Pumped refrigerant loop cooling system for cooling High thermal density heat loads
a technology of heat load and cooling system, which is applied in the field of cooling of electrical and electronic components, can solve the problems of increasing thermal density, reducing the life of equipment, and unreliable performance, and achieves the effect of high thermal density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
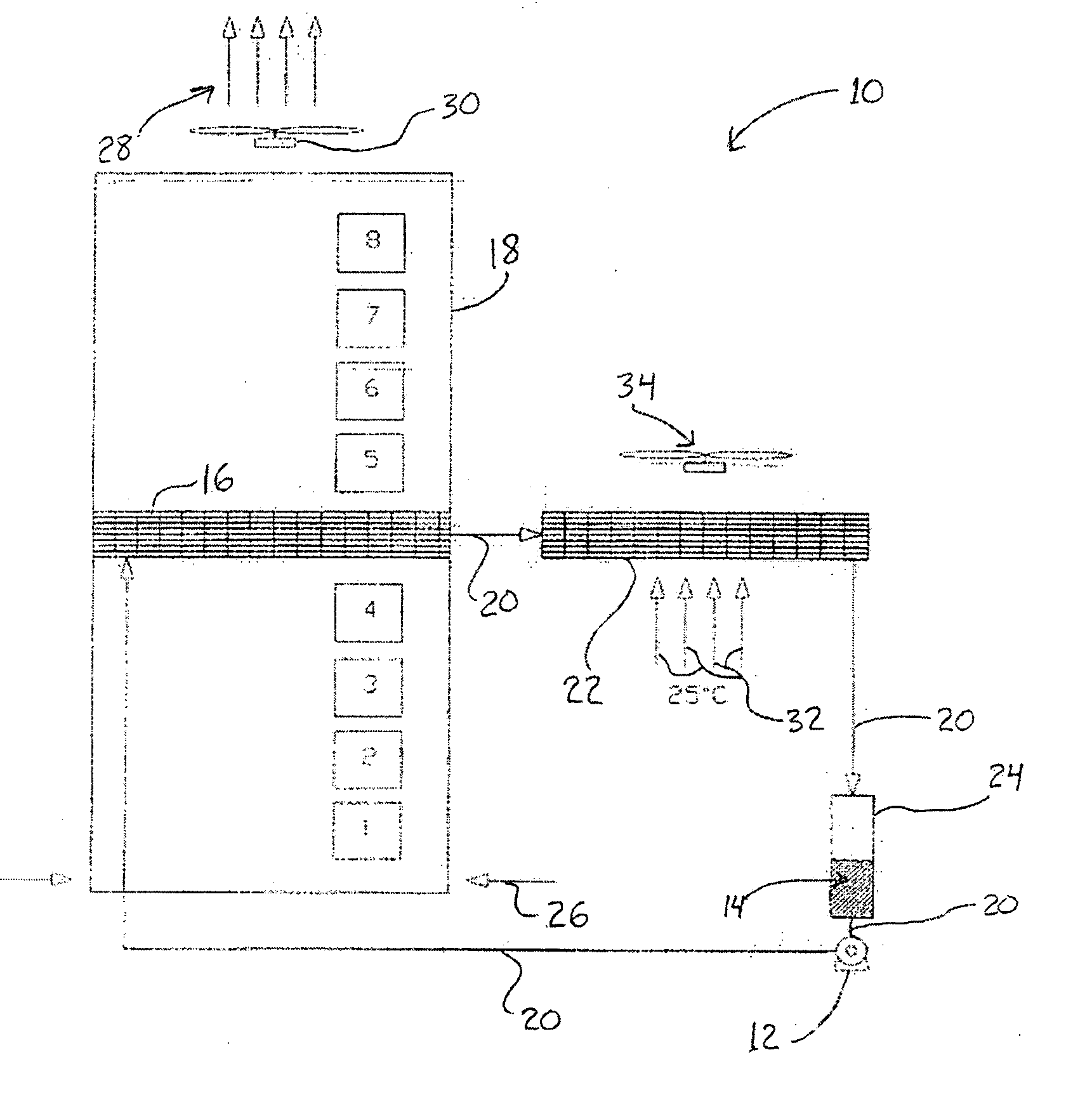
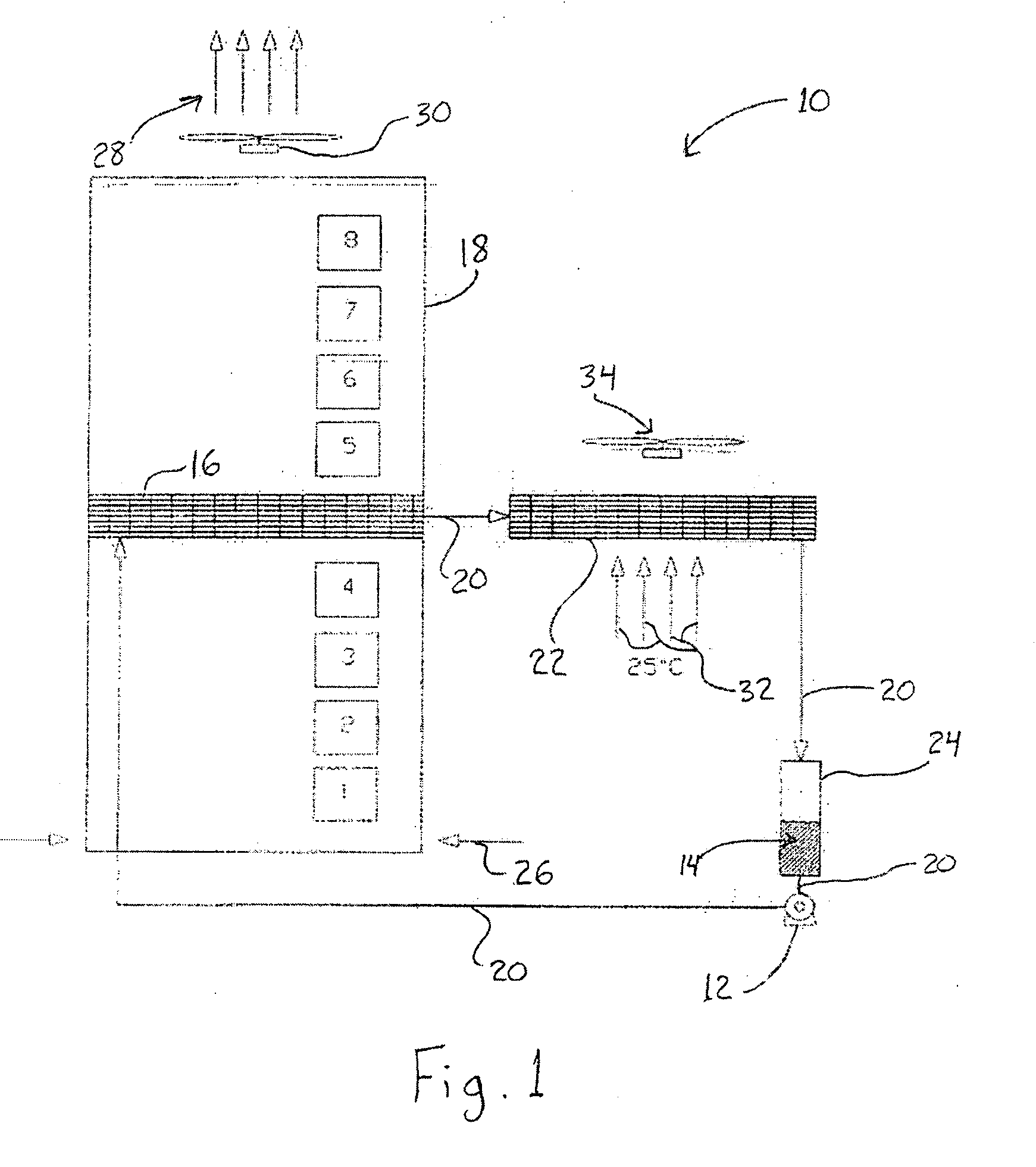
[0015]Referring to the Figure, the disclosed cooling system, illustrated as a pumped refrigerant loop system 10, includes a refrigerant pump 12 which pumps a vaporizable refrigerant 14. The vaporizable refrigerant may be any fluid which changes from a liquid to a vapor with the addition of heat and has other thermophysical properties suitable for the application. One such refrigerant is R-134a, well known to those skilled in the art. There are many other refrigerants suitable for this application which those skilled in the art could suggest as well.
[0016]Continuing with FIG. 1, the present invention uses the pump 12 to circulate the vaporizable, or volatile, refrigerant 14, as a liquid, to an evaporator device 16 located in close proximity to or in direct contact with the air stream within a computer or telecommunication rack or enclosure 18. Conduits 20 serve to transport refrigerant to the evaporator device 16, a condenser 22, a liquid receiver 24, and back to the pump 12.
[0017]Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com