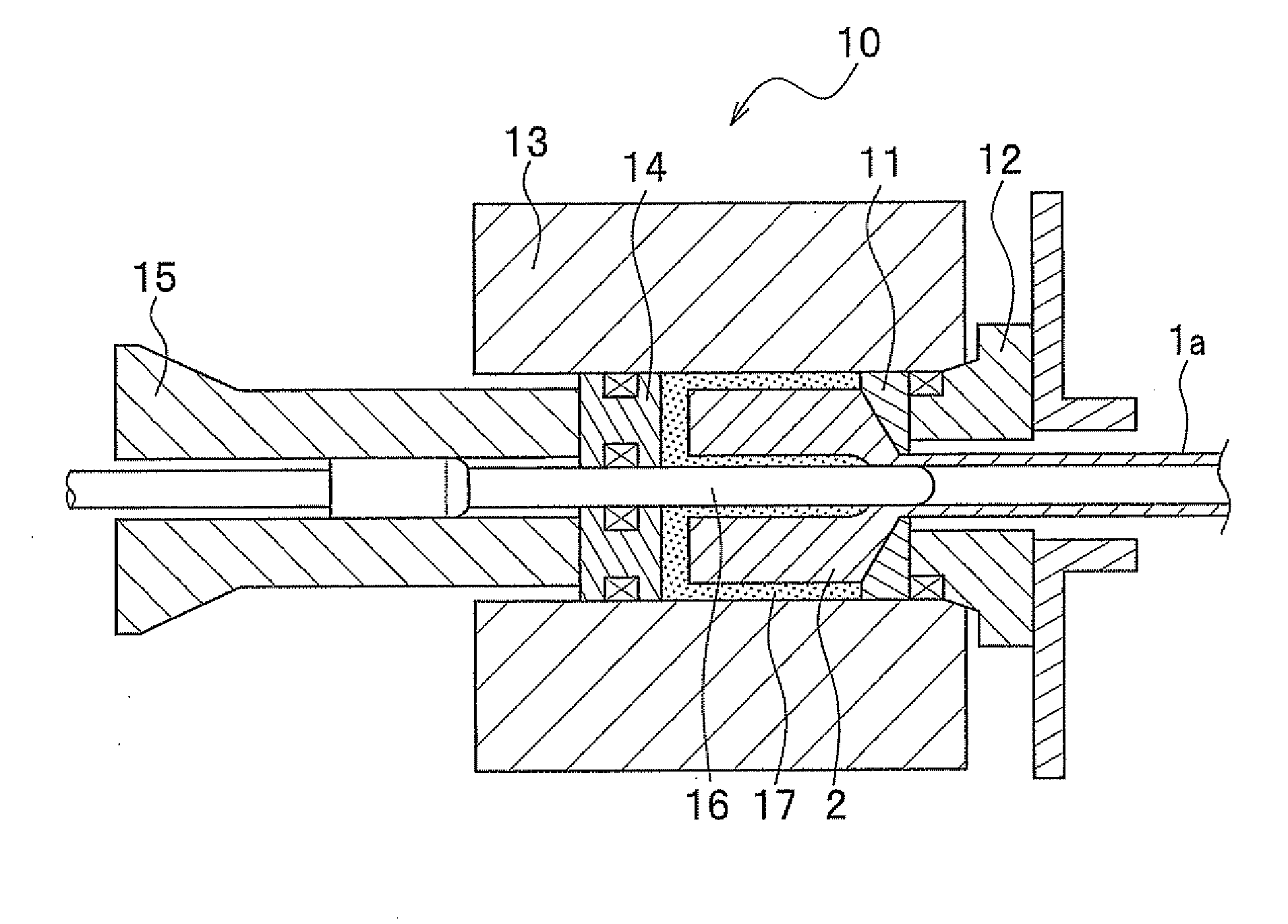
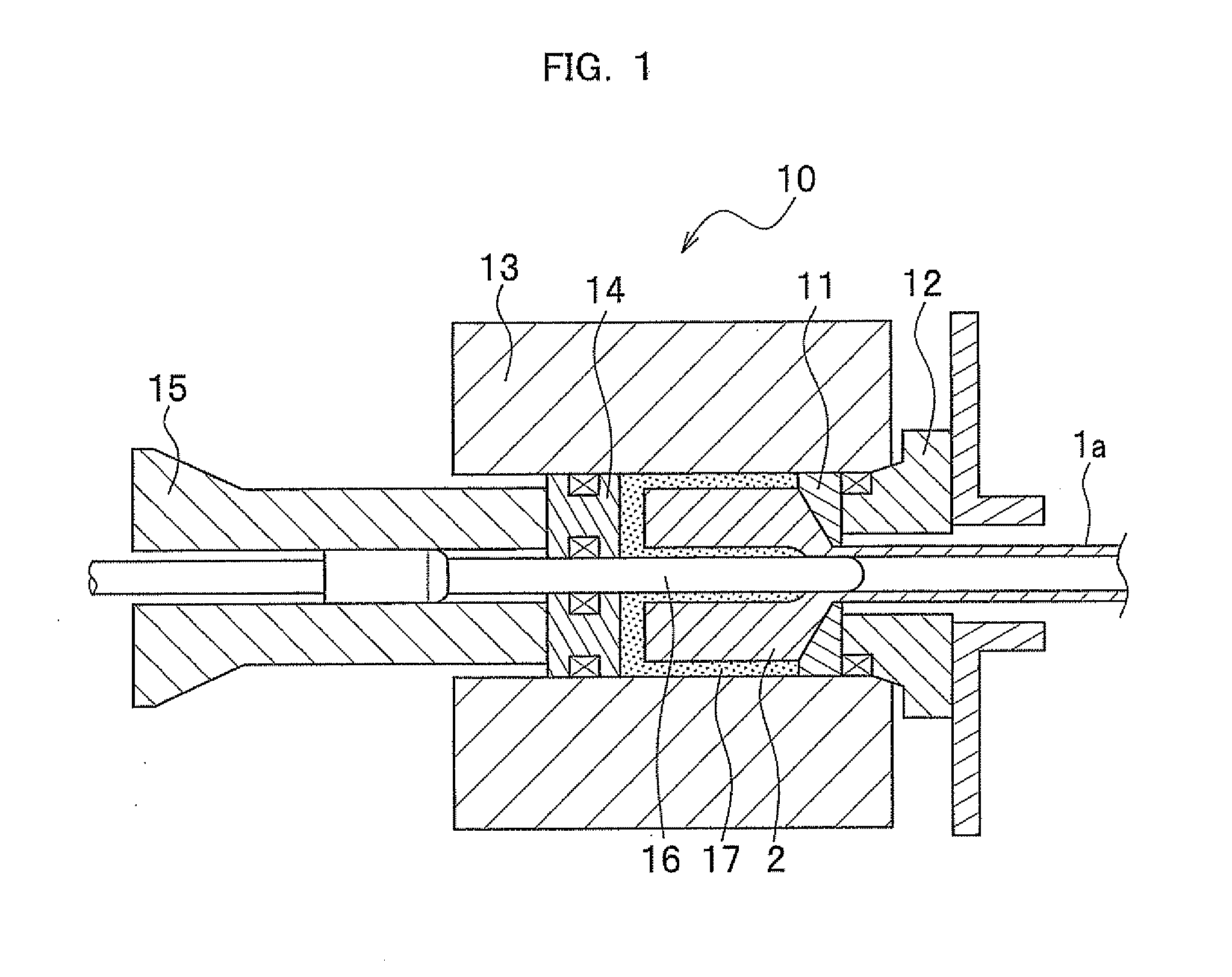
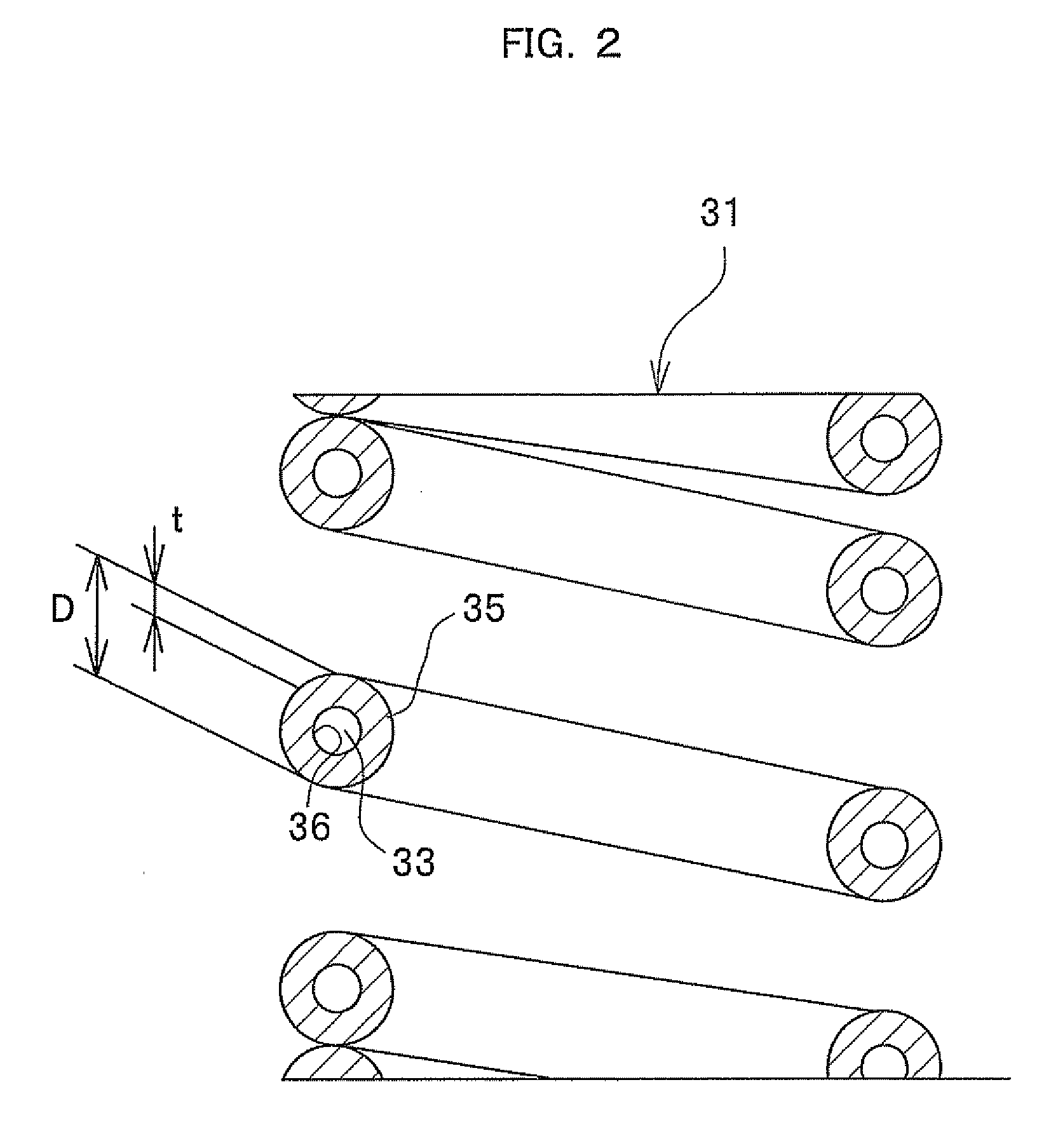
Seamless steel pipe, hollow spring utilizing seamless steel pipe, and process for manufacturing the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Weight Reduction Effect
[0180]Table 2 shows a comparison between weight reduction effects of coiled spring. As shown in Table 2, coiled springs used were: a coiled spring (solid-core material) made of SiCr steel as solid-core material; a conventional hollow coiled springs (conventional hollow material) obtained using S45C or the like; and hollow coiled springs as example product made of SiCr steel or high-strength SiCrV steel, each having a coil inner diameter of φ 45 mm and an applied maximum load of 2750 N.
TABLE 2Coil inner diameter: φ 45 mmApplied maximum load: 2,750 NSolid-coreExample productmaterialConventionalhigh-strengthMaterial UsedSiCr steelhollow materialSiCr steelSiCrV steelHardness after quenchingHv545Hv440Hv545Hv580and temperingTS (MPa)1,8501,4801,8502,020Material diameter (mm)8.09.18.38.1Winding number5.467.15.755.39Thickness (mm)—2.2752.22.03Thickness ratio—25%26.5%25%Free height (mm)811028581Closed height (mm)41624541InnerOutside895716895972diameter-sideTS ratio of o...
