Nano-composite magnet, quenched alloy for nano-composite magnet, and method for producing them and method for distinguishing them
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
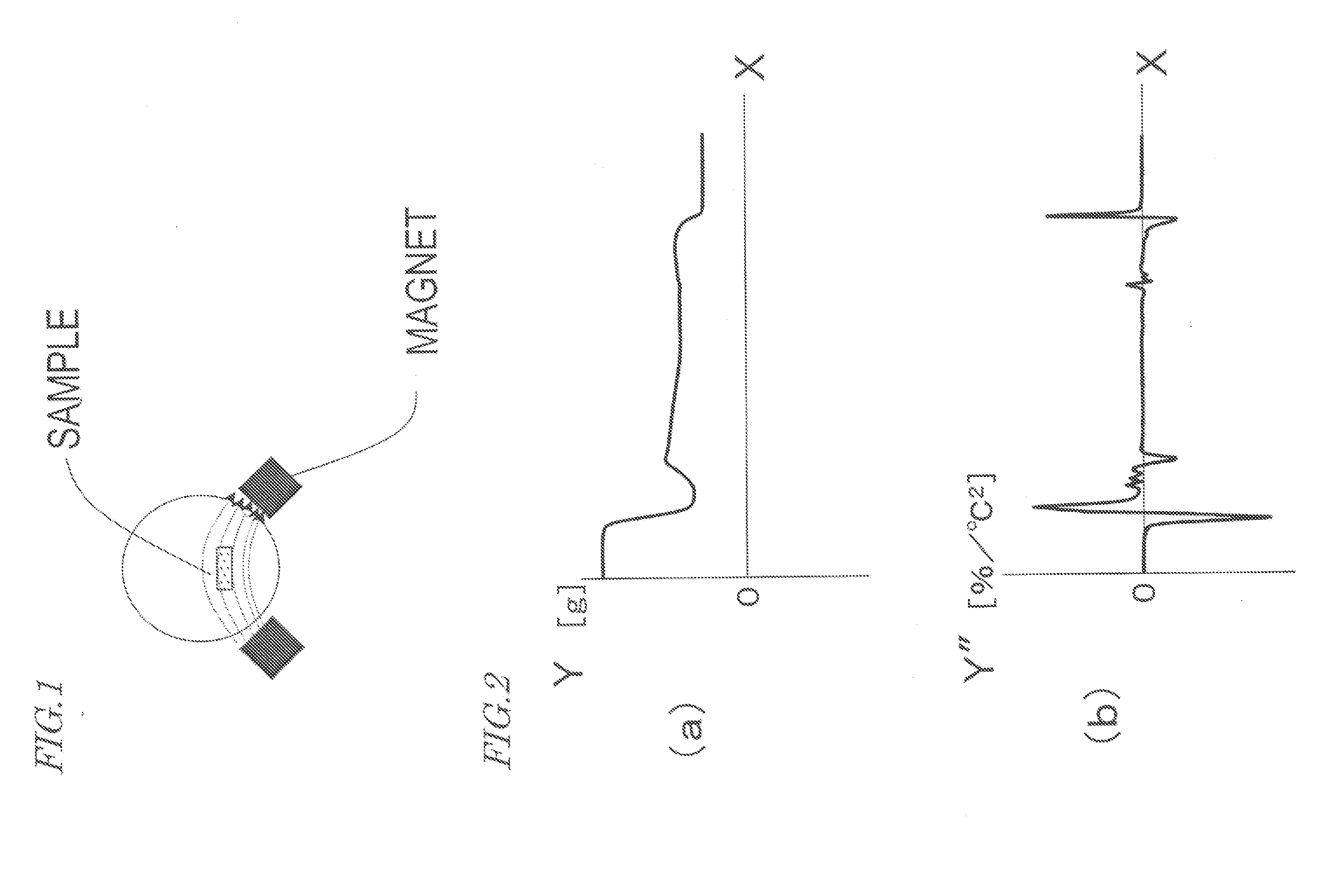
[0108] In a first specific example of the present invention, a molten alloy having a composition Nd7Pr1FebalB12Ti4 was quenched using the melt-quenching machine shown in FIG. 6, thereby making a rapidly solidified alloy in the shape of a ribbon with a thickness of 50 μm to 130 μm. The melt was teemed at a pressure of 30 kPa and at a temperature (melt surface temperature) of 1,400° C. The temperature of the molten alloy was measured on an infrared thermal imagery.
