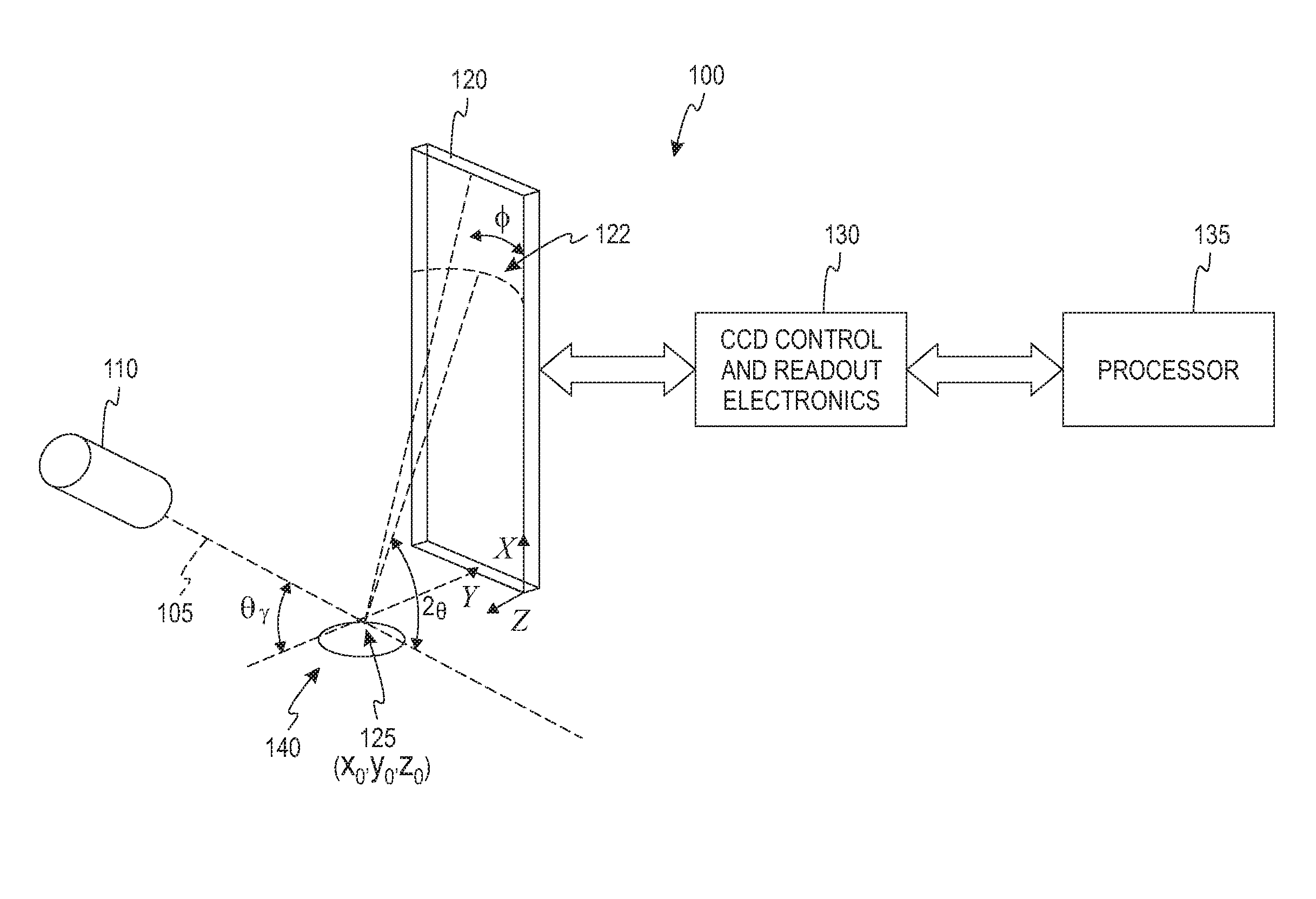
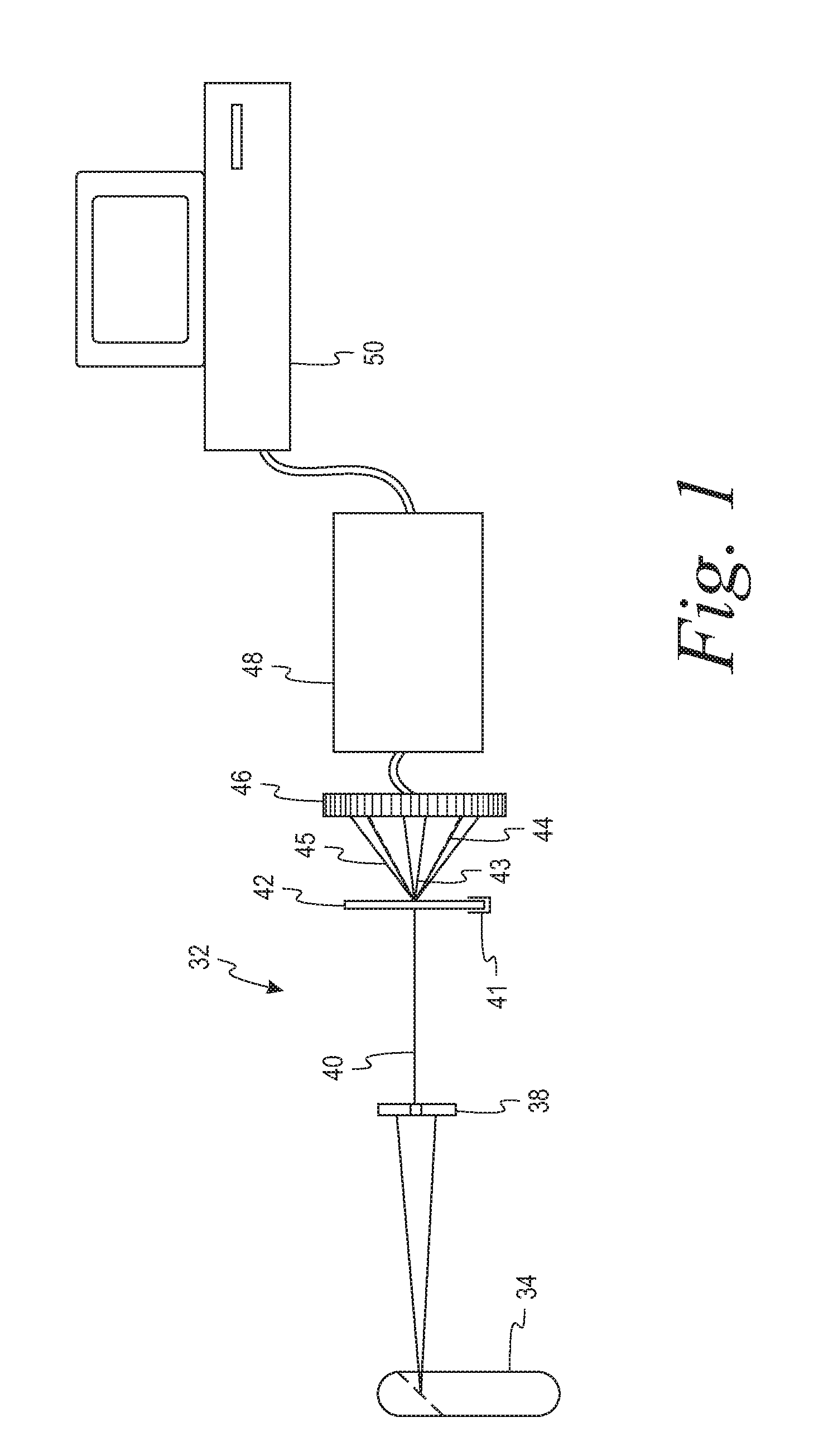
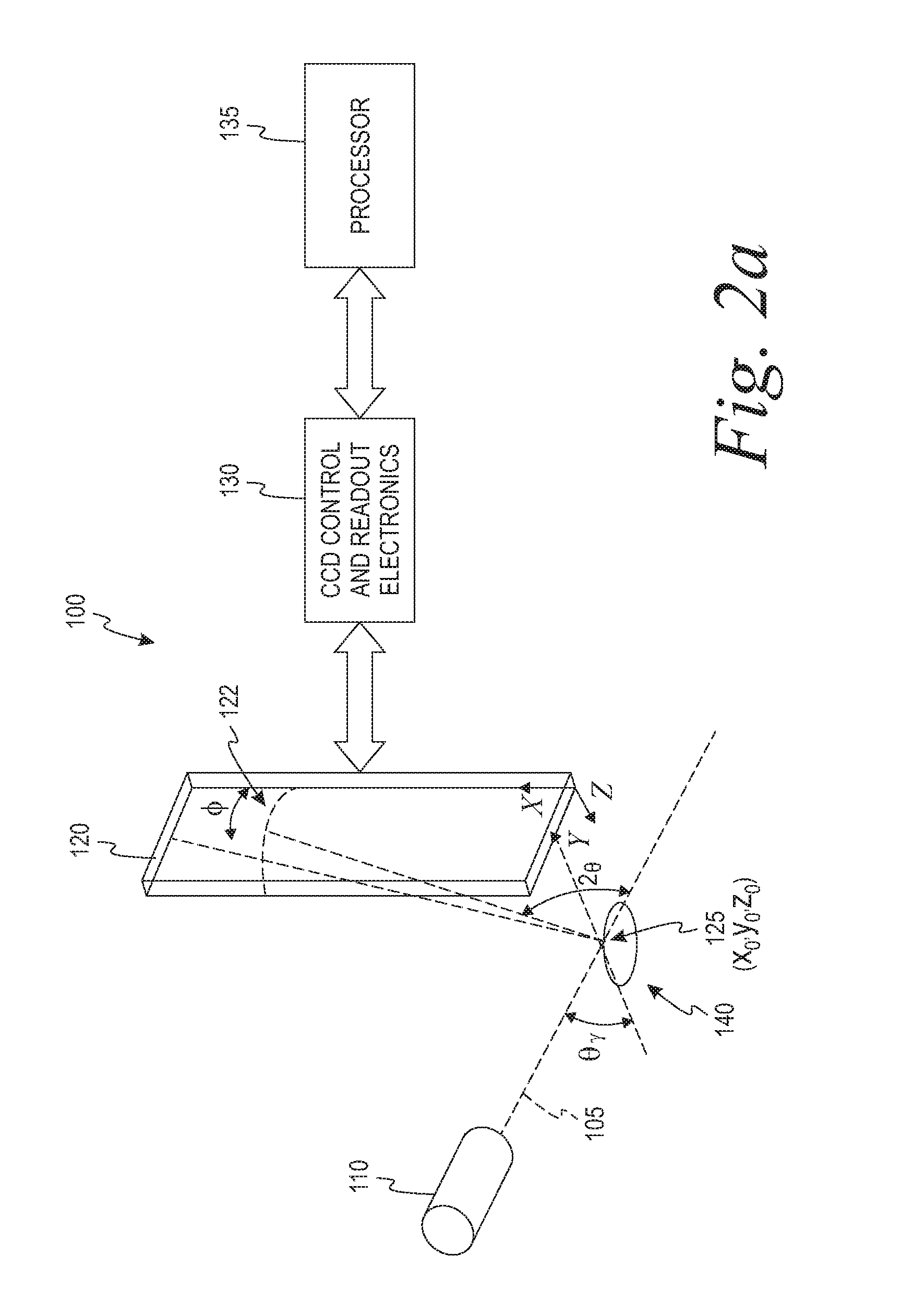
Instrument and method for x-ray diffraction, fluorescence, and crystal texture analysis without sample preparation
a technology of crystal texture and instrument, which is applied in the direction of instruments, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, x/gamma/cosmic radiation measurement, etc., can solve the problems of destroying any water ice that msl may encounter, corresponding increases in power consumption, mass and risk, and evaporation in the low pressure environment of mars, so as to eliminate the need for sample preparation and reduce the need for power consumption. , the effect of reducing the need for sampl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Al 6061
[0095]FIGS. 7a-7e show results from a piece of aluminum-6061 obtained using the second prototype XRD / XRF instrument 100 in a 2-hour data run with the X-ray source 110 operating at an electron beam current of 100 microamps. FIG. 7a shows a density plot of the photon count intensity binned in the plane of event energy vs. event diffraction angle. In this space, photons which are due to XRF (e.g., due to contaminants in this case) appear as horizontal lines 205, as shown, and photons due