Therapeutic agent for motor neuron disease
a technology for motor neuron disease and therapeutic agents, applied in the field of motor neuron disease therapy and/or preventive agents, can solve the problems of no therapeutic agents effective for als, no neuronal cell death inhibitors, and atrophy of voluntary muscles, and achieve the effects of preventing neuronal cell death, and preventing als ons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
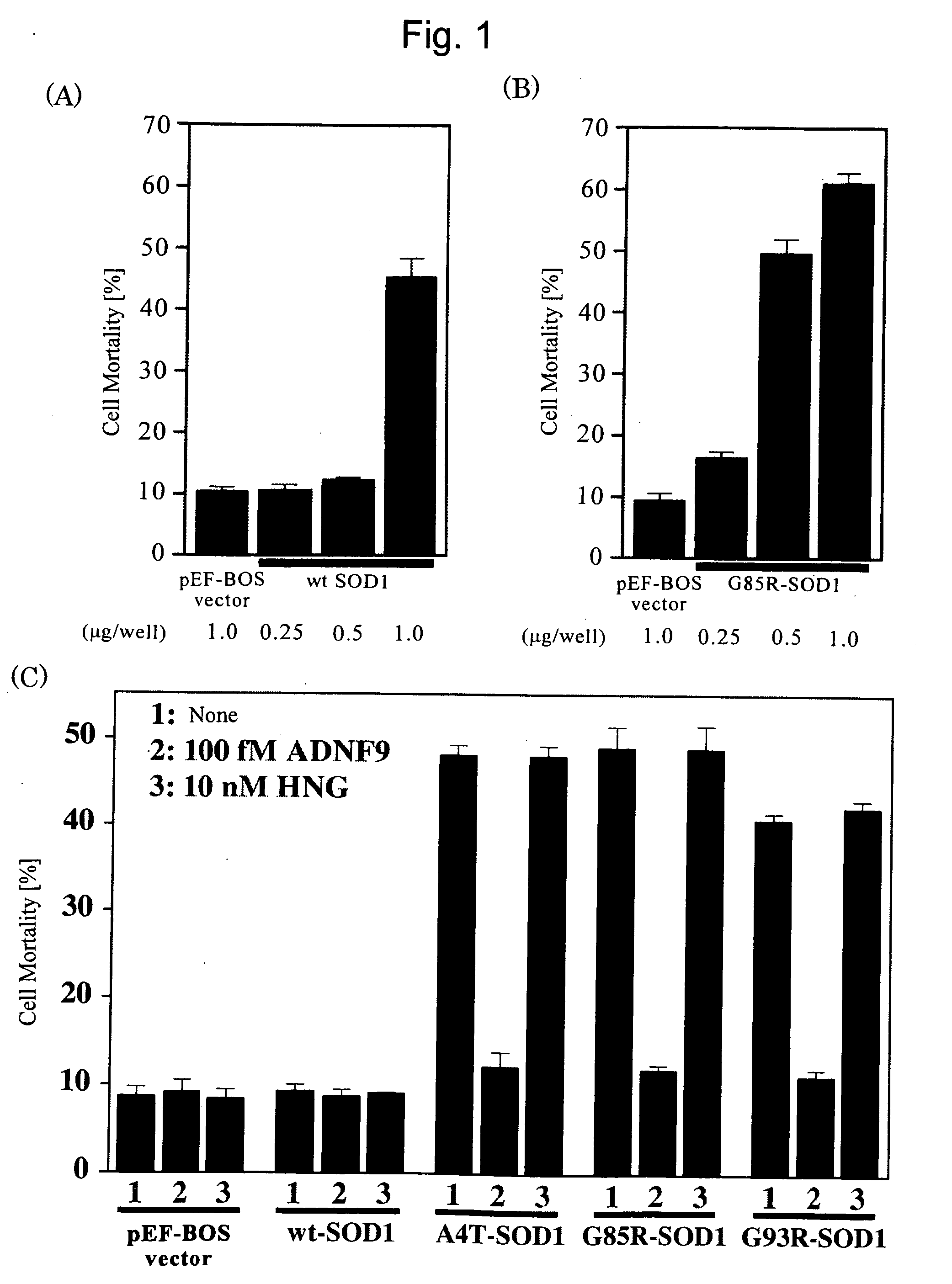
Inhibition of SOD1 Mutant Gene-Induced Neuronal Cell Death by ADNF
(1) Test Materials
[0072]Wild-type SOD1 cDNA (SEQ ID NO: 4) and SOD1 mutant (A4T-SOD1, G85R-SOD1, and G93R-SOD1) cDNAs were kindly provided by Dr. Shoji Tsuji (Faculty of Medicine, the University of Tokyo). Kinase-inactive CaMKII and CaMKIV cDNAs were kindly provided by Dr. Howard Schulman, Stanford University, US. ADNF (SALLRSIPA: SEQ ID NO: 1) and ADNF8 (ALLRSIPA: SEQ ID NO: 2) were