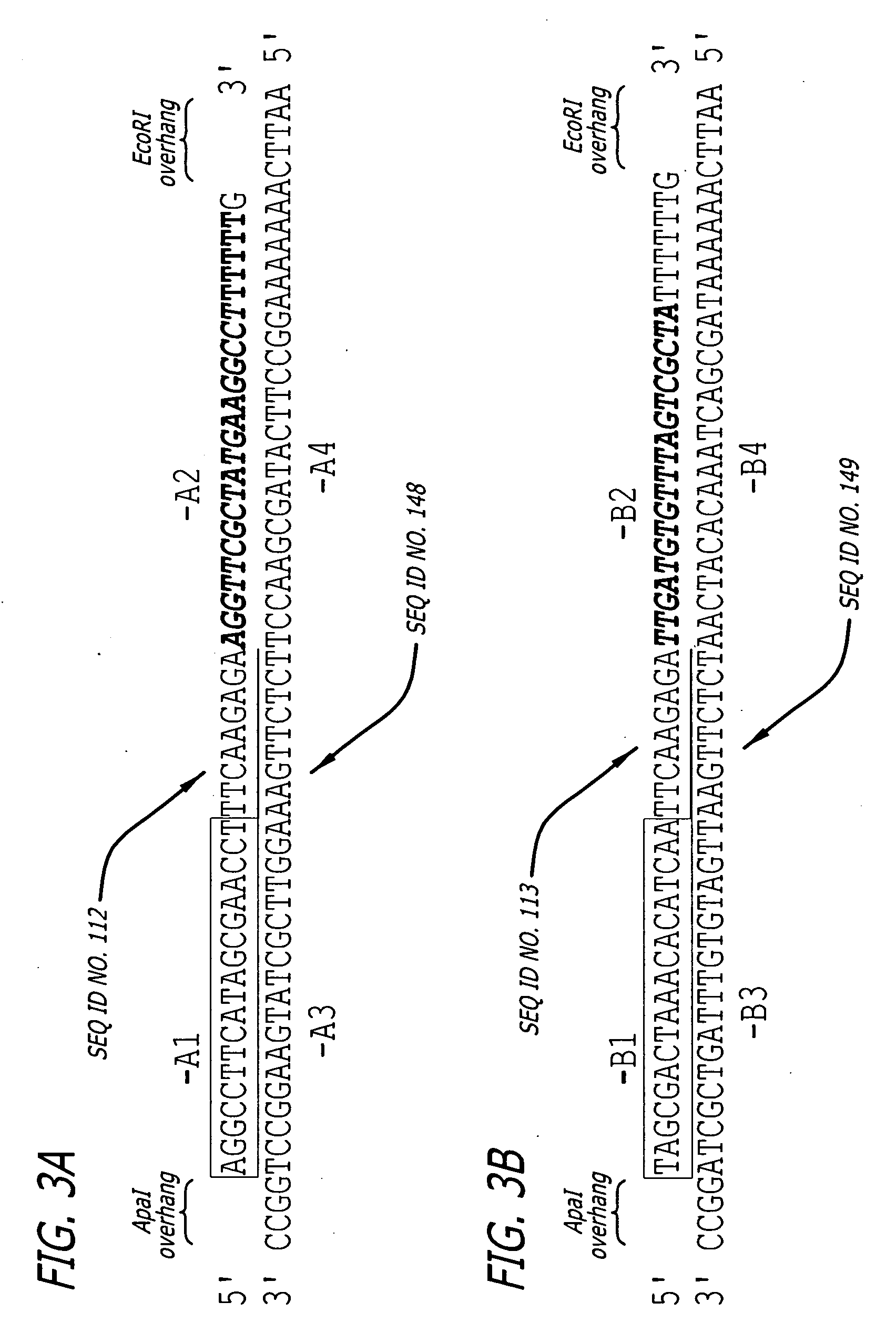
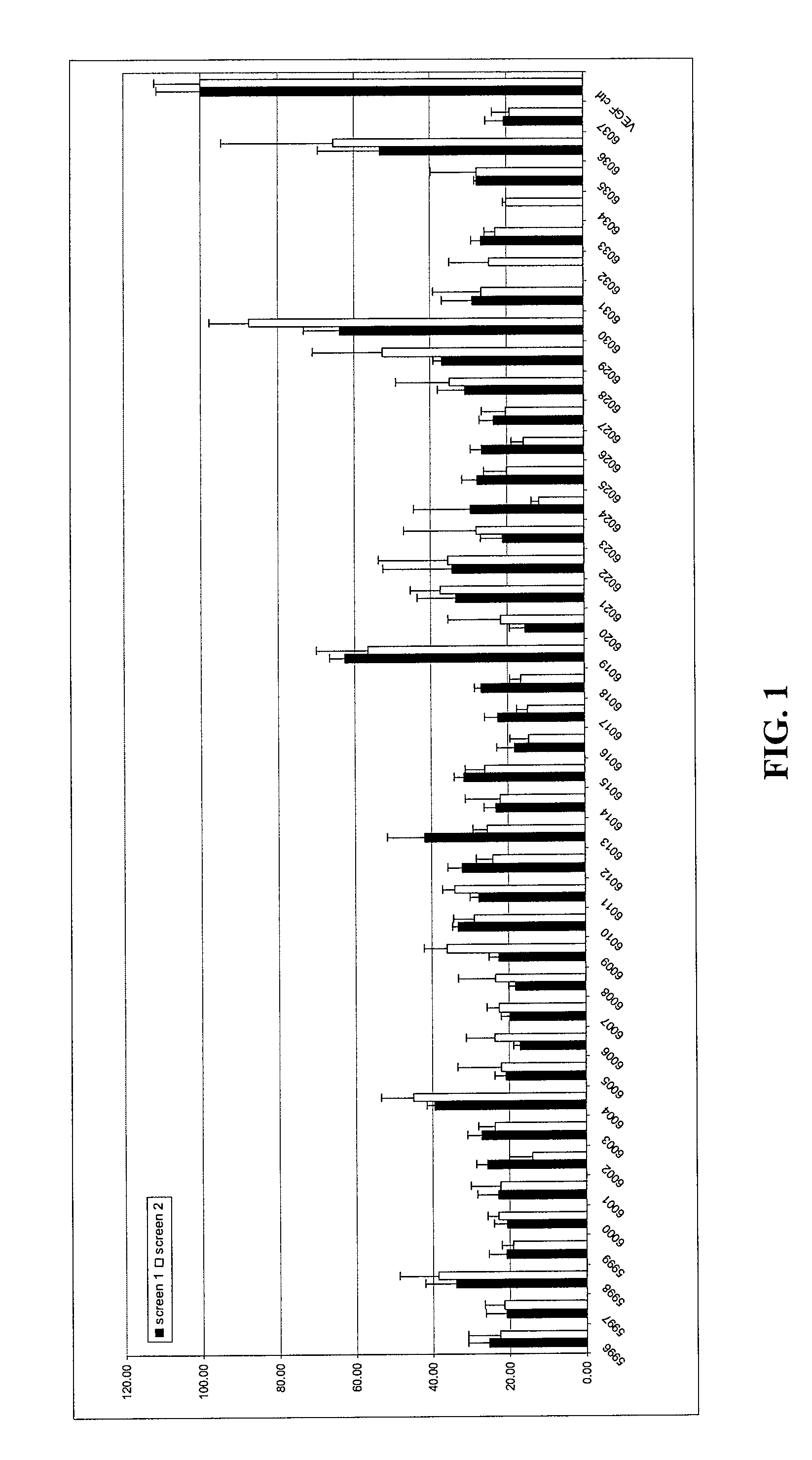
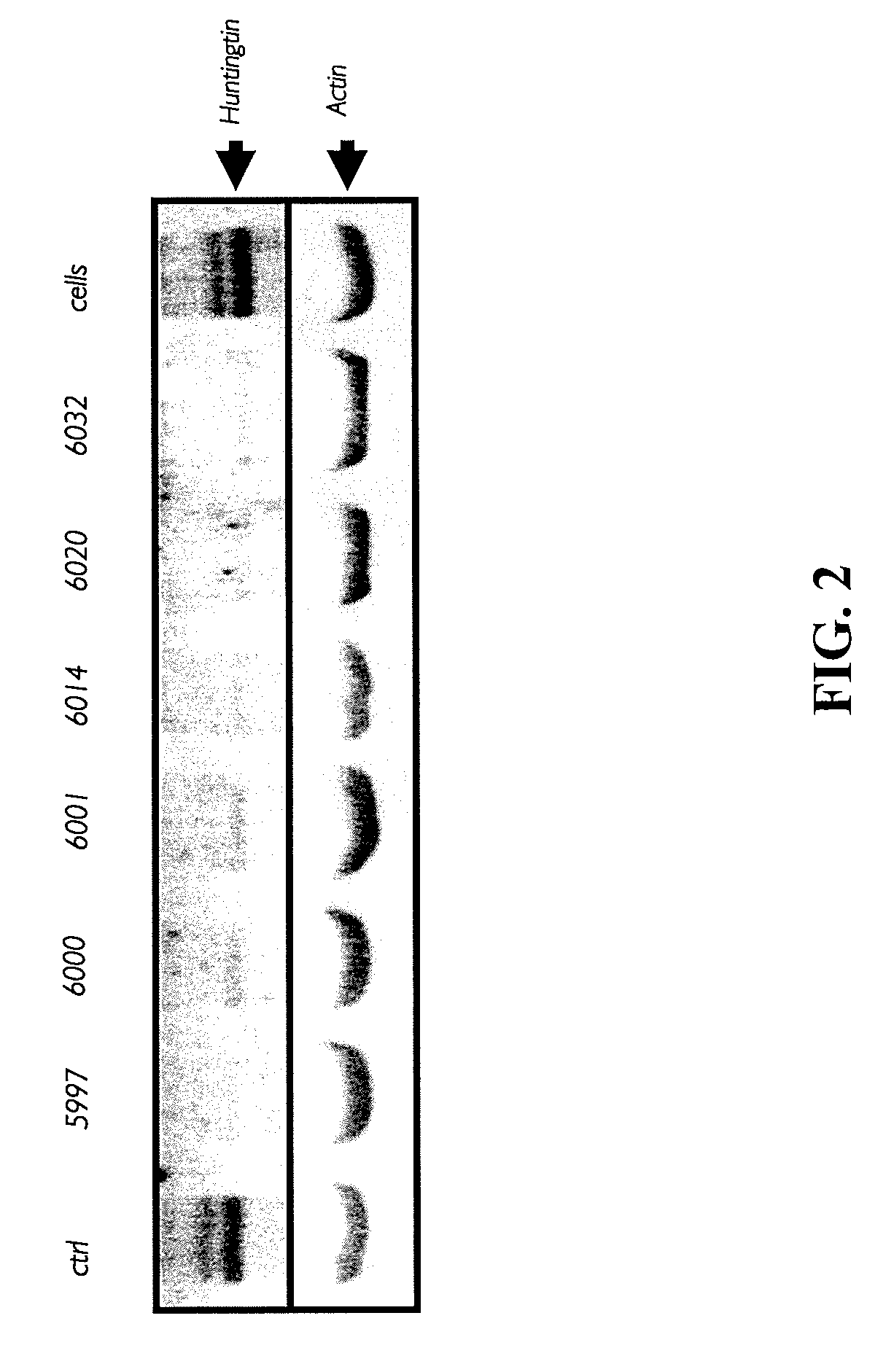
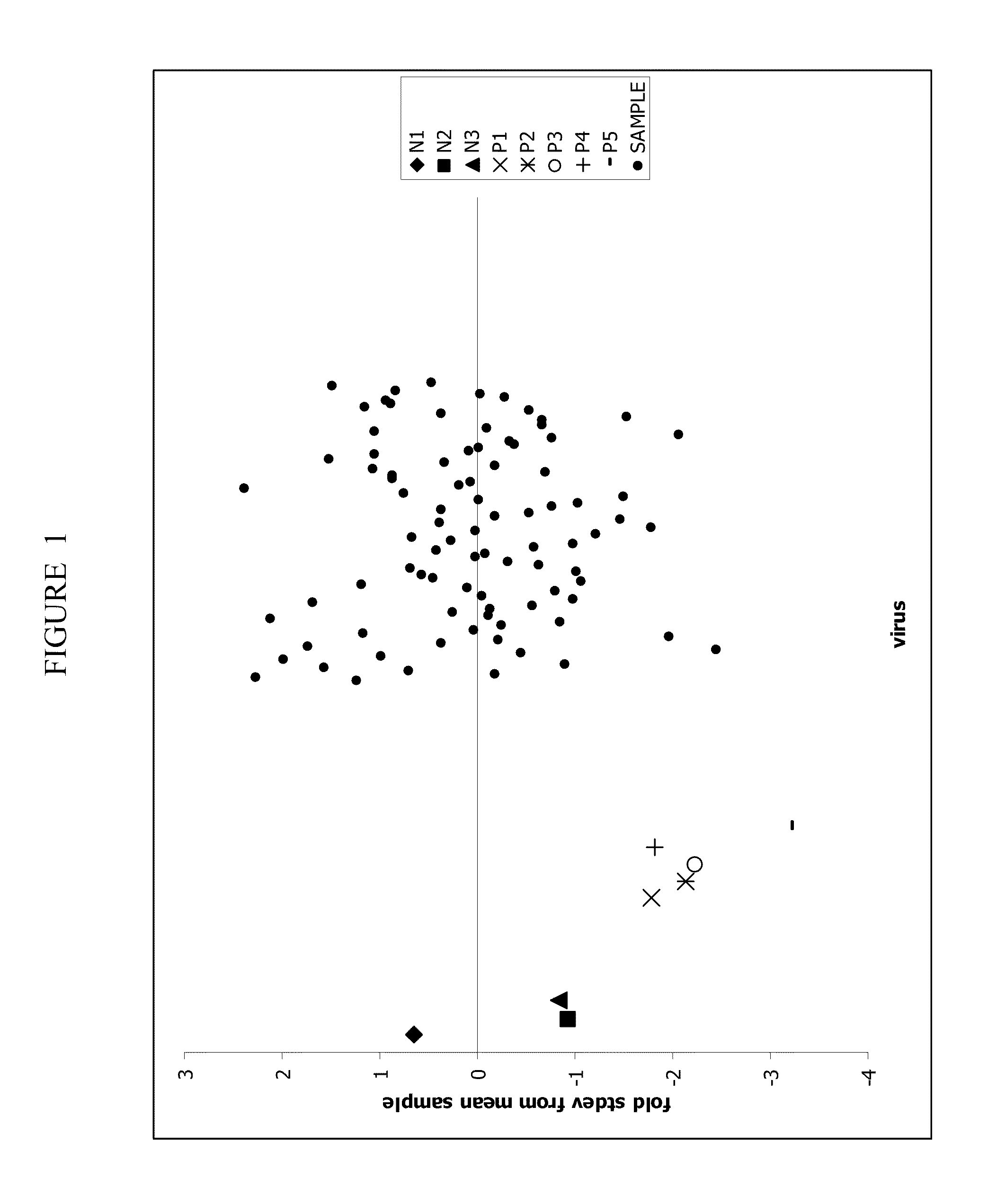
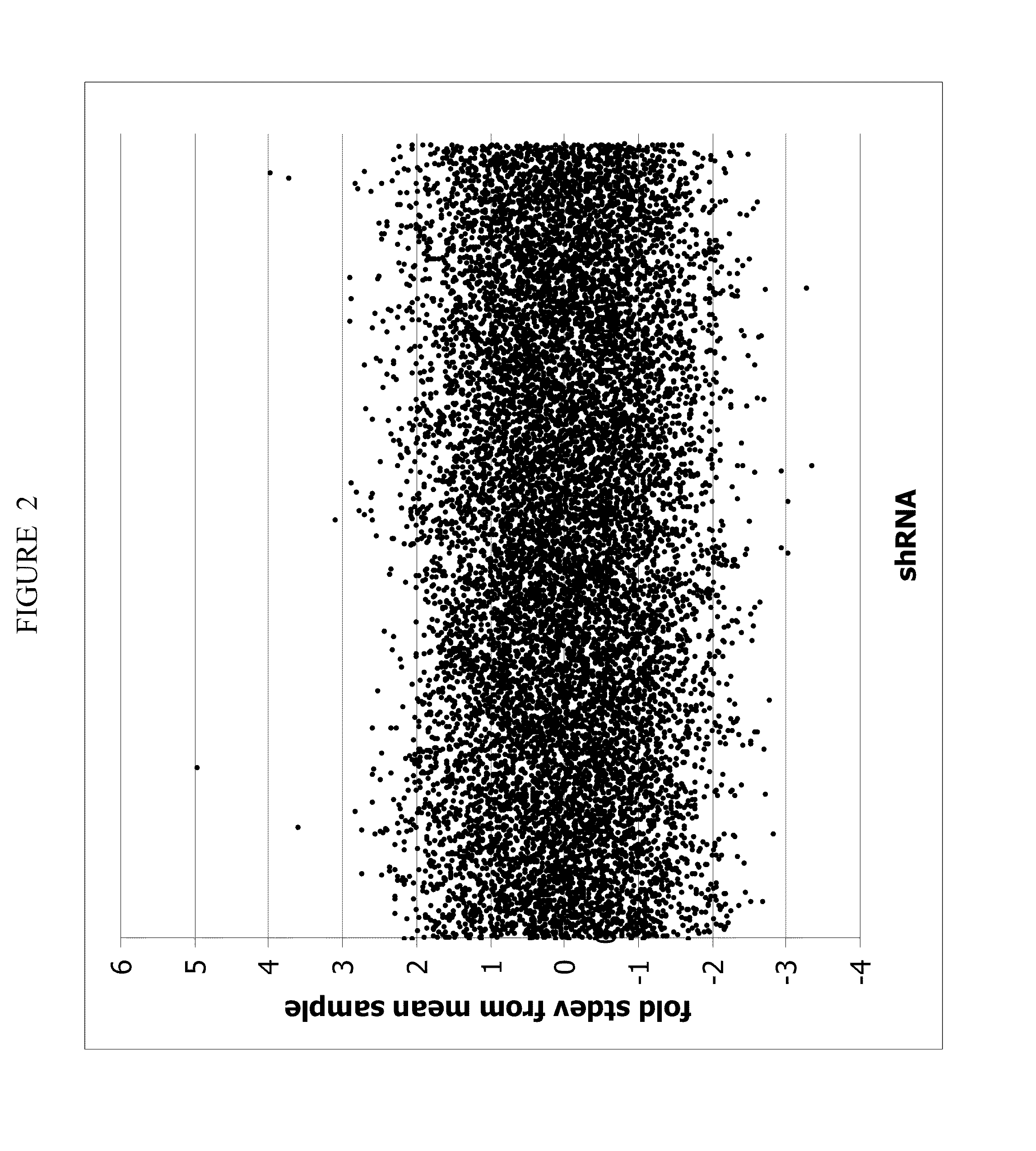
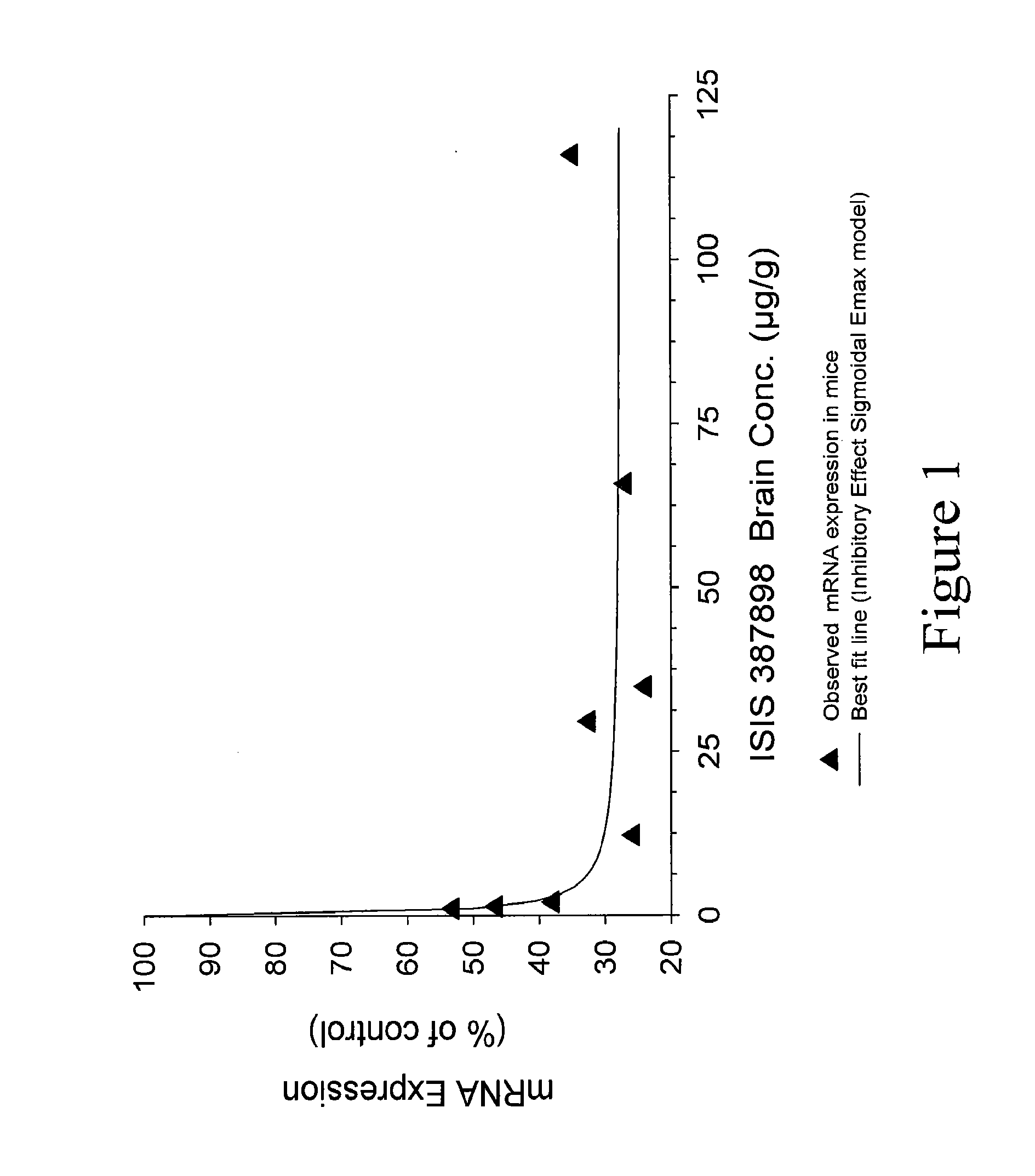
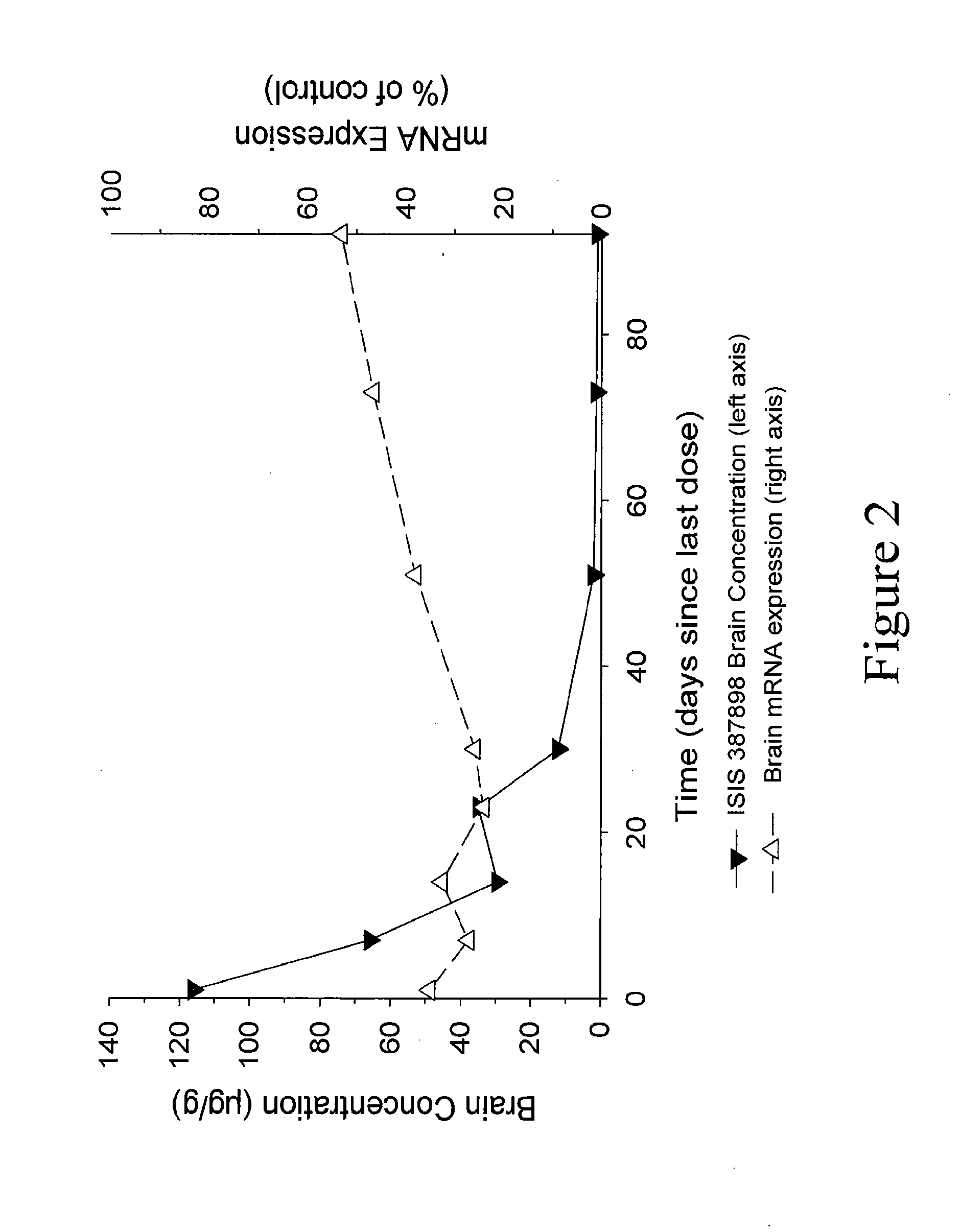
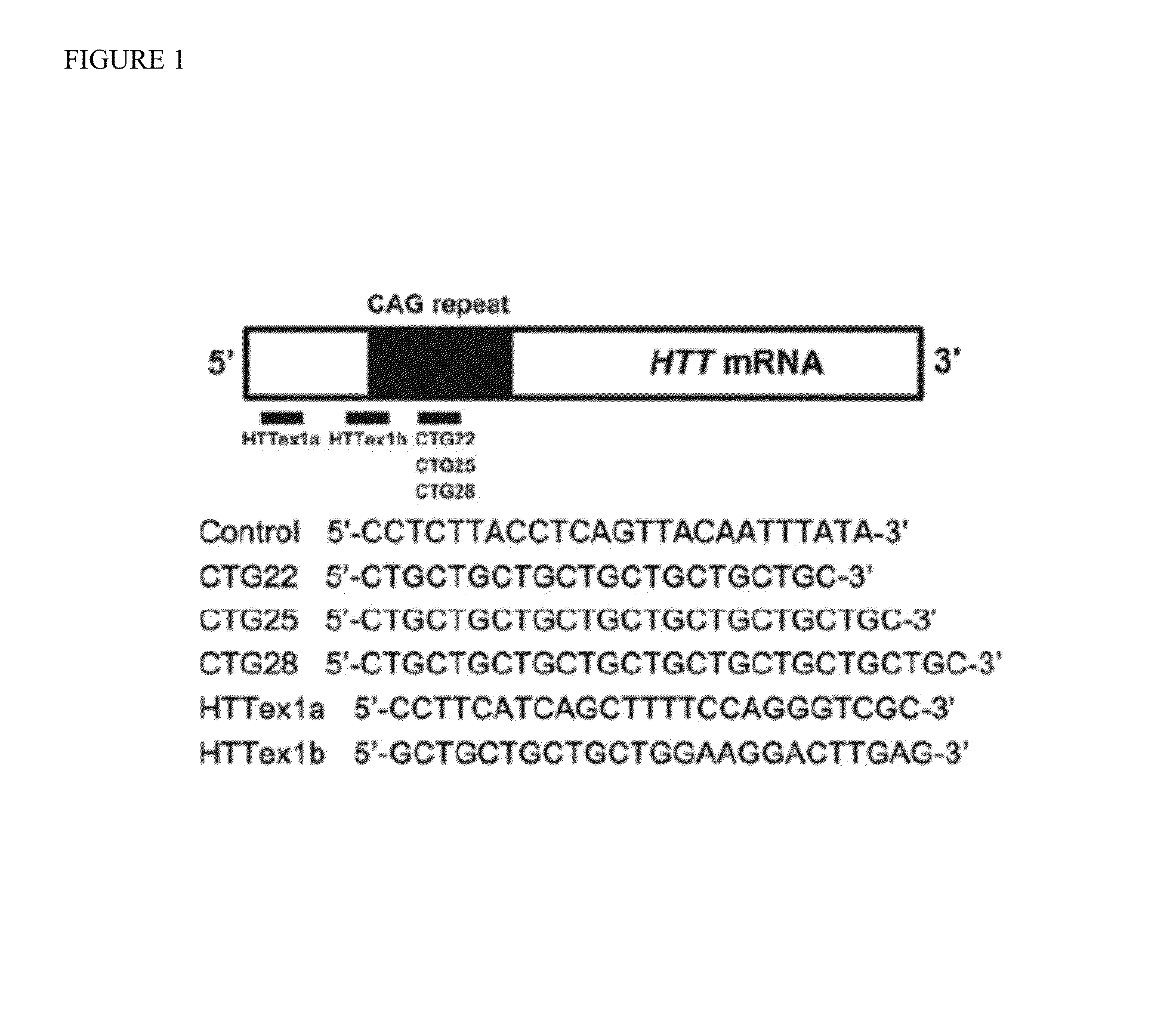
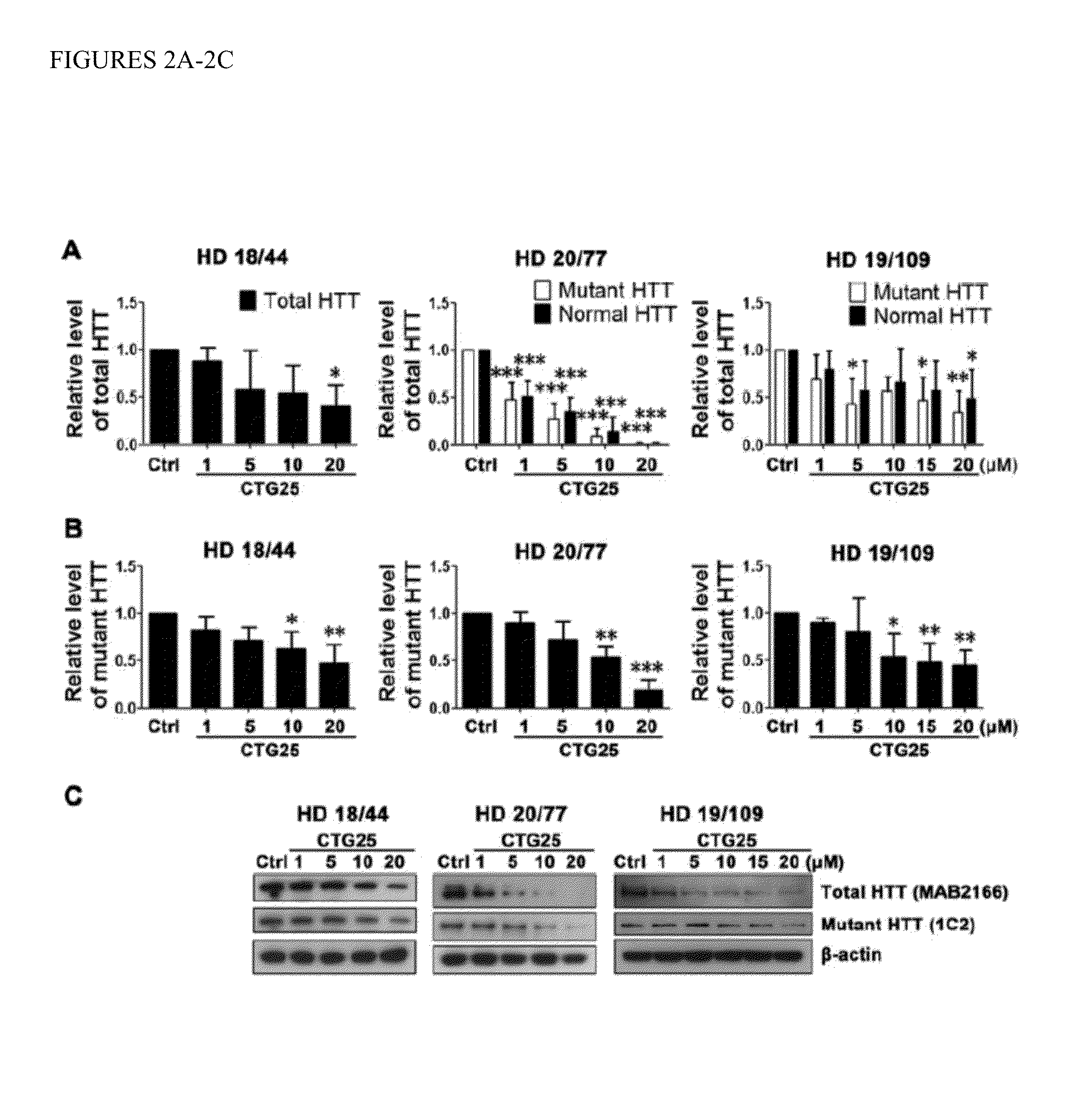
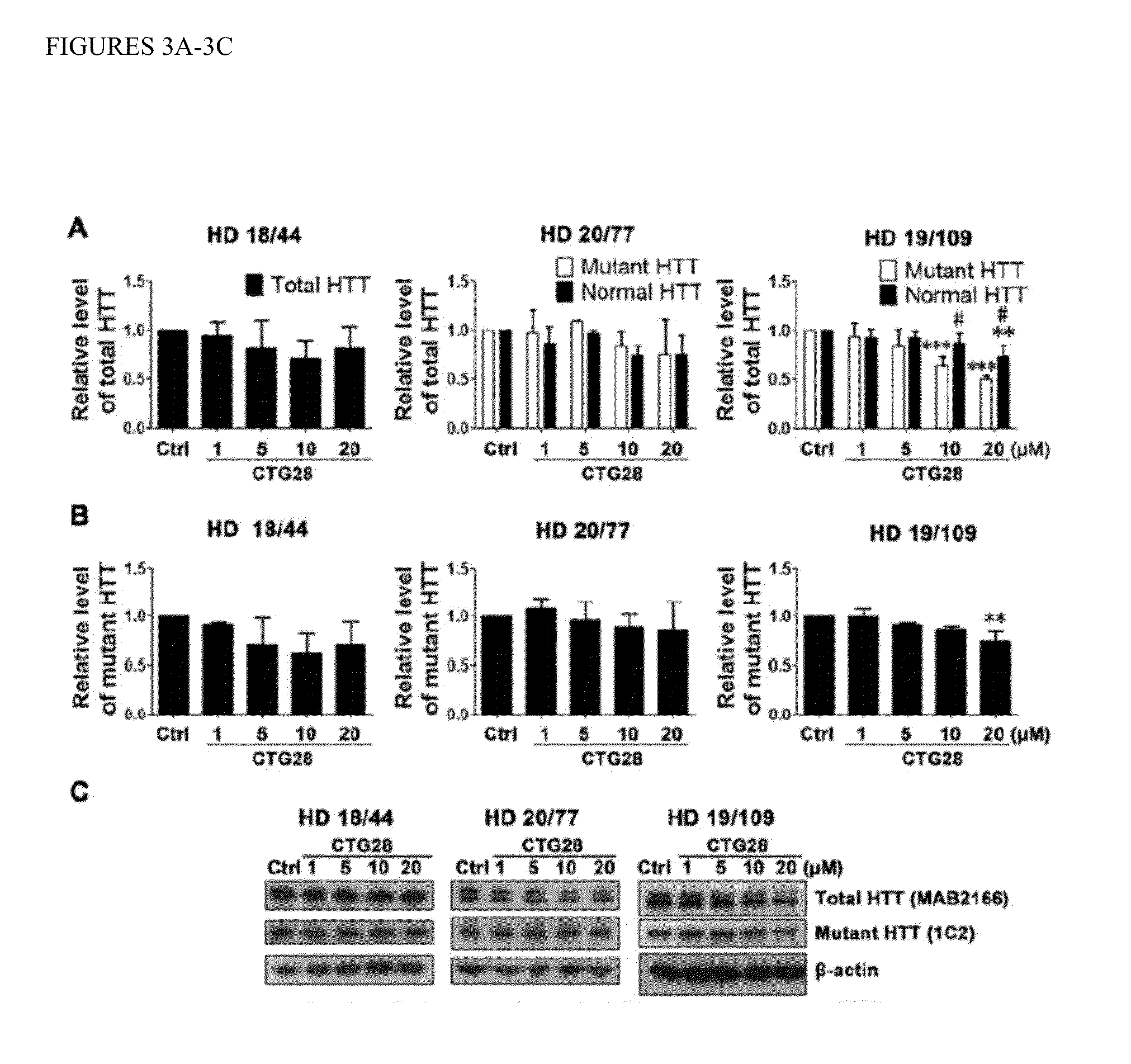
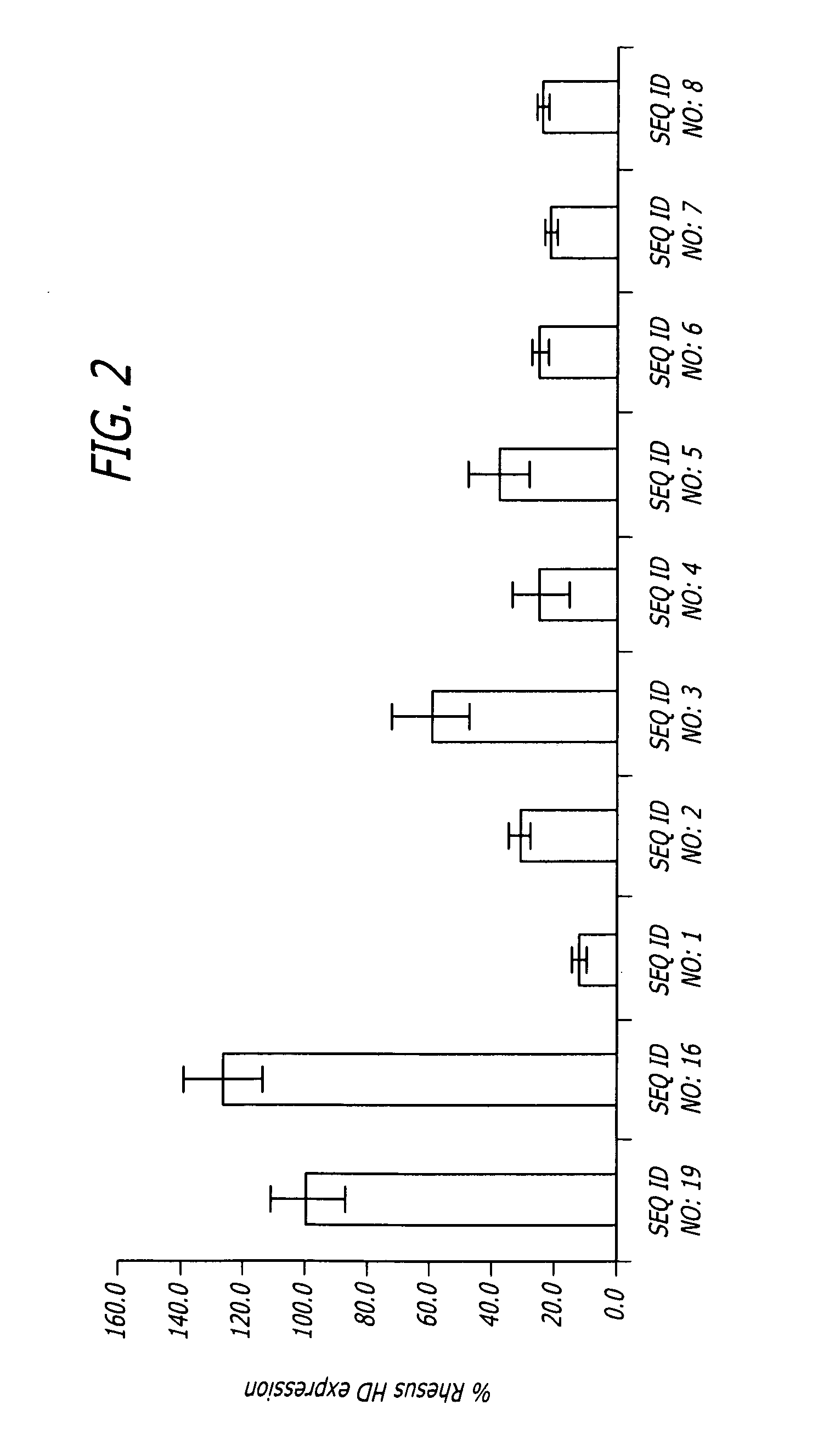
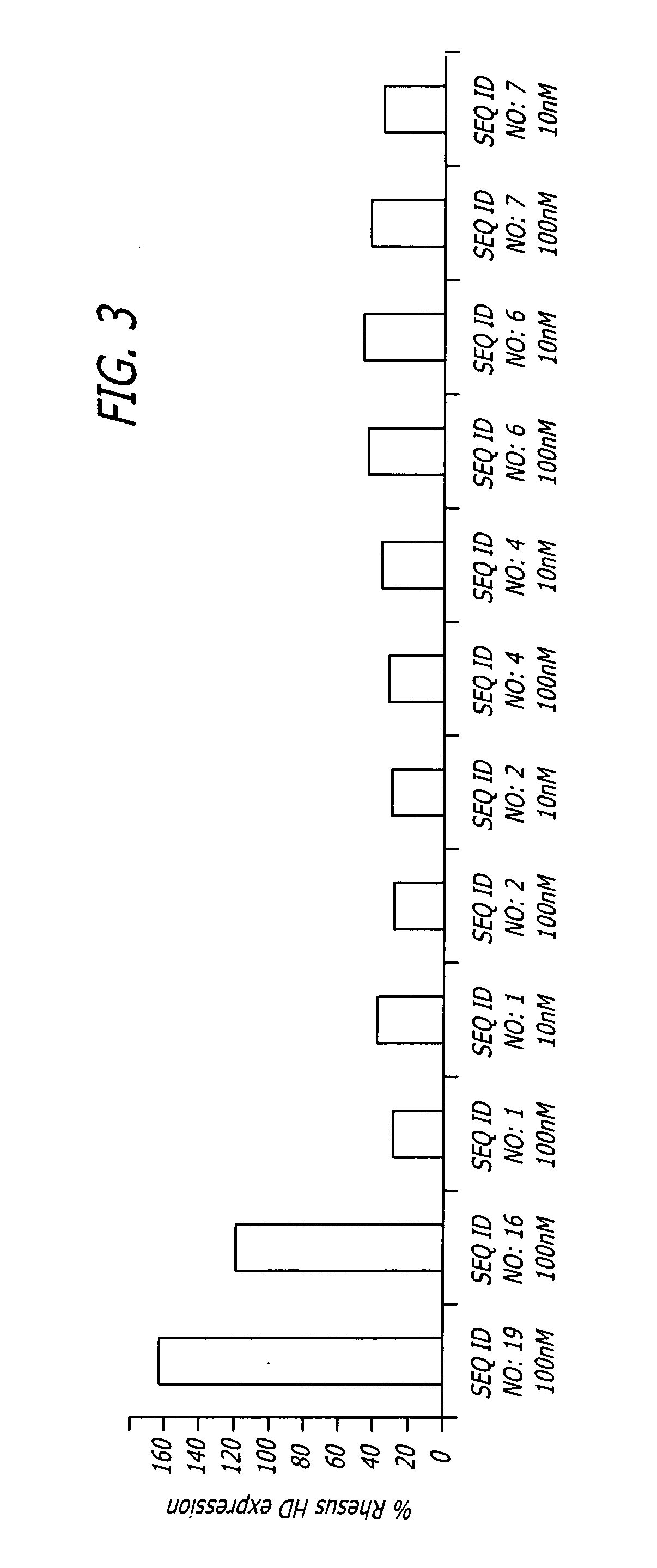
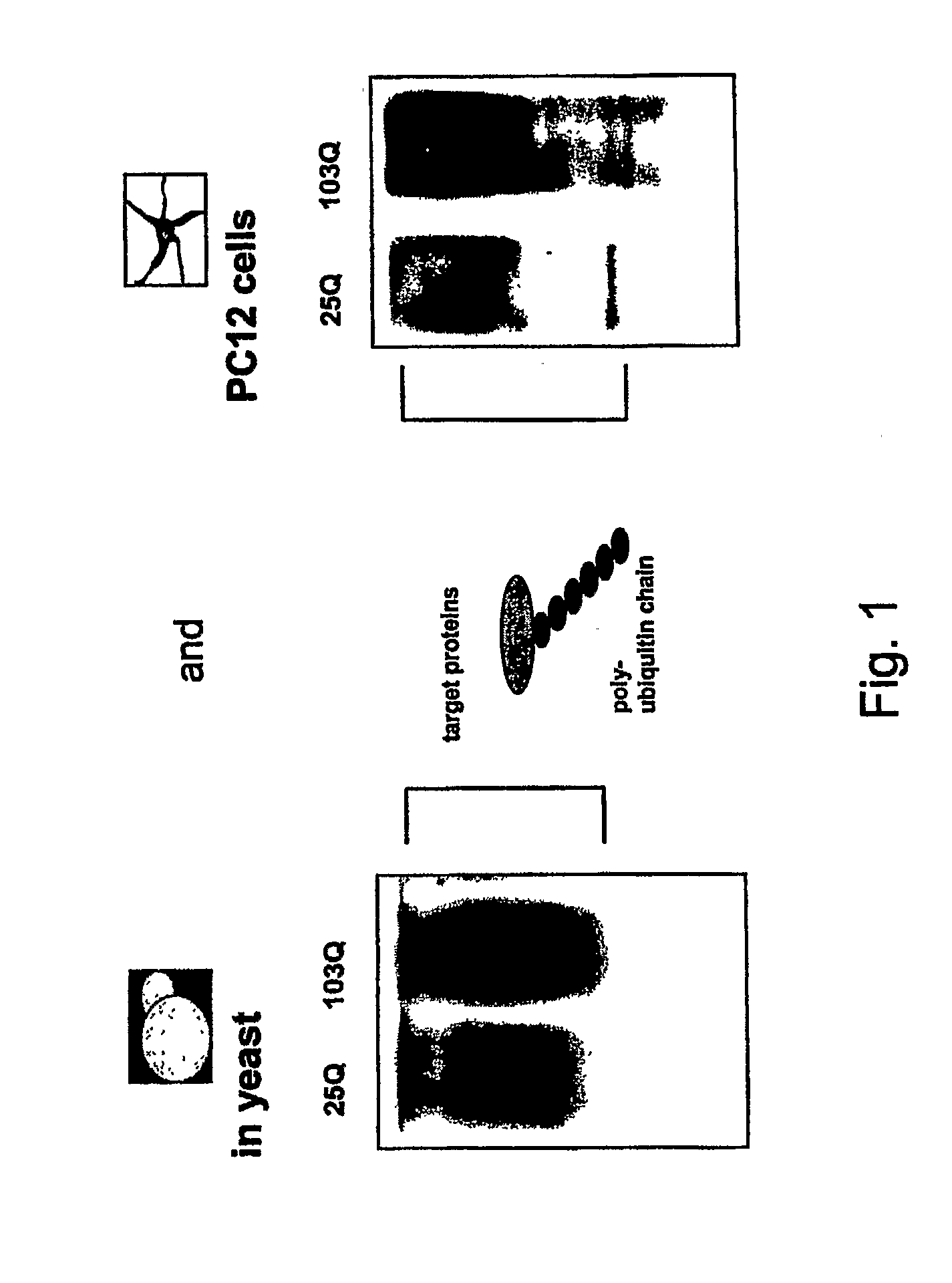
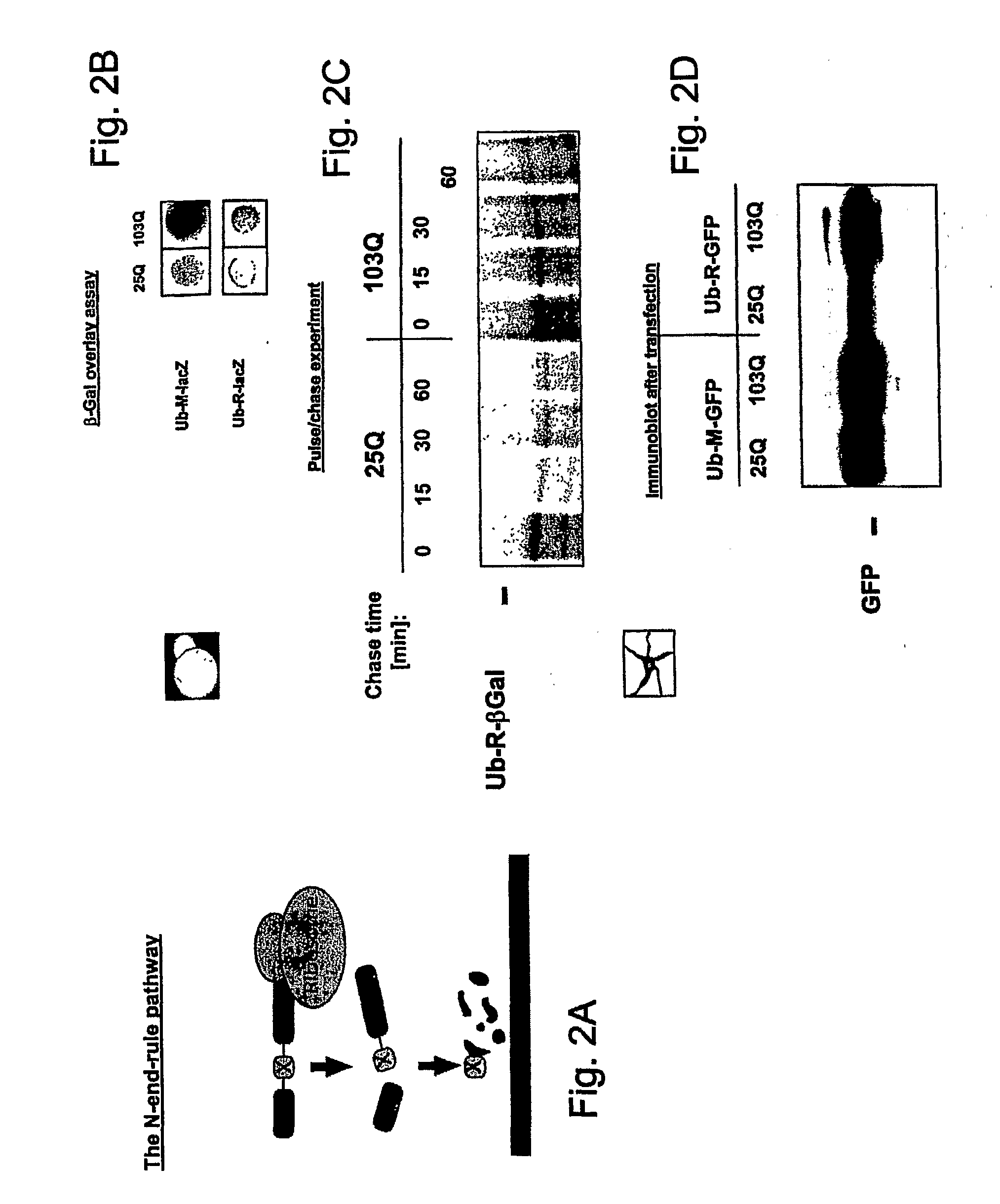
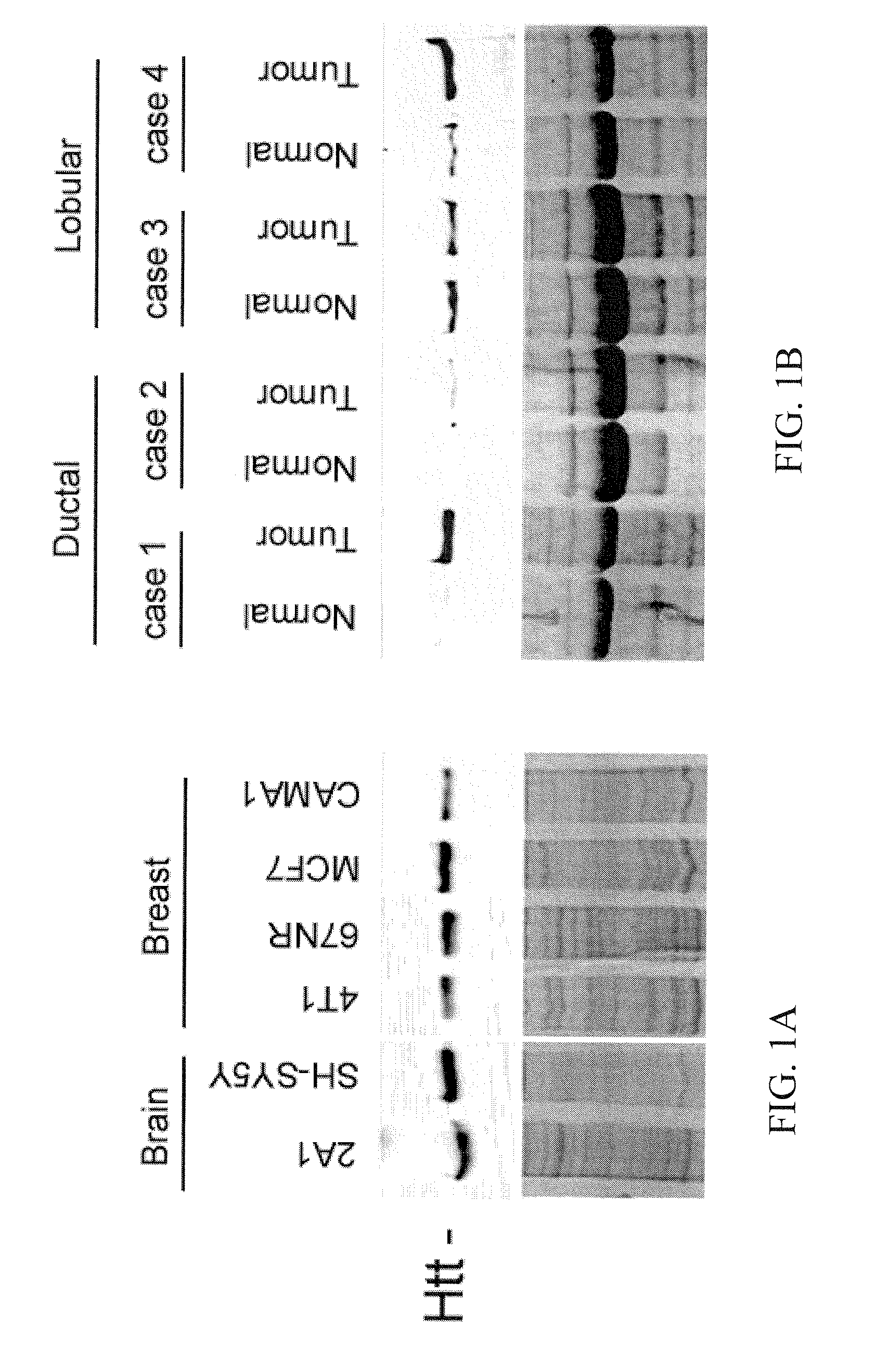
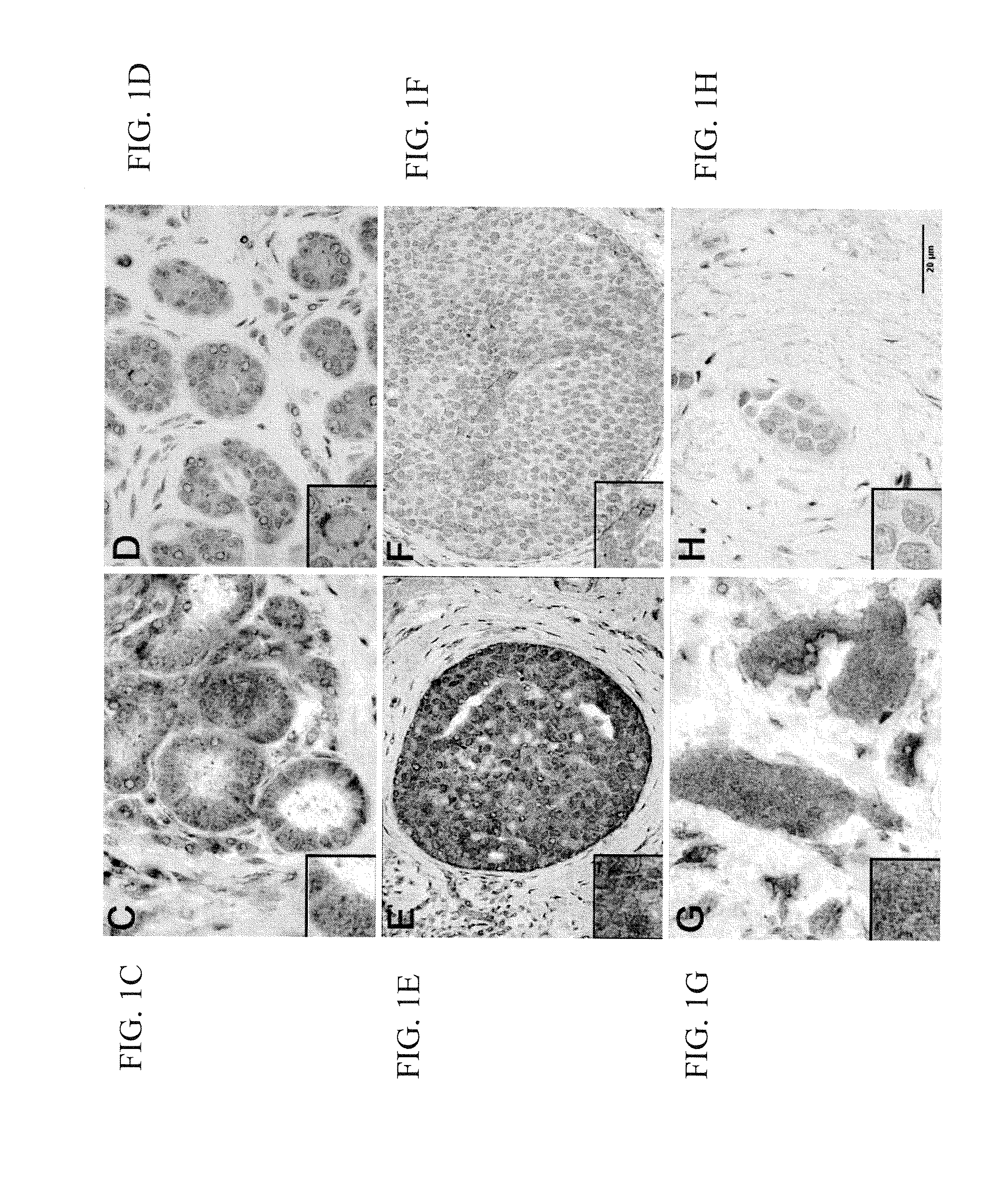
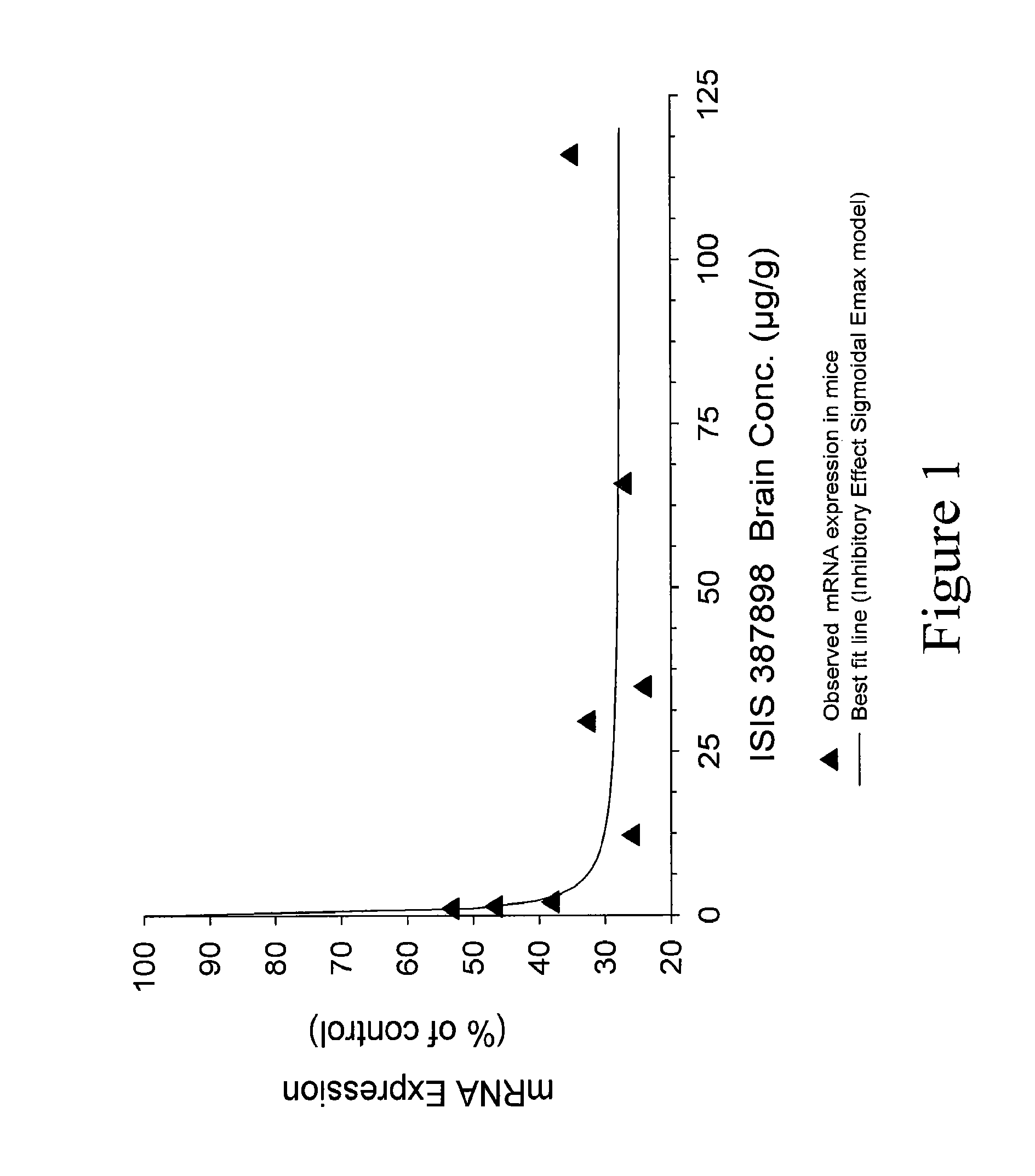
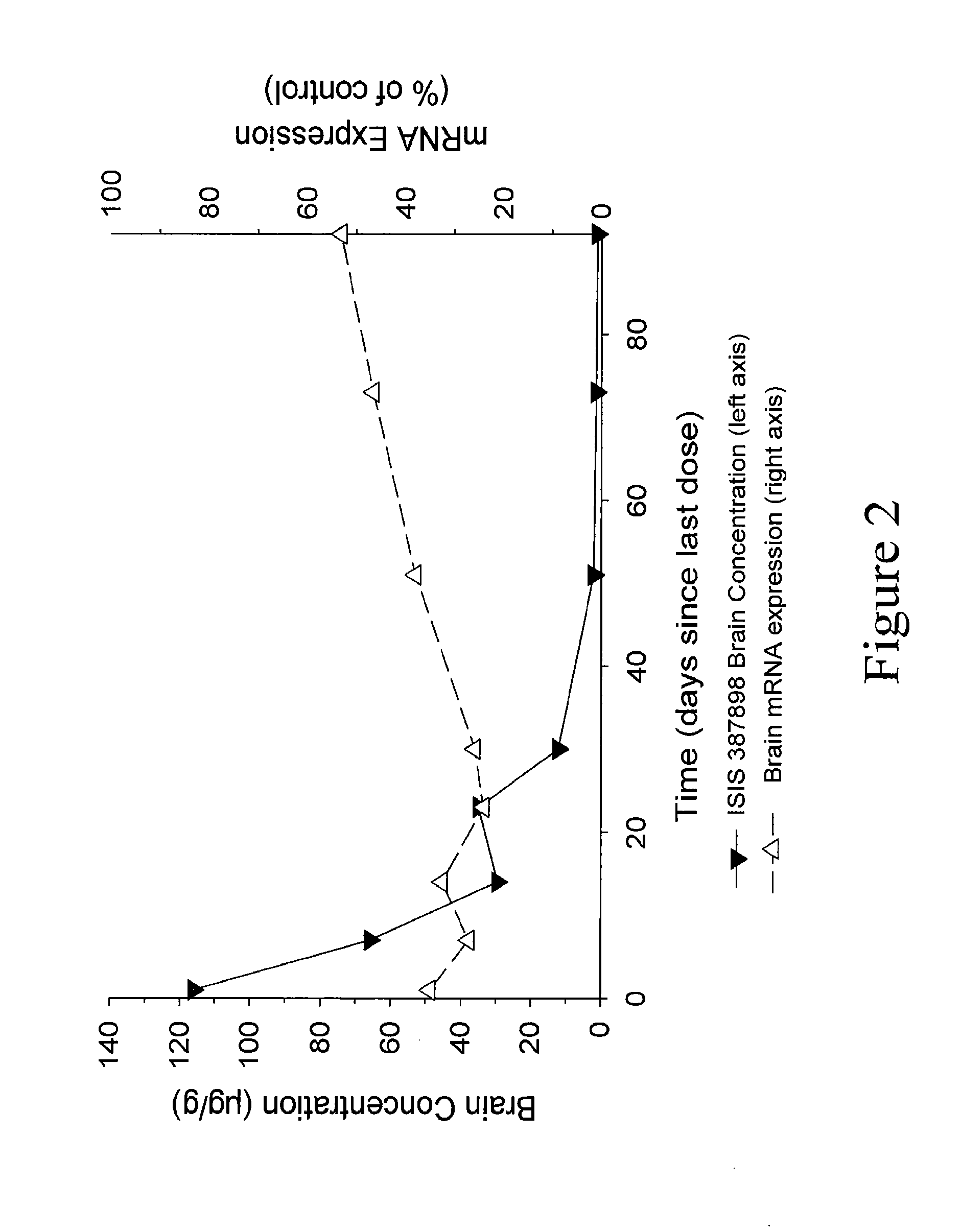
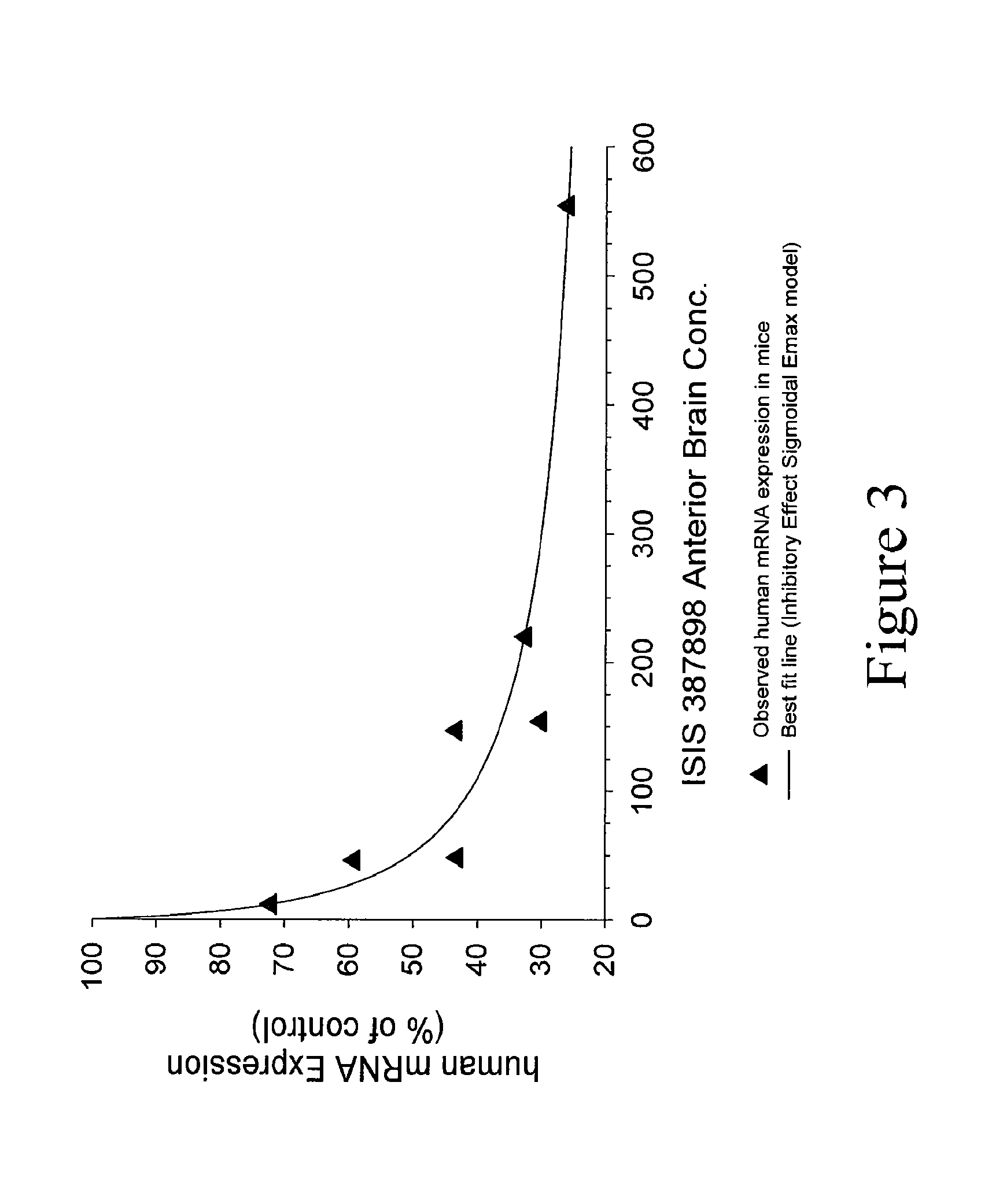
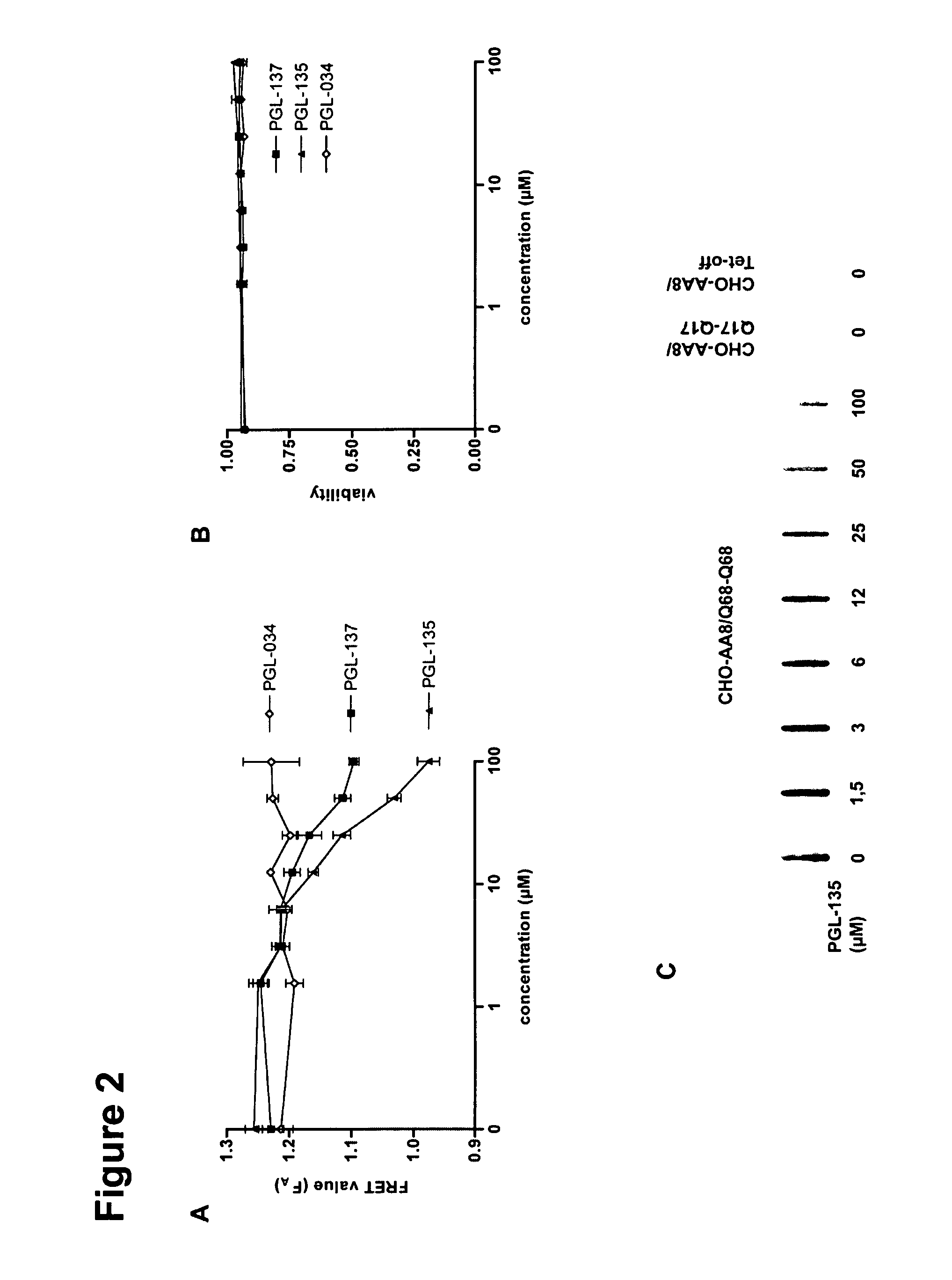
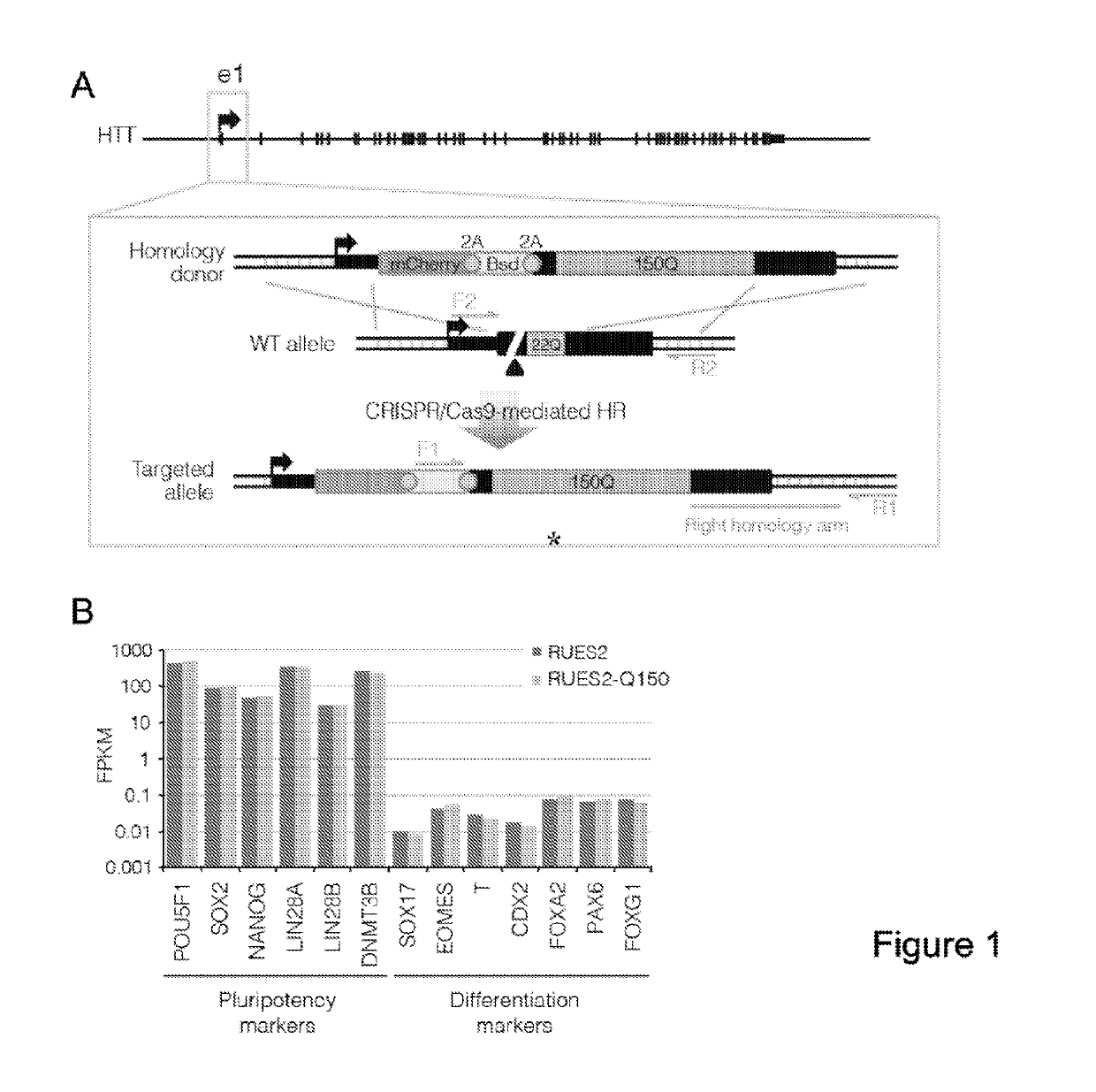
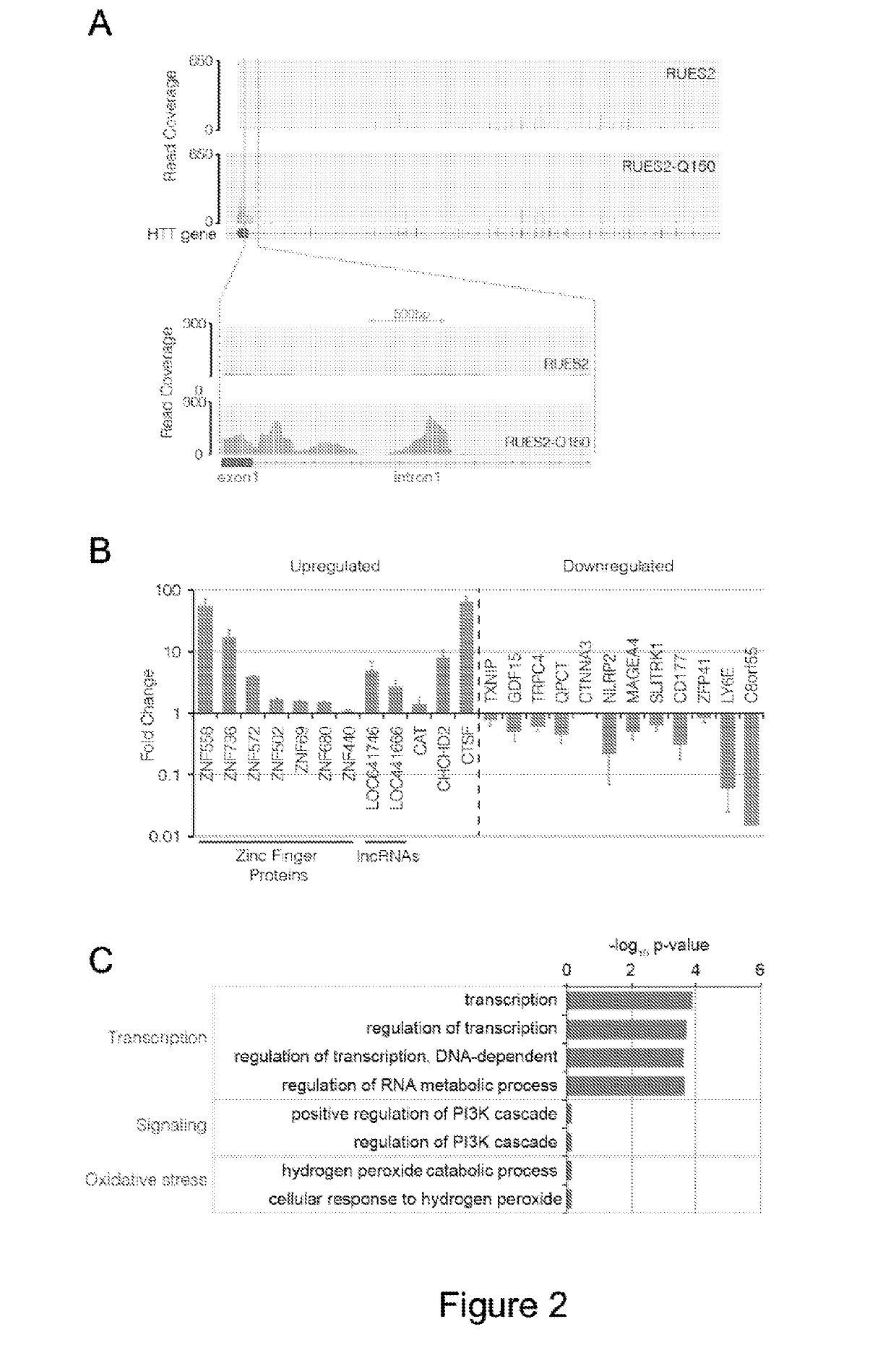
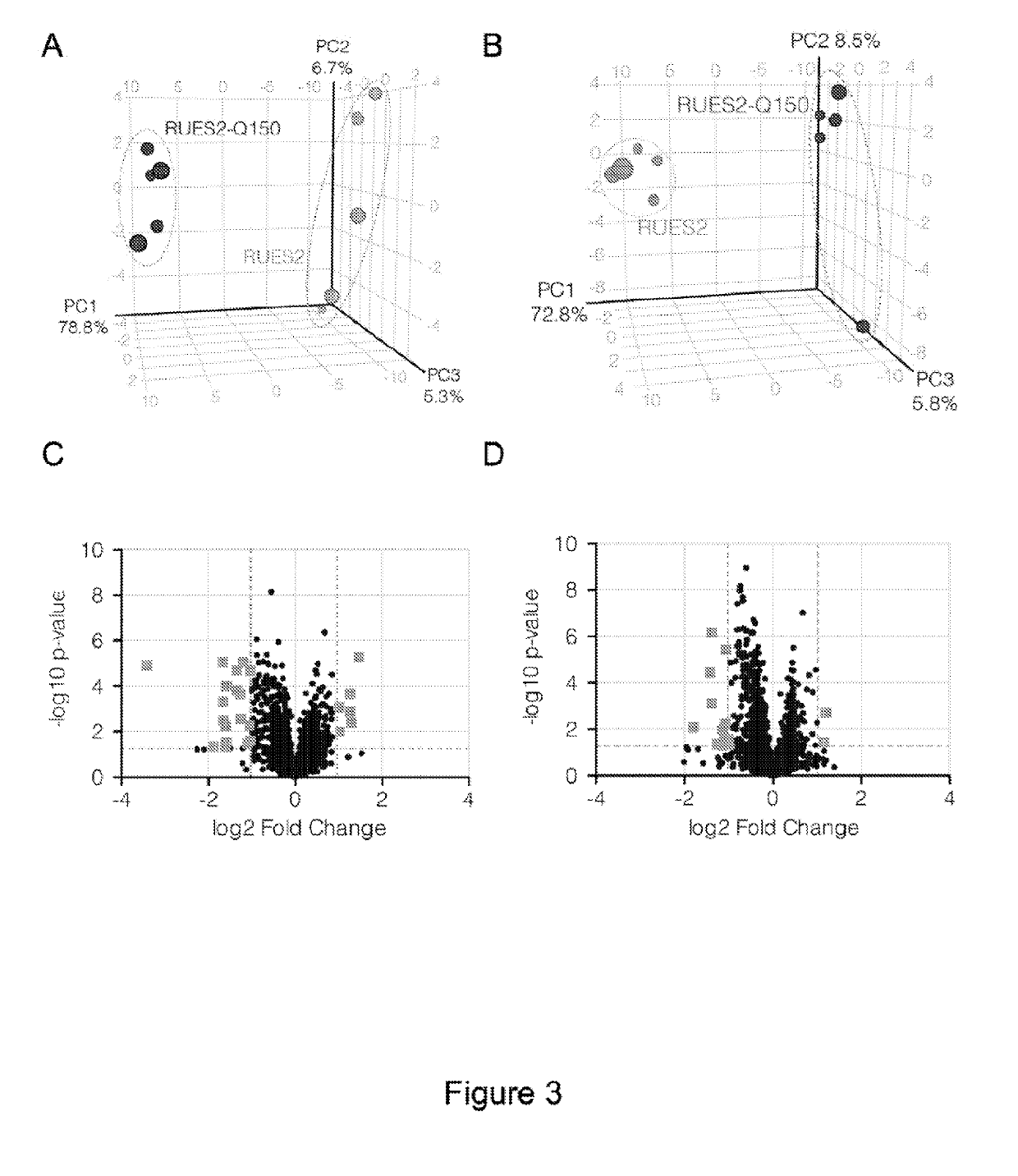
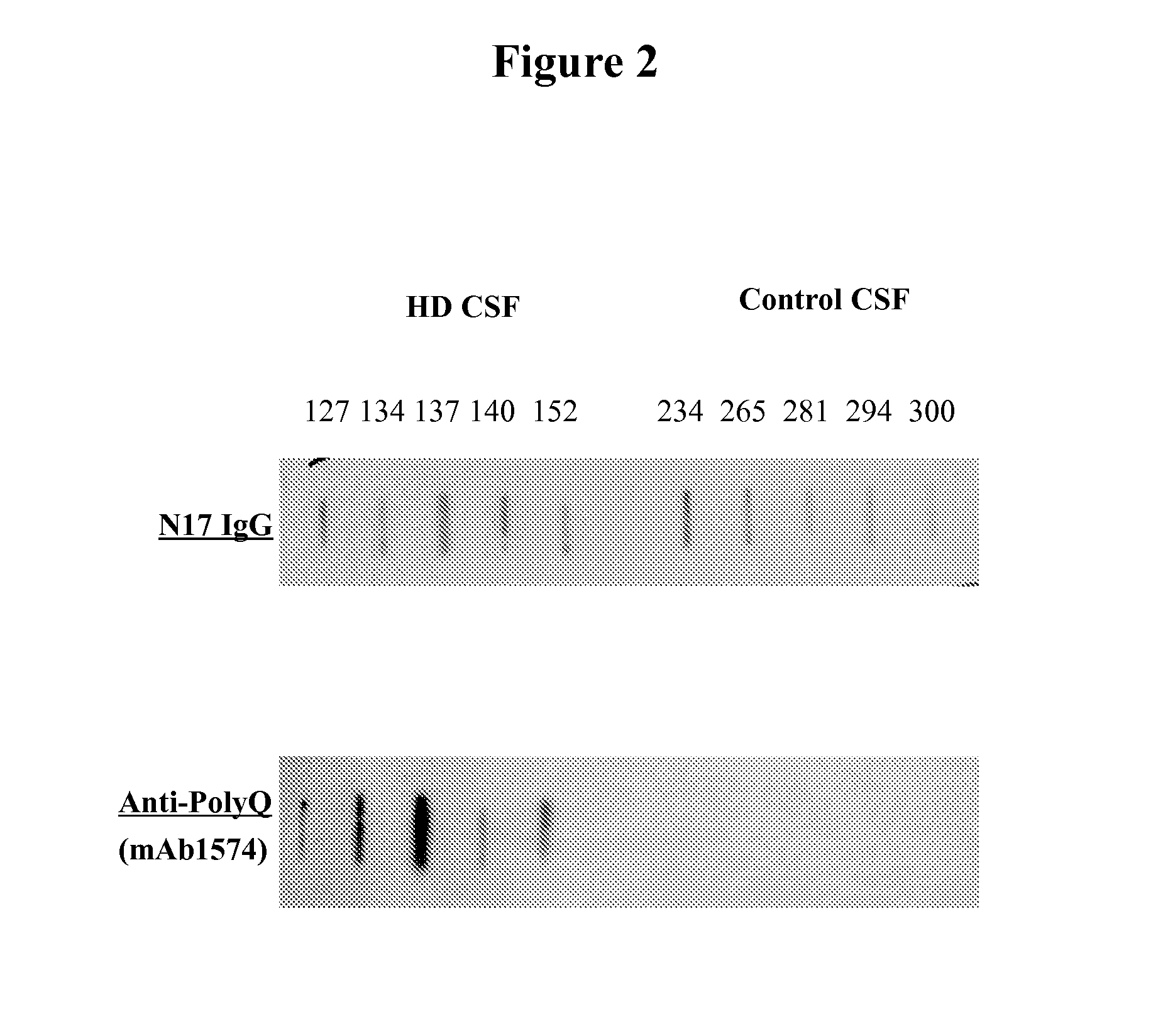
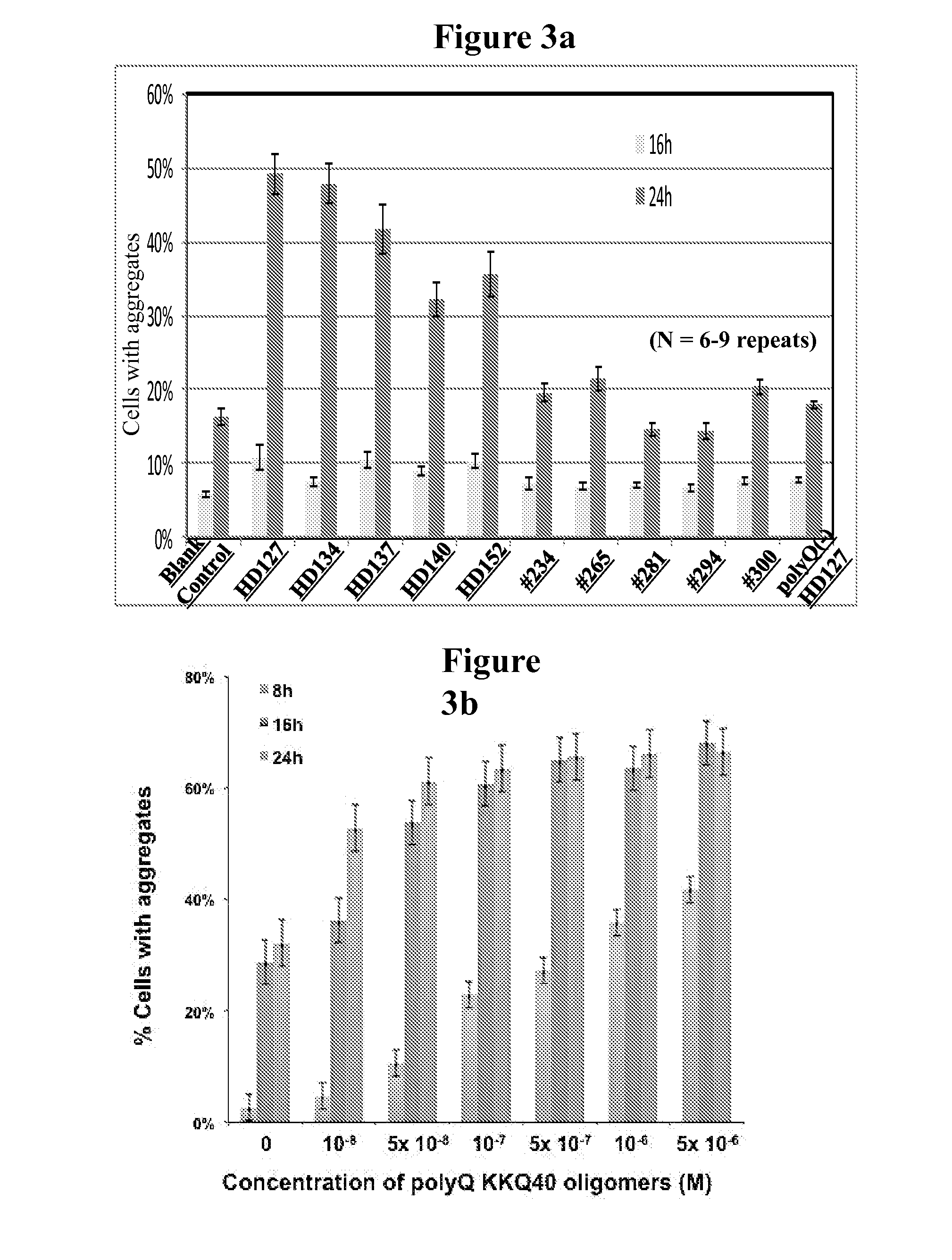
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Huntingtin Protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A protein that is highly expressed in the nervous system as well as other tissues; its size and structure vary due to polymorphisms. Expanded CAG TRINUCLEOTIDE REPEATS have been identified in the Huntingtin (HD) Gene of patients with HUNTINGTON DISEASE and are associated with abnormal PROTEIN AGGREGATES. Huntingtin interacts with proteins involved in a variety of gene expression and cellular processes; it is also essential for embryonic development.
Inhibition of the Expression of Huntingtin Gene
InactiveUS20080015158A1Inhibit expressionAvoid developmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaMammal
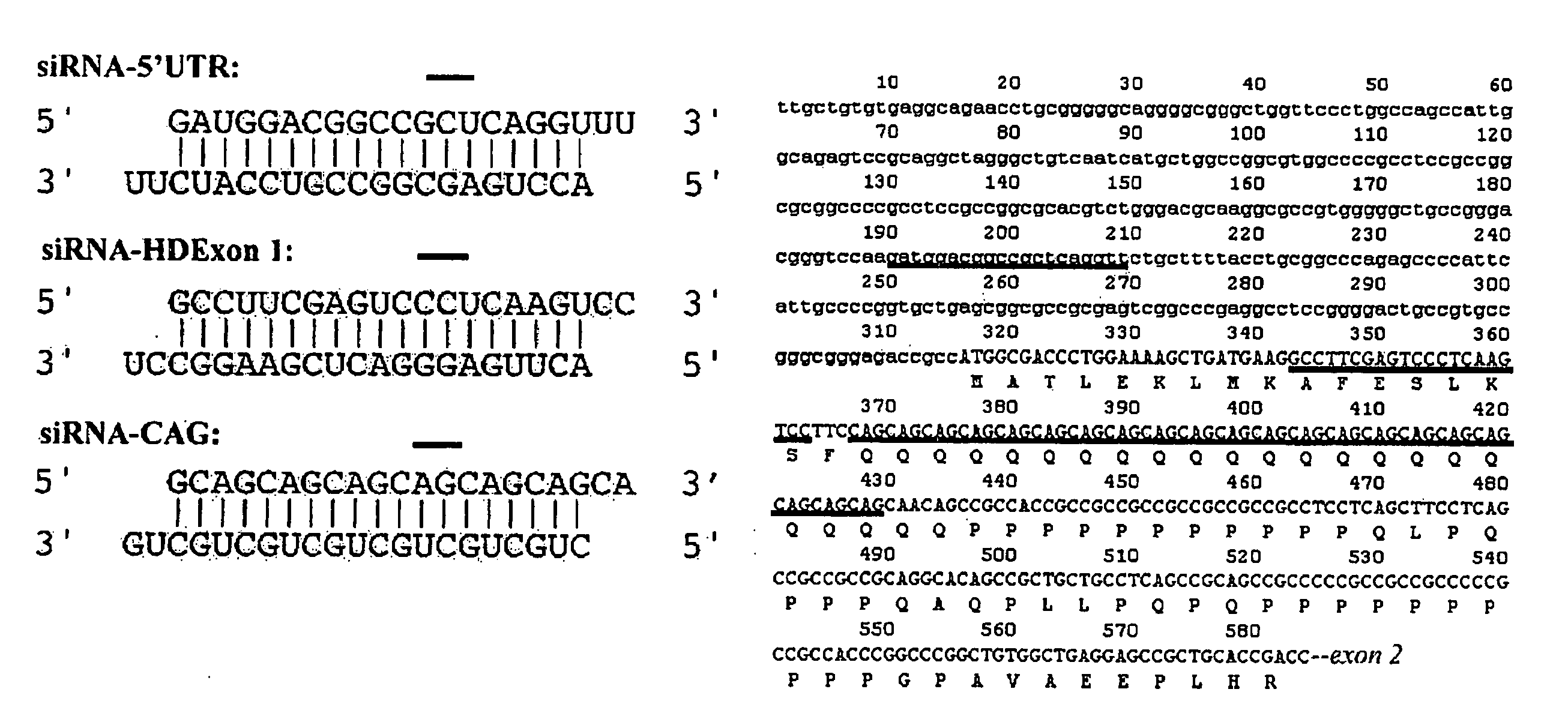
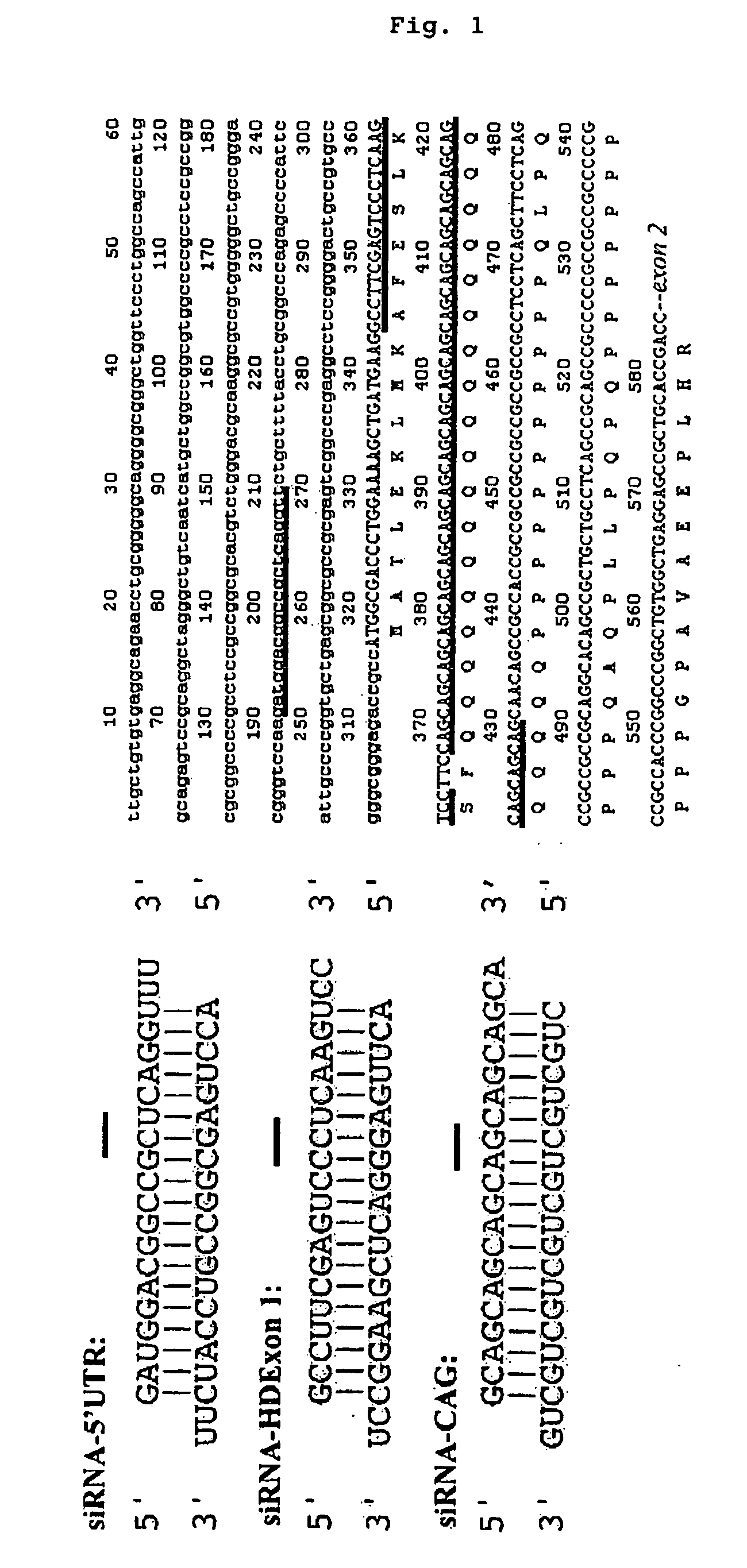
It is intended to provide methods for suppressing the huntingtin gene expression by using a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), huntingtin gene expression inhibitors to suppress the huntingtin gene expression, and preventives and / or remedies of Huntington's disease. Targeting against a specific sequence of mRNA at immediately upstream of CAG repeats in HD genes of Huntington's disease, the huntingtin gene expression is suppressed by using a dsRNA homologous to the sequence. In this invention, a short siRNA (short double-stranded RNA) having bp as short as around 21-23 bp can be effectively used as the dsRNA homologous to a specific RNA sequence in a region at immediately upstream of CAG repeats. The dsRNA of this present invention can be used as a huntingtin gene expression inhibitor, or a preventive and / or a remedy of Huntington's disease by administering or introducing into a living body or a living cell in mammals for the prevention and / or treatment of Huntington's disease.