Geothermal system utilizing supplemental ground heat from drainage fields
a geothermal system and drainage field technology, applied in the field of geothermal system utilizing supplemental ground heat from drainage fields, can solve the problems of rapid reduction of heat recovery efficiency of these systems, rapid drop in heat recovery of heat recovered by these systems, and reducing the heat transfer coefficient between the wastewater, so as to increase the heat conductivity of the soil, increase the efficiency of geothermal system, and increase the rate of heat recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
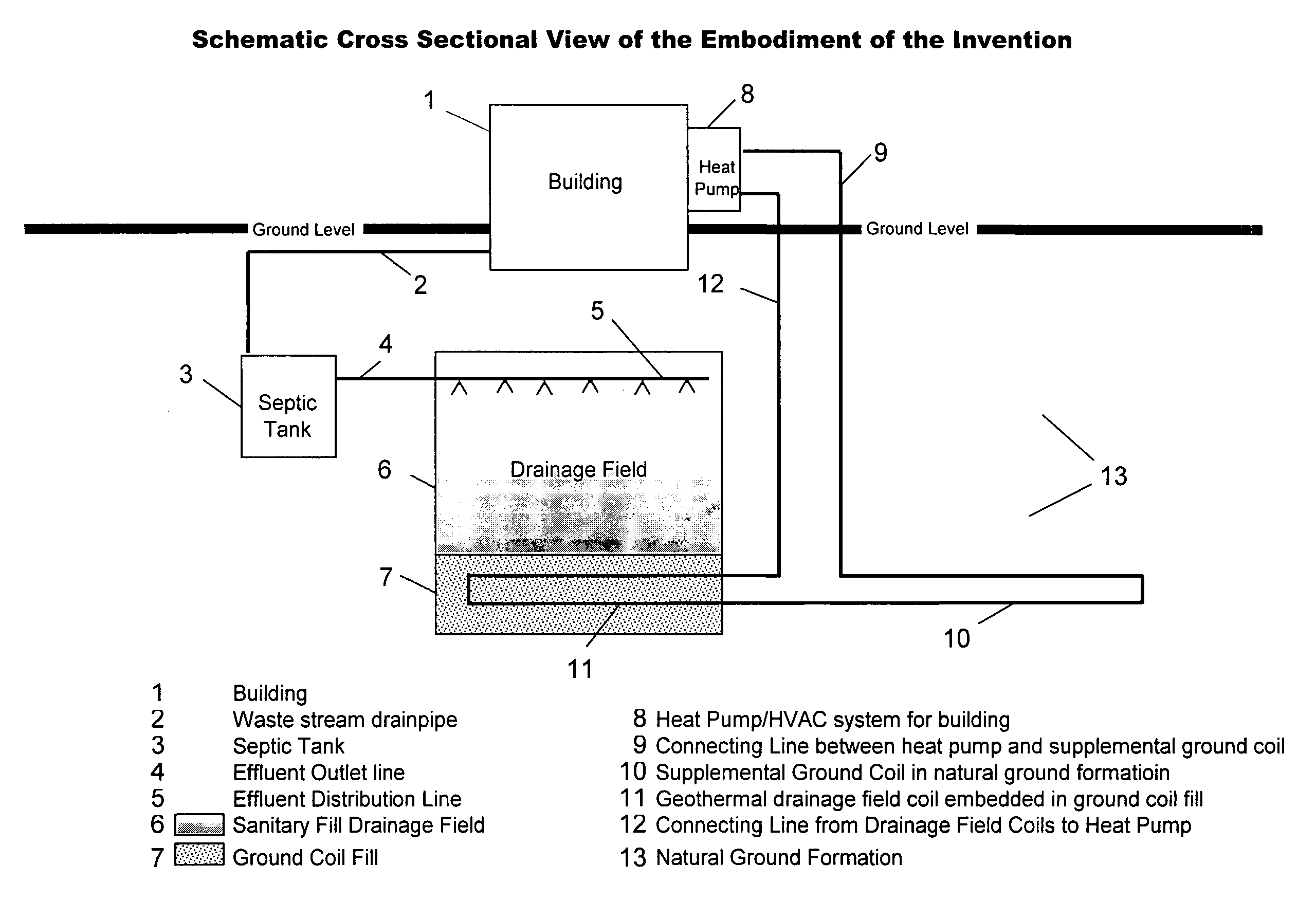
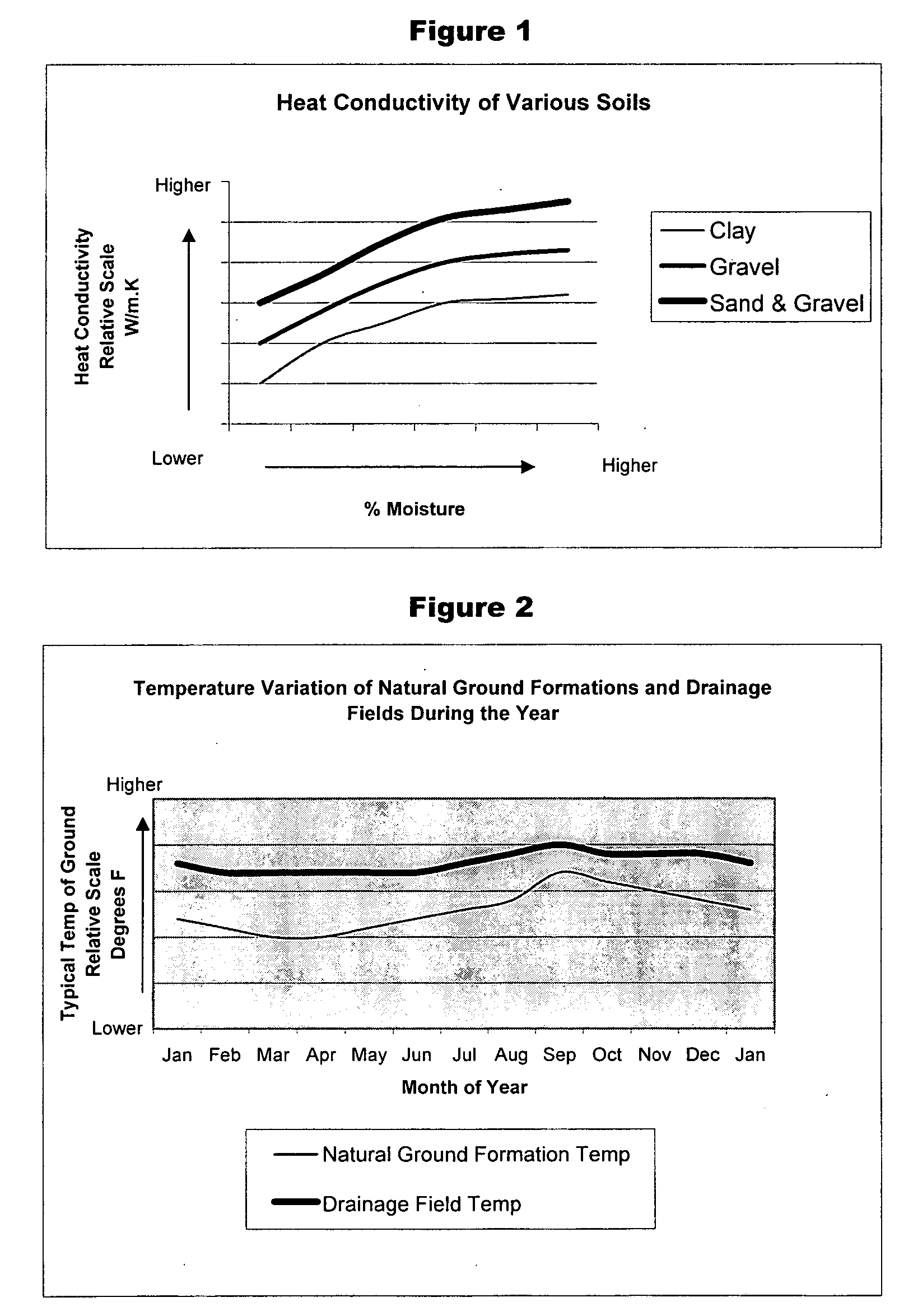
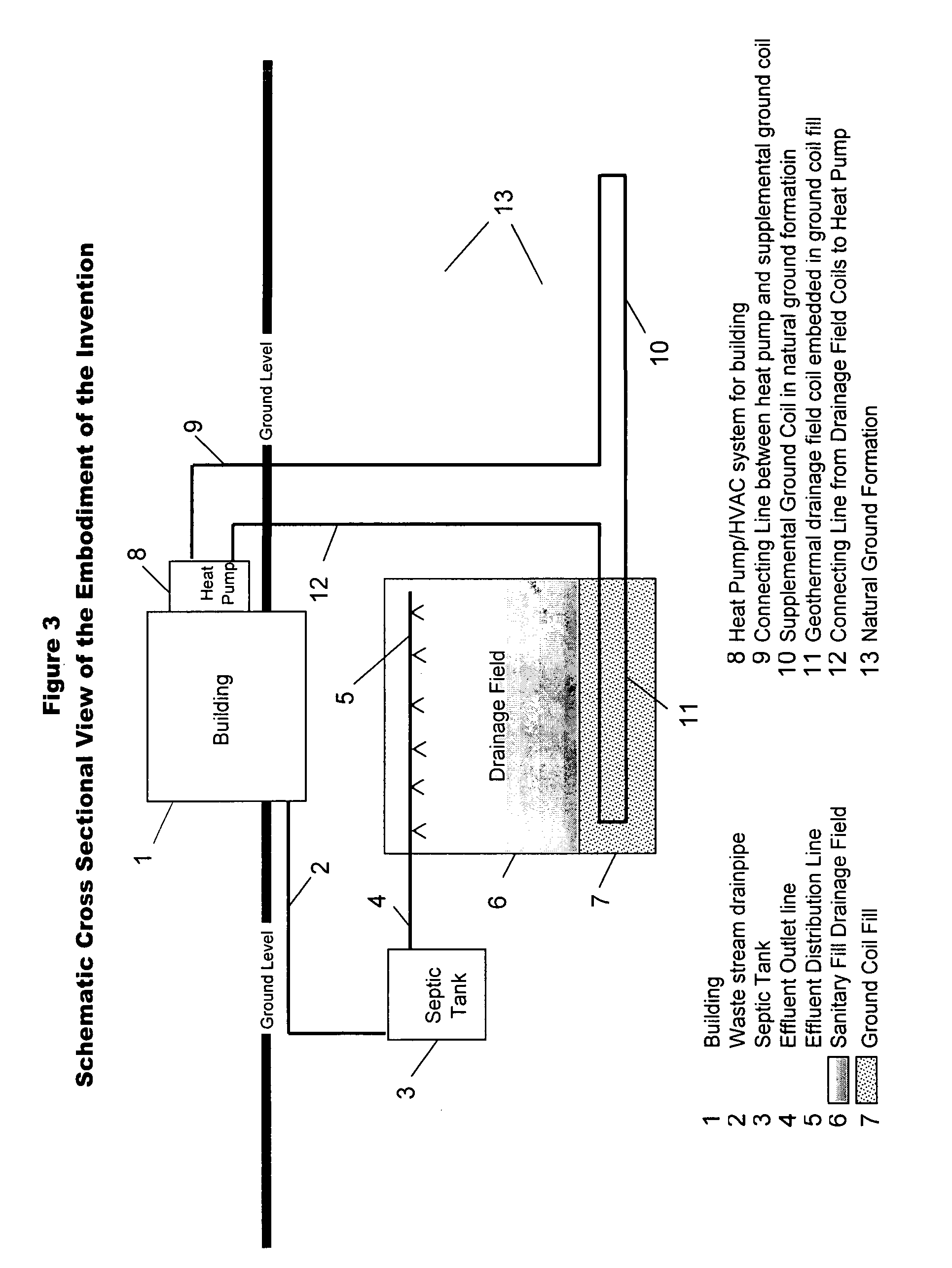
[0016] Referring to FIG. 3, the waste stream from building 1 flows through the waste stream drain pipe 2 into the septic tank 3 where anaerobic bacterial digestion takes place. The effluent form the septic tank, 3 flows through the effluent outlet line 4 into the effluent distribution lines 5 and is distributed into the sanitary fill drainage field 6. The effluent percolates through the effluent drainage field 6 where it is subjected to further bacterial digestion and is clarified by the filtering action of the sanitary fill in the drainage field 6. As the effluent percolates through the drainage field 6, the temperature of the field rises due to the sensible heat of the effluent and heat from the biological digestion in the septic tank 3 and in the drainage field 6. This in turn causes the temperature of the fill 7 below the drainage field to also rise.
[0017] A circulating water feed heat pump 8 is used to provide heating and air conditioning for building 1. During the heating sea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com