High efficiency microwave amplifier
a microwave amplifier and high-efficiency technology, applied in the direction of push-pull amplifiers, phase splitters, gain control, etc., can solve the problems of inefficiency of common microwave power amplifiers, difficult heat management, and needing bulky and costly cooling systems, so as to reduce undesirable radiofrequency interference, improve efficiency, and reduce harmonics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
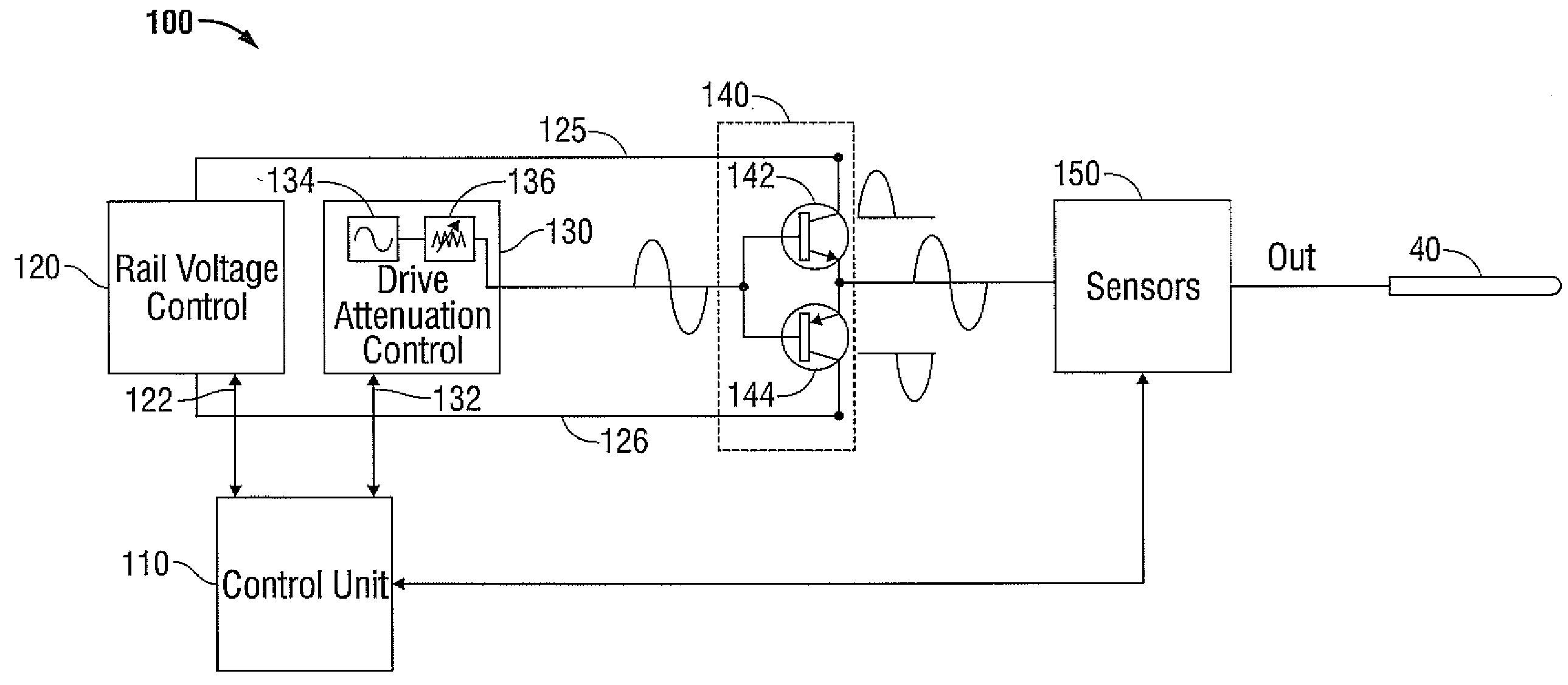
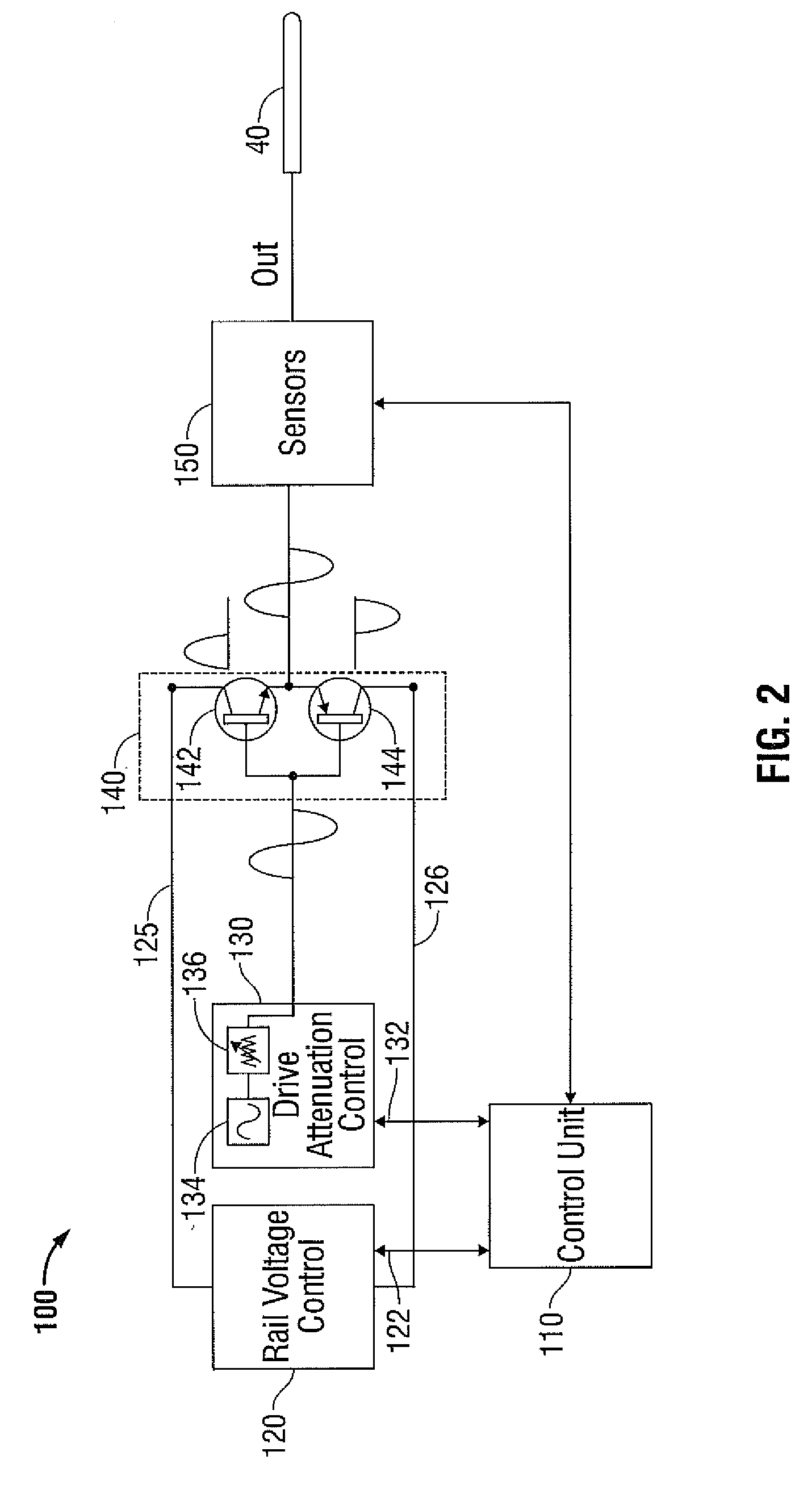
[0031]Particular embodiments of the present disclosure are described hereinbelow with reference to the accompanying drawings; however, it is to be understood that the disclosed embodiments are merely exemplary of the disclosure, which may be embodied in various forms. Well-known functions or constructions are not described in detail to avoid obscuring the present disclosure in unnecessary detail. Therefore, specific structural and functional details disclosed herein are not to be interpreted as limiting, but merely as a basis for the claims and as a representative basis for teaching one skilled in the art to variously employ the present disclosure in virtually any appropriately detailed structure.