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Methods and sequences to suppress primate huntington gene expression
InactiveUS20060257912A1Inhibit expressionLower Level RequirementsGenetic material ingredientsFermentationPrimateGene
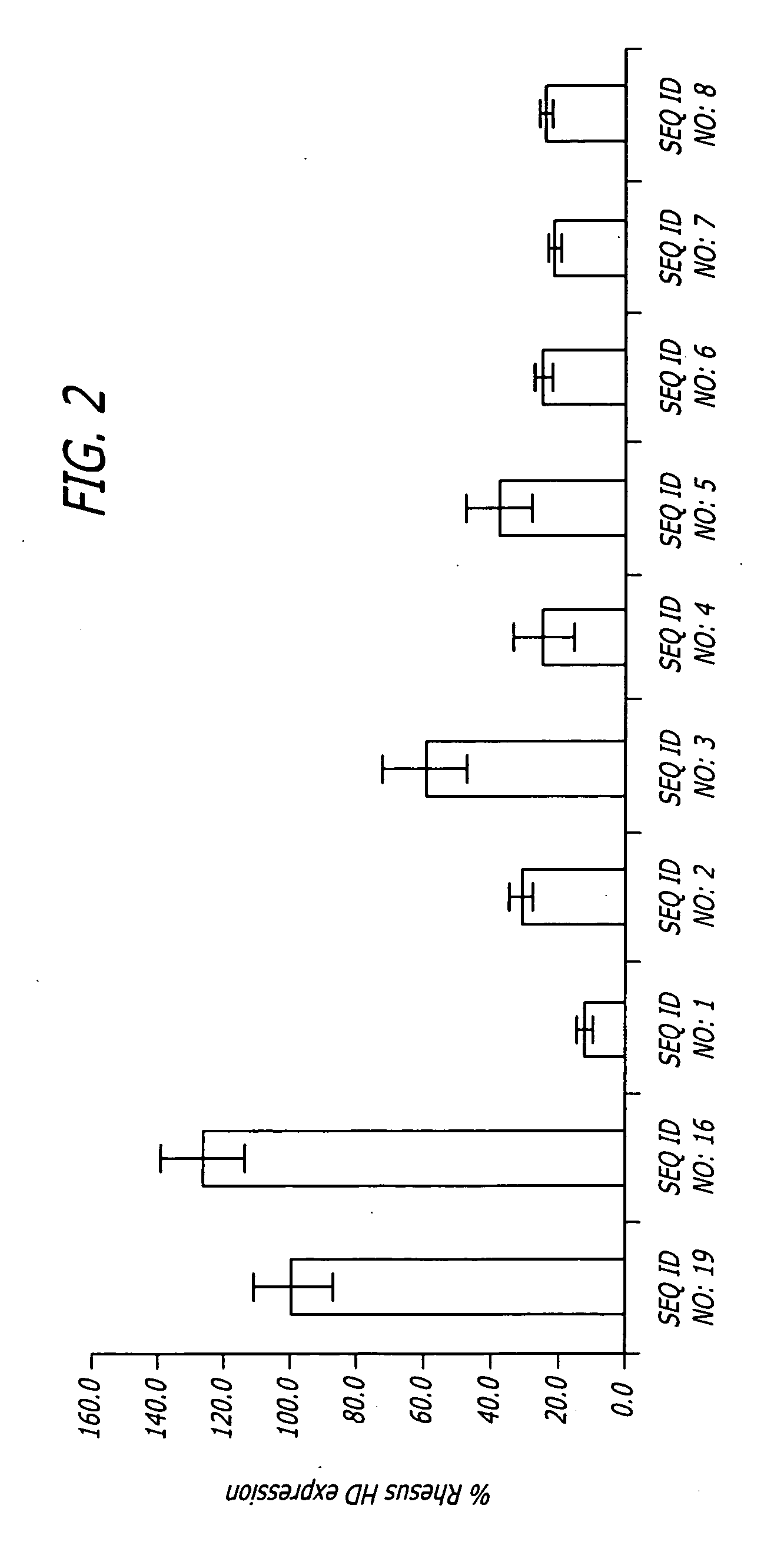
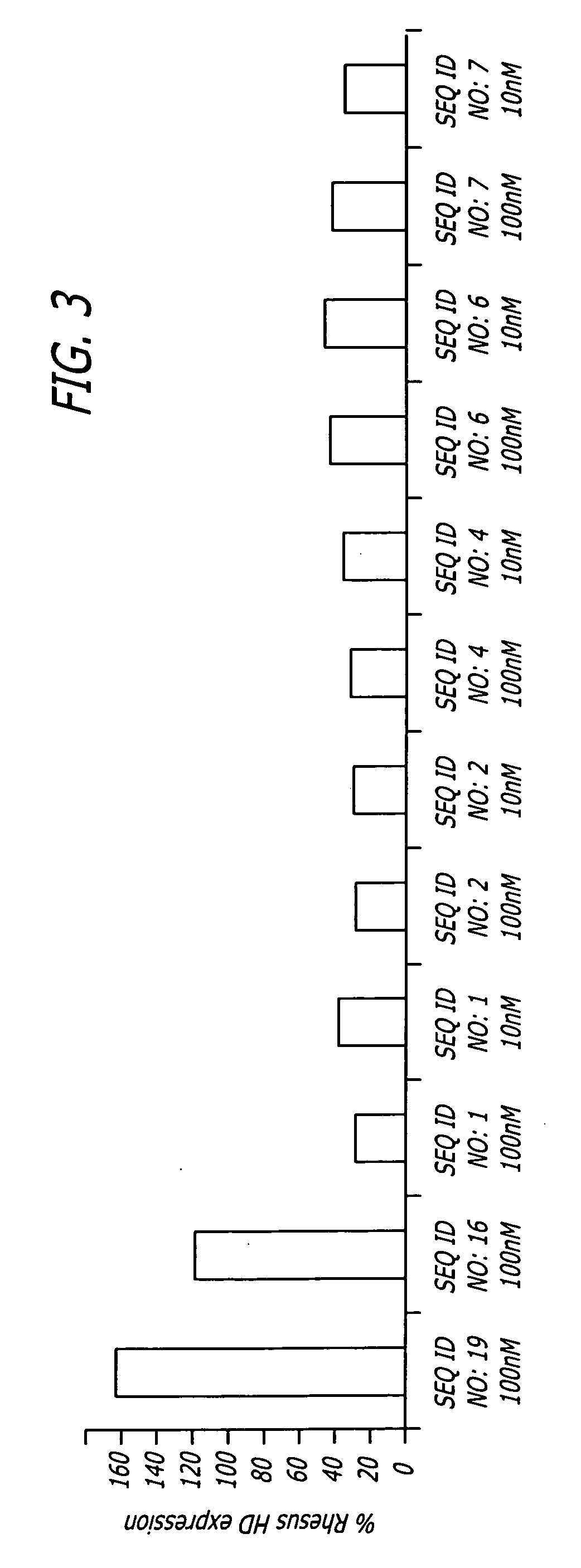
Disclosed herein are sequences, molecules and methods used to suppress the expression of HD genes encoding for huntingtin protein in primates including Macaca mulatta and Homo sapiens. These sequences, molecules and methods aid in the study of the pathogenesis of HD and can also provide a treatment for this disease.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and sequences to preferentially suppress expression of mutated huntingtin
InactiveUS20070161590A1Suppress expression and formationInhibit expressionSpecial deliverySugar derivativesHuntingtons choreaNucleotide sequencing
Disclosed herein are methods and sequences to preferentially suppress the expression of the mutated huntingtin (“htt”) protein over expression of the normal htt protein. Also disclosed are methods comprising screening an individual for the heterozygous presence of one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms within the individual's Huntington's genes; administering nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences that preferentially suppress the expression of amino acid sequences encoding for mutated huntingtin (“htt”) over suppressing the expression of amino acid sequences encoding for normal htt by targeting an area of a Huntington's disease gene that is heterozygous for the presence of one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and sequences to suppress primate huntington gene expression in vivo
InactiveUS20100325746A9Inhibit expressionLower Level RequirementsBiocideNervous disorderDiseasePrimate
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and sequences to suppress primate huntington gene expression
ActiveUS20100008981A1Inhibit expressionLower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseasePrimate
