GFRalpha3 and its uses
a technology of gfralpha and its receptors, applied in the field of gfralpha, can solve the problems of different malignancies and pathological disorders, and achieve the effects of facilitating identification and characterization, high throughput, and facilitating trapping and detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cloning of Mouse GFRα3
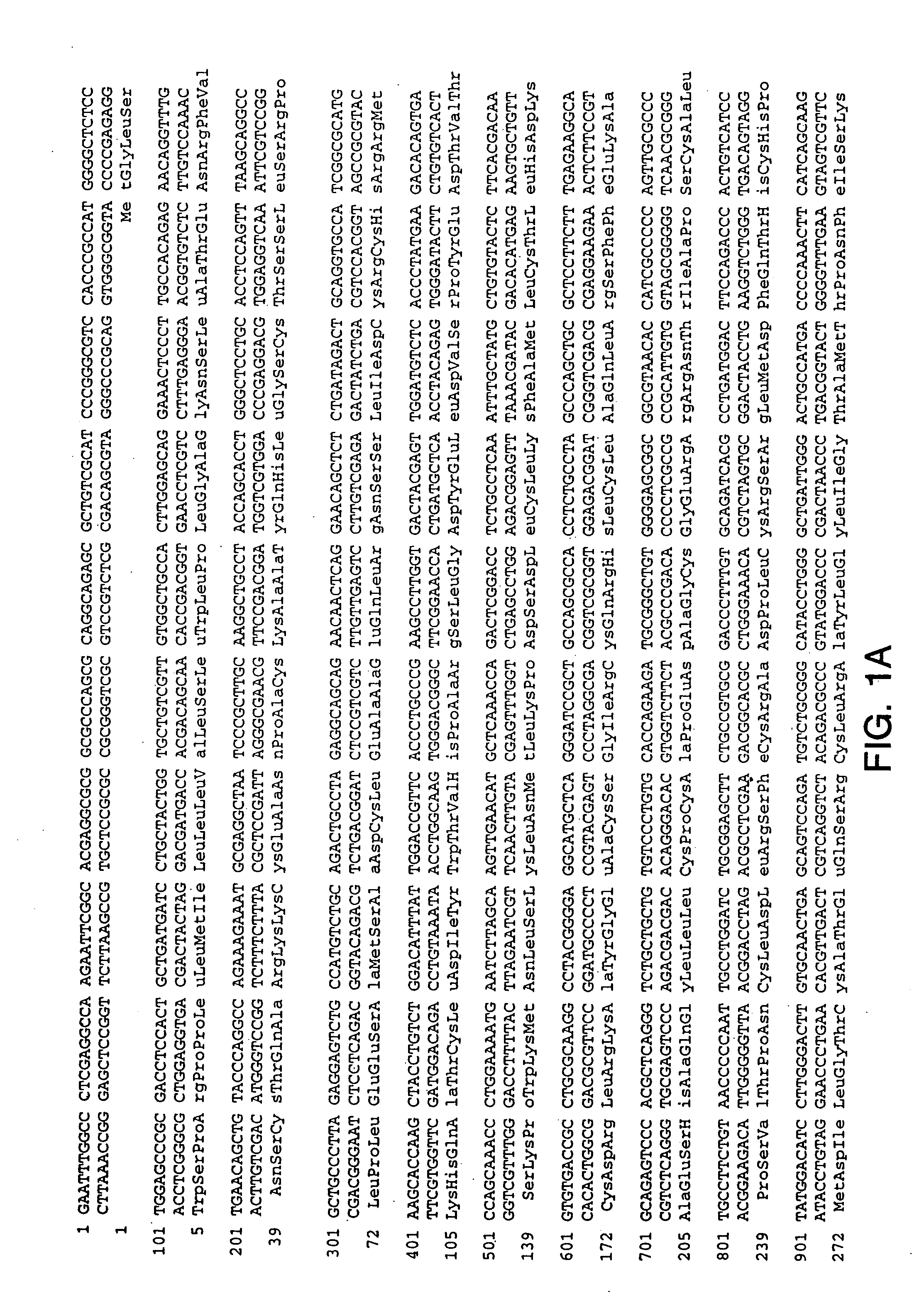
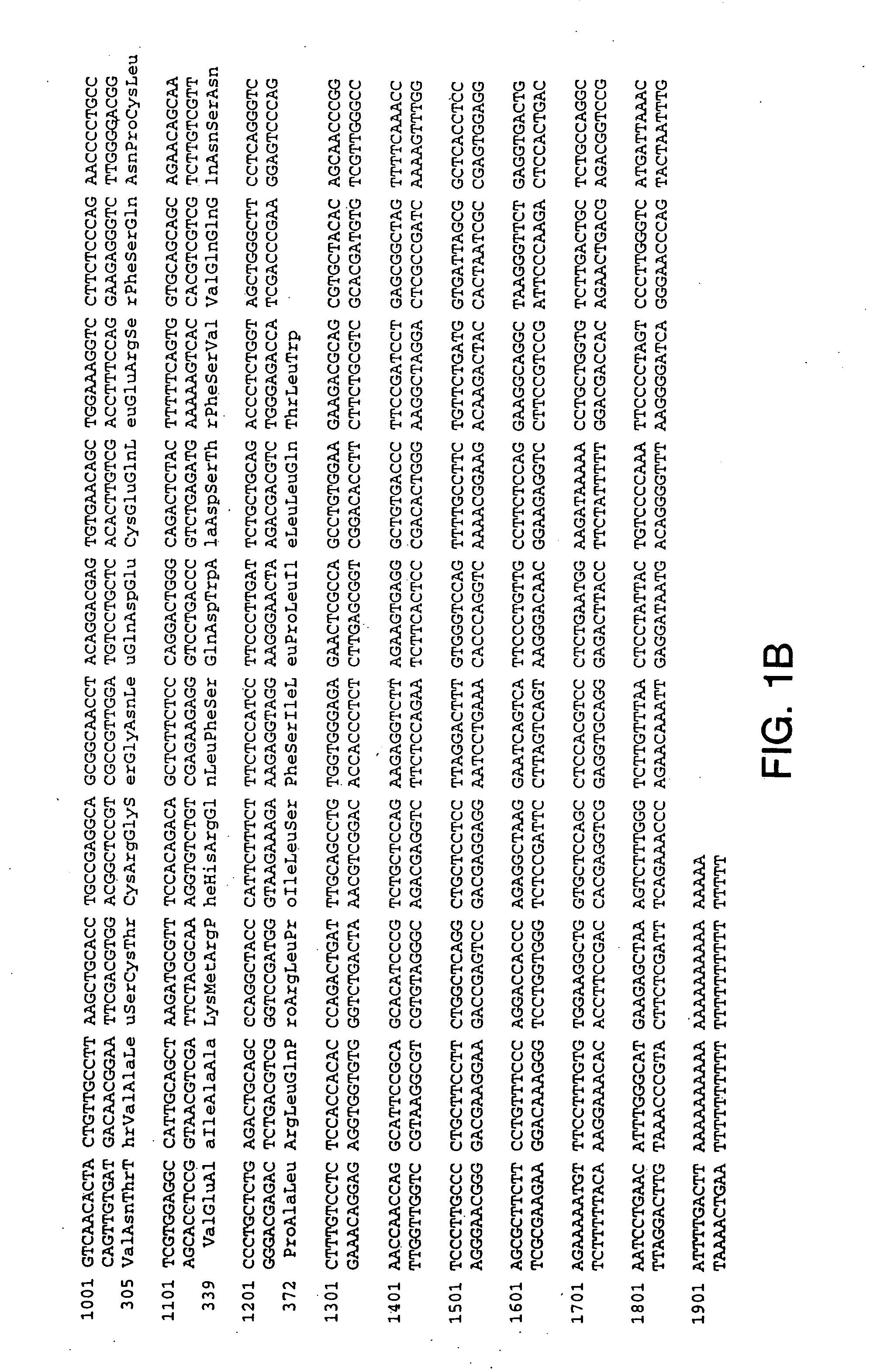
[0276] Using sequences from the neurturin receptor, now known as GFRα2 (“glial-cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor family receptor alpha”), a novel, potential member of the GFRα family was identified as a mouse EST in a public gene database (Accession Numbers W99197 (SEQ ID NO: 1), AA041935 (SEQ ID NO: 2) and AA050083 (SEQ ID NO: 3)). A DNA fragment corresponding to this potentially new receptor was obtained by Marathon PCR using mouse E15 cDNA (Clontech, Inc. USA) as template and PCR primers derived from the mouse EST. The PCR product was then used to screen a lambda gt10 mouse E15 library (Clontech, Inc. USA) to obtain a full length clone. The nucleotide sequence of the full length mouse cDNA is provided as