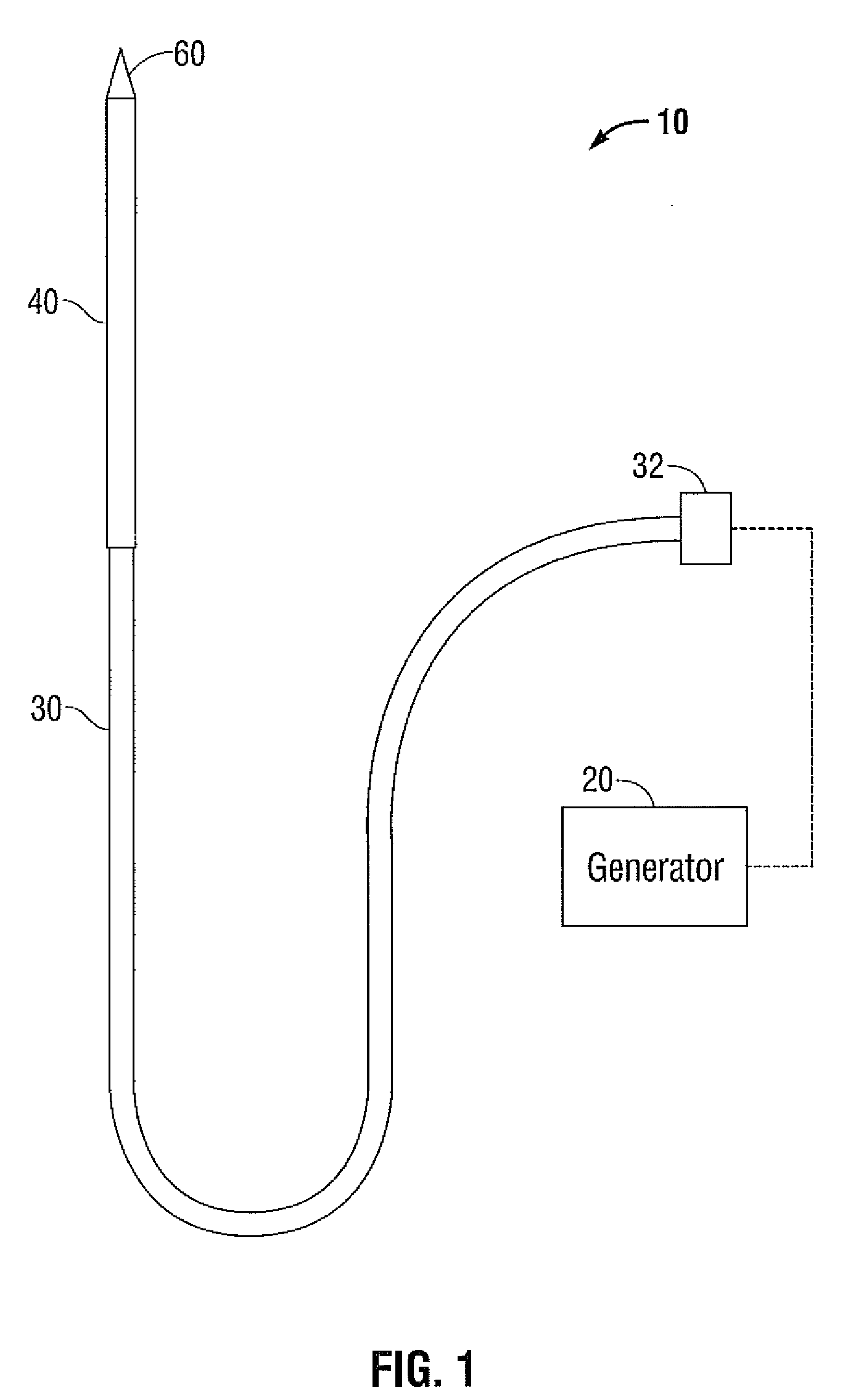
[0032]FIG. 1 shows an embodiment of a microwave ablation system 10 in accordance with the present disclosure. The microwave ablation system 10 includes an electromagnetic surgical ablation probe 40 connected by a cable 30 to a connector 32, which may further operably connect the probe 40 to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com