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Isolated nucleic acid duplex for reducing huntington gene expression
InactiveUS7902352B2Inhibit expressionLower Level RequirementsNervous disorderSugar derivativesDiseasePrimate
Disclosed herein are sequences, molecules and methods used to suppress the expression of HD genes encoding for huntingtin protein in primates including Macaca mulatta and Homo sapiens. These sequences, molecules and methods aid in the study of the pathogenesis of HD and can also provide a treatment for this disease by reducing HD mRNA without causing death, locomotor impairment or cellular alterations of the Macaca mulatta and Homo sapiens.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Compositions and methods for inhibiting expression of huntingtin gene
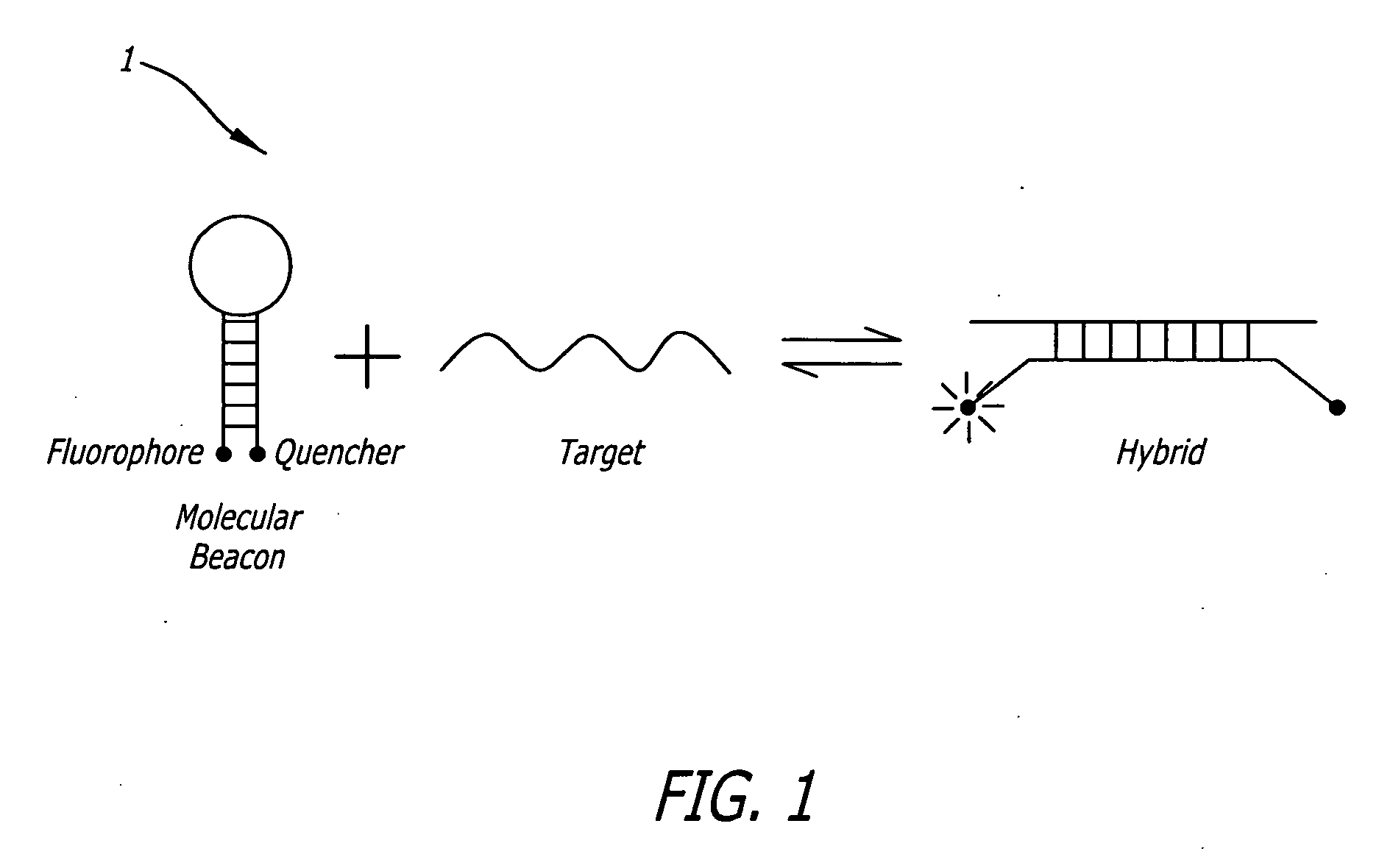
The invention relates to a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) for inhibiting the expression of the Huntingtin gene (HD gene), comprising an antisense strand having a nucleotide sequence which is less than 25 nucleotides in length and which is substantially complementary to at least a part of the HD gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the dsRNA together with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier; methods for treating diseases caused by the expression of the HD gene, or a mutant form thereof, using the pharmaceutical composition; and methods for inhibiting the expression of the huntingtin gene in a cell.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Target sequences and methods to identify the same, useful in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20110105587A1Organic active ingredientsCompound screeningHuntingtons choreaCell Aggregations
The present invention relates to methods and assays for identifying agents capable of inhibiting the mutant huntingtin protein, inhibiting or reducing cell death, in particular cell death associated with polyglutamine-induced protein aggregation, which inhibition is useful in the prevention, amelioration and / or treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, and Huntington's disease more generally. In particular, the present invention provides methods and assays for identifying agents for use in the prevention and / or treatment of Huntingtons disease. The invention provides polypeptide and nucleic acid TARGETs and siRNA sequences based on these TARGETS.
Owner:GALAPAGOS NV
Modulation of huntingtin expression
ActiveUS20120252879A1Avoid symptomsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaHuntingtin Protein
