Conjugate Electrospinning Devices, Conjugate Nonwoven and Filament Comprising Nanofibers Prepared by Using the Same
a technology of conjugating electrospinning and nanofibers, which is applied in the direction of spinnerette packs, filament/thread forming, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the electric force, failing to overcome the interface or surface tension of spinning dopes, and deteriorating the quality of the product, etc., to achieve the effect of simple facility and process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0111]Poly (ε-caprolactone) polymer (product of Aldrich, USA) having a number average molecular weight of 80,000 was dissolved in a mixed solvent of methylene chloride and N,N-dimethyl formamide (volume ratio: 75 / 25) at a concentration of 13 wt %, to prepare a spinning dope. The surface tension of the polymer spinning dope was 35 mN / m, the spinning dope viscosity was 35 centipoises at a room temperature, the electric conductivity was 0.02 mS / m, and the permittivity was 90.
[0112]Polyurethane resin (Pellethane 2103-80AE of Dow Chemical Company) having a number average molecular weight of 80,000 was dissolved in N,N dimethyl formamide at 8 wt. %.
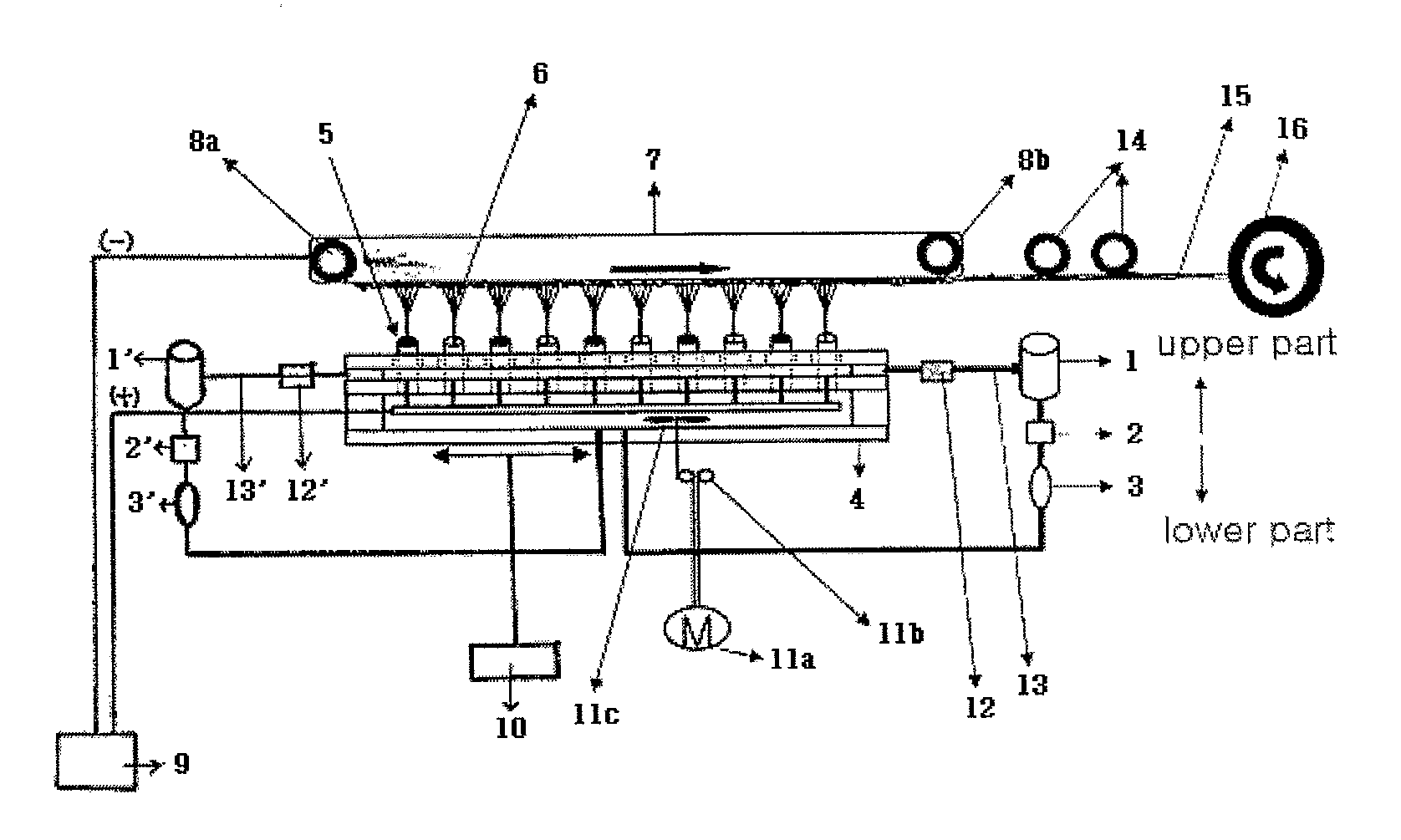
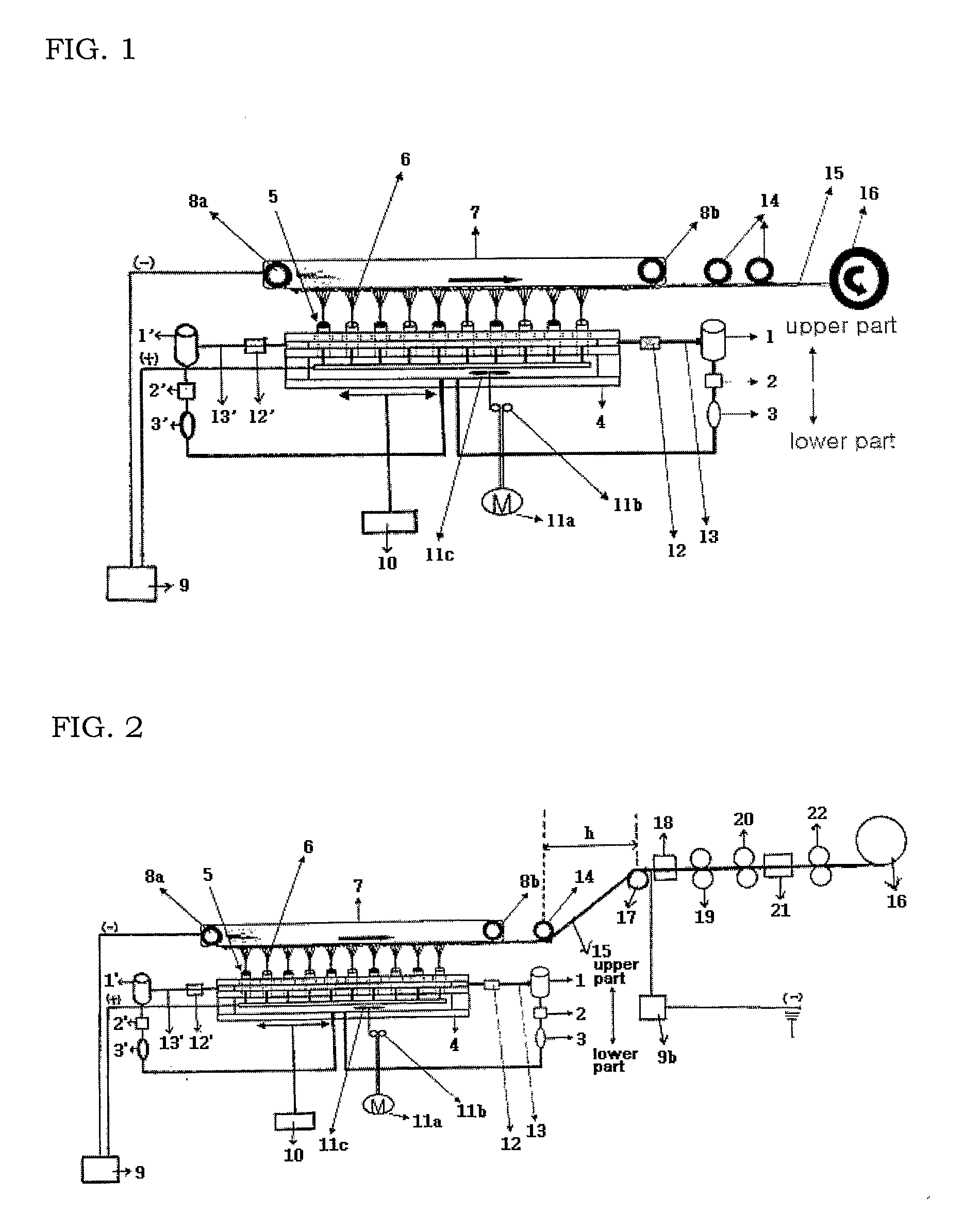
