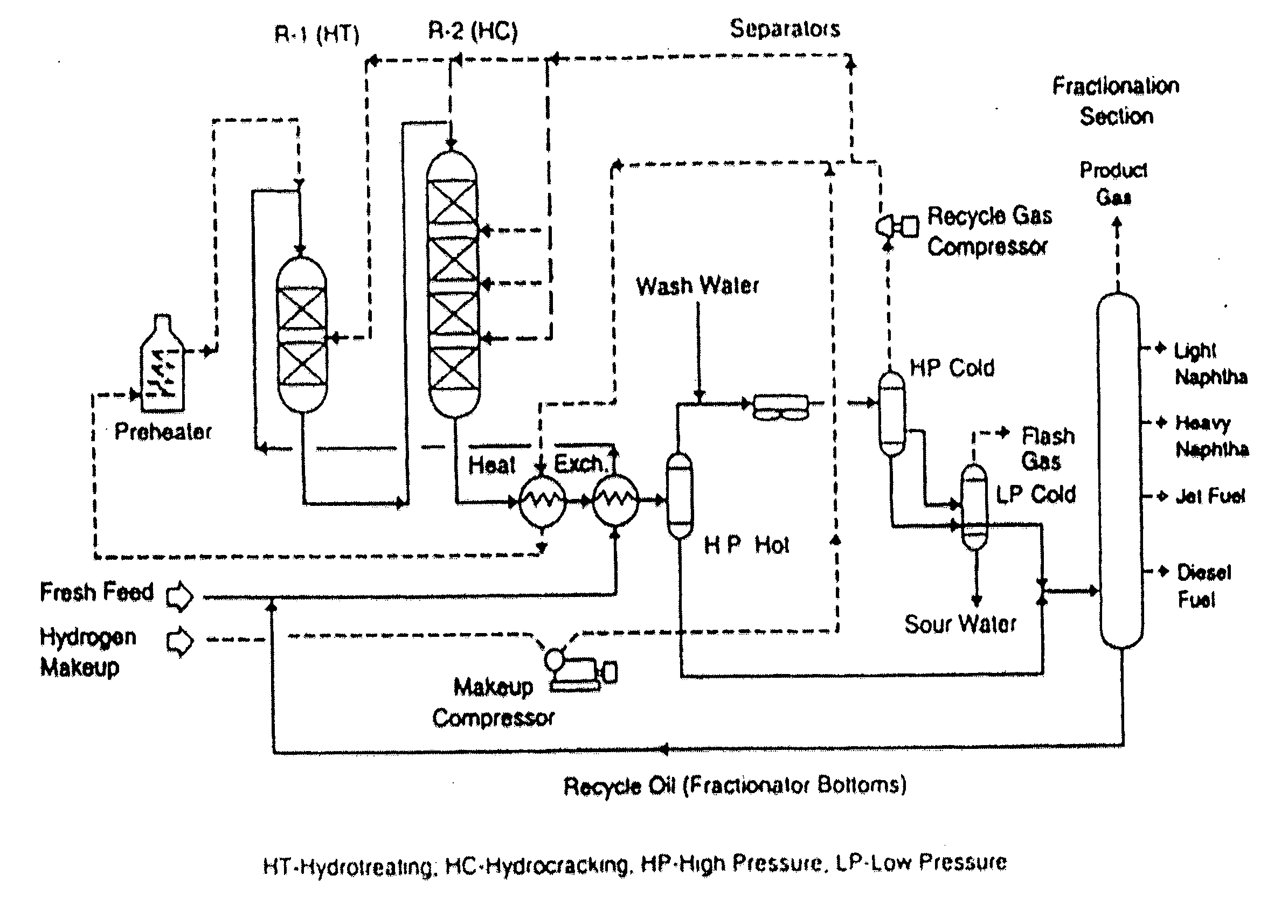
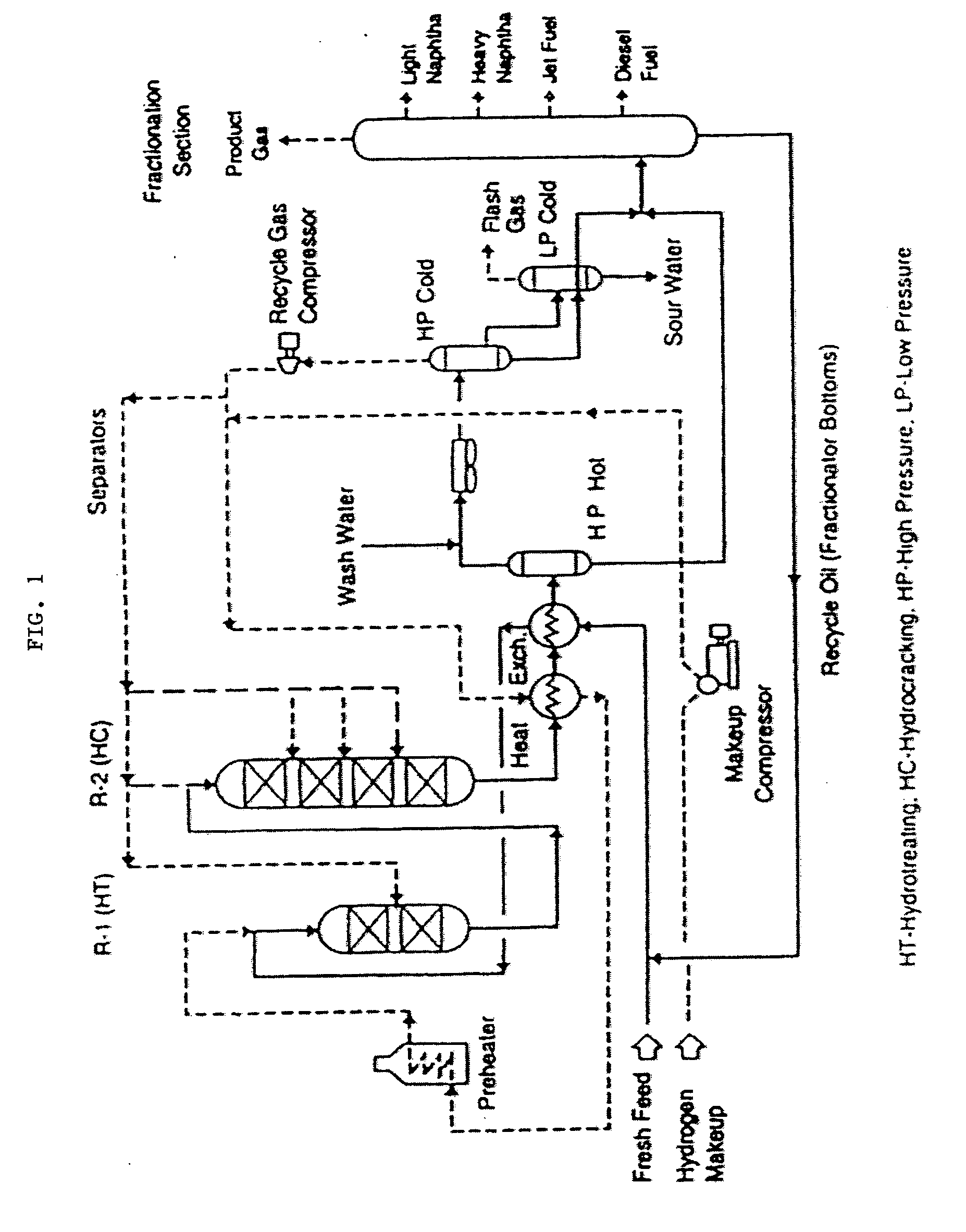
Hydrocracking catalysts for vacuum gas oil & de-metalized oil blend
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] Several catalysts were prepared using nickel (Ni) / molybdenum (Mo) metals loadings along with the four different support materials identified above. The four catalyst formulations created in this manner were characterized using gas sorption analyzer, temperature programmed reduction (TPR) and temperature programmed de-sorption (TPD). Moreover, the catalyst formulations were tested in a batch reactor and compared against a commercial catalyst. The outcome of this work showed that the formulation including MCM-41 catalyst support, resulting in NiMo-MCM-41, has performed better than the commercial catalyst on heavy hydrocarbons, in particular, VGO / DMO blends. NiMo-MCM-41 showed higher hydrodesulfurization (HDS) and hydrogenation activities. In addition, it had higher conversion and higher diesel yield than commercial catalyst.
[0021] Most of the hydrocracking catalysts of commercial interest are dual functional in nature, consisting of both a hydrogenation-dehydrogenation compone...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com