synthesized (Glazner G W, et al., 1999, J Neurochem 73: 2341-2347). IPAL peptide (IPALDSLKPANEDQKIGIEI: SEQ ID NO: 3, Zamostiano R, et al., 1999, Neurosci Lett 264: 9-12) was purchased from the Peptide Institute (Osaka, Japan). An anti-SOD1 antibody was purchased from MBL (Nagoya, Japan). PD98059, SB20380, AG490, KN93, KN92, and HA1004 were purchased from Calbiochem-Novabiochem (San Diego, USA).
[0073]F11 cell, the hybrid cell of rat embryonic day 13 (E13) primary cultured neuronal cell with mouse neuroblastoma NTG18 cell, was cultured in ...
example 2
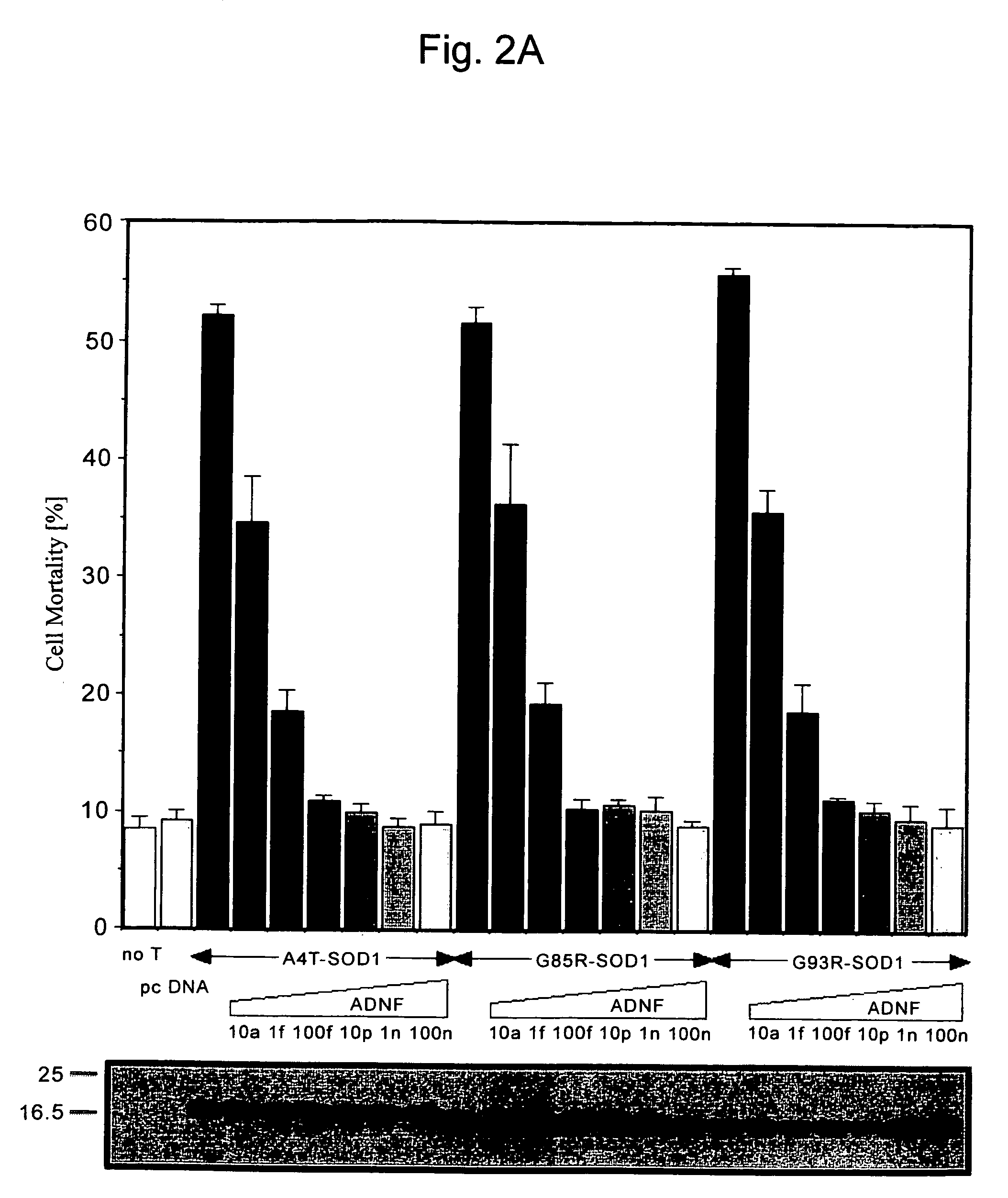
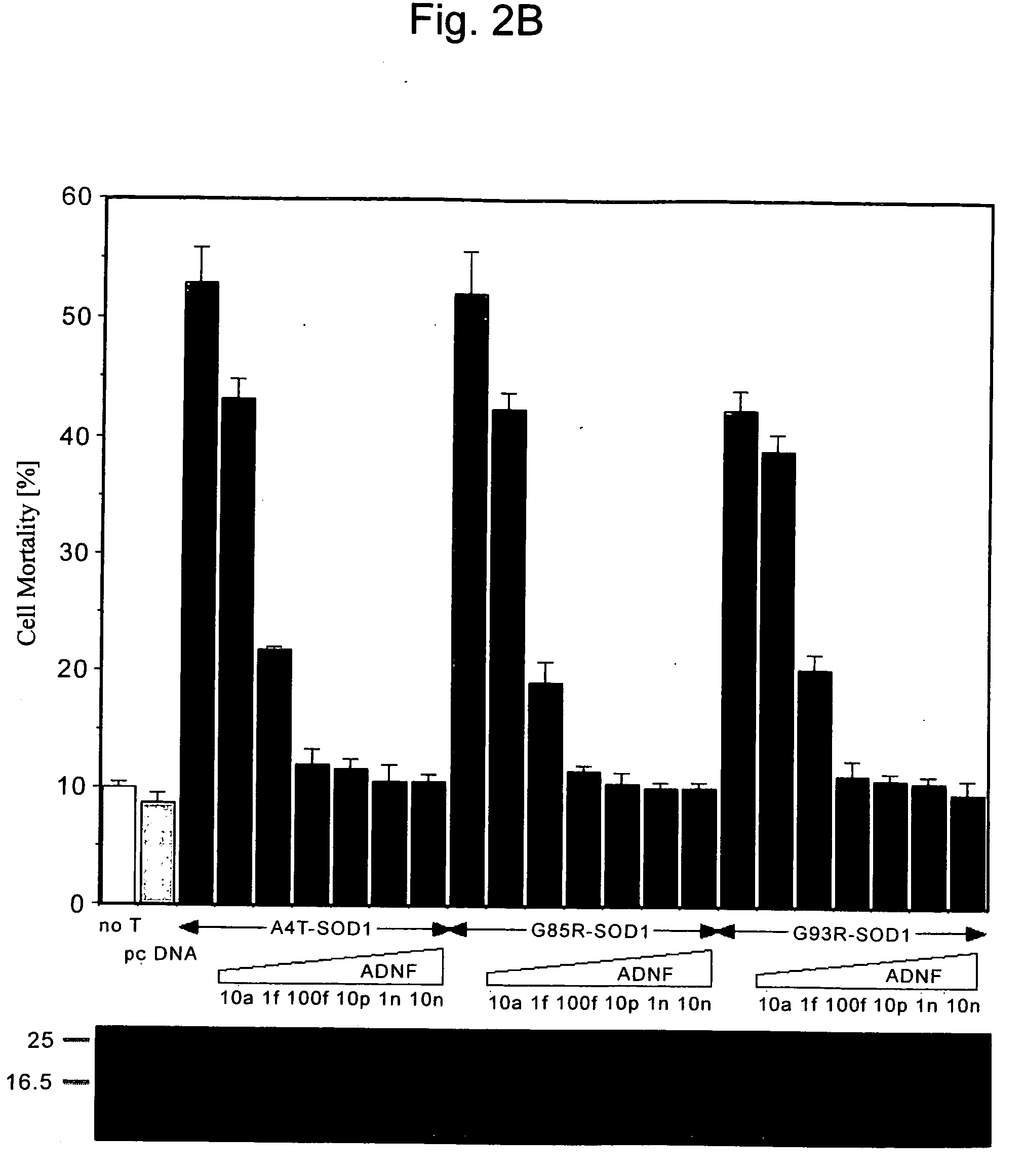
Dose-Dependent Inhibitory Effect of ADNF on Neuronal Cell Death
[0082]F11 or NSC34 cells were used to confirm the dose-dependent effect of ADNF on neuronal cell death induced by transformation with SOD1 mutant genes (A4T-SOD1, G85R-SOD1, and G93R-SOD1).