[0109] The rapid cooling conditions were controlled by adjusting the pressure of the argon (Ar) atmosphere within the quenching chamber and the surface velocity Vs of the rotating chill roller. More specifically, the surface velocity Vs of the chill roller was varied within the range of 5 m / s to 20 m / s in the atmosphere having pressures of 1.3 kPa, 33 kPa and 62 kPa.
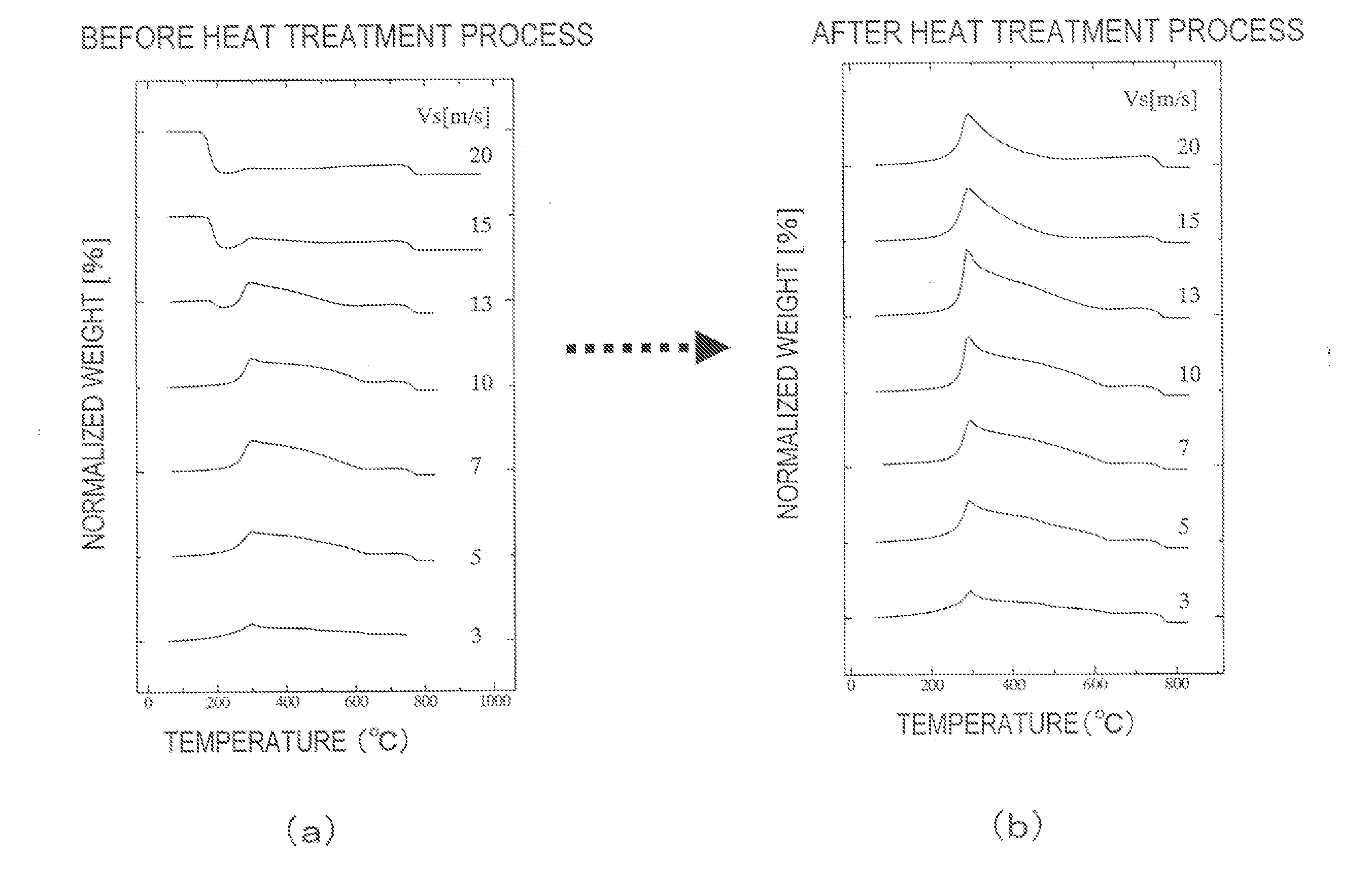
[0110]FIG. 7 is a graph showing rapid cooling procedures in situations where the roller surface velocities Vs are changed from 5 m / s to 7 m / s, 10 m / s, 13 m / s a...
