Epitaxial substrate for field effect transistor
a field effect transistor and substrate technology, applied in the direction of basic electric elements, electrical appliances, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of deterioration of pinch-off characteristics, increased drain leakage, and low and achieve the effect of reducing the mobility of unnecessary current components and reducing the number of transistors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
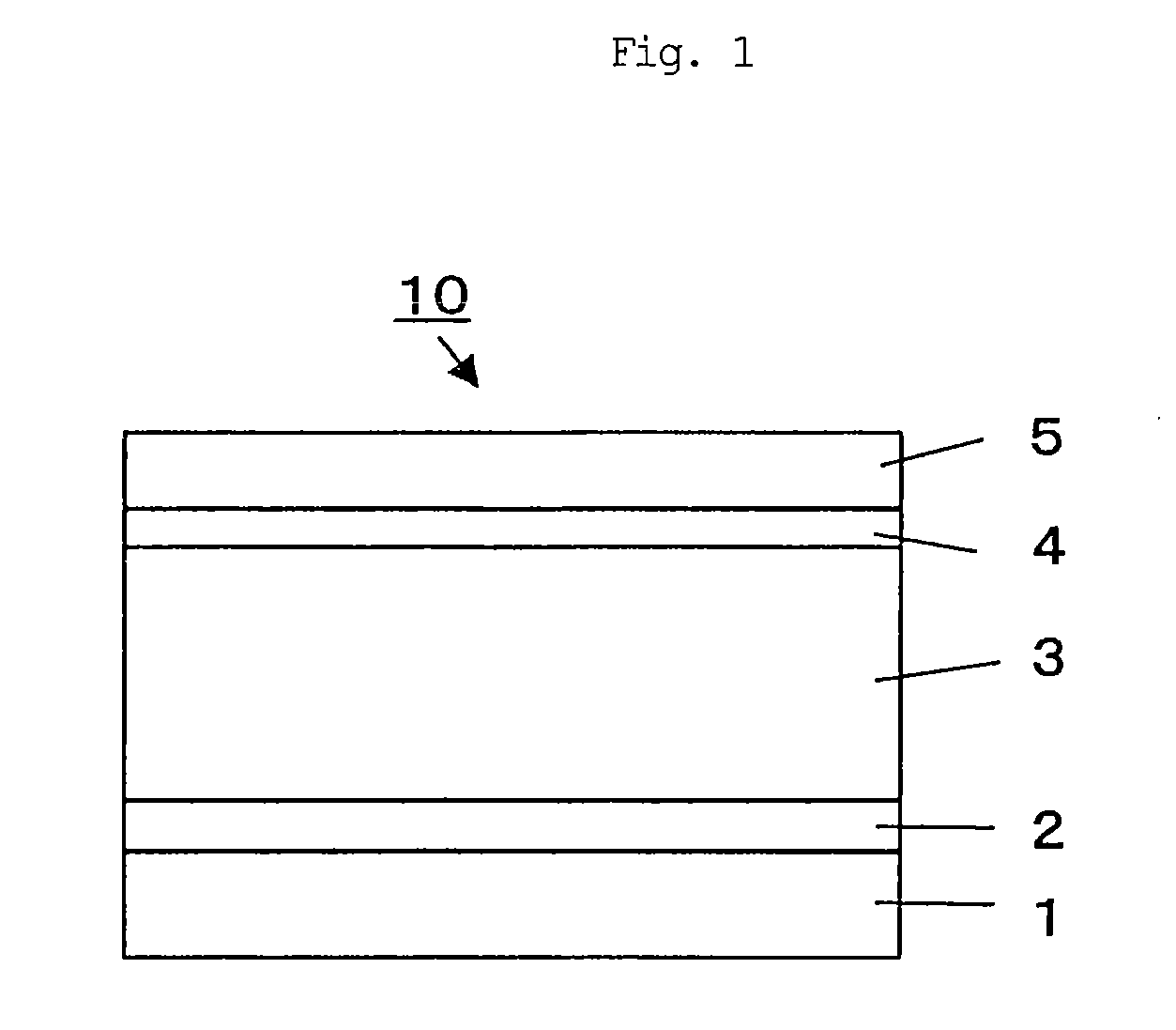
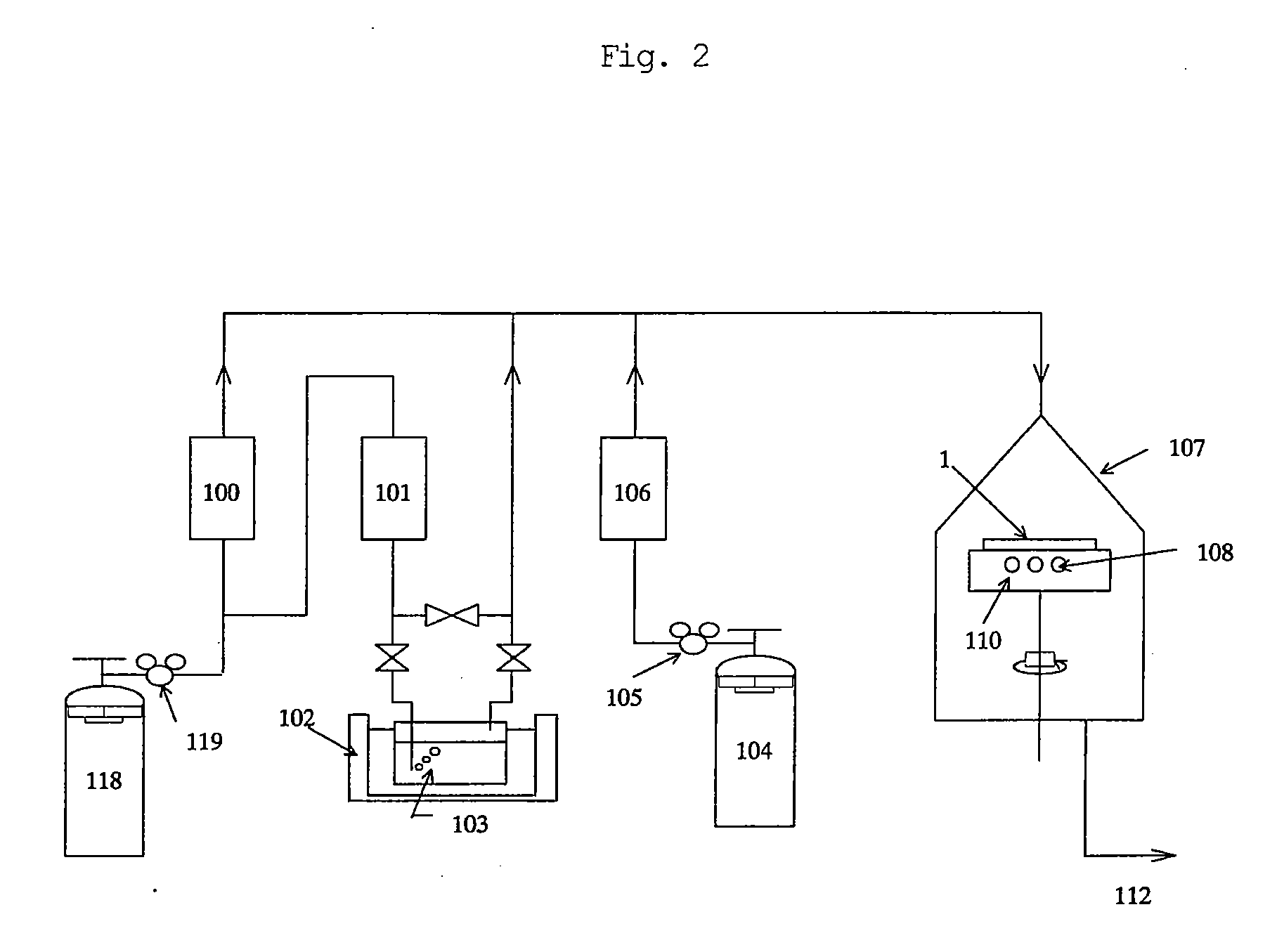
[0088]Using the apparatus shown in FIG. 2, an epitaxial substrate for FET having the layer structure shown in FIG. 1 was prepared as follows. A sapphire monocrystal substrate was heated to 600° C., hydrogen as a carrier gas was allowed to flow in an amount of 60 SLM, ammonia was allowed to flow in an amount of 40 SLM, TMA was allowed to flow in an amount of 40 sccm from a container in a temperature-controlled bath set to a temperature of 30° C., and biscyclopentadienyl was allowed to flow from a container in a temperature-controlled bath set to a temperature of 30° C. (0 sccm in sample (a), 200 sccm in sample (b) and 1,000 sccm in sample (c)). Thus, AlN first buffer layer was grown to a thickness of 500 angstroms. Growth rate in this case was 470 angstroms / min.
