Processes and Device for Low Temperature Separation of Air
a technology of low temperature separation and process, which is applied in the direction of refrigeration and liquid storage, lighting and heating equipment, solidification, etc., can solve the problems of turbine damage, inability to unconditionally lower the temperature at the turbine inlet, etc., and achieve the effect of low equipment cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
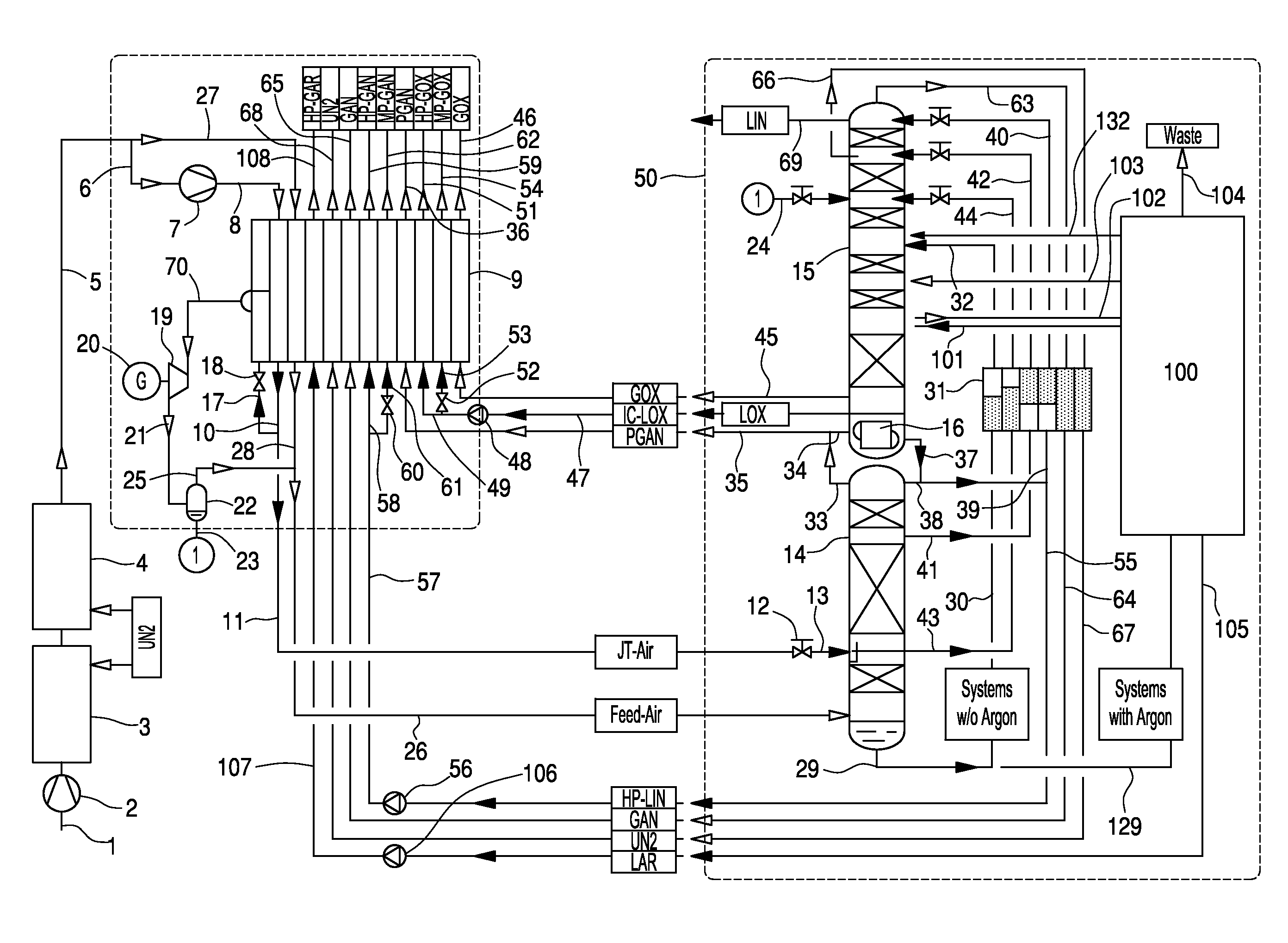
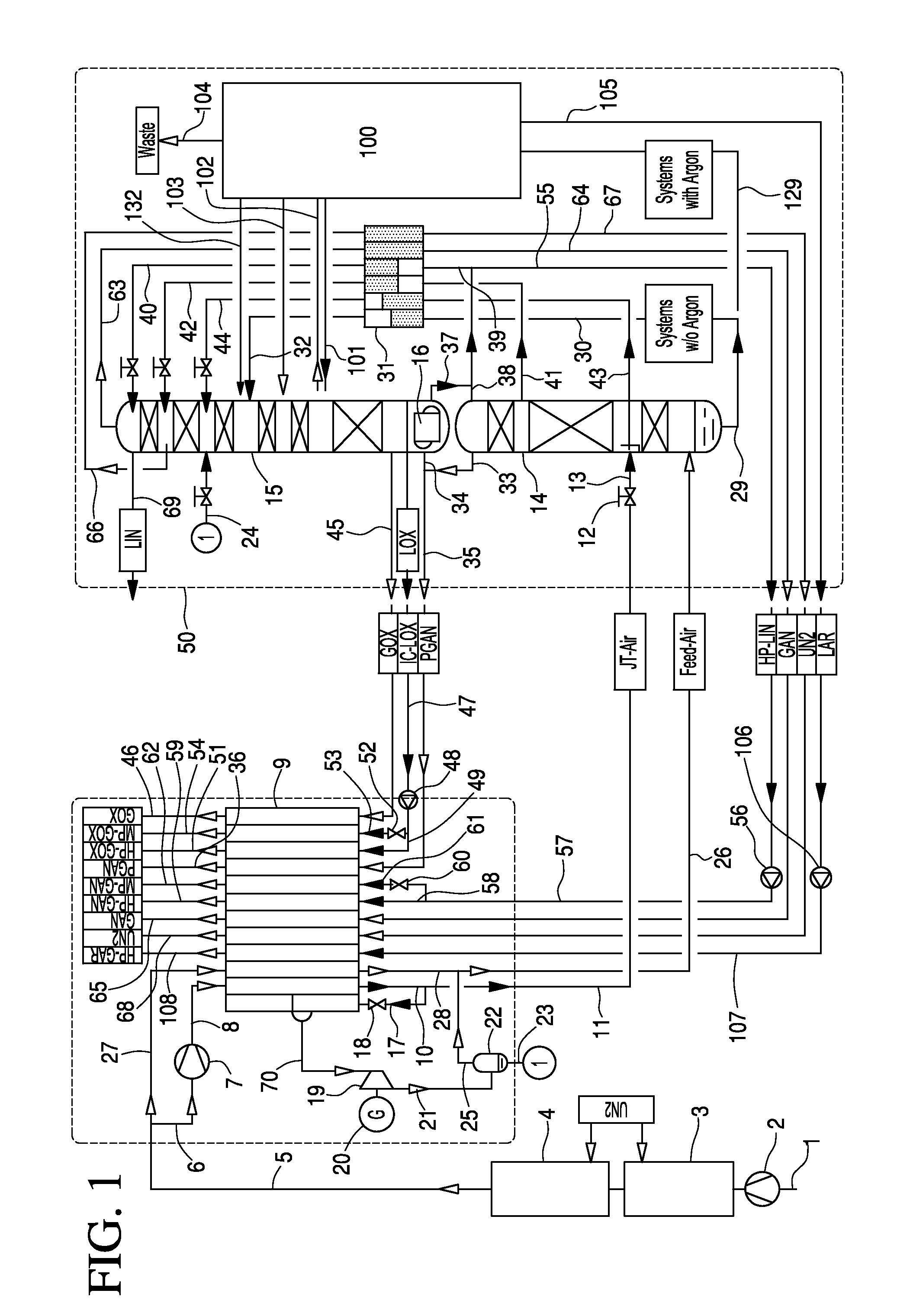
