Methods and sequences to suppress primate huntington gene expression in vivo
a technology of nucleic acid molecules and primate huntington, which is applied in the direction of biocide, animal repellents, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of slow destruction of the affected individual's ability to walk, think, talk and reason, and reduce the cell's ability to create the protein for which it encodes, so as to suppress the expression of the hd gene, and reduce the level of huntingtin within the cell
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
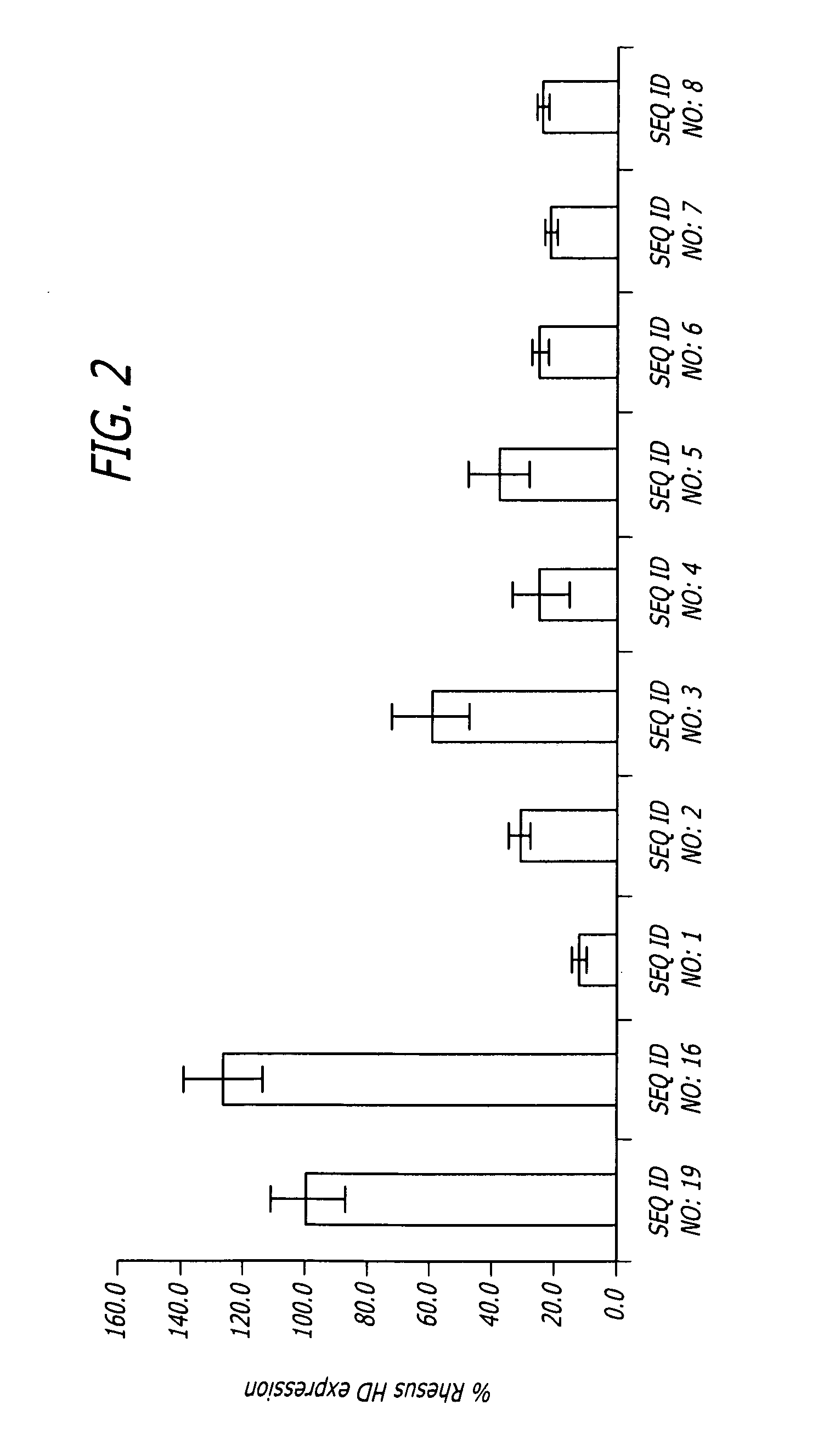
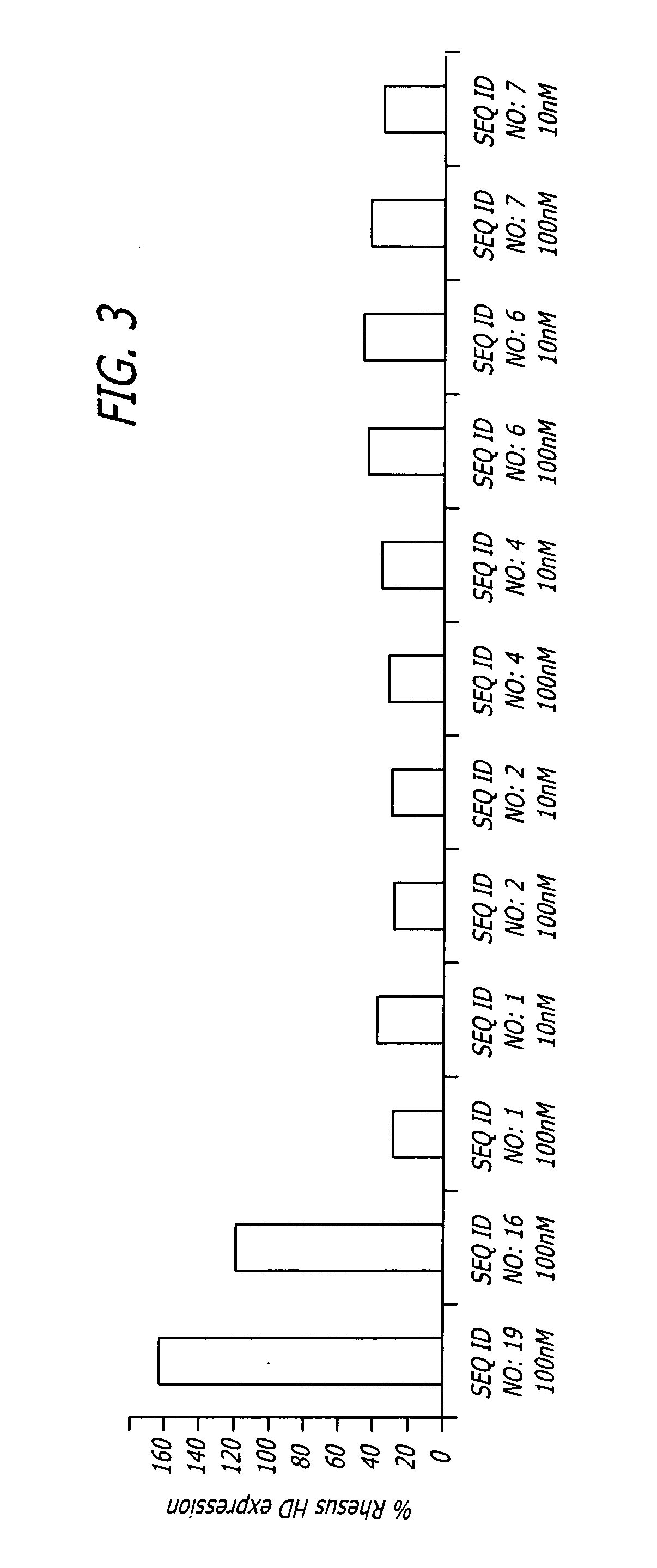
Injection of shNA of SEQ. ID. NO: 17 Locally and Significantly Reduces the Amount of HD mRNA
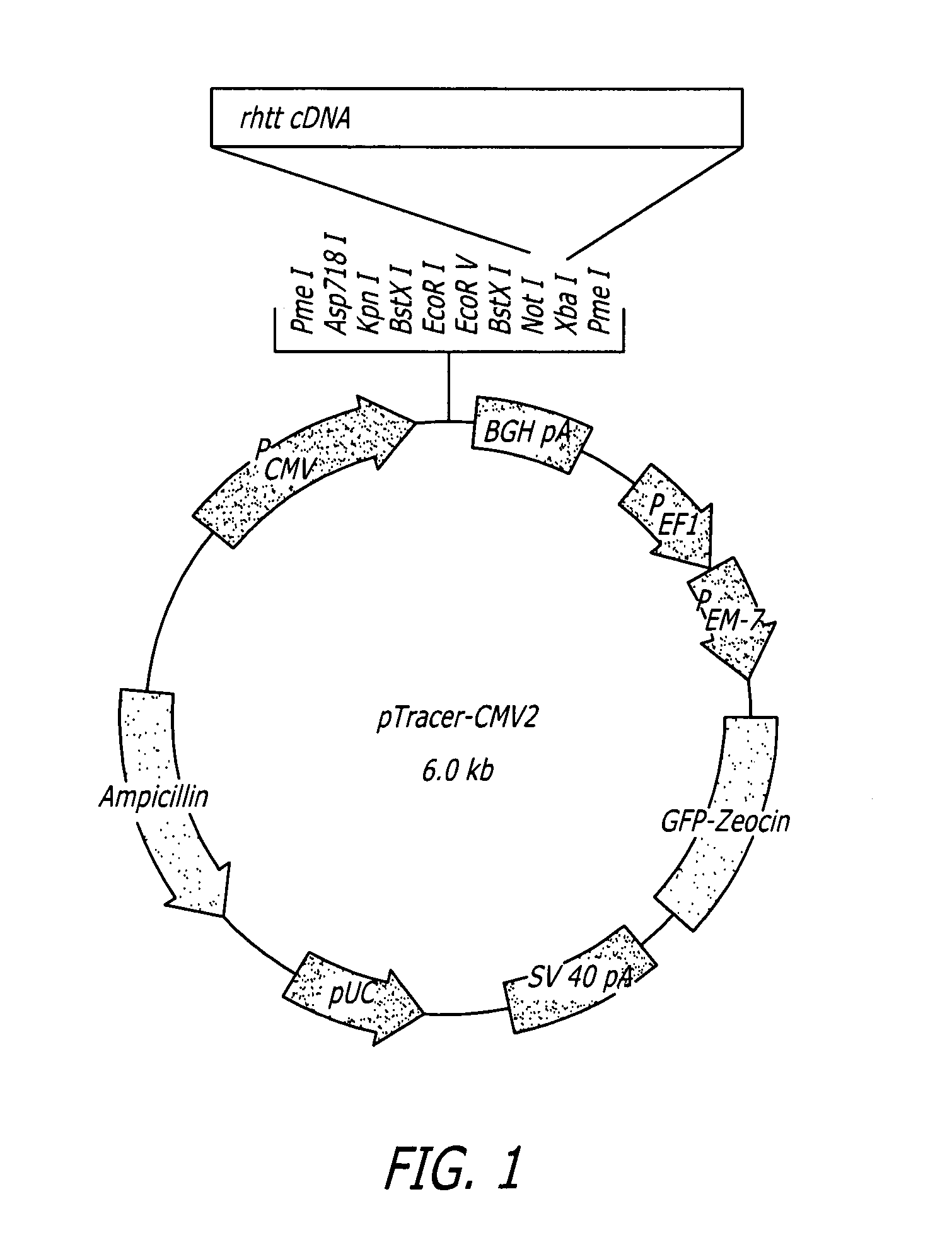
[0098]To verify that the shNA sequences disclosed above are effective in vivo, 3*1011 viral particles comprising AAV vectors including shNAs of SEQ ID. NO: 26 or SEQ. ID. NO: 17 or a control shNA (SEQ. ID. NO: 18) under regulation of the human U6 promoter upstream of GFP sequence under control of CMV promoter were injected into Rhesus moneys as follows:
