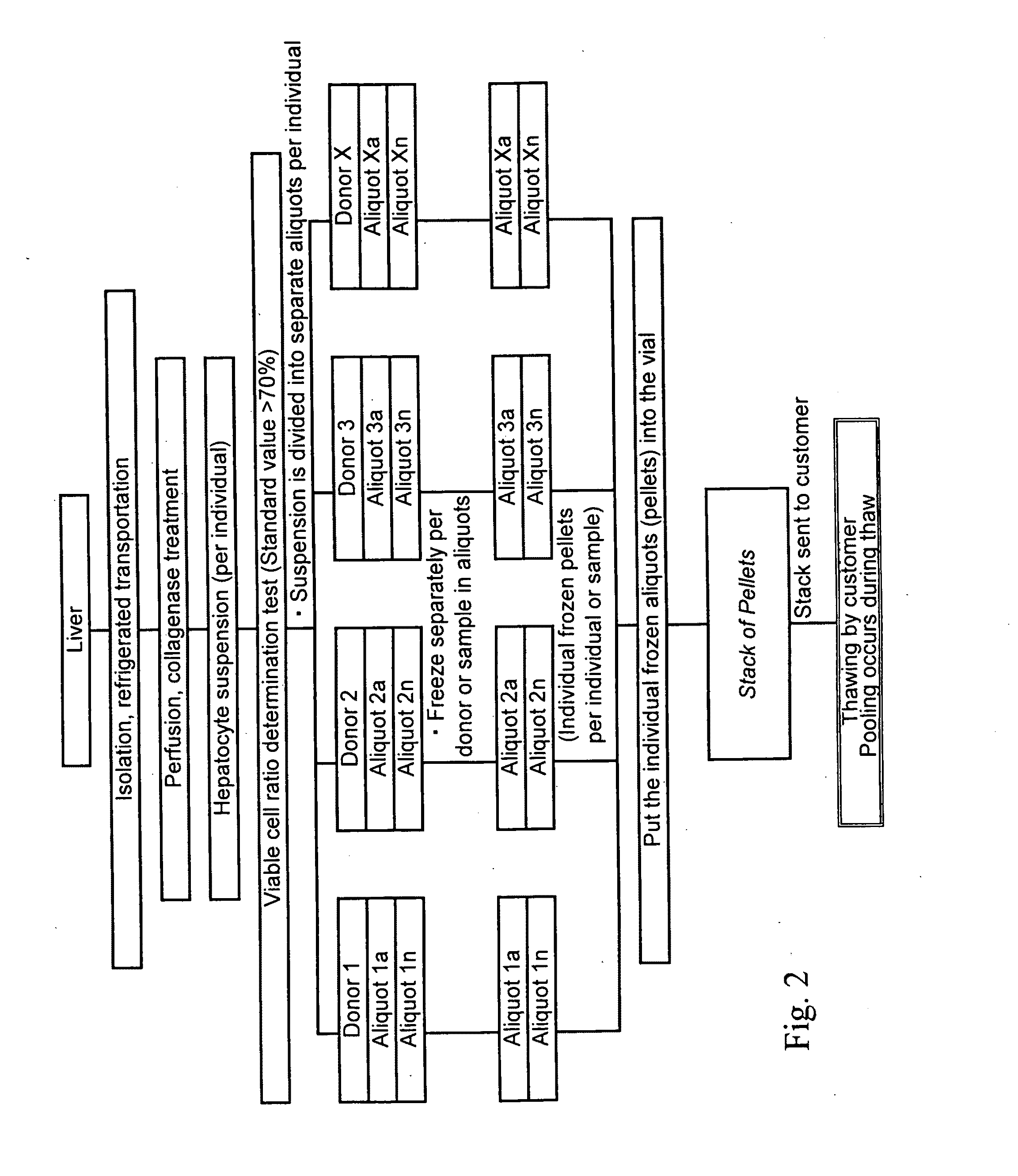
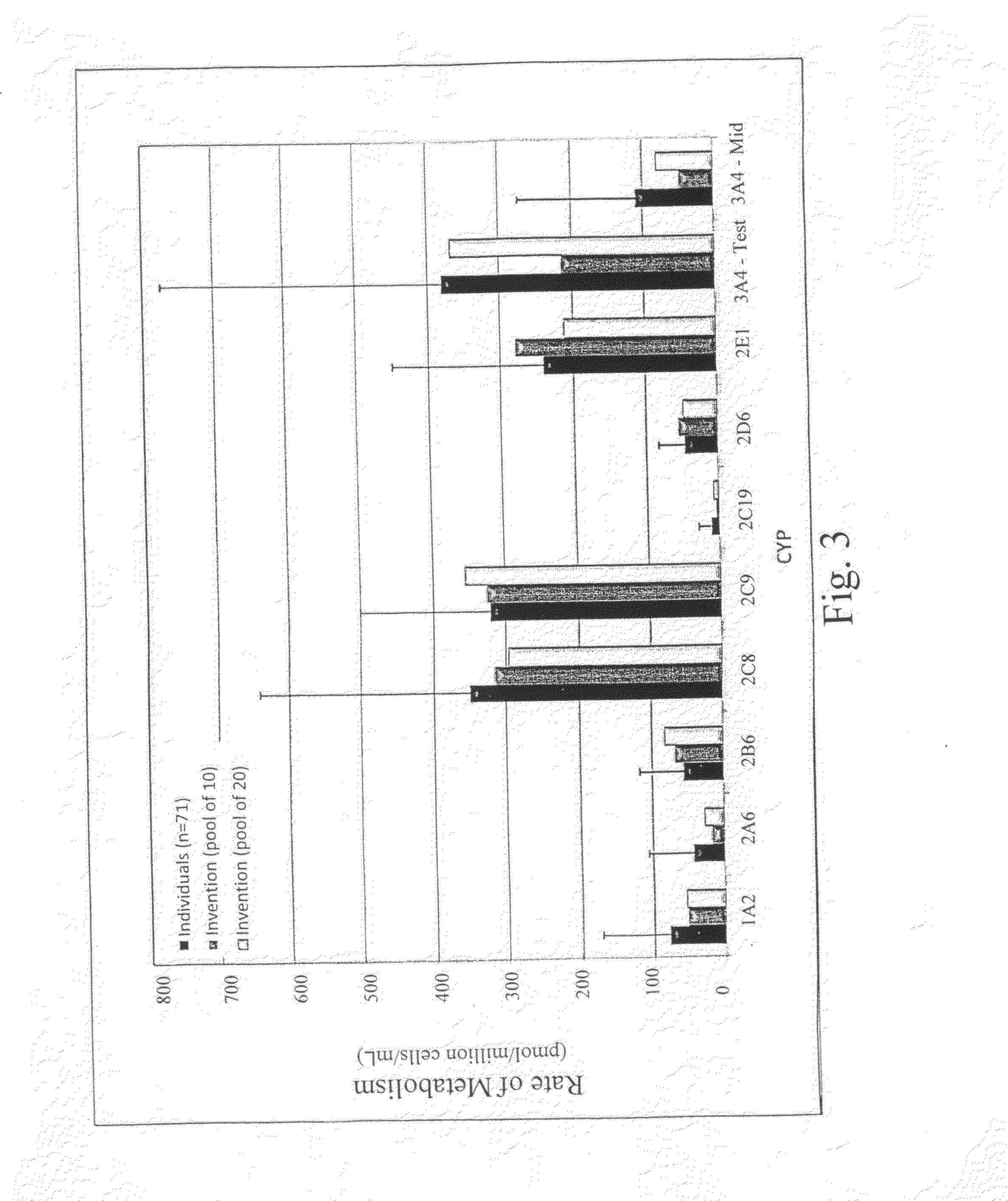
Cryopreservation of cells and subcellular fractions
a cell and subcellular technology, applied in the field of cryopreservation of self-sustaining bodies, can solve the problems of limiting the ability to conduct experiments using such a system, and affecting the viability of cells after thawing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Isolation of Hepatocytes
A. Reagent Preparation
[0040]Various reagents for use in the following Example were prepared. To prepare about 20 L of 1-×Perfusion Buffer 1 (1×-PB1), the following reagents were dissolved in 18 L of high purity water: 137.9 g NaCl, 7 g KCl, 3.3 g KH2PO4, 42 g NaHCO3, 19.8 g glucose, and 3.8 g ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA). The pH was then adjusted to 7.4, as required, using 1-10 N NaOH or HCl at room temperature. Additional high purity water was added to reach a final volume of 20 L.
[0041]Next, 10 L of Perfusion Buffer 2 (PB2) was prepared by dissolving the following reagents in 9 L of high purity water: 69 g NaCl, 3.5 g KCl, 1.675 g KH2PO4, 21 g NaHCO3, 10 g glucose, 2.2 g CaCl2, and 1.45 g MgSO4. The pH was adjusted to 7.4, as required, using 1-10 N NaOH or HCl at room temperature. The final volume was adjusted to 10 L using additional water. PB2 is combined with collagenase (Worthington Biochemical Corp., Freehold, N.J.; 90 units / mL).
[0042]The de...
example 2
Preparation and Pre-Pooling of Cryopreserved Hepatocyte Pellets
A. Cleaning, Autoclaving and Assembling of the Pellet Holder