example 2
[0126] In a second specific example of the present invention, a molten alloy having a composition Nd6.2FebalCo6B11C1Ti5 was quenched, thereby making a rapidly solidified alloy in the shape of a ribbon with a thickness of 50 μm to 130 μm. The rapid cooling conditions and resultant magnet performance are shown in the following Table 1. The conditions not shown in Table 1 are the same as those set for the first specific example described above:
TABLE 1RollersurfaceChamberQuenching rateQuenching ratevelocity Vspressure(1400-900° C.)(900-700° C.)(BH)max[m / s][kPa][105 K / s][105 K / s][kJ / m2]10306.002.42120153015.83.12125173019.13.52120
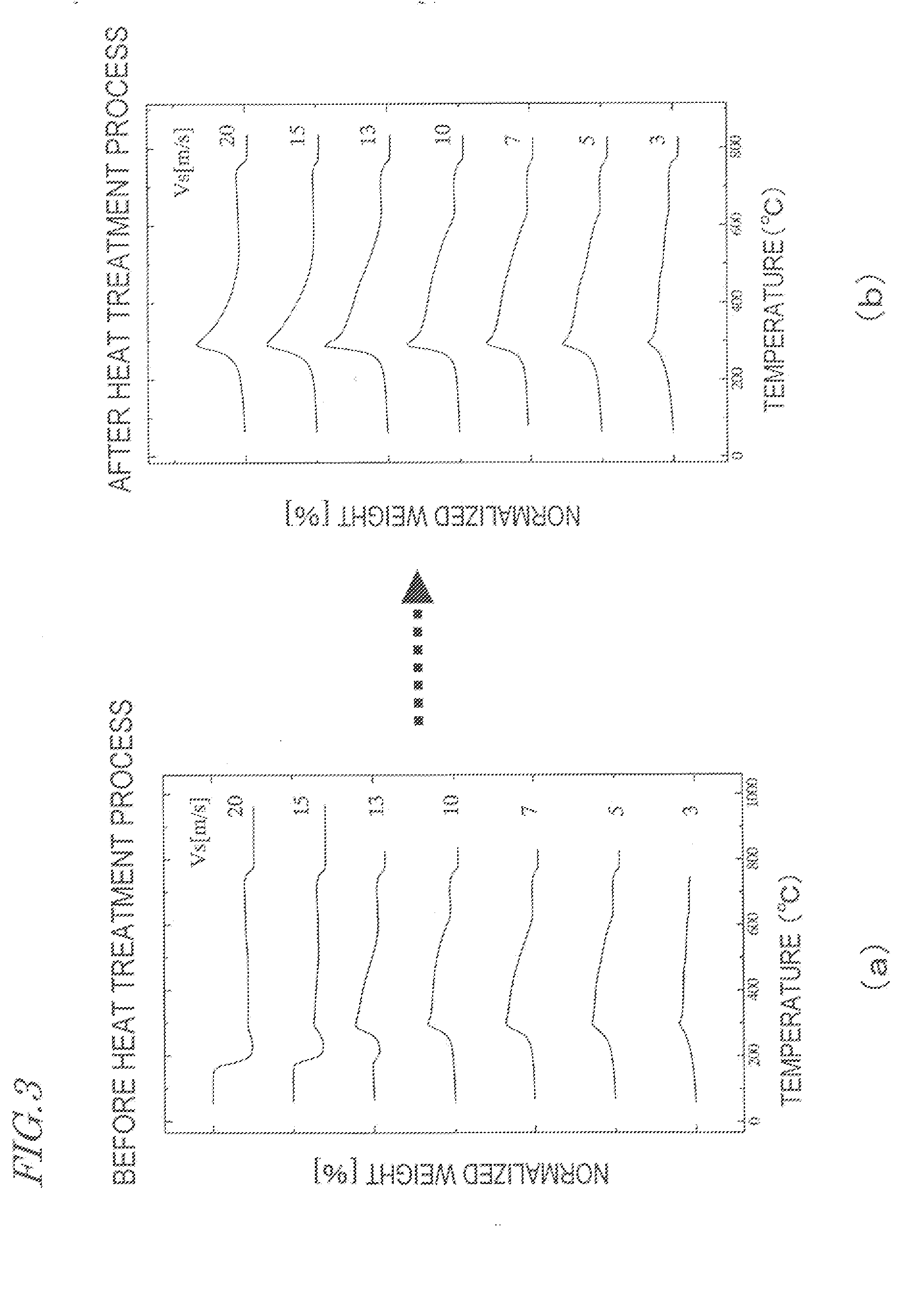
[0127]FIG. 13 is a graph showing the second derivatives of the thermogravimetric curves of this specific example.
[0128] The ω phase produced in the rapidly solidified alloy of this specific example had a Curie temperature of 650° C. to 700° C. This Curie temperature is higher than that of the ω phase of the first specific example due to the difference in allo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com