SEQ ID NO: 4 (FIG. 1A-1B). The protein sequence (SEQ ID NO: 5; see FIG. 1A-1B) encoded by the isolated DNA was designated GFRα3, since it was determined to be a novel protein with sequence identity to GFRα1 (formerly the GDNF Receptor alpha) and GFRα2 ...
example 2
Isolation of cDNA Clones Encoding Human GFRα3
[0278] To identify rapidly whether a human homolog of this new receptor might exist, an expressed sequence tag (EST) DNA database (a proprietary EST database, LIFESEQ™, Incyte Pharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, Calif.) was searched and an EST (INC3574209) was identified having the sequence:
(SEQ ID NO: 10)GCGCTGNNTGNCNGNANGNGGGGGCGGGAGGTGCCGGTCGAGGGAGCCCCGCTCTCAGAGCTCCAGGGGAGGAGCGANGGGAGCGCGGAGCCCGGCCGCCTACAGCTCGCCATGGTGCGCCCCCTGAACCCGCGACCGCTGCCGCCCGTAGNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNGCCTCTCGCAGCCGGAGACCCCCTTCCCACAGAAAGCCGACTCATGAACAGCTGTCTCCAGGCCAGGAGGAAGTGCCAGGCTGATCCCACCTGC.
This sequence had 61% identity to the murine GFRα3.
[0279] To clone the corresponding full length cDNA, a panel of cDNA libraries were screened with primers:
(SEQ ID NO: 11)newa3.F 5′ GCC TCT CGC AGC CGG AGA CC 3′(SEQ ID NO: 12)newa3.R 5′ CAG GTG GGA TCA GCC TGG CAC 3′
DNA from the libraries was screened by PCR amplification, as per Ausubel et al., Current Proto...
example 3
Use of GFRα3 as a Hybridization Probe
[0286] The following method describes use of a nucleotide sequence encoding GFRα3 as a hybridization probe.
[0287] DNA comprising the coding sequence of GFRα3 (shown in SEQ ID NO: 4, SEQ ID NO: 14 or SEQ ID NO: 16), or a fragment thereof, is employed as a probe to screen for homologous DNAs (such as those encoding naturally-occurring GFRα3 or variants of GFRα3) in human tissue cDNA libraries, human tissue genomic libraries, RNA isolated from tissues, tissue preparations in situ, or chromosome preparations (such as for chromosome mapping).
[0288] Hybridization and washing of filters containing either library DNAs is performed under the following high stringency conditions. Hybridization of radiolabeled GFRα3-derived probe to the filters is performed in a solution of 50% formamide, 5×SSC, 0.1% SDS, 0.1% sodium pyrophosphate, 50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 6.8, 2× Denhardt's solution, and 10% dextran sulfate at 42° C. for 20 hours. Washing of the filt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com