[0089]The substrate temperature was increased to 1,040° C., and the flow rate of TMA was changed to 0 sccm. Then, TMG was allowed to flow in an amount of 40 sccm from a container in a temperature-controlled bath set to a tempe...
example 2
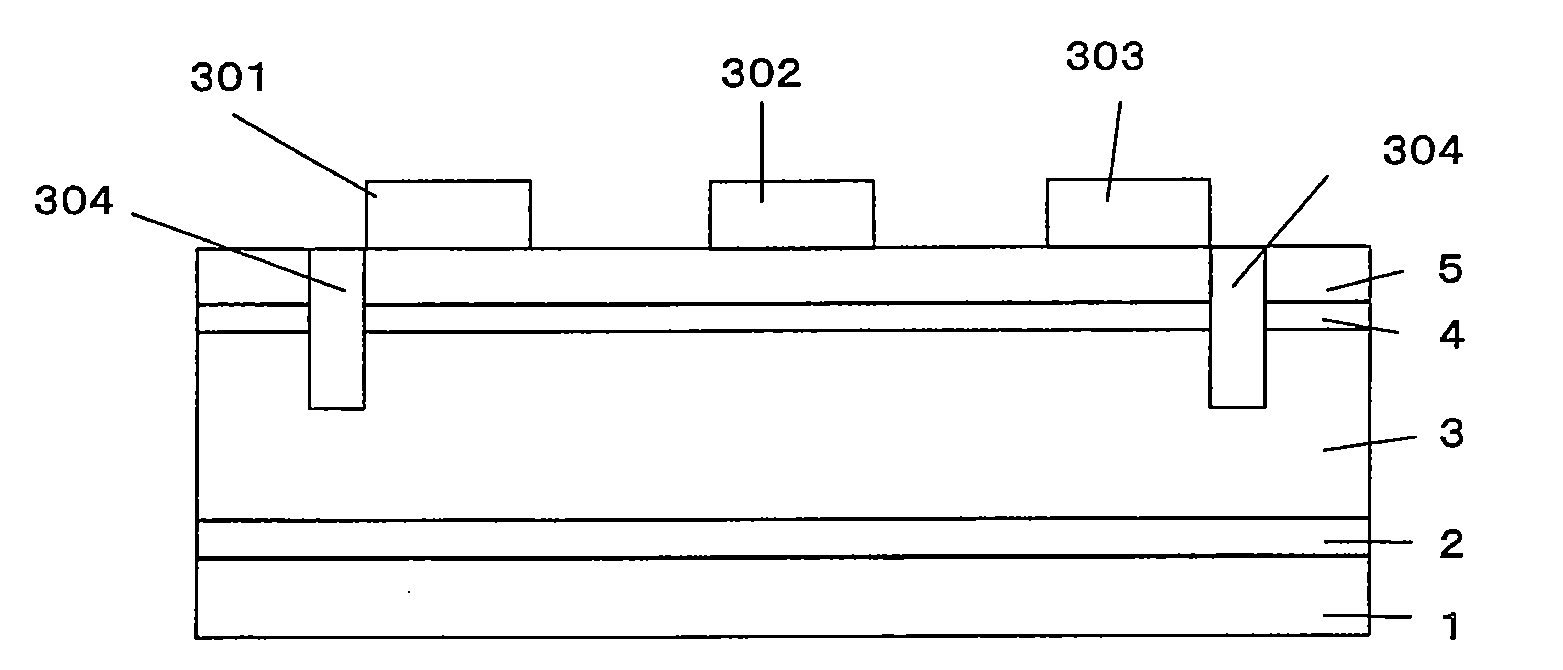
[0091]Using the apparatus shown FIG. 2, GaN-HEMT having the layer structure shown in FIG. 3 was prepared. In FIG. 3, the parts corresponding to the respective parts in FIG. 1 are indicated by the same reference numerals. A sapphire monocrystal substrate as the ground substrate 1 was heated to 600° C., hydrogen as a carrier gas was allowed to flow in an amount of 60 SLM, ammonia was allowed to flow in an amount of 40 SLM, TMA was allowed to flow in an amount of 40 sccm from a container in a temperature-controlled bath set to a temperature of 30° C., and biscyclopentadienyl was allowed to flow from a container in a temperature-controlled bath set to a temperature of 30° C. (0 sccm in sample (d), and 1,000 sccm in samples (e) and (f)) Thus, AlN first buffer layer 2 was grown to a thickness of 500 angstroms. Growth rate in this case was 470 angstroms / min.
[0092]The substrate temperature was increased to 1,040° C., and the flow rate of TMA was changed to 0 sccm. TMG was allowed to flow in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com