Provided herein are methods, compounds, and compositions for reducing expression of huntingtin mRNA and protein in an animal. Such methods, compounds, and compositions are useful to treat, prevent, delay, or ameliorate Huntington's disease, or a symptom thereof.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers (PMOS) and their use in suppression of mutant huntingtin expression and attenuation of neurotoxicity
InactiveUS20160017327A1Improve neurotoxicityDecrease HTT protein expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesHuntingtons choreaADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides antisense phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers which are useful for the suppression or inhibition of the HTT gene involved in Huntington's disease. The oligomers can selectively suppress mutant forms of the HTT protein while allowing the normal protein to be expressed in sufficient quantity to retain its function in the cell. Methods for treatment of Huntington's disease are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods and sequences to suppress primate huntington gene expression in vivo
InactiveUS20070261126A1Inhibit expressionLower Level RequirementsBiocideNervous disorderDiseasePrimate
Disclosed herein are sequences, molecules and methods used to suppress the expression of HD genes encoding for huntingtin protein in primates including Macaca mulatta and Homo sapiens. These sequences, molecules and methods aid in the study of the pathogenesis of HD and can also provide a treatment for this disease by reducing HD mRNA without causing death, locomotor impairment or cellular alterations of the Macaca mulatta and Homo sapiens.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Embryonic cell-based therapeutic candidate screening systems, models for huntington's disease and uses thereof
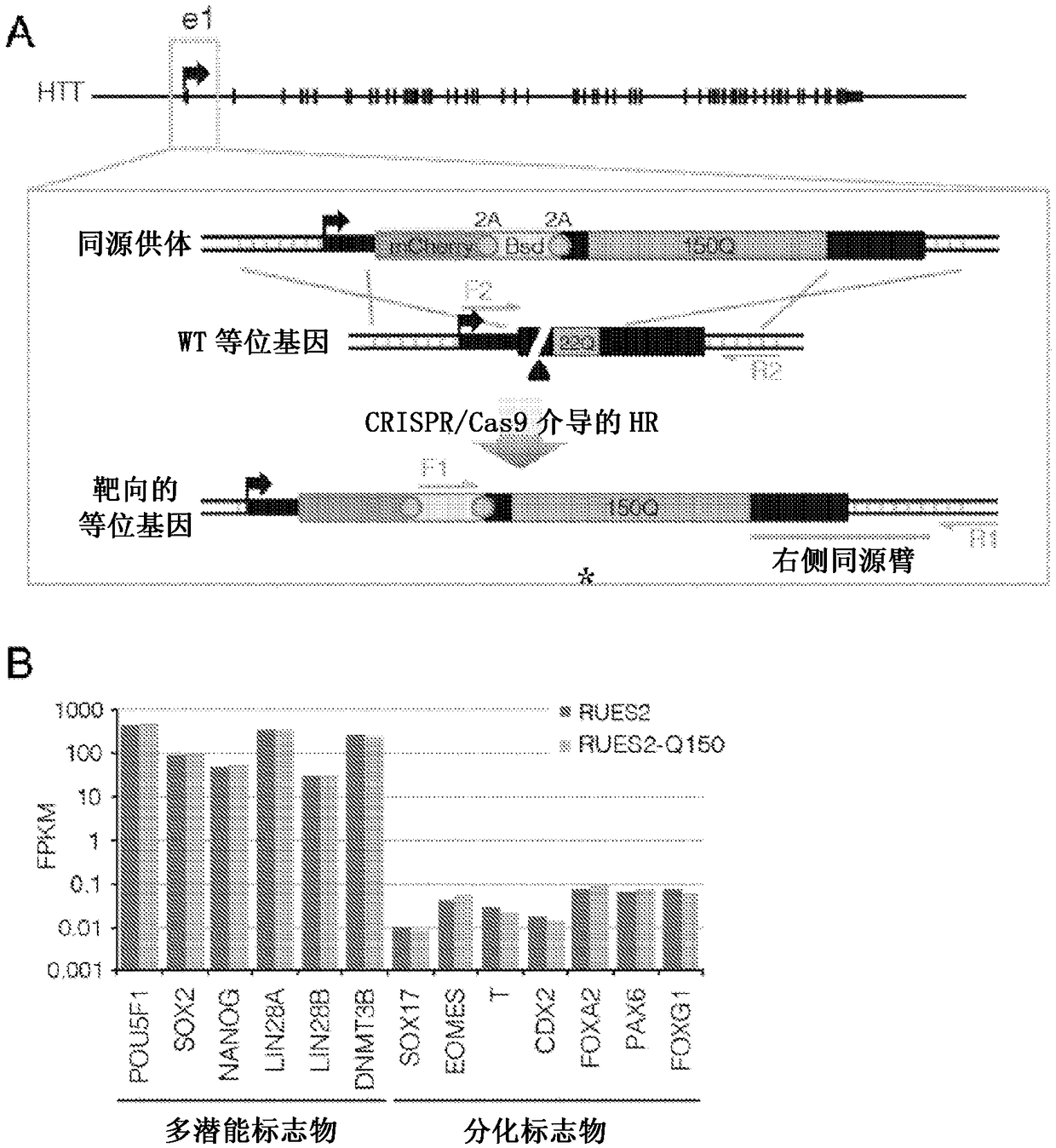
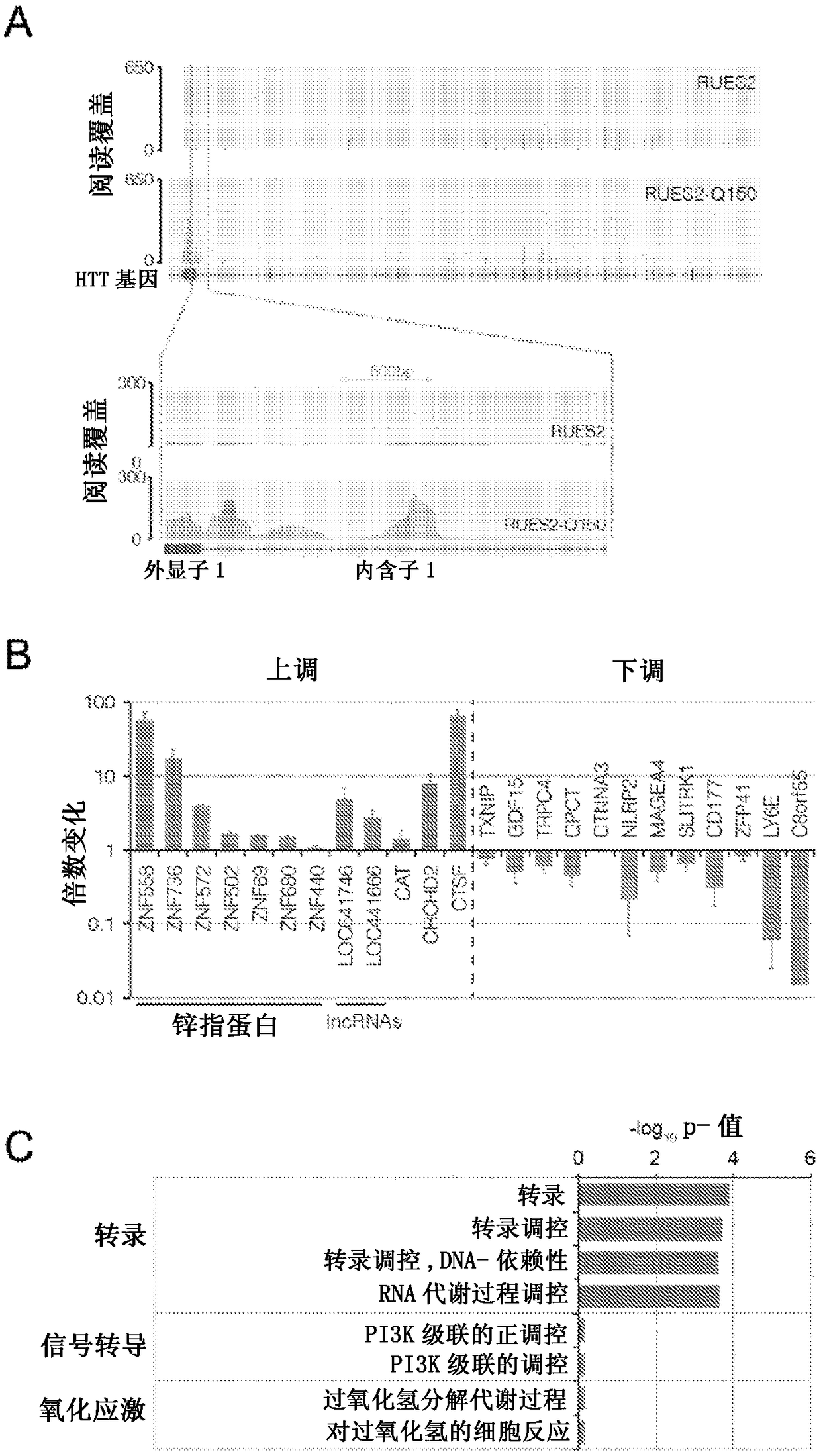
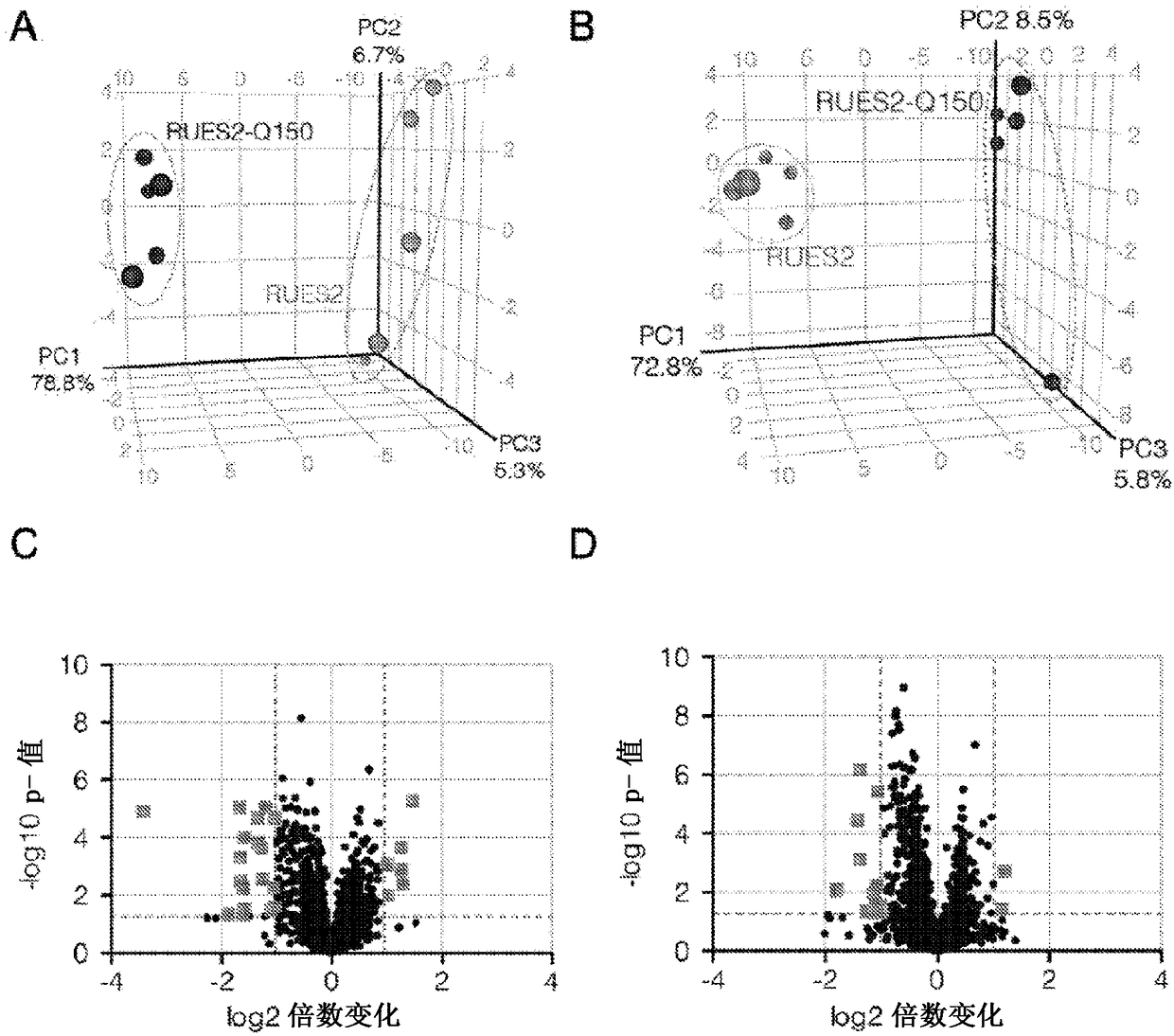
Compositions and methods disclosed concern an isogenic population of in vitro human embryonic stem cells comprising a disease form of the Huntingtin gene (HTT) at the endogenous HTT gene locus in thegenome of the cell; wherein the disease form of the HTT gene comprises a polyQ repeat of at least 40 glutamines at the N-terminus of the Huntingtin protein (HTT). The cell lines of the disclosure comprise genetically-defined alterations made in the endogenous HTT gene that recapitulate