TABLE 3Experimental designAge,Animal #yrsHemisphereRNA constructTarget16LeftSEQ. ID. NO: 17Putamen, CaudateRightSEQ. ID. NO: 17Putamen, Caudate215LeftSEQ. ID. NO: 18PutamenRightSEQ. ID. NO: 17Putamen319LeftSEQ. ID. NO: 26PutamenRightSEQ. ID. NO: 17Putamen
[0099]Huntington (HD) mRNA was quantified by qPCR using total RNA isolated from tissue punches and laser microdissected sections (LMD). Huntingtin protein was quantified by western blot analysis using total protein isolated from tissue punches.
[0100]The injection of a vector comprising shNA of ...
example 2
Injection of shNA of SEQ. ID. NO: 17 Does Not Cause Great Anatomical Aberrations and Does Not Impair the Endoplasmic Reticulum of the Transduced Cells
[0104]The animals were injected according to the protocol of the previous example. Histopathological analyses were conducted by analyzing GFP fluorescence, hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining, huntingtin immunofluorescent staining, calnexin immunofluorescent staining and protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) immuofluorescent staining. The results of those studies show that HD suppression does not cause any detectable neuro-anatomical abnormalities in the injected areas. Some evidence of perivascular cuffing in virally transduced regions was observed, but this cuffing did not correlate with HD suppression. Further, staining for calnexin and PDI did not reveal any obvious alterations in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of the transduced cells.
example 3
Injection of shNA of SEQ. ID. NO: 17 Does Not Alter Spontaneous Activity and Tends to Improve Fine Locomotor Activity
[0105]The animals were injected according to the protocol of Working Example 1. Spontaneous activity and fine motor activity were also measured by EthnoVision and mMAP equipment, respectively. EthnoVision is a video tracking system that can be used to measure distance traveled, body movement speed and vertical activity. Associated computer software is able to quantify each of these parameters. mMAP (monkey Movement Analysis Panel) was used to objectively measure the time of fine motor movements of the small hand muscles in retrieving food items presented to the test animal.
[0106]HD suppression within the caudate and putamen did not cause alterations in spontaneous activity of the animals. Fine locomotor activity was not impaired in any of the animals. Further, all animals tended to improve in fine motor skills post-virus injection.
[0107]It is to be understood that the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cytotoxicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com