Cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Characterization of Cartilage Derived Chondrogenic Activity
[0028] Articular (metatarsophalangeal joints), scapular and nasal cartilage (300 grams wet weight per tissue) were prepared from newborn calves. Epiphyseal cartilage was dissected from fetal bovine femurs (7-8 months). The tissues were finely minced and homogenized with a Polytron (top speed, 2×30 seconds) in 20 volumes of 1.2 M GdnHCl, 0.5% CHAPS, 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.2, containing protease inhibitors and extracted overnight at 4° C. as described by Luyten et al., in J. Biol. Chem. 264:13377 (1989), which is hereby incorporated by reference. The disclosure of this article is hereby incorporated by reference. Sorgente et al., (Biochem Biophys. Acta. 1972 282:441) disclosed these procedures extract >90% of the lower molecular weight matrix while leaving most of the high molecular weight proteoglycans behind. The extracts were concentrated and exchanged with 6 M urea by diafiltration using an Ultrasette™ (Filtron Technology In...
example 2
PCR Amplification of cDNAs Encoding Cartilage-Derived Morphogenetic Proteins
[0034] Total RNA from bovine articular chondrocytes (metatarsophalangeal joints) was extracted using a modified acid guanidine-phenol-chloroform method described by Chomczynski et al., in Anal. Biochem. 162:156 (1987) and by Luyten et al., in Exp. Cell. Res. 210:224 (1994). Poly(A)+ RNA was isolated using magnetic beads (PolyATract™, Promega, Madison, Wis.). Four degenerate oligonucleotide primers corresponding to highly conversed motifs in the C-terminal region of the