Huntington's Disease in humans. Furthermore, the cell lines have isogenic controls that share a similar genetic background. Differentiating cell lines committed to a neuronal fate and fully differentiated cell lines are also provided and they also display phenotypic abnormalities associated with the length of the polyQ repeat of the HTT gene. These cell lines are used as screening tools in drug discovery and development to identify substances that fully or partially revert these phenotype abnormalities.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Compositions and Methods for Treatment of Protein Misfolding Diseases
InactiveUS20080045607A1Simple processHigh activityBiocideCompound screeningHuntingtons choreaHuntington's disease
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Antibodies specific for proteins having polyglutamine expansions
InactiveUS6291652B1Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansADAMTS ProteinsTherapeutic treatment
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Use of Huntingtin Protein for the Diagnosis and the Treatment of Cancer
InactiveUS20110039789A1Increased phosphorylationImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningOncologyHuntingtin Protein
The present invention relates to new methods of treatment of cancer, in particular of breast cancer, and methods of screening of compounds useful in the treatment of cancer. The present invention further provides new prognostic and / or diagnostic markers in human cancer.
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +1
Modulation of huntingtin expression
Provided herein are methods, compounds, and compositions for reducing expression of huntingtin mRNA and protein in an animal. Such methods, compounds, and compositions are useful to treat, prevent, delay, or ameliorate Huntington's disease, or a symptom thereof.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
RNAi induced huntingtin gene suppression
The present invention provides for a double stranded RNA comprising a first RNA sequence and a second RNA sequence wherein the first and second RNA sequence are substantially complementary, wherein the first RNA sequence has a sequence length of at least 19 nucleotides and is substantially complementary to SEQ ID NO. 1. Said double stranded RNA is for use in inducing RNAi against Huntingtin exon 1sequences. The double stranded RNA of to the invention was capable of reducing neuronal cell death and huntingtin aggregates in an animal model.
