Low molecular weight heparins including at least one covalent bond with biotin or a biotin derivative, method for making same and use thereof
a low molecular weight, heparin technology, applied in the field can solve the problems of limiting the use conditions, not being able to induce a sufficient regioselectivity, not being able to biotinylate all the functionalizable polysaccharide chains of low molecular weight heparins, etc., to achieve rapid neutralization and reduce the risk of hemorrhage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
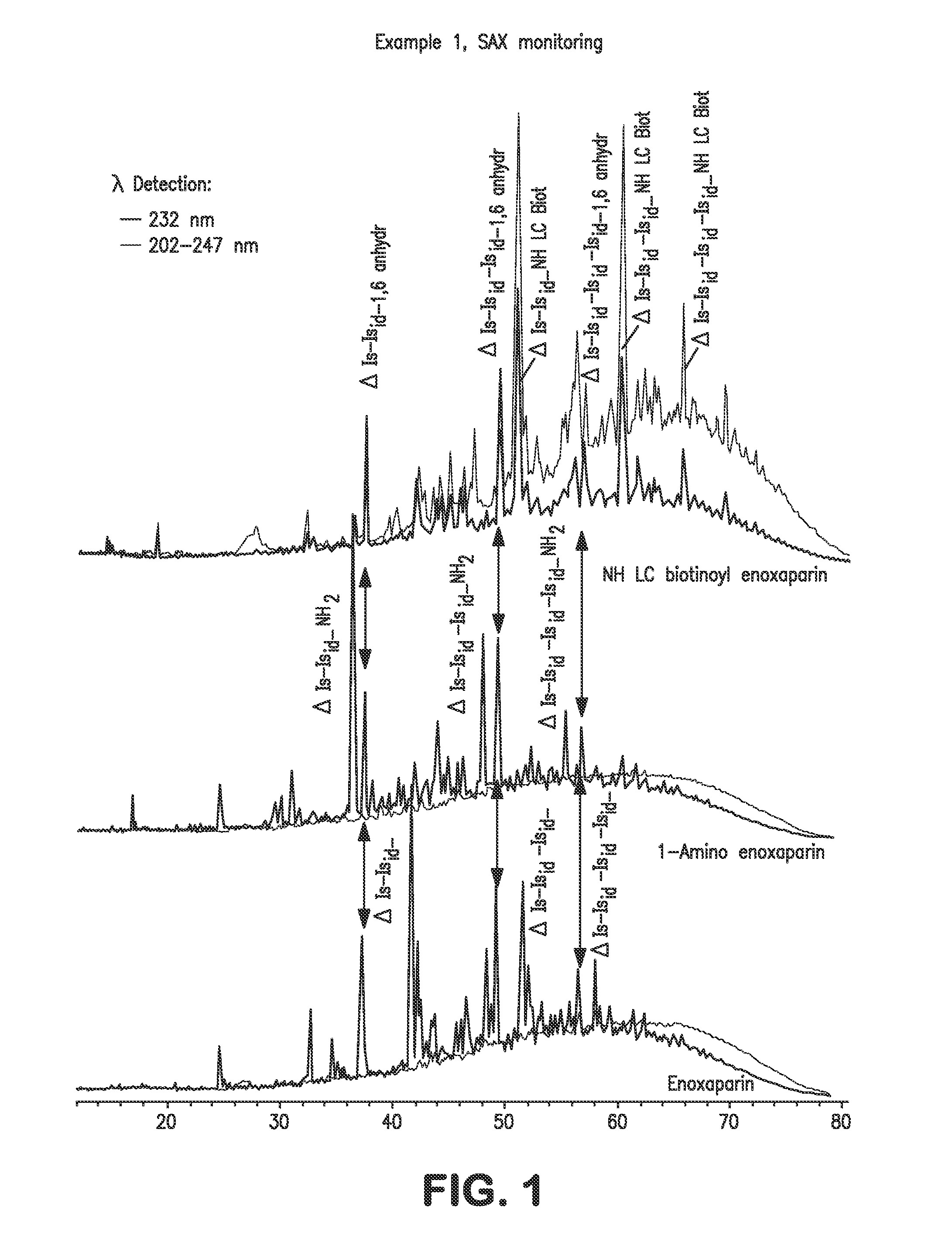
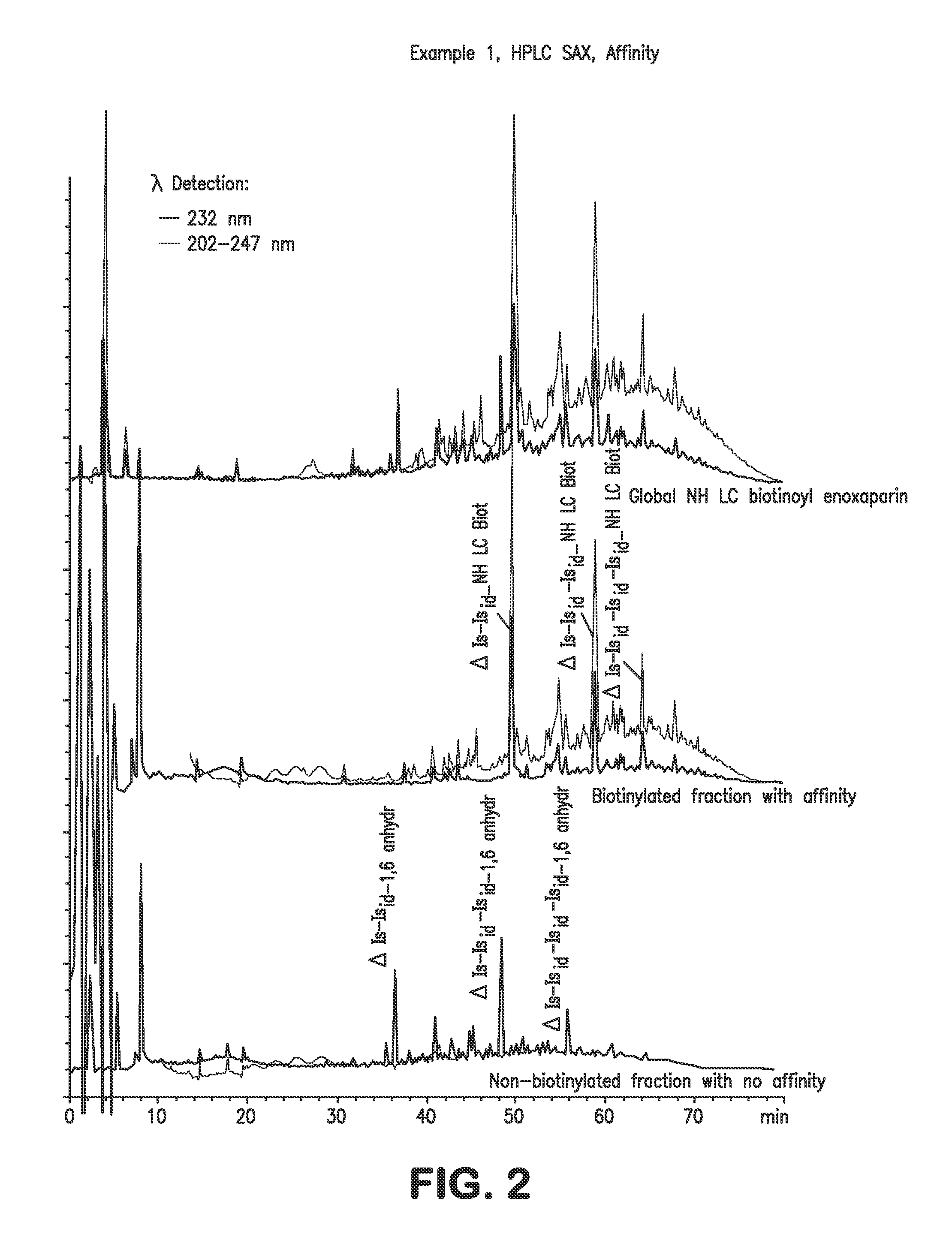
example 1
NH LC Biotinoyl Enoxaparin
[0064]Enoxaparin is a low molecular weight heparin obtained according to the process described in U.S. Pat. RE38,743. It is converted into the biotinylated derivative according to the reaction sequence in Scheme 2: enoxaparin is converted via a reductive amination reaction into compound 1 having an amino function at its reducing end, and this derivative is then converted into the biotinylated compound 2 via reaction with 3-sulfosuccinimidyl 6-biotinamido hexanoate, sodium salt.
1.1: 1-Amino Enoxaparin
[0065]1 g of enoxaparin is dissolved in 40 ml of aqueous 5 M ammonium chloride solution. 1 g of sodium cyanoborohydride is added to the solution obtained. The mixture is maintained at 60° C. for 24 hours. The solution is cooled to a temperature in the region of 20° C. and diluted with water (qs 100 ml). The filtrate obtained is desalified on a column of Sephadex G10 and then freeze-dried. 824 mg of a white lyophilizate are obtained. The observed yield is 82%. Th...