BMPs were used; S1: 5′-GGITGG(C / A)AIGA(C / T)TGGAT(A / C / T)(A / G)TIGC(A / C / G / T)CC-3′ (SEQ ID NO: 1) corresponding to amino acids [GW(Q / N)DWI(I / V)AP] (SEQ ID NO: 2); S2: 5′-GGITGG(A / T)(G / C)(I)GA(G / A)TGGAT(T / C / A)ATI(A / T)G(A / C / G / T)CC-3′ (SEQ ID NO: 3) corresponding to amino acids [GWSEWIISP] (SEQ ID NO: 4); AS1: 5′-A(A / G)A / G)GT(C / T)TG(A / C / G / T)AC(A / G)AT(A / G)GC(A / G)TG(A / G)TT-3′ (SEQ ID NO: 5) corresponding to amino acids [NHAIVQTL] (SEQ ID NO: 6); AS2: ...
example 3
Library Screening
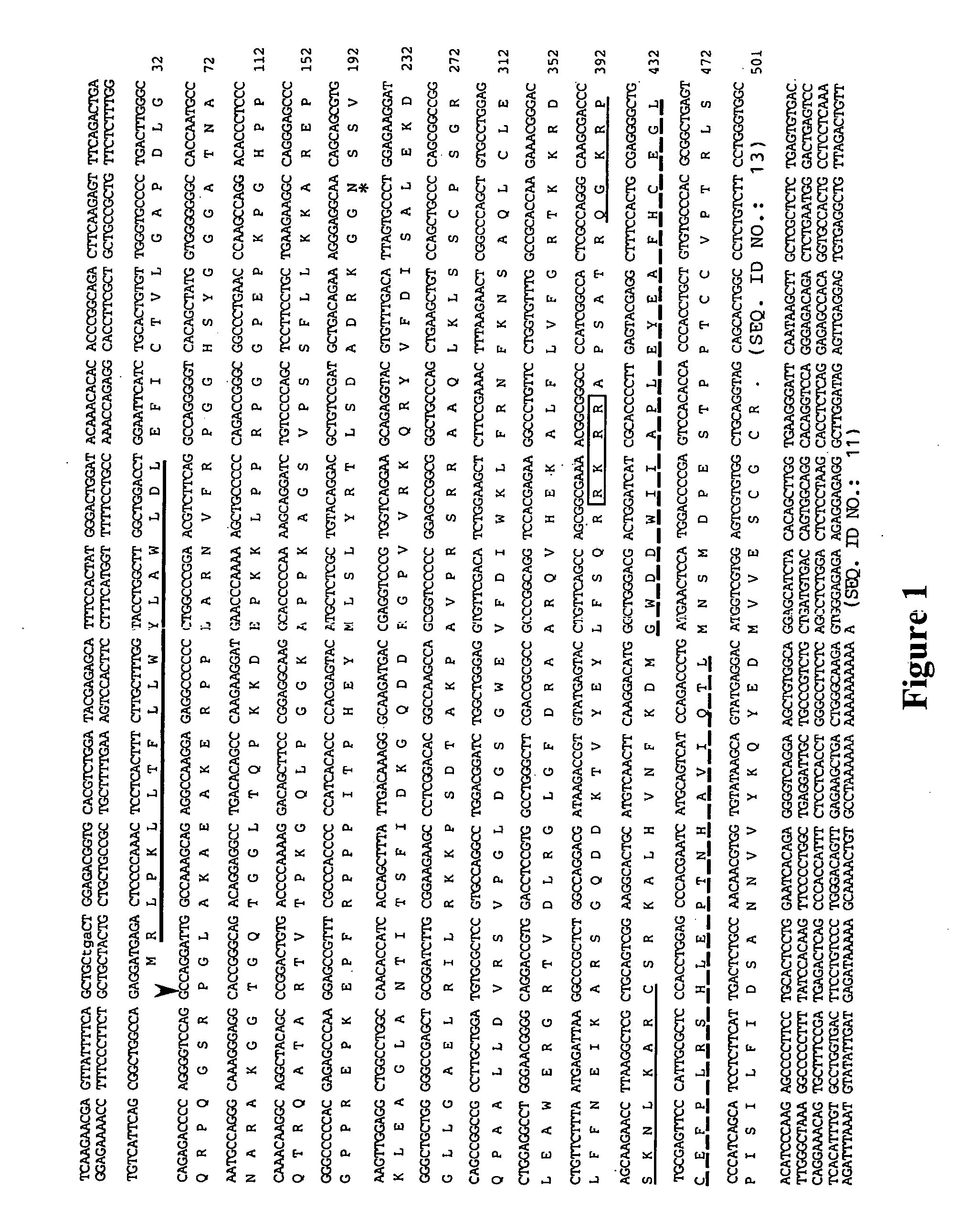
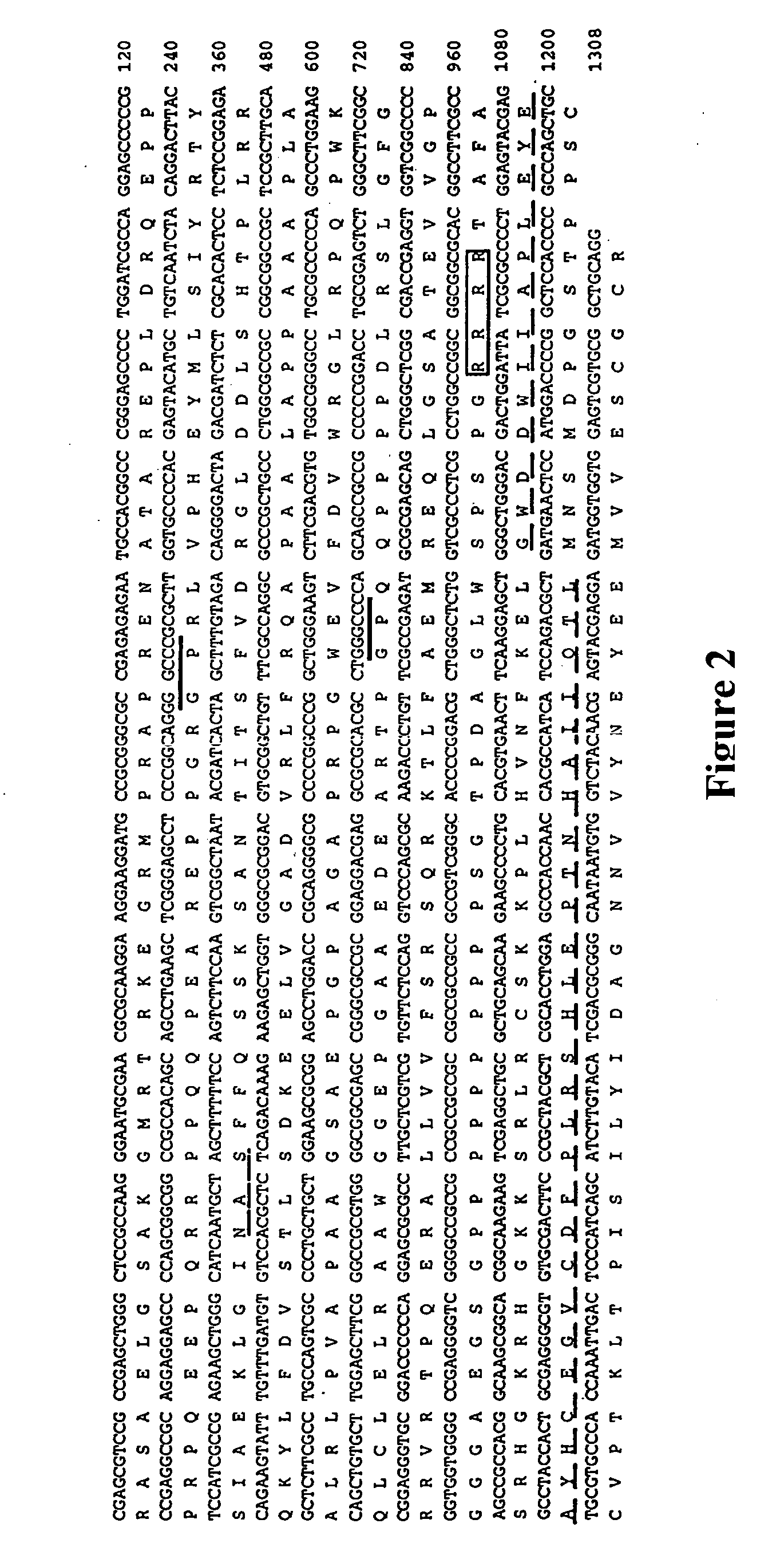
[0038] A 120 bp PCR fragment encoding part of the C-terminal domain of novel B like genes (dashed line, FIG. 1) was used to screen two cDNA libraries. One library, from adolescent human articular cartilage poly(A)+ RNA (kindly provided by Dr. Bjorn Olsen, Harvard, Boston, Mass.), was primed with oligo dT and constructed in the λgtl 1 vector. The other was a bovine oligo dT and random primed articular cartilage cDNA library constructed in the UNIZAP®XR vector (Stratagene, La Jolla, Calif.). Approximately 1×106 plaques from each library were screened by standard procedures. Hybridizations were performed for 20 hours at 42° C. in 6×SSC, 1× Denhardt's solution, 0.01% tRNA, 0.05% sodium pyrophosphate and the membranes (DuPont 137 mm nylon membranes, New England Nuclear, MA) were washed to final stringency of 6×.SSC, 0.1% SDS at 55° C. for 20 minutes.
[0039] Thus, cloned inserts having novel BMP-like sequences were isolated, radiolabeled and used to screen both human and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com