Owner:尤尼克尔生物制药股份有限公司
Compounds for the Modulation of Huntingtin Aggregation, Methods and Means for Identifying Such Compounds
InactiveUS20100298280A1Increase the number ofAvoid rapid degradationBiocideCompound screeningAbnormal tissue growthAmyloid disease
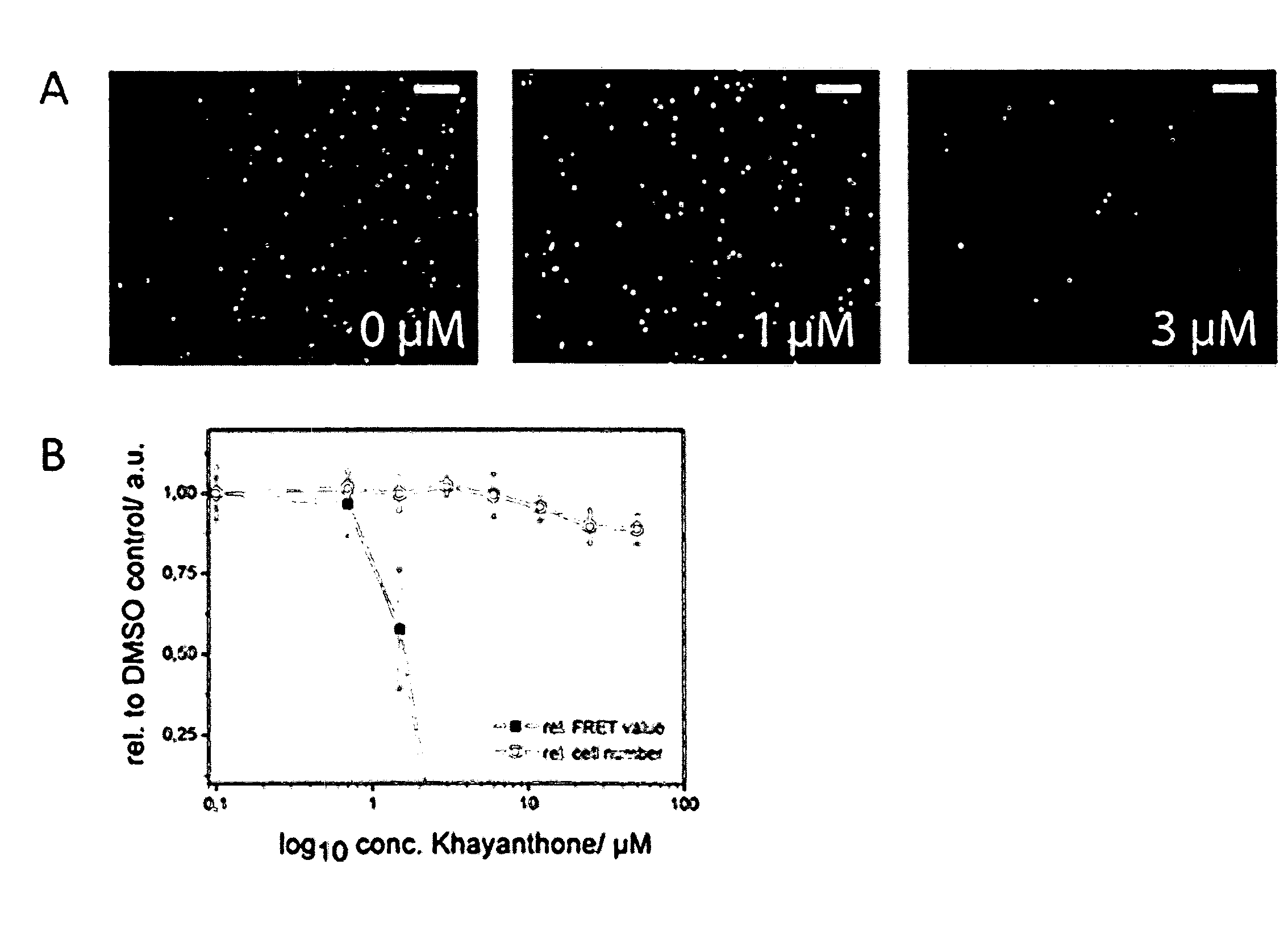
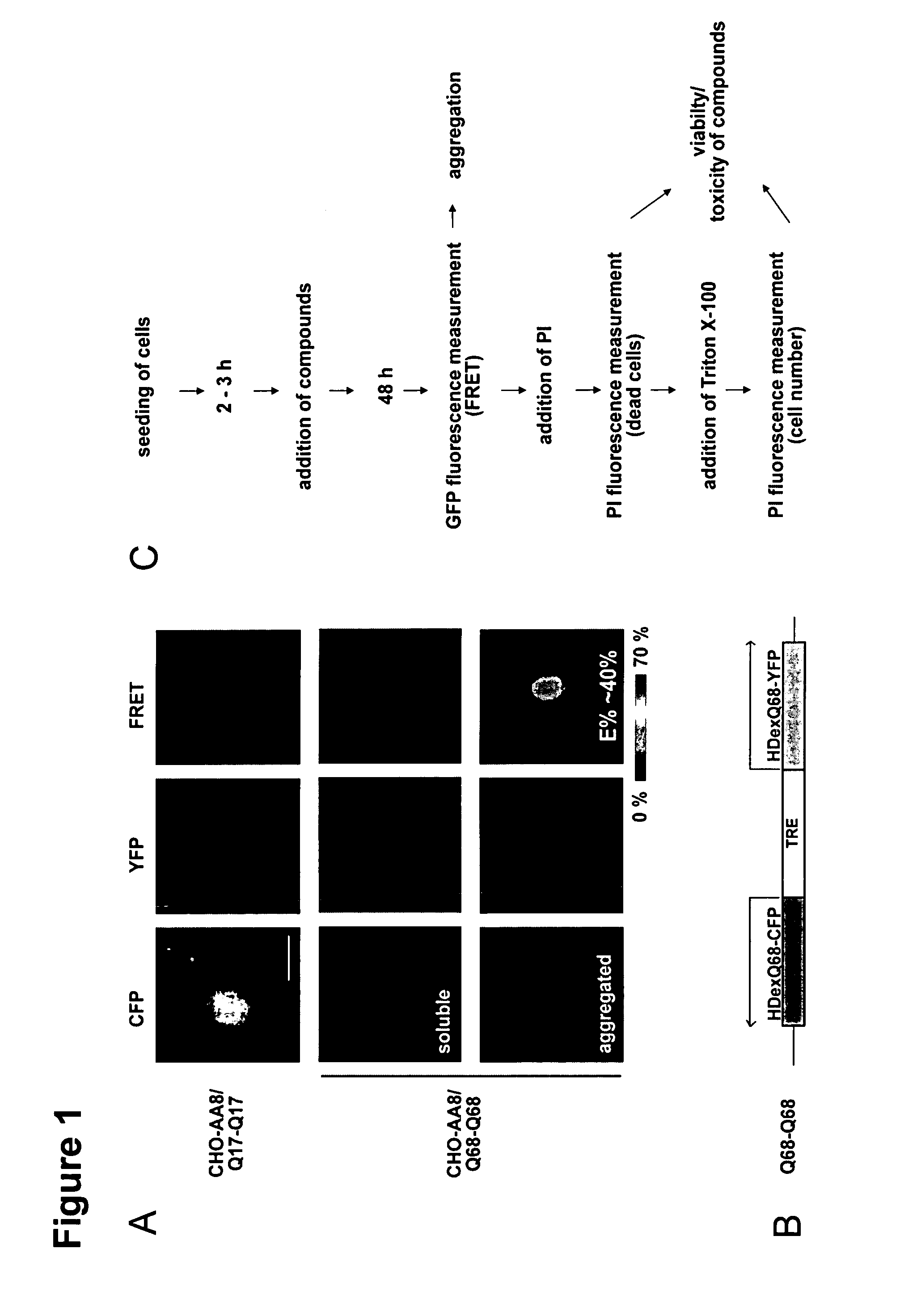
The present invention relates to tetranortriterpenoid compounds and pharmaceutical compositions thereof, which are provided for use in the treatment, diagnosis and / or prevention of trinucleotide repeat disorders (like a polyglutamine diseases, e.g Huntingdon's disease), amyloid diseases, neurodegenerative disease, protein misfolding diseases or tumors. The tetranortriterpenoid compounds of the present invention are further provided for the reduction and / or inhibition of the aggregation of amyloidogenic proteins, preferably of polyglutamine proteins (such as huntingtin) as well as for increasing proteasome activity. The present invention furthermore relates to nucleic acids, comprising the nucleotide sequences of two huntingtin fragments, as well as to cells and kits, which are useful in methods for assessing the aggregation of huntingtin and in methods for identifying compounds, which modulate the aggregation of huntingtin.
Owner:KIOSCHIS SCHNEIDER PETRA +5
Embryonic Cell-Based Therapeutic Candidate Screening Systems, Models for Huntington's Disease and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20190195863A1Inaccurate disease modelingOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaDisease
Compositions and methods disclosed concern an isogenic population of in vitro human embryonic stem cells comprising a disease form of the Huntingtin gene (HTT) at the endogenous HTT gene locus in the genome of the cell; wherein the disease form of the HTT gene comprises a polyQ repeat of at least 40 glutamines at the N-terminus of the Huntingtin protein (HTT). The cell lines of the disclosure comprise genetically-defined alterations made in the endogenous HTT gene that recapitulate Huntington's Disease in humans. Furthermore, the cell lines have isogenic controls that share a similar genetic background. Differentiating cell lines committed to a neuronal fate and fully differentiated cell lines are also provided and they also display phenotypic abnormalities associated with the length of the polyQ repeat of the HTT gene. These cell lines are used as screening tools in drug discovery and development to identify substances that fully or partially revert these phenotype abnormalities.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLLER UNIV
Protective effects of inhibiting the interaction of calmodulin and mutant huntingtin protein
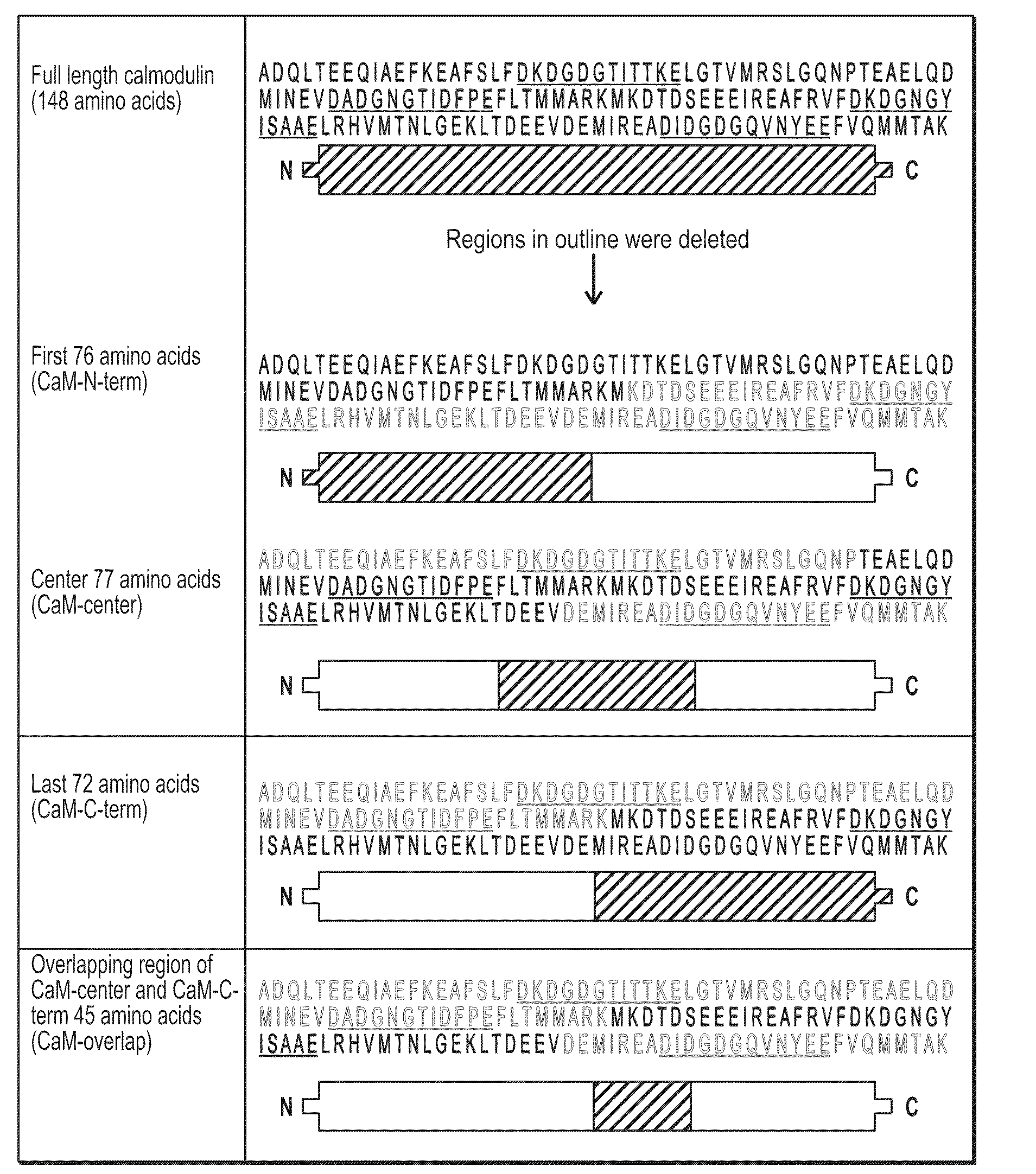
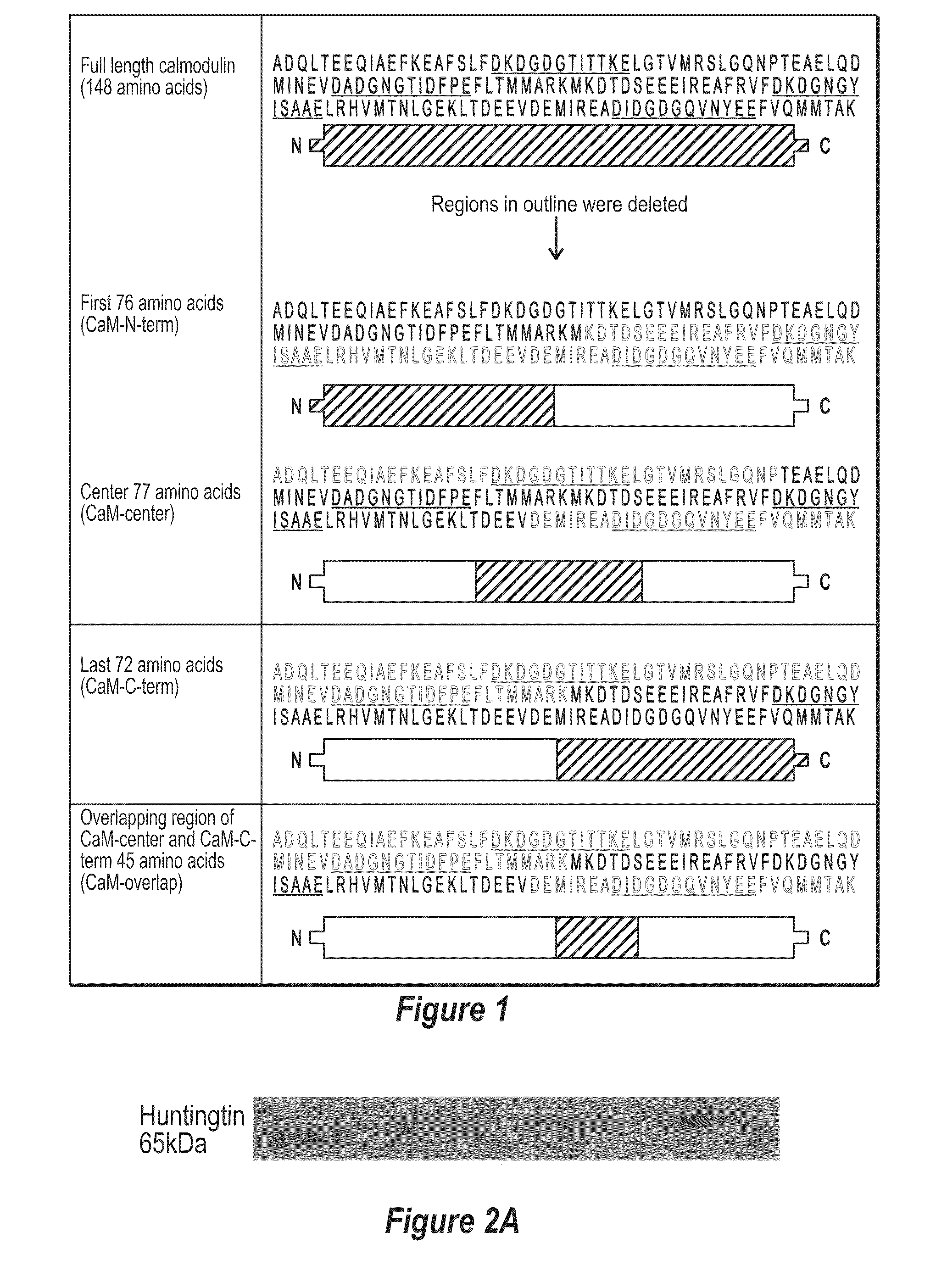
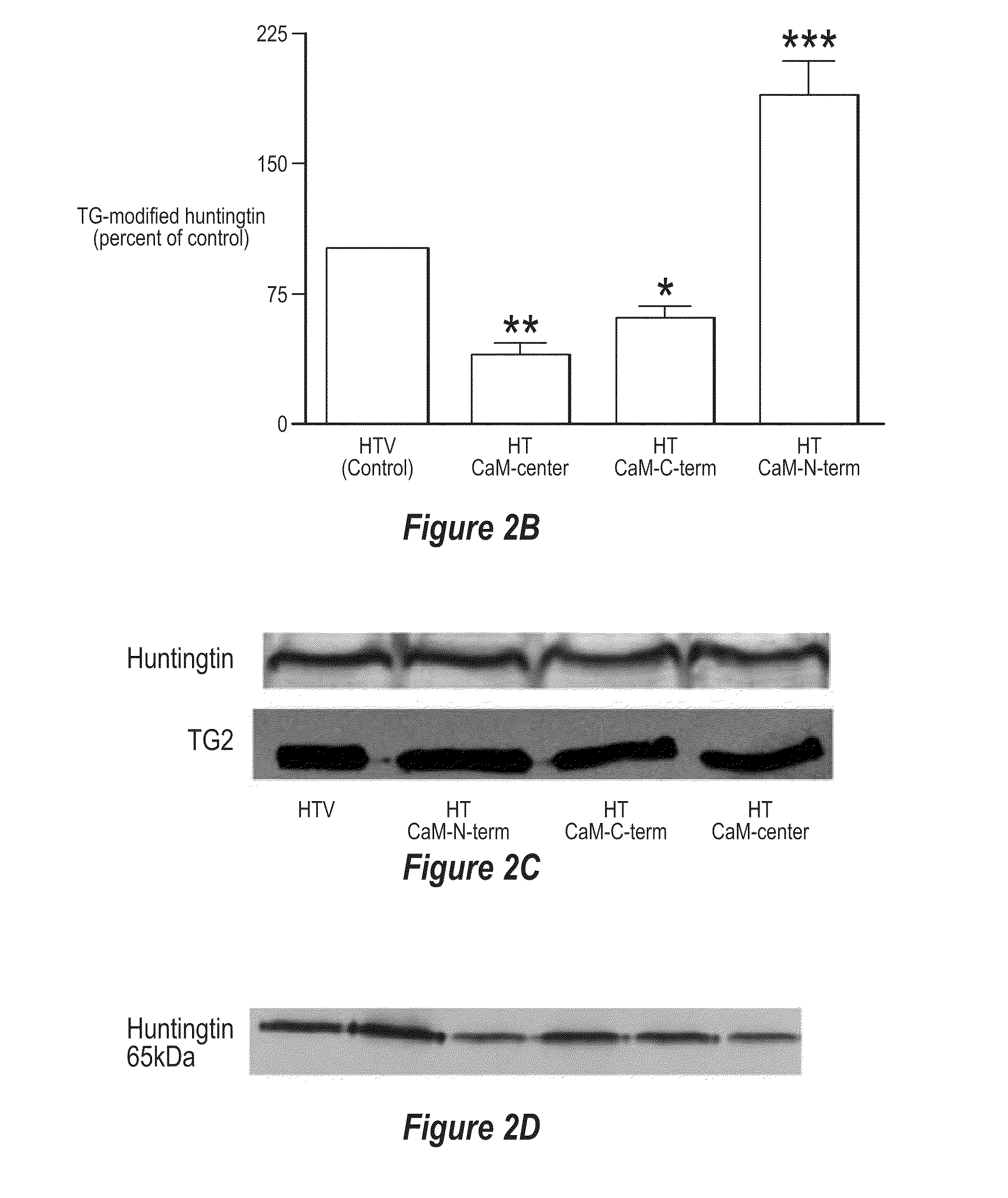
An artificial polypeptide can be used in a treatment for Huntington's disease. The inventive polypeptide sequence is capable of interacting with mutant huntingtin so as to inhibit interactions between mutant huntingtin or a fragment of mutant huntingtin and calmodulin. The inventive polypeptide sequence can be a portion of calmodulin described herein or an analog or derivative thereof that binds with the polyglutamate portion of a mutant huntingtin protein. For example, polypeptide sequence can include a sequence of KDTDSEEEIREAFRVFDKDGNGYISAAELRHVMTNLGEKLTDEEV (SEQ ID NO: 1) or a portion thereof analog thereof or derivative thereof.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
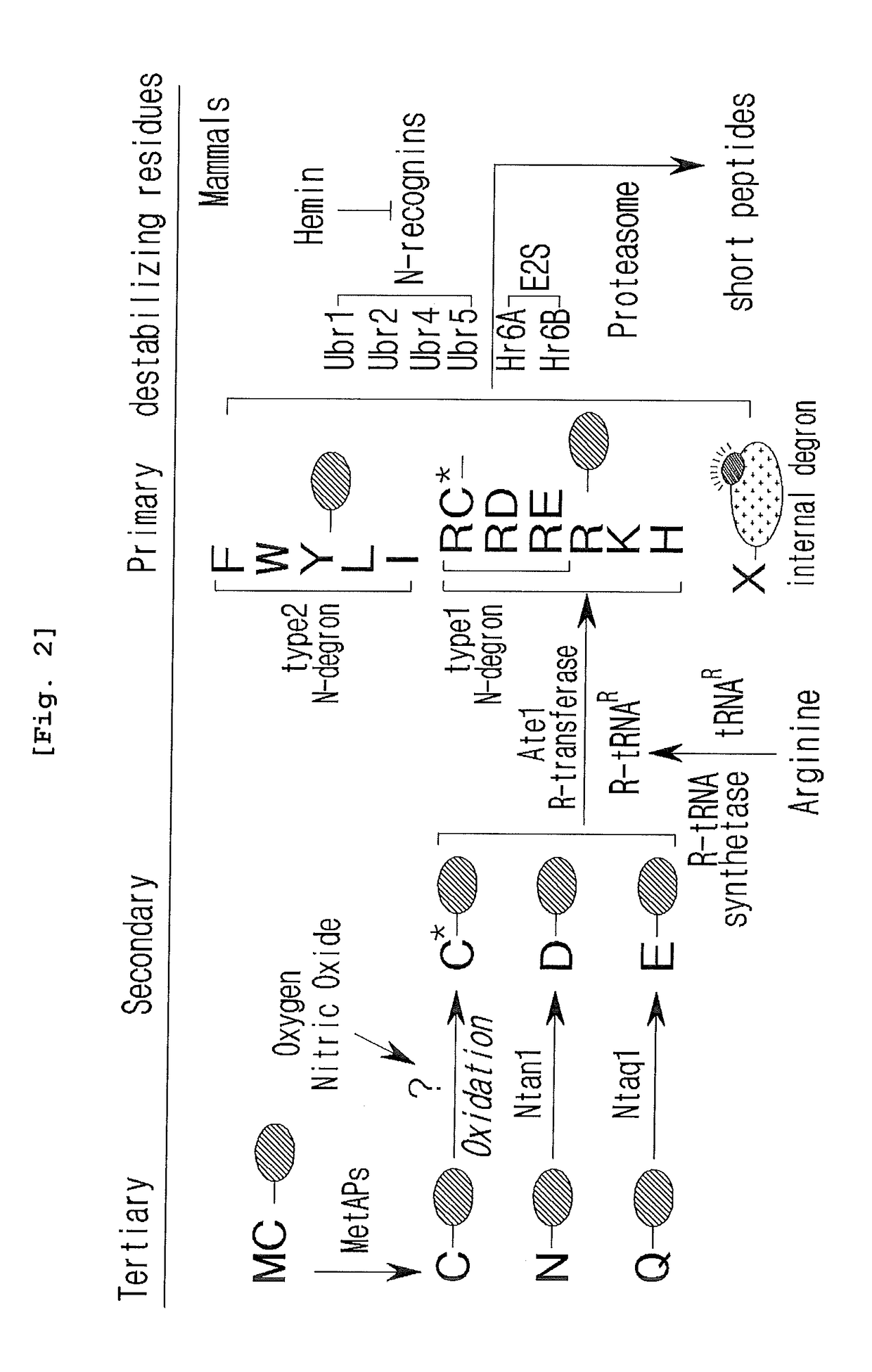
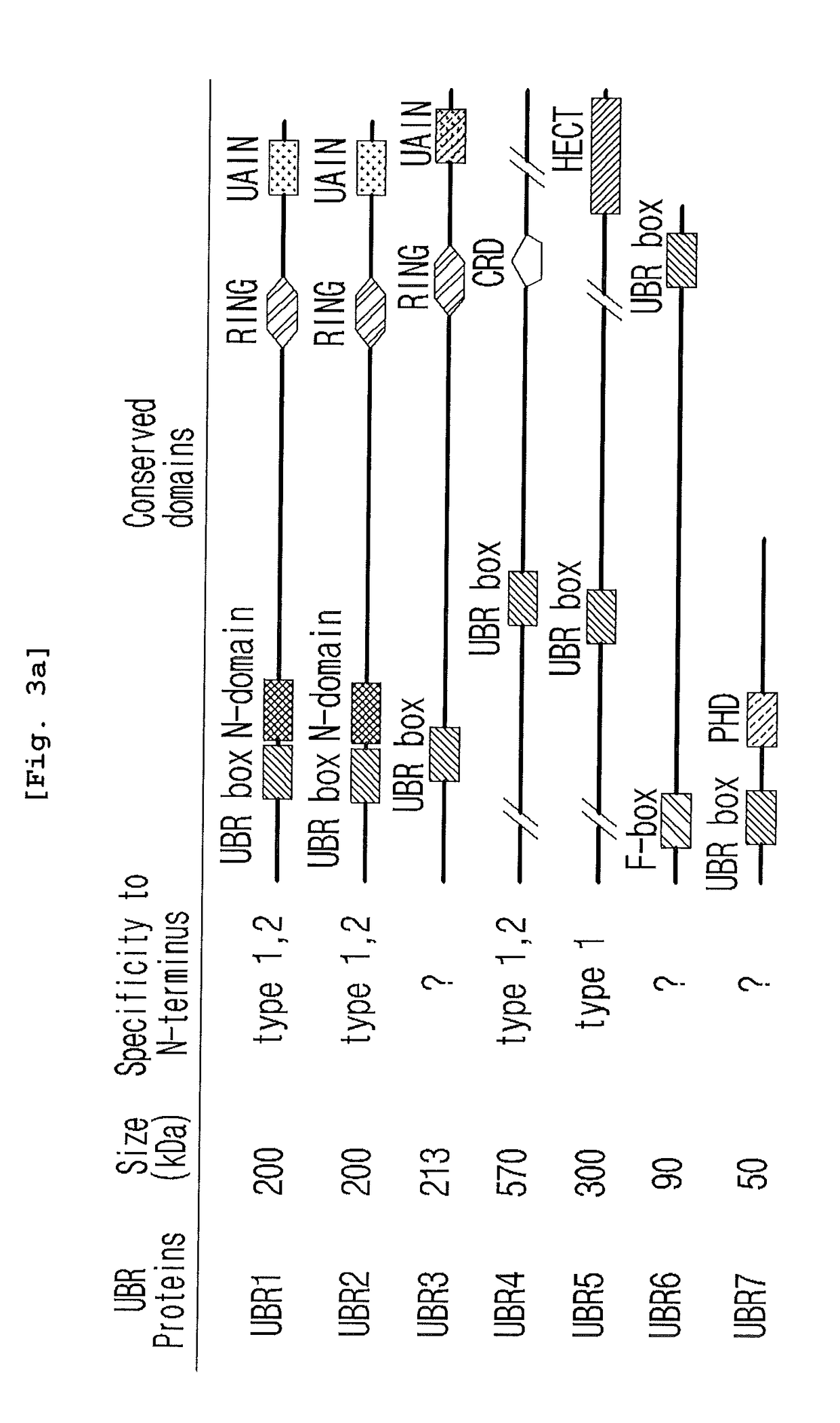