example 2
[0186]Next, the seamless steel pipe and the method for producing the same according to the present invention will be explained with reference to Examples which meet requirements of the present invention and Comparative Examples which do not meet requirements of the present invention, with making a comparison therebetween.
[0187]For Test No. 1 to 9, first, cylindrical billets were made of KHV10N (manufactured by Kobe Steel Ltd.) as steel material. The billets were formed so as to have the outer diameter of 143 mm and the inner diameter of 52 mm. The billets were heated at 950 to 1400° C. as shown in Table 1. Each of the heated billets for Test No. 1 to 9 was subjected to hot isostatic extrusion processing using a hot isostatic extruder at a corresponding temperature (extrusion temperature), to thereby produce a seamless steel pipe. Subsequently, the seamless steel pipes of Test No. 1 to 9 were subjected to spheroidizing annealing processing at 680° C. for 16 hours, and Pilger mill rol...
example 3
[0200]Next, coiled springs were produced from: the seamless steel pipes which meet requirements of the present invention; the seamless steel pipe which do not meet requirements of the present invention; and a solid-core steel material. For each spring, a fatigue test was conducted. It should be noted that the steel materials are the same as in >.
[0201]First, seamless steel pipe was produced by hot isostatic extrusion at an extrusion temperature of 1,150° C., and then coiled springs (all hollowed product) of Test No. 10 and 11 each having an outer diameter of 76.0 mm, an inner diameter of 54.8 mm, a height of 153.5 mm, and a winding number of 6.76 were produced.
[0202]The coiled spring of Test No. 11 has surface flaw (artificial flaw corresponding to contiguous flaw), formed on the outer periphery surface and the inner periphery surface thereof.
[0203]The coiled spring of Test No. 11 was obtained by: forming a seamless steel pipe under the same conditions as those in Test No. 10; a sur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com