[0083]F11 or NSC34 cells were transformed with pEF-BOS, A4T-SOD1, G85R-SOD1, or G93R-SOD1 cDNA in the presence of increasing concentrations (10 aM, 1 fM, 100 fM, 10 pM, 1 nM, and 100 nM) of ADNF. After 72 hours, cell mortality was measured by Trypan blue exclusion assay.
[0084]Although 10 aM ADNF hardly exhibited cell death inhibition, 100 fM ADNF completely decreased cell mortalities induced by these three types of SOD1 mutant genes to the level of the control (FIG. 2A). In this regard, the complete protective action of ADNF on cell death caused by the SOD1 mutant genes was observed at the concentrations equal to or above 10 nM. These results demonstrated the dose-dependent inhibitory activity of ADNF against neuronal cell death caused...
example 3
Analysis on Neuroprotective Action of ADNF
[0089]Intracellular signaling by ADNF was examined. F11 cells were transformed with pEF-BOS or SOD1 mutant (A4T-SOD1, G85R-SOD1, or G93R-SOD1) cDNA and reacted with 10 nM wortmannin (PI3 kinase inhibitor), 100 μM genistein (tyrosine kinase inhibitor), 50 μM PD98059 (MEK inhibitor), 20 μM SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor), 1 μM AG490 (JAK kinase inhibitor), 5 μM KN93 (calcium / calmodulin-dependent kinase inhibitor), or 10 μM HA1004 (protein kinase A inhibitor) in the presence or absence of 100 nM ADNF. After 72 hours of the transformation, cell mortality was measured by Trypan blue exclusion assay.
[0090]The results obtained using A4T-SOD1, G85R-SOD1, and G93R-SOD1 are respectively shown in FIGS. 3A to 3C.
[0091]The neuroprotective effect of ADNF was not affected by wortmannin (W), PD98059 (PD), SB203580 (SB), AG490 (AG), and HA1004 (HA), but it was inhibited by genistein (G) and KN93 (KN) (FIGS. 3A to 3C). This suggests that ADNF exerts its neuropr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| humidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hydrophobic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com