[0113]The two kinds of spinning dopes were stored in the main tanks 1 and 1′, quantitatively measured by the metering pumps 2 and 2′, and supplied to the spinning dope drop devices 3 and 3′, thereby discontinuously changing the flow of the spinning dopes. Thereafter, the spinning dopes were supplied to the nozzle block 4 as shown in FIG. 6, and...
example 2
[0114]Poly (ε-caprolactone) polymer (product of Aldrich, USA) having a number average molecular weight of 80,000 was dissolved in a mixed solvent of methylene chloride and N,N-dimethyl formamide (volume ratio: 75 / 25) at a concentration of 13 wt %, to prepare a spinning dope. The surface tension of the polymer spinning dope was 35 mN / m, the spinning dope viscosity was 35 centipoises at a room temperature, the electric conductivity was 0.02 mS / m, and the permittivity was 90.
[0115]Polyurethane resin (Pellethane 2103-80AE of Dow Chemical Company) having a number average molecular weight of 80,000 was dissolved in N,N dimethyl formamide at 8 wt. %.
[0116]The two kinds of spinning dopes were stored in the main tanks 1 and 1′, quantitatively measured by the metering pumps 2 and 2′, and supplied to the spinning dope drop devices 3 and 3′, thereby discontinuously changing the flow of the spinning dopes. Thereafter, the spinning dopes were supplied to the nozzle block 4 as shown in FIG. 6, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com