Source-coupled differential low-swing driver circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
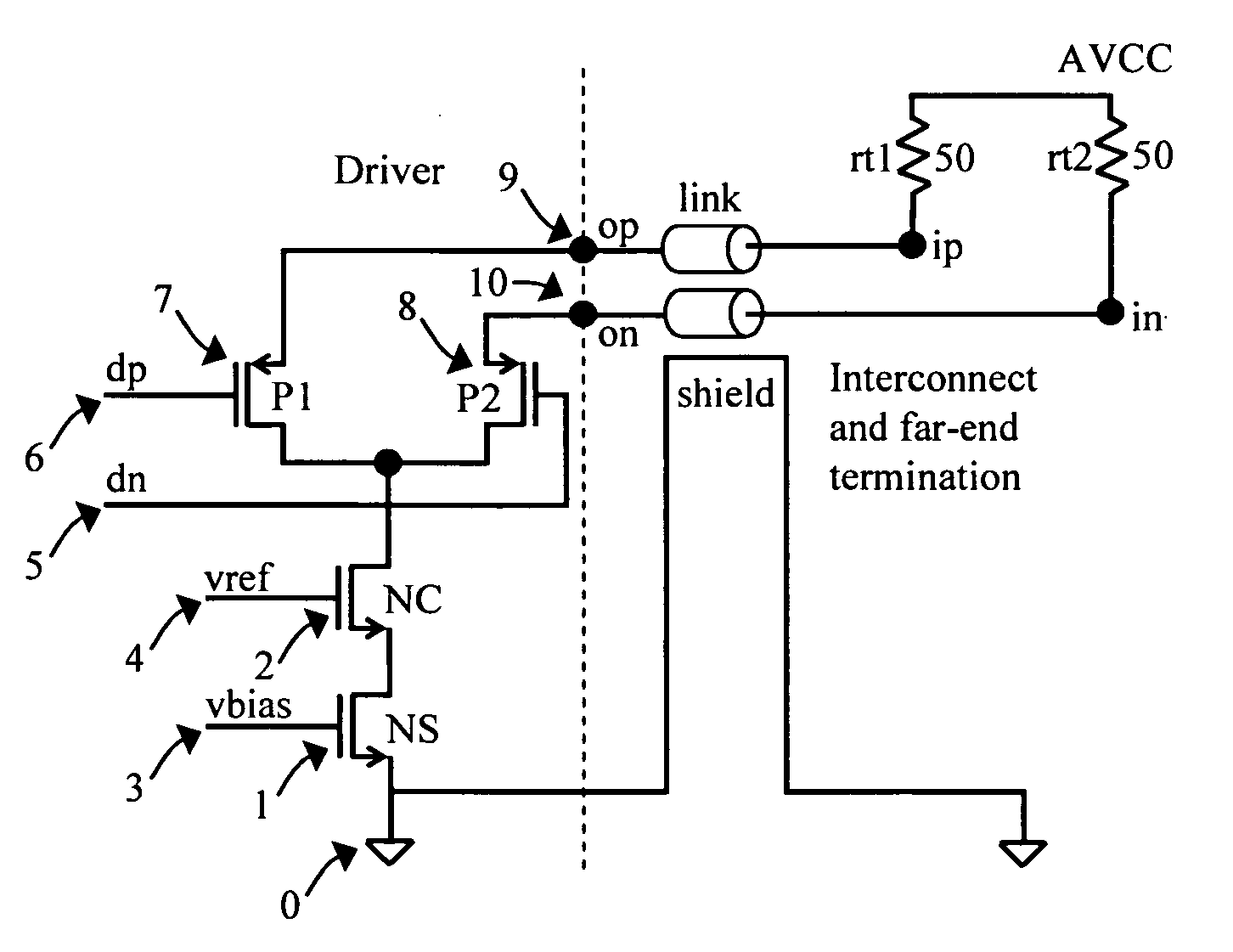
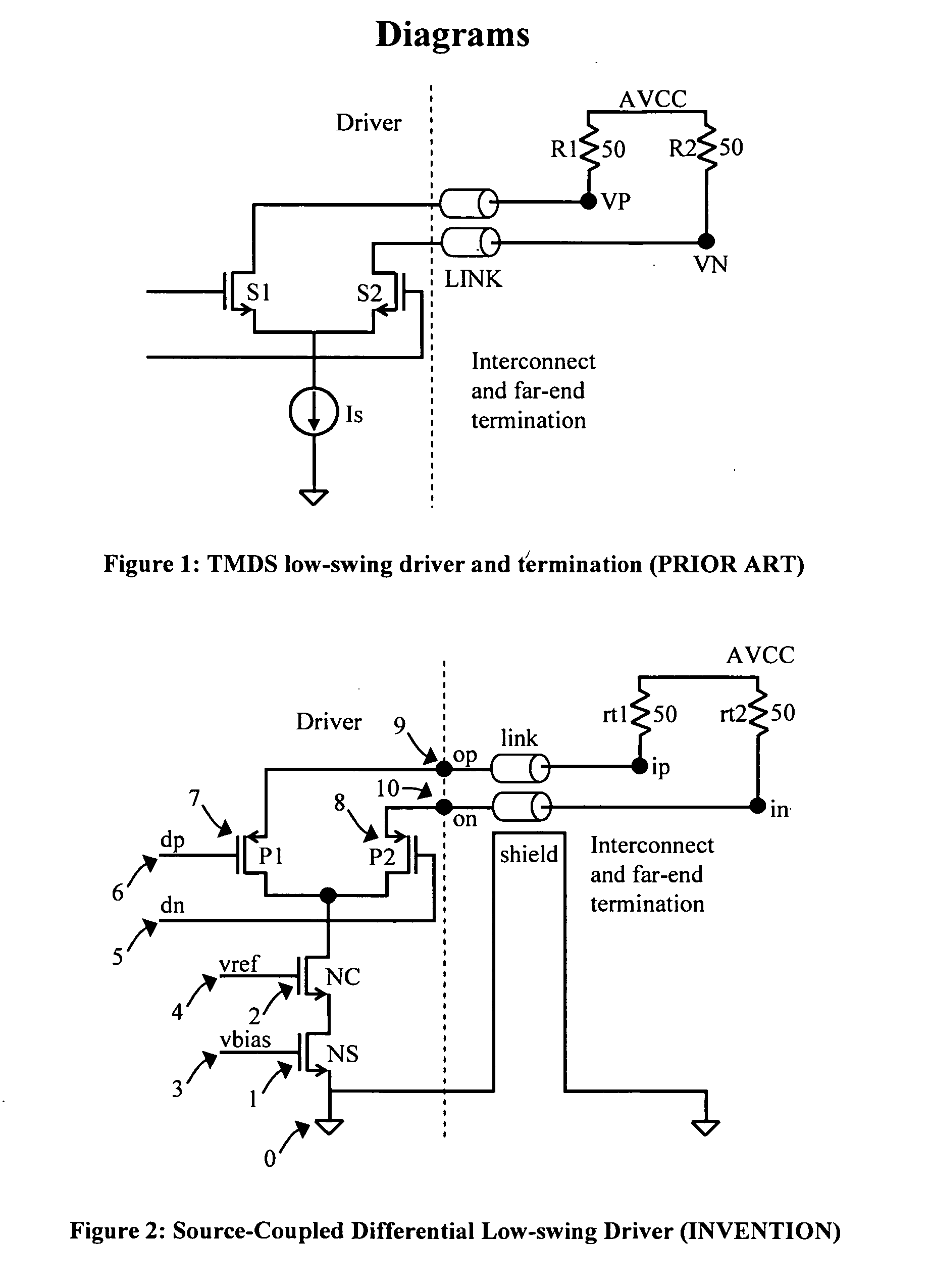
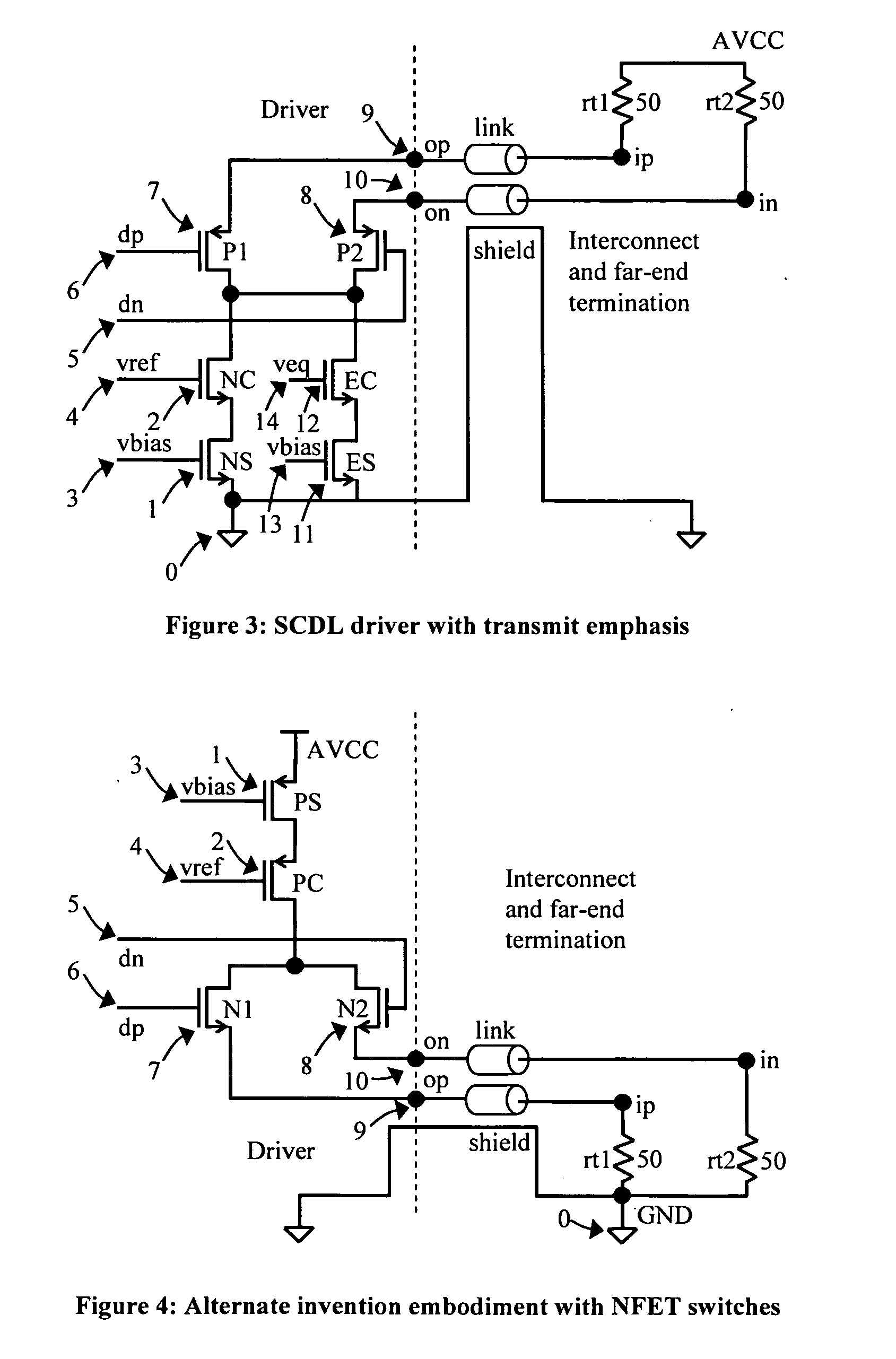
[0011]A prior art embodiment of a TMDS differential signaling output driver and termination architecture is illustrated in FIG. 1. In this driver implemented in CMOS technology, a tail current source connects through two NFET switch devices to output signal wires which are terminated at the far-end of the cable in a single-ended manner to a common reference power supply AVCC. When switch S1 turns ‘off’ and S2 turns ‘on’ driven by input signals to the gates of these devices, the current source current Is is diverted to flow through the output signal wire connecting to far-end node VN and through terminating resistance R2, thereby pulling node VN lower by a voltage value corresponding to the product of the current and the terminating resistance. In typical embodiments of the prior art, the terminating resistors are 50 Ohms in value and the current source is 10 mA, resulting in a 500 mV drop in voltage. Simultaneously, since switch S1 turns ‘off’, no current flows through the output si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com