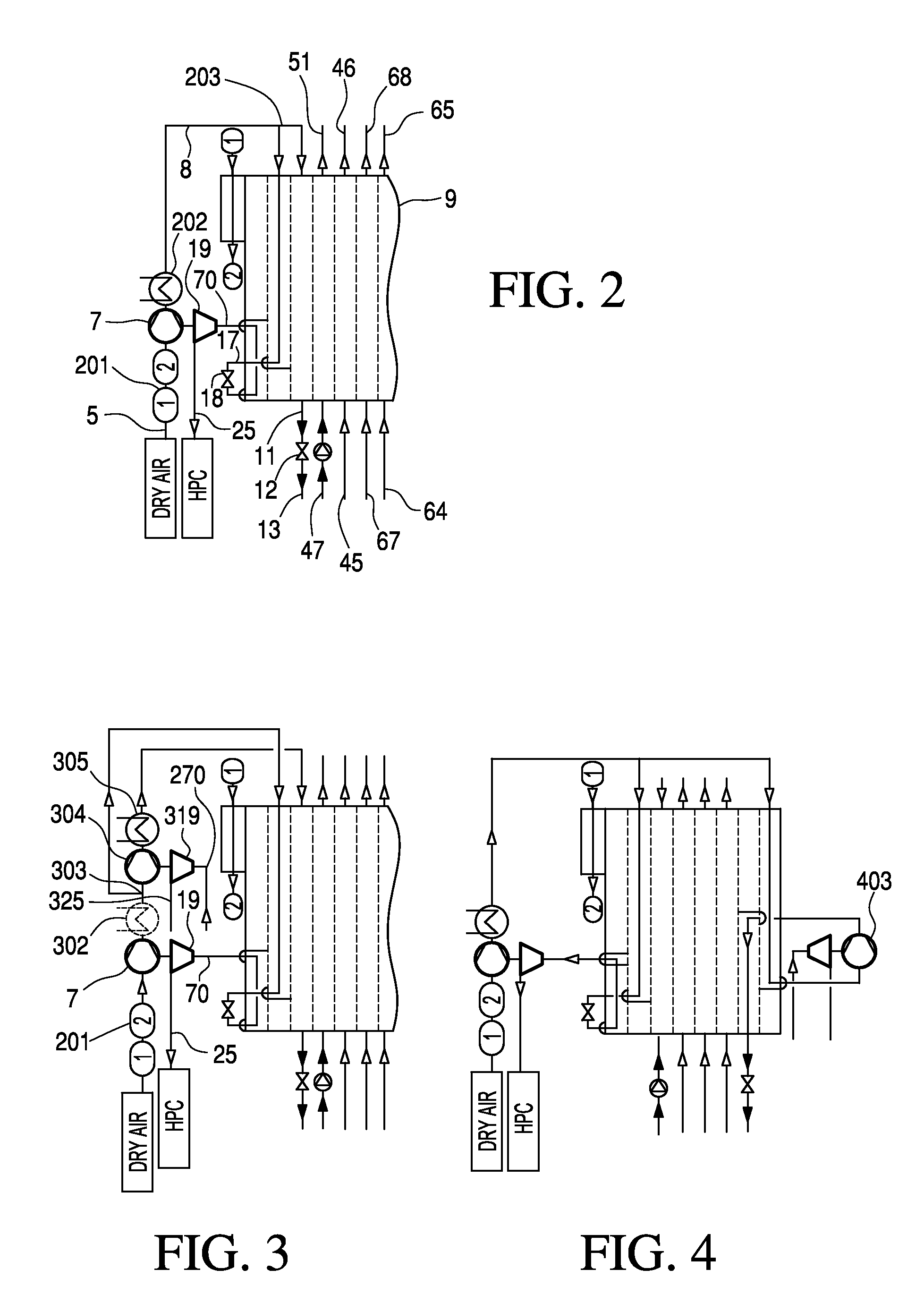
[0030]In the embodiment of FIG. 1, the distillation-column system 50 comprises, in the part which serves for the nitrogen-oxygen separation, a high-pressure column 14, a low-pressure column 15, and a main condenser 16 constructed as a condenser-evaporator, at which the two columns stand relative to heat exchange.
[0031]Atmospheric air is sucked in as main air stream 1 to an air compressor 2, and is brought there to a first pressure that corresponds roughly to the operating pressure of the high-pressure column 14, is cooled down in a primary cooling 3 to roughly ambient temperature, and is conducted to an adsorptive air purification 4. A first portion of the purified main air stream 5 is further compressed as a “first air stream”6 in a recompressor 7 at a second pressure of at least 50 bars, for example roughly 60 bars. The high-pressure air 8 is conducted to the hot end of a main heat exchanger 9 and is cooled down and pseudo-liquefied in the main heat exchanger. The pseudo-liquefied...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com