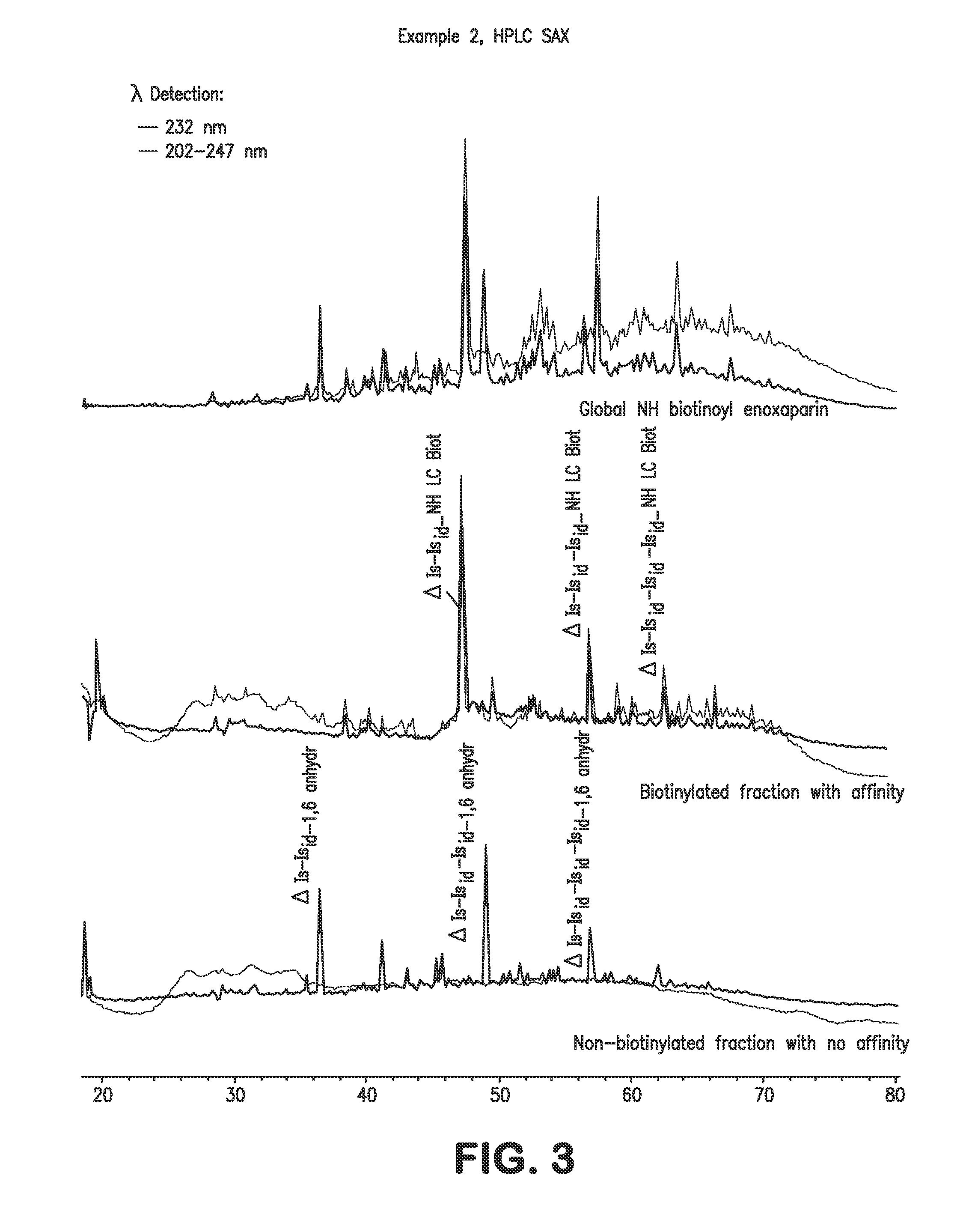
example 2
NH Biotinoyl Enoxaparin
[0072]Enoxaparin, a low molecular weight heparin obtained according to the process described in U.S. Pat. RE38,743, is converted into the biotinylated derivative according to the reaction sequence described in Scheme 3: enoxaparin is converted via a reductive amination reaction into compound 1 containing an amino function at its reducing end, and this derivative is then converted into the biotinylated compound 3 via reaction with the biotinoyl-3-sulfosuccinimidyl ester, sodium salt.
[0073]200 mg of 1-amino enoxaparin are dissolved in 5 ml of 0.5 M sodium hydrogen carbonate solution at a temperature in the region of 20° C. 107 mg of sulfo-NHS-biotin are added to the solution obtained. The solution is stirred at a temperature in the region of 20° C. for 1 hour 30 minutes. The suspension obtained is diluted with 10 ml of 0.5 M sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. 107 mg of sulfo-NHS-biotin are added and the mixture obtained is stirred for 3 hours. The reaction medi...
example 3
NH-LC-LC Biotinoyl Enoxaparin
[0079]Enoxaparin, a low molecular weight heparin obtained according to the process described in U.S. Pat. RE38,743, may also be converted into a biotinylated derivative according to the reaction sequence described in scheme 4: enoxaparin is converted via a reductive amination reaction into compound 1 containing an amino function on its reducing end, and this derivative is then converted into the biotinylated compound 4 by reaction with the ester 3-sulfo-succinimidyl 6-biotinamidohexanoyl hexanoate, sodium salt.
[0080]200 mg of 1-amino enoxaparin are dissolved in 5 ml of 0.5 M sodium hydrogen carbonate solution at a temperature in the region of 20° C. 164 mg of sulfo-NHS-LC-LC-biotin are added to the solution obtained. The solution is stirred at a temperature in the region 20° C. for 2 hours. The suspension is diluted with 10 ml of 0.5 M sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. 164 mg of sulfo-NHS-LC-LC-biotin are added and the mixture obtained is stirred for 5...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com