Prevention and Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Autophagy Activity Mediated by A Synthetic Ligand or Arginylated BIP Binding to the P62 ZZ Domain
ActiveUS20180243244A1Easy to useNervous disorderDipeptide ingredientsLysosomal proteolysisInclusion bodies
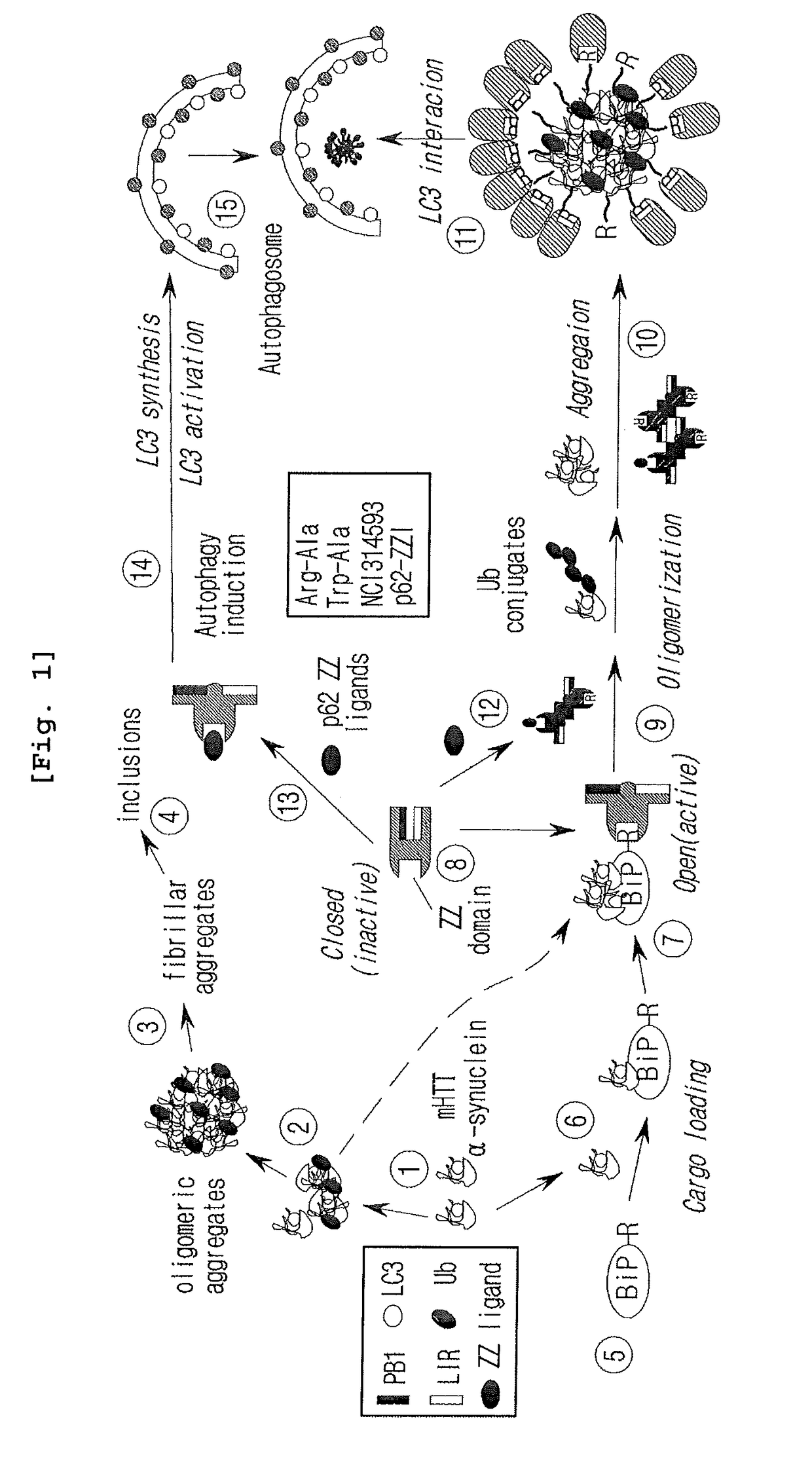
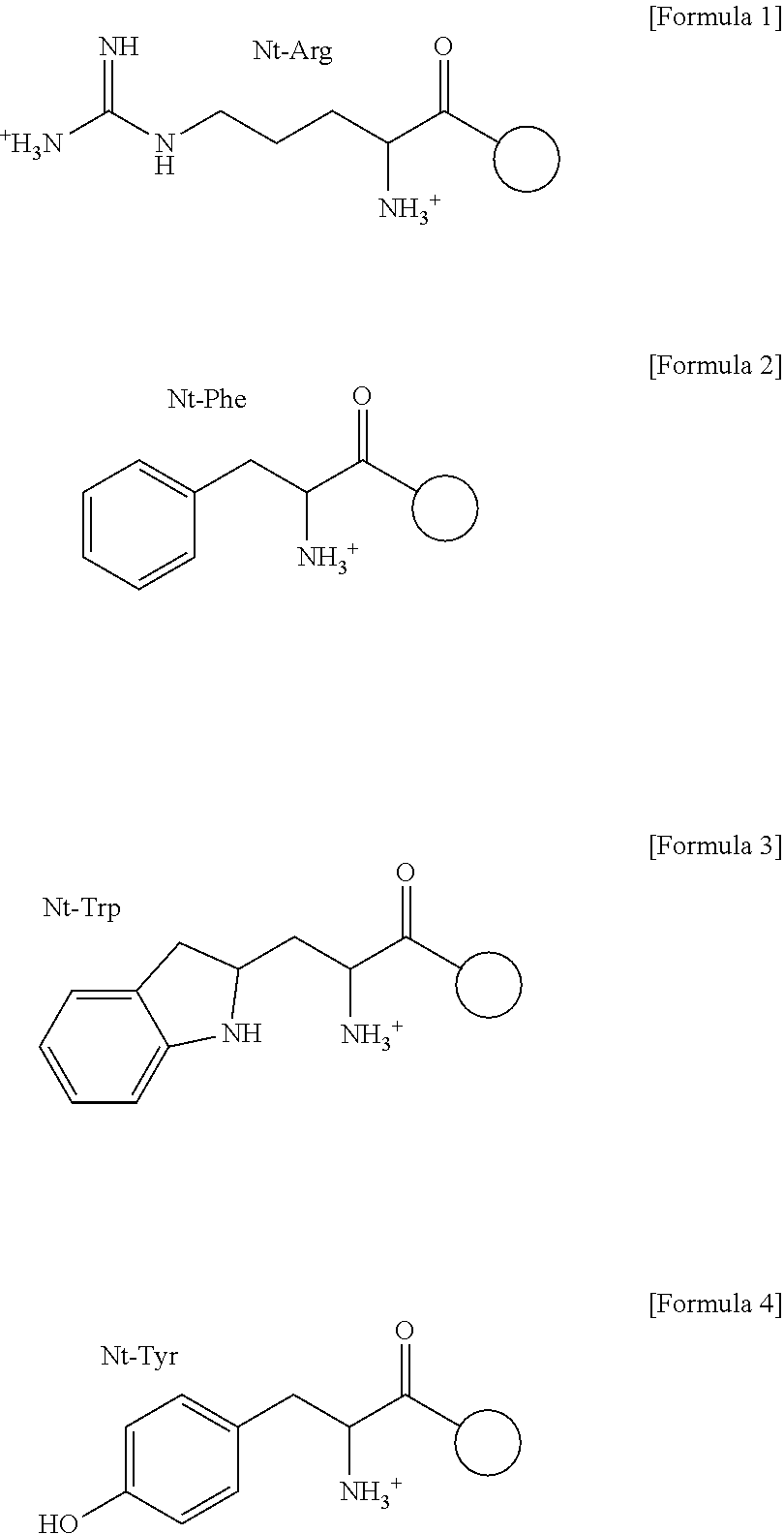
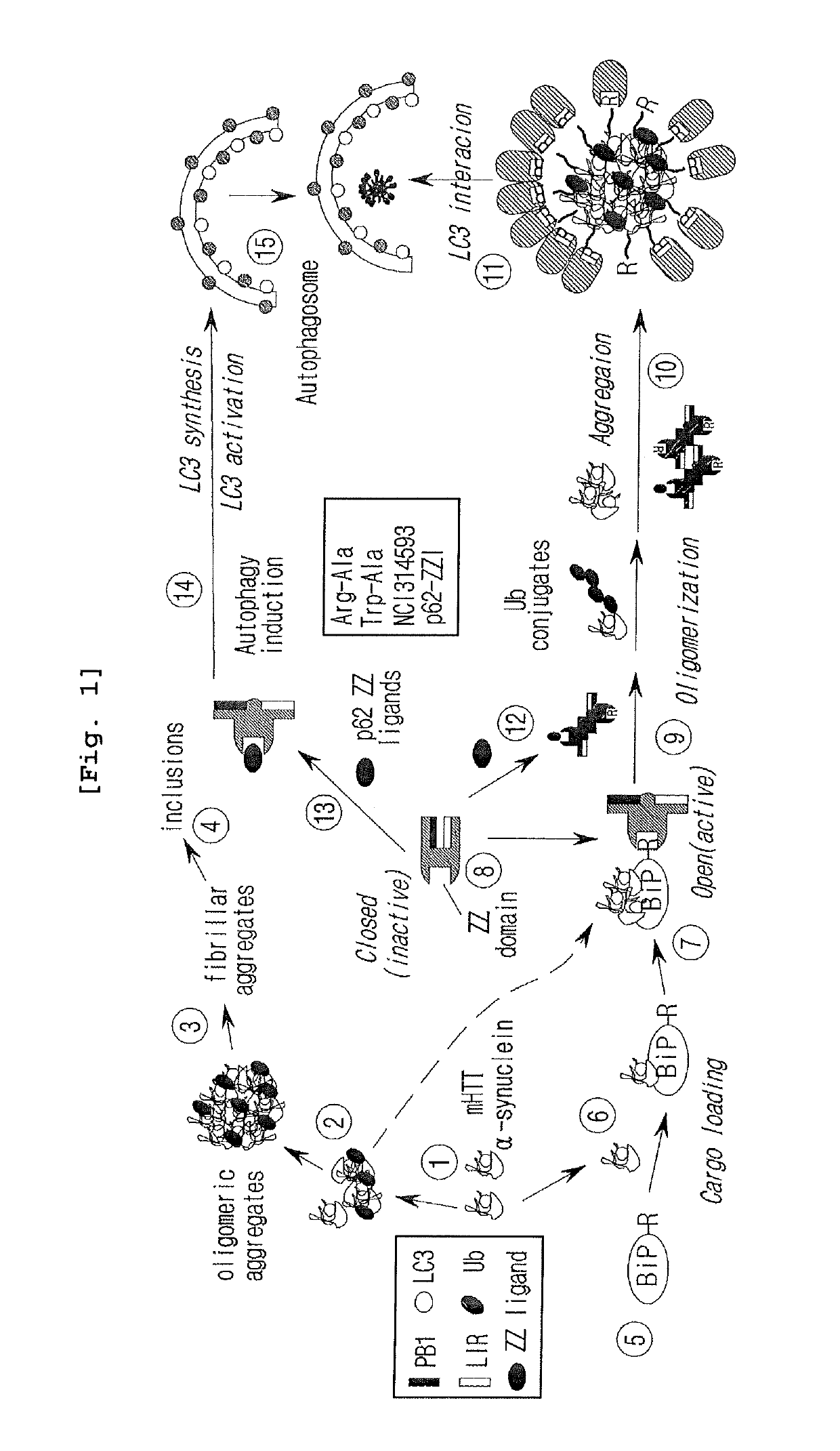
The pharmacokinetics and key technologies of the present invention are summarized in FIG. 1. Particularly, malignant misfolded proteins such as mutant huntingtin and alpha-synuclein are coagulated and grow into oligomeric coagulum (①, ②, fibrillar coagulum (③) and eventually inclusion body (④). Young neurons produce a large amount of Nt-Arg through N-terminal arginylation (⑤) of vesicle chaperones such as BiP secreted into the cytoplasm, and then arginylated BiP (R-BiP) is secreted binds to the misfolded proteins (⑥). As a ligand, the Nt-Arg of R-BiP binds to the p62 ZZ domain (⑦), and the normally inactivated closed form of p62 is changed to an open form, leading to structural activation (⑧). As a result, PB1 and LC3-binding domains are exposed. The PB1 domain induces oligomerization (⑨), leading to the concentration as a p62 body (⑩) that is a coagulum capable of being degraded by autophagy. Then, p62 binds to LC3, which is protruding from the autopagosomal membranes, leading to the completion of autophagy targeting (⑪) and lysosomal proteolysis. Since autophagy proteolysis including steps (⑤)-(⑪) is strong in young neurons, cytotoxic protein coagulums (①-⑤) do not accumulate. However in aged neurons, autophagy proteolysis including steps ⑤-⑪ is weakened, and protein coagulums (①-⑤) accumulate and become cytotoxic. In this invention, p62 is intentionally activated (⑫, ⑬) by using low mass ligands of the p62 ZZ domain to effectively remove huntingtin and alpha-synuclein protein coagulums. Particularly, in step ⑫, p62 ligated with a ligand accelerates the oligomerization of p62-R-BiP-misfolded protein (⑨) and the formation of autophagy coagulum (⑩). In step (⑬), the ligand-p62 conjugate acts as an autophagy activator (⑭) to induce the synthesis of LC3 and the conversion of LC3-I into LC3-II in order to accelerate the formation of autophagosomes (⑮).
Owner:AUTOTAC BIO
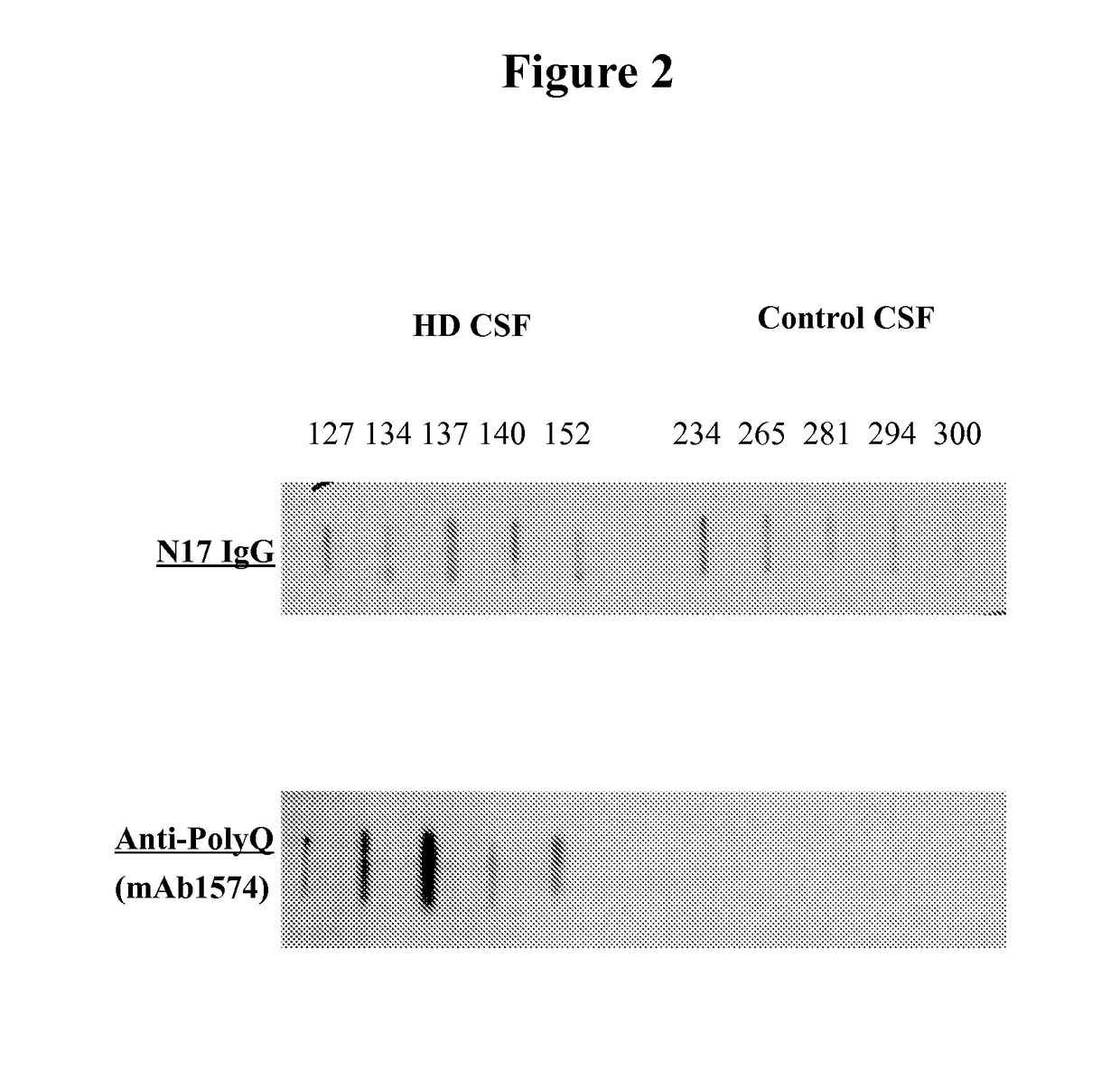
Diagnostic and monitoring system for Huntington's disease
ActiveUS9989540B2The process is simple and fastDisease diagnosisBiological testingHuntingtons choreaMedicine
The invention provides assays that identify Huntington's disease and monitor the progression and severity of conditions associated with variant Huntingtin protein (Httn). In particular, the invention provides assays that monitor the severity and progression of Huntington's Disease as well as predict the onset of symptoms. The invention also provides assays for identifying drugs for treating Huntington's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Probes for imaging huntingtin protein
ActiveCN108135172ABiocideIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsCompound (substance)Imaging agent
Owner:CHDI FOUND
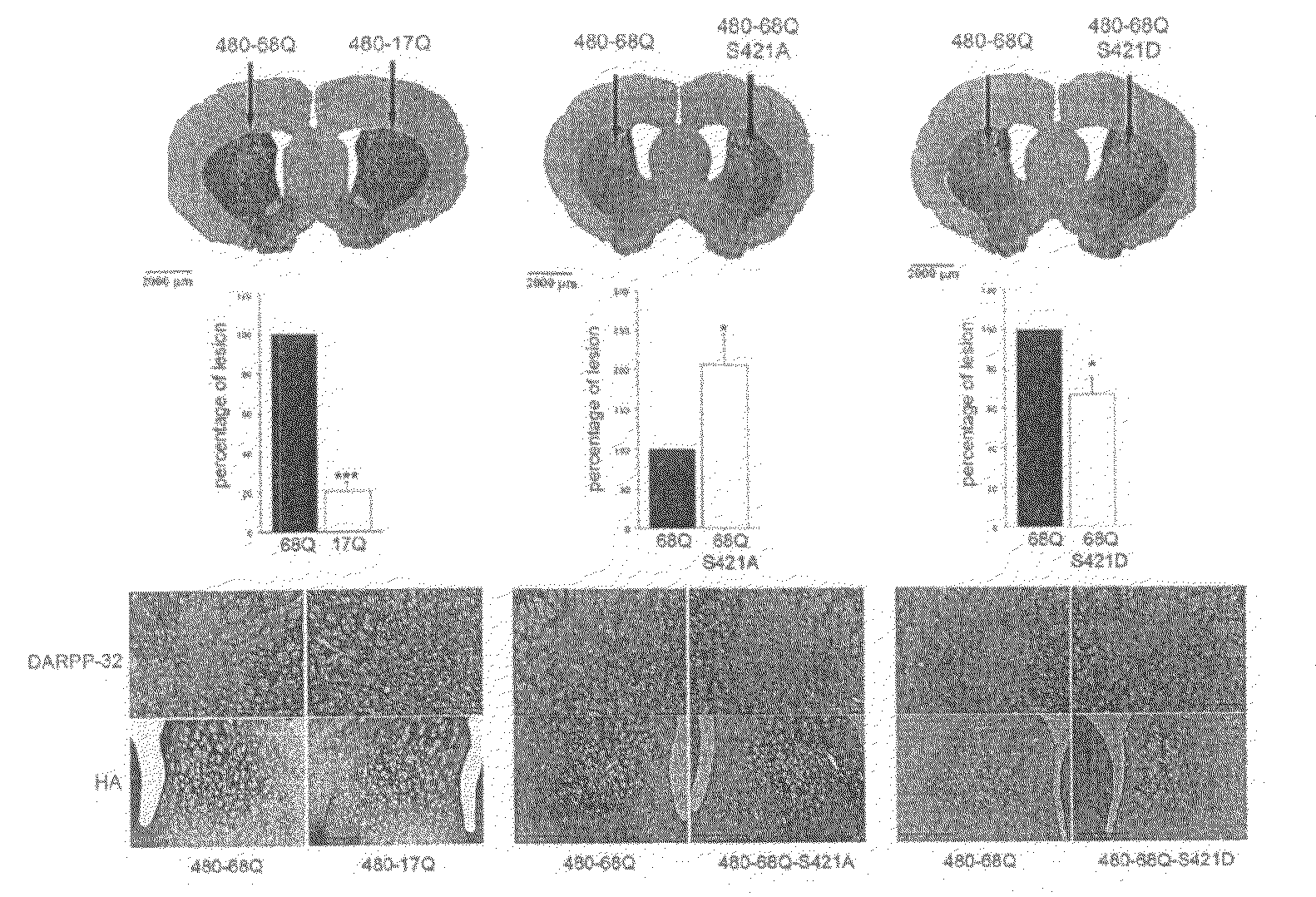
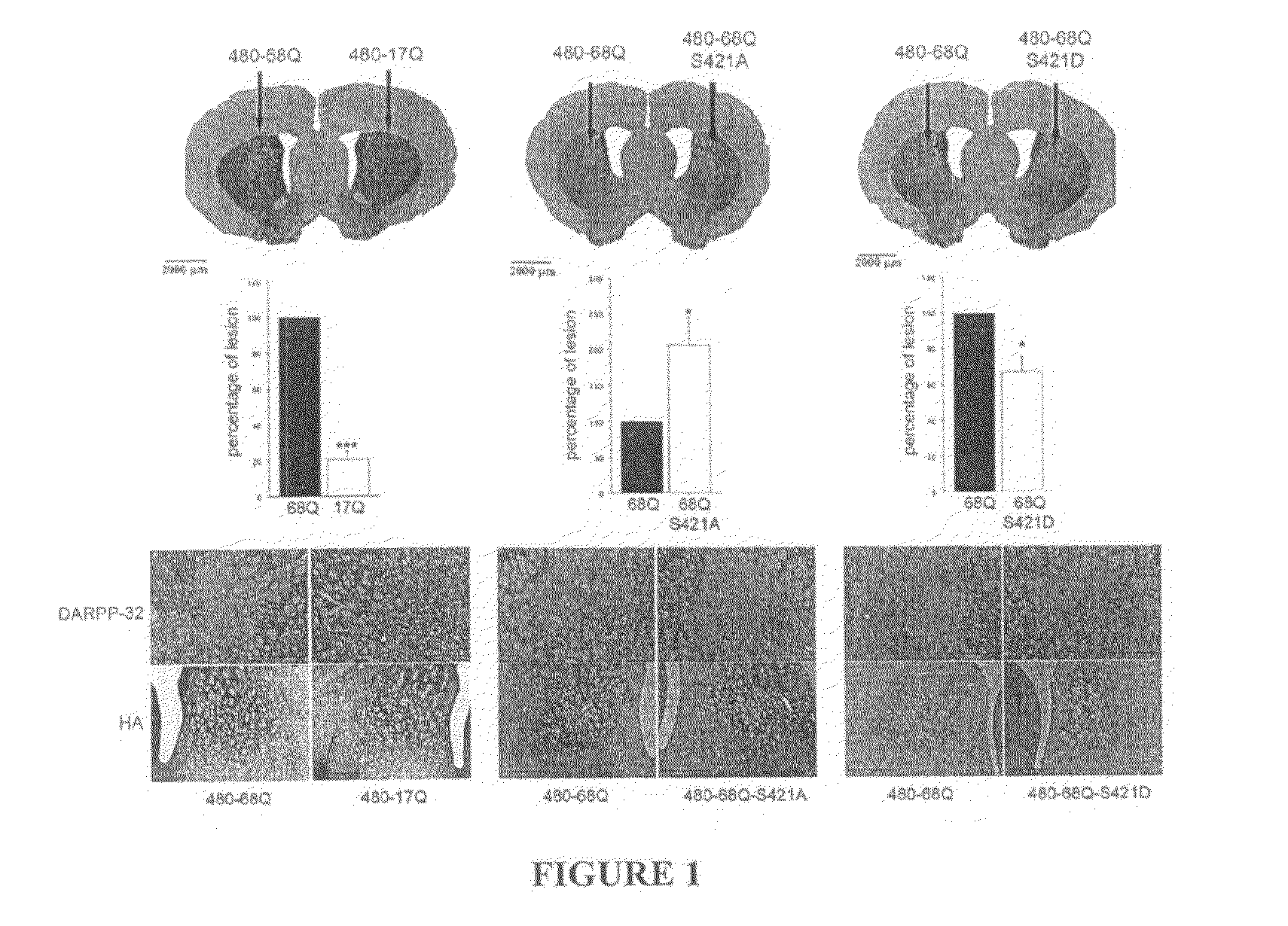
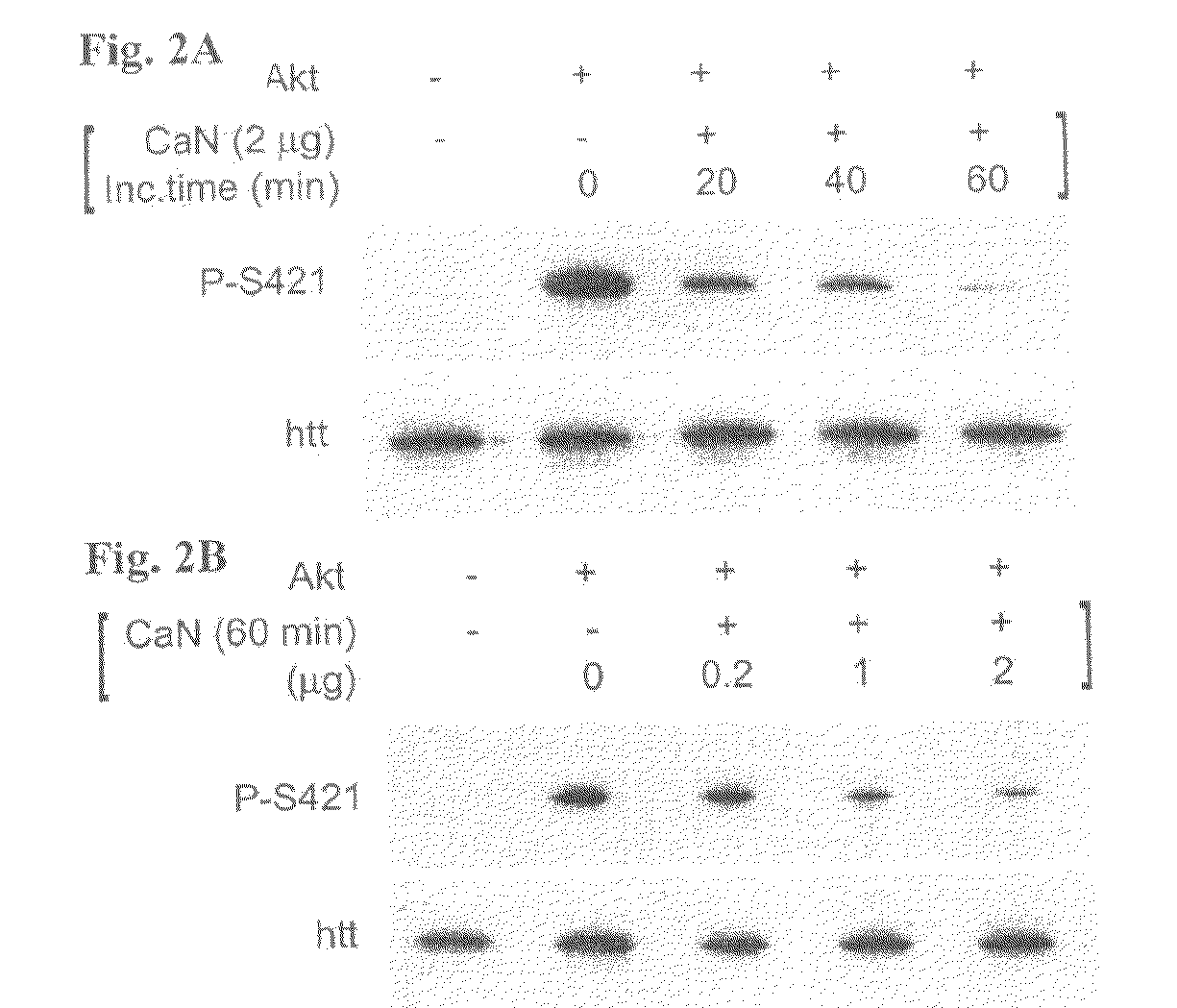
Method For Treating Huntington's Disease by Inhibiting Dephosphorylation of Huntingtin at S421
InactiveUS20080300178A1Increased phosphorylationDecreasing polyQ-huntingtin-induced toxicityBiocideCompound screeningHuntingtons choreaPhosphorylation
The present invention relates to a method for treating patients having Huntington's disease by a drug increasing the phosphorylation of huntingtin at position S421, thereby decreasing the polyQ-huntingtin-induced toxicity.