to XRD from crystallized regions with discrete atomic plane spacings (Miller indices) appear as arcs 210, as shown, and trace out Bragg's law for n=1. After applying Bragg's law to compute d-spacing for individual photons, the XRD arcs 210 of FIG. 7a are straightened out as vertical lines 211 in FIG. 7b, while the horizontal XRF lines 205 of FIG. 7a remain as horizontal lines 206. The XRD feature apparent at 1.73 Å is an instrument feature.
[0096]In each of FIGS. 7a-7b, several of the XRD arcs 21...
example 2
[0098]FIG. 8 shows data from a bulk sample of hematite showing both diffraction and fluorescence features. As with FIG. 7b, the hematite data is binned and plotted in the space of energy (E) vs. d-spacing, as shown in FIG. 8. XRD data is shown as vertical lines 221, while the XRF data is shown as horizontal lines 225. FIG. 8 is labeled to show some of the expected and detected diffraction features, particularly showing the d-spacings of 1.49 Å, 1.70 Å, 2.21 Å, 2.52 Å, and 2.70 Å. A faint d-spacing vertical line is also observable at 3.69 Å. FIG. 8 is also labeled to show the expected fluorescence features (e.g., Fe Kβ, Fe Kα, and Ti Kα).
[0099]Because d-spacing information acts as an effective “fingerprint” for any given mineral, the specific combination of vertical features 221 in FIG. 8 can be used to identify the sample. D-spacing values for thousands of organic and inorganic substances are available in commercial and freely available digital databases (e.g.,...
example 3
Aerosol Identification
[0103]Applications involving aerosols require a high detection limit to measure trace elements and require high sensitivity to permit analysis of minute amounts of material. A typical aerosol filter configured to collect particles on its surface (e.g., the Nuclepore® filter) holds about 20 μg / cm2 of aerosol mass. For a X-ray beam 105 having a spot size area of about 2 mm2, which is the case for the current example, the total aerosol mass observed by the beam is about 0.4 μg.
[0104]FIGS. 9a-9c show an example of an aerosol filter, analyzed using the disclosed XRD / XRF instrument 100 and techniques disclosed herein, showing measurements of at least 9 elements with X-ray fluorescence and identifying at least three major minerals in the analyzed sample (i.e., calcite, hematite, and halite). The aforementioned second prototype of the XRD / XRF instrument 100 (see generally FIG. 2b) was used to analyze data from micrograms of dust collected on a thin polycarbonate Nuclep...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle θC | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com