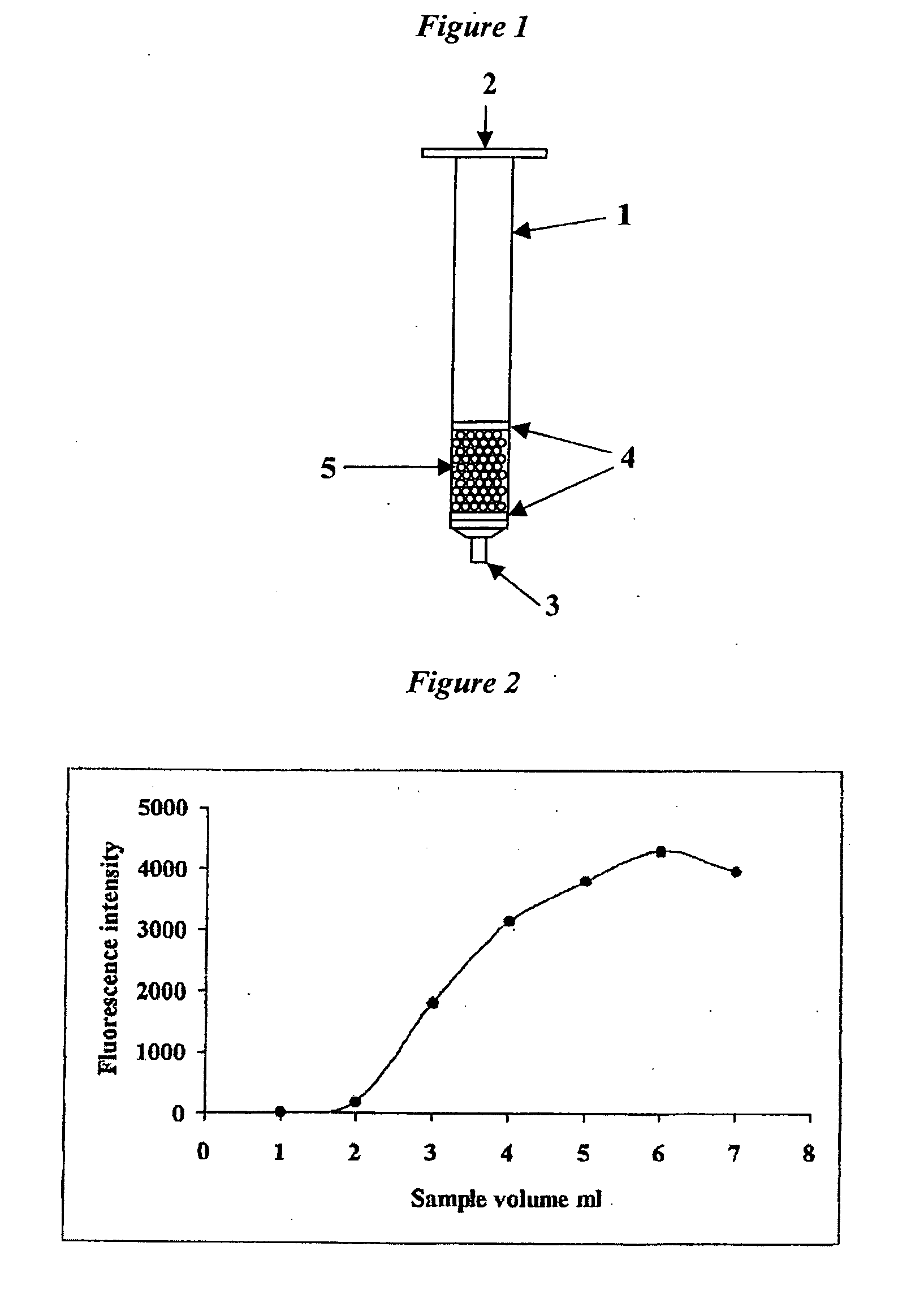
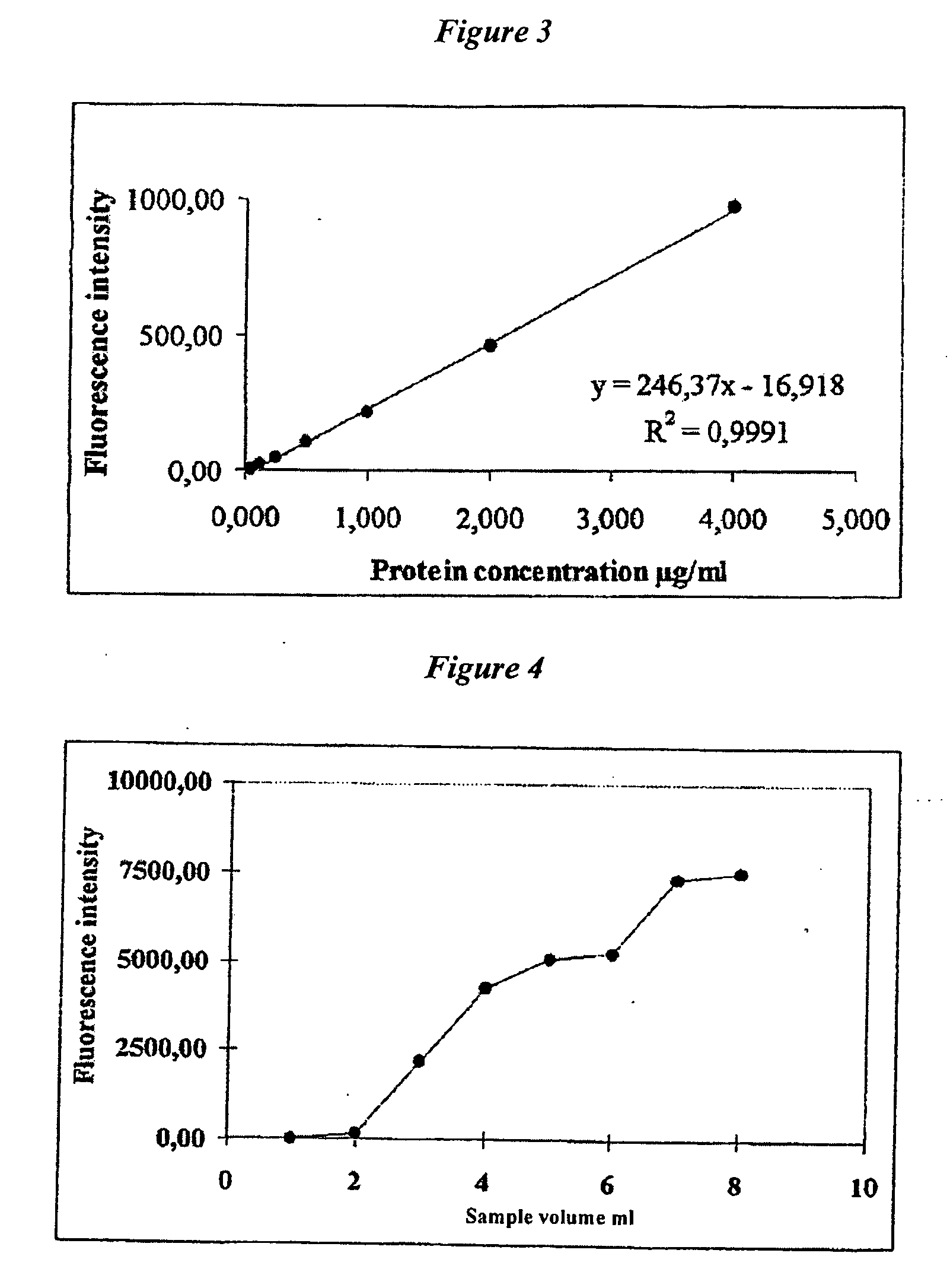
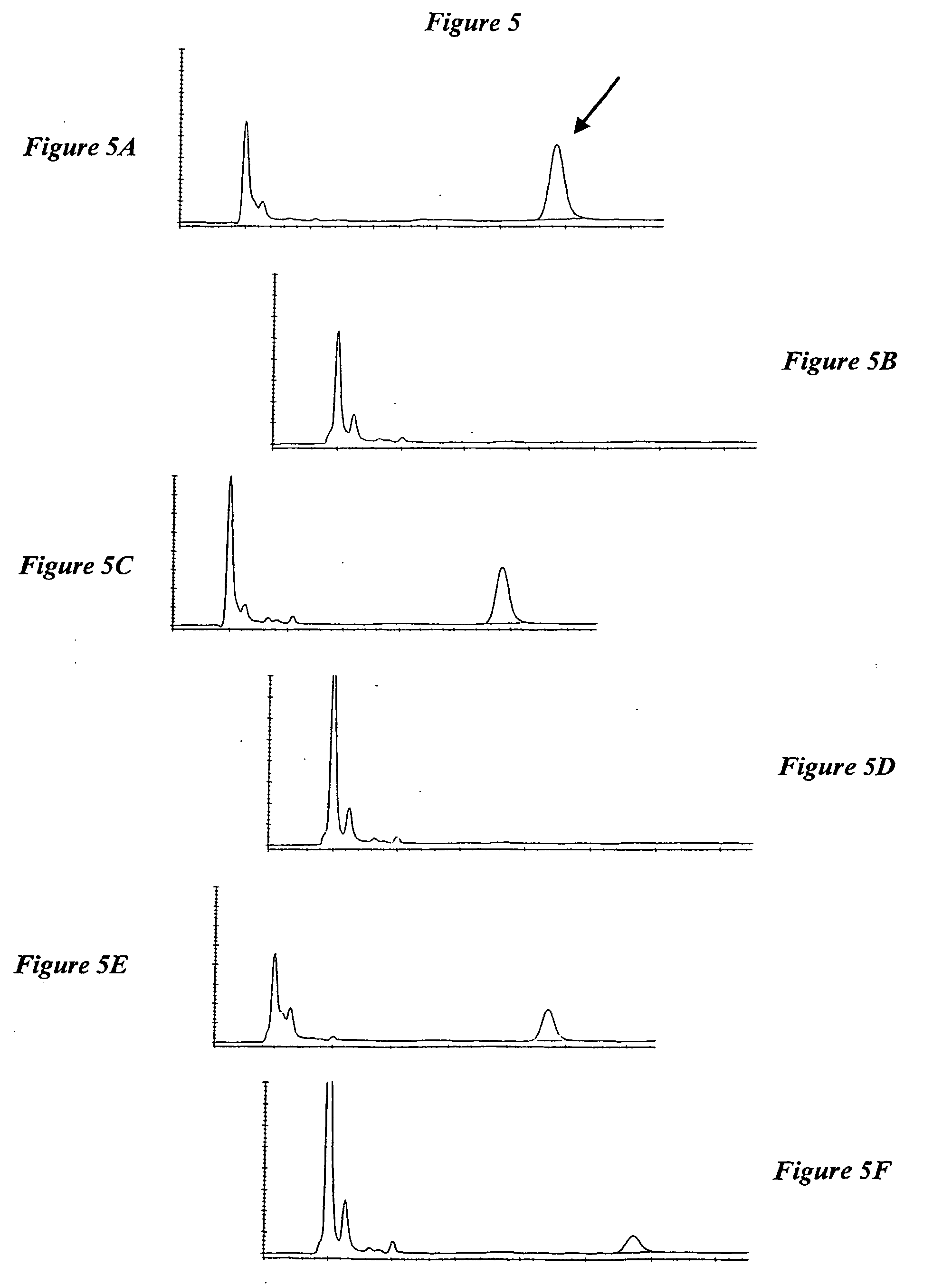
Separation of Unconjugated and Conjugated Saccharide by Solid Phase Extraction
a solid phase extraction and conjugate technology, applied in the field of vaccine quality control, can solve the problems of reduced effective dose of immunogenic conjugate, increased levels of uncharacterised breakdown products, slow techniques, etc., and achieves faster and more reproducible separation and improved quality control of conjugate vaccines.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
1. CRM-Hib Glycoconjugate Vaccine
1.1 Samples and Reagents
[0148]Hib oligosaccharide and CRM-Hib (Hib oligosaccharide covalently attached to CRM197) were produced by Chiron Vaccines (Siena, Italy). NaOH for chromatography were Sodium Hydroxide 1 N (C. Erba, Milan, Italy). Ribitol standard was of purity≧99% (HPLC) (Fluka, Switzerland). Trifluoroacetic acid was of purity≧99.5% (T) (Fluka, Switzerland). Isolute™ C18 solid-phase extraction cartridges (200 mg) were purchased from International Sorbent Technology (Mid Glamorgan, UK); Bio-Select™ C18 and C4 solid-phase extraction cartridges (50 mg) were purchased from Vydac.
1.2 Quantitative Determination of Saccharide in CRM-Hib Glycoconjugate Vaccines
[0149]CRM-Hib standards (1.0 mL with a saccharide concentration range of 0.18-1.8 μg / mL) and ribitol standard (0.075-0.75 μg / ml) were treated with 50 μl of hydrochloric acid (HCl) 6 M (final HCl concentration: 0.3 M); samples were heated at 1100° C. for 2 hours in a closed screw-cap test tube t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com