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +1
Nucleic acids encoding a polyglutamine fusion protein
InactiveUS7179897B2Reduce aggregationReduce fluorescenceSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsAmyloidDNA
Methods of identifying compounds that disrupt aggregation of aggregation-disposed polypeptides, such as huntingtin or beta-amyloid protein, are disclosed. Furthermore, an artificial polypeptide that contains an extended polyglutamine region and DNA that encodes the polypeptide are also disclosed.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
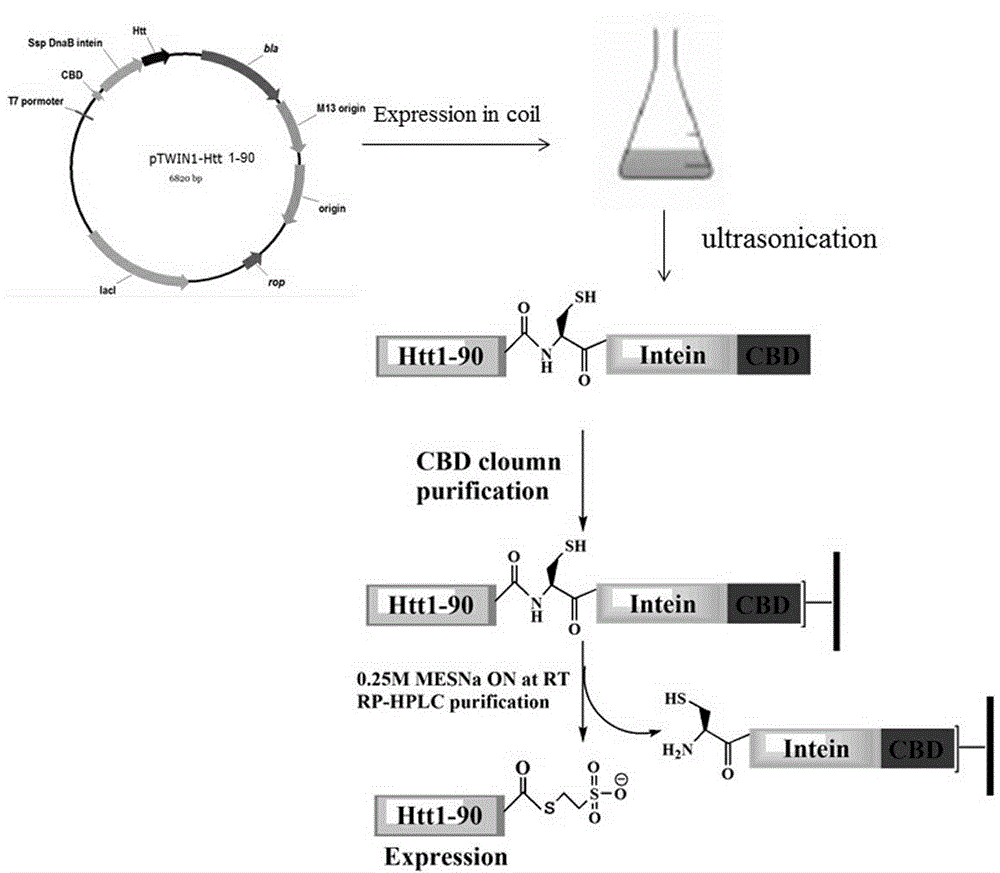
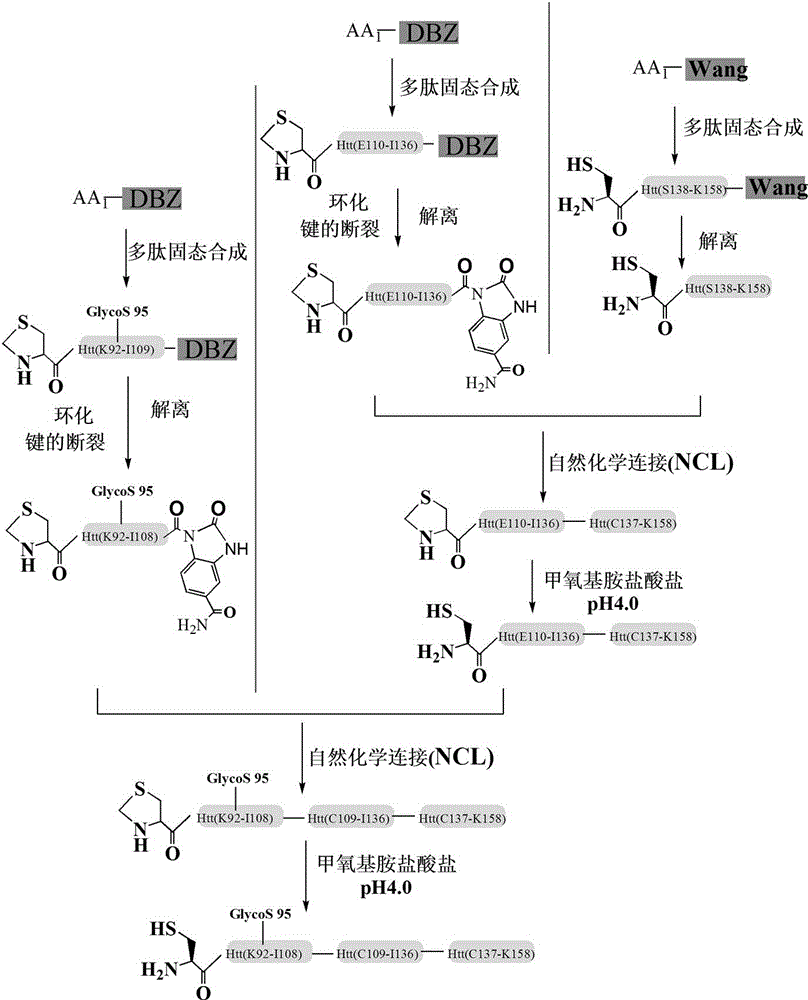
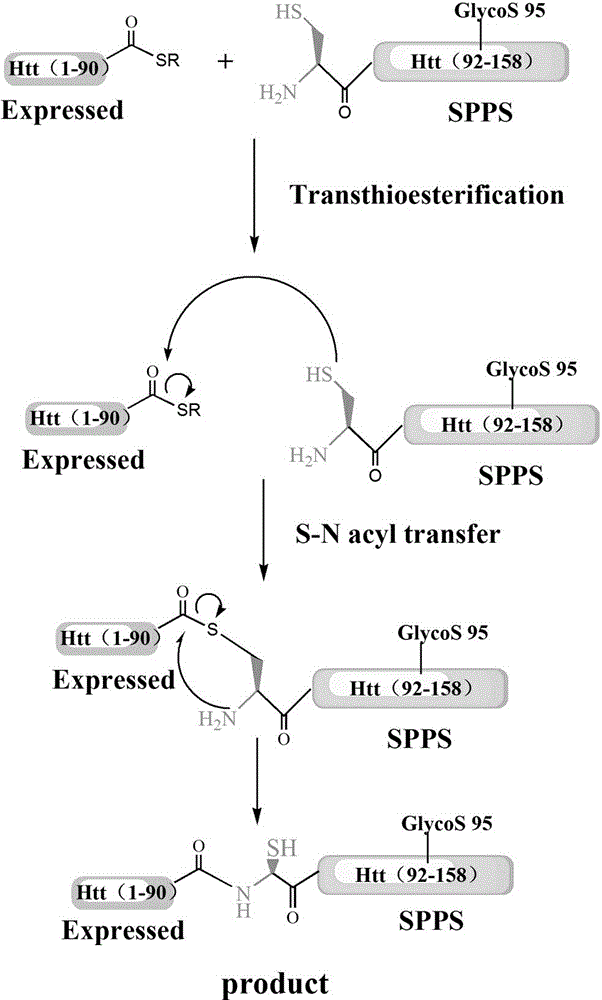
Glycosylation modification method of huntingtin protein
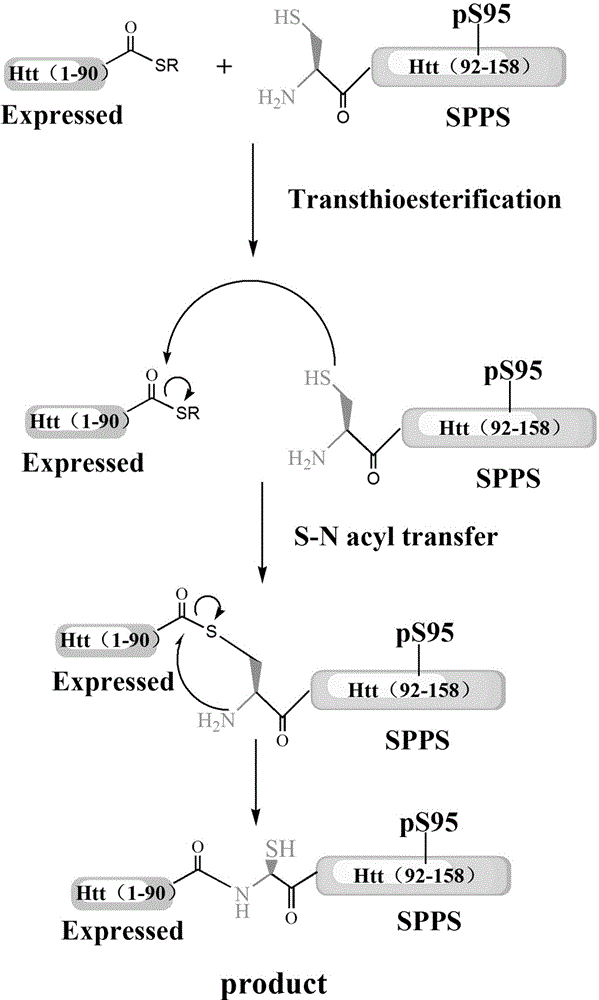
ActiveCN103601797BImprove stabilityPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesEscherichia coliProtein target
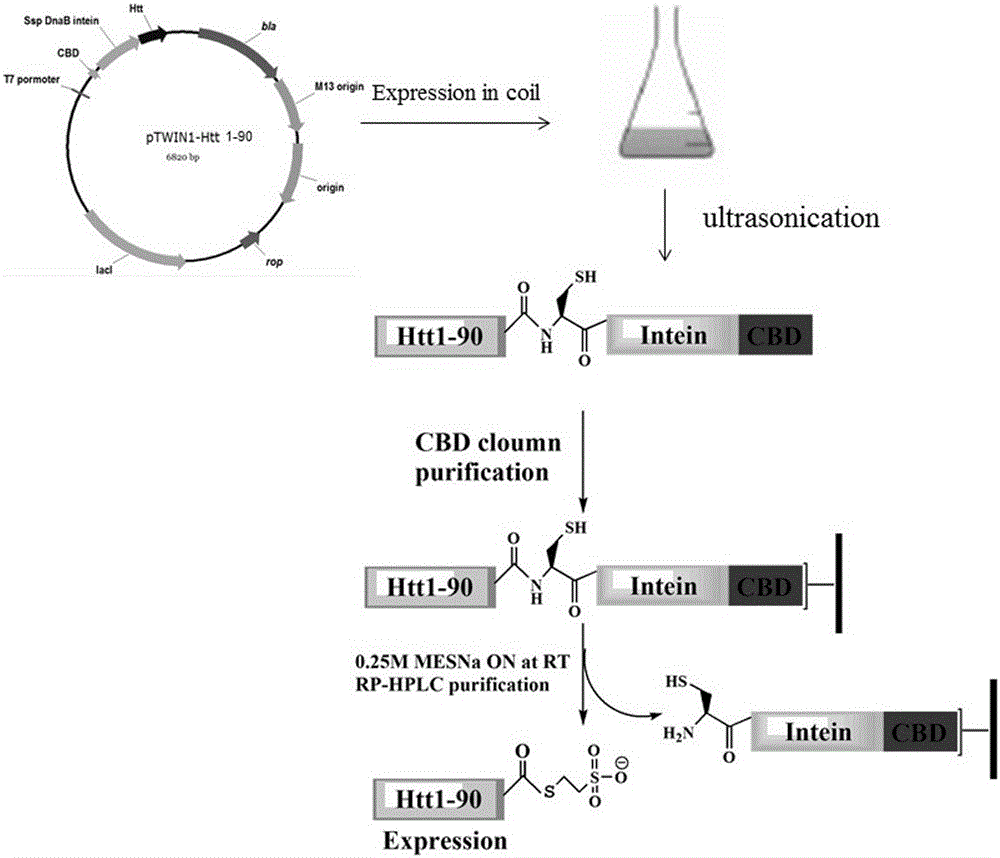
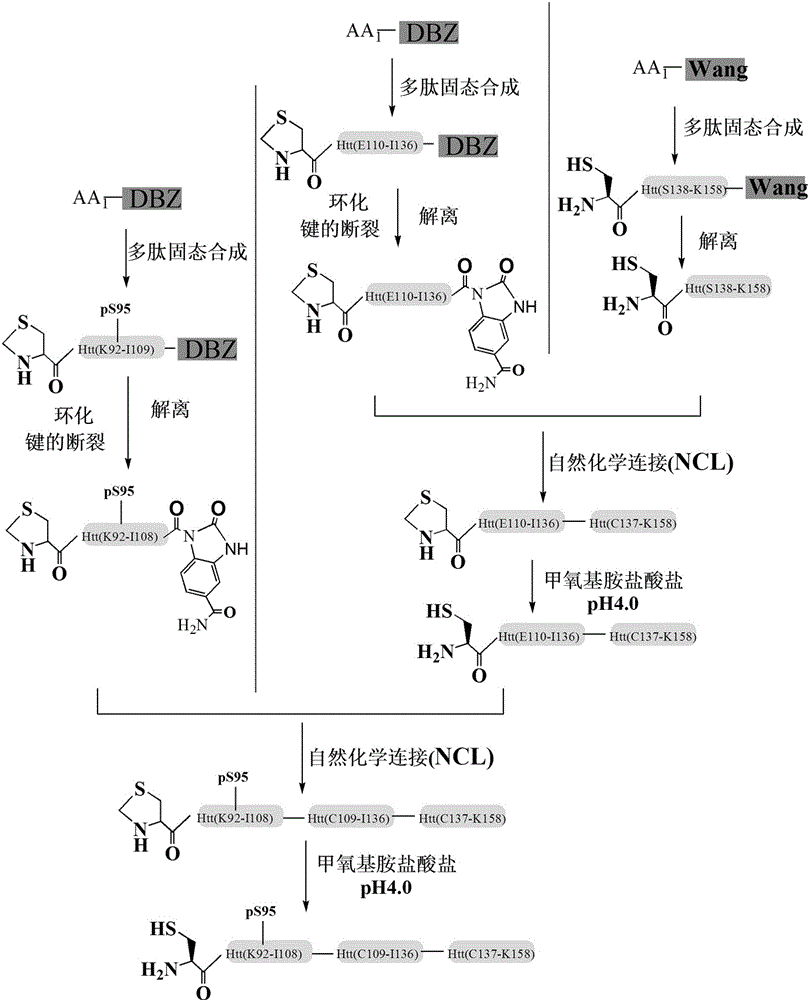
The invention discloses a glycosylation modification method of hungtintin. The glycosylation modification method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a recombinant protein Htt(1-90), to be specific, a. obtaining a hungtintin gene, b. constructing a recombinant expression plasmid pTWIN1-htt, c. constructing a recombinant escherichia coli strain DH5 alpha-htt for expressing the hungtintin, and d. expressing the recombinant protein; (2) purifying the recombinant protein Htt(1-90); (3) obtaining a glycosylation modified Htt(Cys-K92-K158) polypeptide by using an SPPS (stable protein plasma solution) method; (4) purifying the Htt(Cys-K92-K158) polypeptide; (5) coupling the Htt(Cys-K92-K158) polypeptide with the recombinant protein Htt(1-90) so as to obtain a glycosylation modified target protein Htt(1-158); (6) purifying the glycosylation modified target protein Htt(1-158). The glycosylation modification on the hungtintin shows that the glycosylated hungtintin has relatively strong stability; the influence of the temperature and the time on absorption peaks of the hungtintin shows that the hungtintin subjected to glycosylation modification is relatively stable.
Owner:浙江璞题生物科技有限公司
Application of carbon-based nanomaterials in the preparation of drugs for alleviating or treating hd
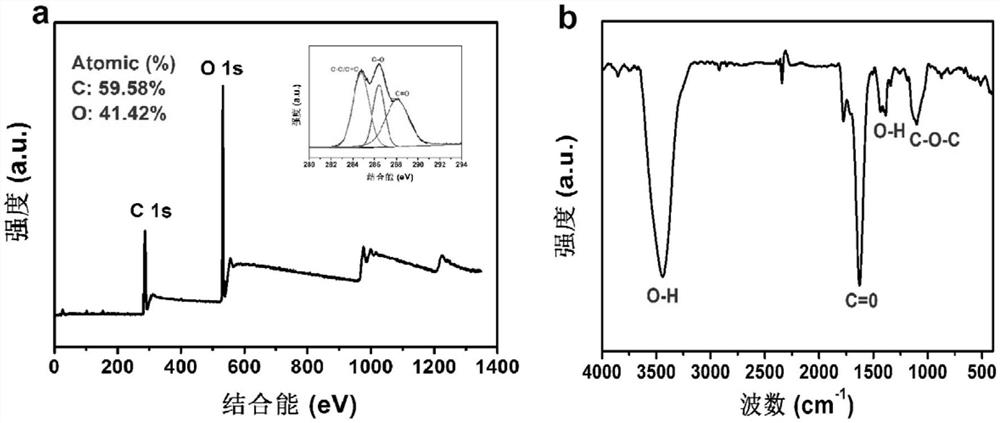
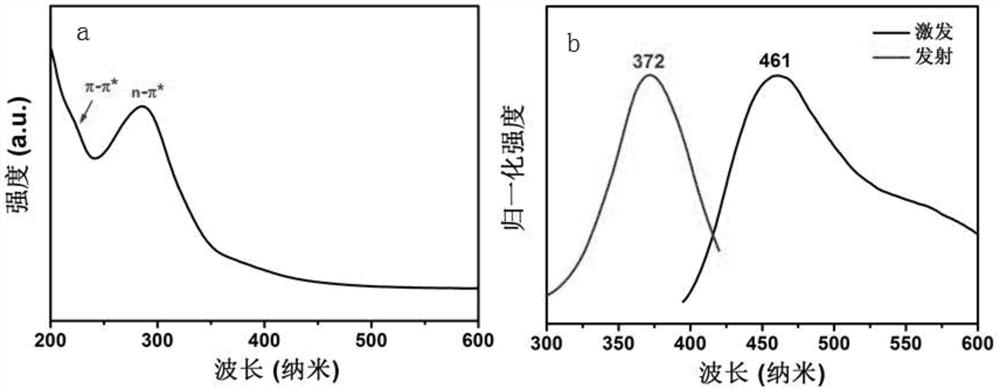
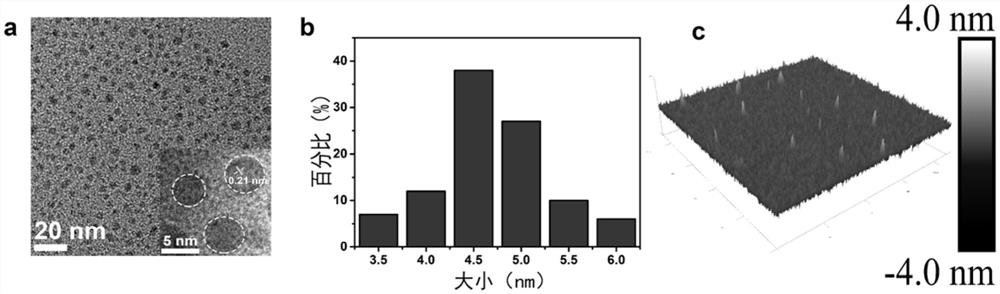
ActiveCN110251532BEffective treatmentSmall particle sizeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCarbon based nanomaterialsPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses the application of carbon-based nanomaterials in the preparation of drugs for relieving or treating HD, and solves the problem of high synthesis cost of existing carbon nanomaterials such as fullerenes. The carbon-based nanomaterials have good water solubility, degradability and It can effectively inhibit the aggregation of mutant huntingtin protein mHtt and other significant advantages; through cell experiments and animal experiments, it was found that carbon-based nanomaterials can alleviate the toxicity of mHtt aggregation to neurons and improve the learning and memory ability of HD model mice.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases through autophagy activity mediated by a synthetic ligand or arginylated BIP binding to the P62 ZZ domain
ActiveUS10391067B2Easy to useNervous disorderDipeptide ingredientsLysosomal proteolysisInclusion bodies
Owner:AUTOTAC BIO
Diagnostic and monitoring system for huntington's disease
ActiveUS20160178645A1The process is simple and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHuntingtons choreaSymptom attack
The invention provides assays that identify Huntington's disease and monitor the progression and severity of conditions associated with variant Huntingtin protein (Httn). In particular, the invention provides assays that monitor the severity and progression of Huntington's Disease as well as predict the onset of symptoms. The invention also provides assays for identifying drugs for treating Huntington's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Phosphorylation modification method of huntingtin protein
InactiveCN103601799BInhibit aggregationReduce cohesionPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesEscherichia coliProtein target
The invention discloses a phosphorylation modification method of hungtintin. The phosphorylation modification method of the hungtintin comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a recombinant protein Htt(1-90), to be specific, a. obtaining a hungtintin gene, b. constructing a recombinant expression plasmid pTWIN1-htt, c. constructing a recombinant escherichia coli strain DH5 alpha-htt for expressing the hungtintin, and d. expressing the recombinant protein; (2) purifying the recombinant protein Htt(1-90); (3) obtaining a phosphorylation modified Htt(Cys-K92-K158) polypeptide by using an SPPS (stable protein plasma solution) method; (4) purifying the Htt(Cys-K92-K158) polypeptide; (5) coupling the Htt(Cys-K92-K158) polypeptide with the recombinant protein Htt(1-90) so as to obtain a phosphorylation modified target protein Htt(1-158); (6) purifying the phosphorylation modified target protein Htt(1-158). The phosphorylation modified hungtintin has the advantages that the aggregation of the hungtintin is reduced, the aggregation time of the hungtintin is also improved, after aggregation, the length and the height of the hungtintin are improved, the aggregation of the hungtintin is obviously delayed, and the toxic and side effects of the hungtintin on nerve cells are hindered very well.
Owner:杭州拜善晟生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com