[0051]Pellet holder assembly consists of pellet holder base, pellet holder (cryopreserved pellet receptacle, see Example 3) and the lid.
[0052]1. The pellet holder base (a sturdy 96-well base made of plastic, that the pellet holder is placed on during the cryopreservation process) and lid (a molded plastic top that fits over the top of the pellet holder and pellet holder base that enables sterility during the cryopreservation process) were cleaned using mild soapy water, then rinse with tap water, followed by deionized water;
[0053]2. The pellet holder was cleaned by placing the pellet holder in a 1 L beaker and filling to the level of the holder wells with acetone;
[0054]3. The pellet holder was sonicated for ˜10-15 min;
[0055]4. The acetone was washed off with warm soapy water, and the pellet holder was rinsed first with tap water, then with deionized water;
[0056]...
example 3
Thawing and In Situ Pooling of Cryopreserved Hepatocytes
[0081]To thaw the pre-pooled pellet stacks, a cryo vial containing the selected stack was removed from the vapor phase N2 storage unit and quickly placed into a prewarmed shaking water bath (37±1° C.) so that the level of the water bath was above the high point of the top pellet in the stack. The pooled hepatocyte composition was formed in situ, as the individual pre-pooled pellets thaw and the formerly discrete, frozen suspensions mixed together into a single pooled hepatocyte composition in the cryo vial. For example, a stack of 10 discrete 100 μL pre-pooled pellets thawed into 1 mL of pooled hepatocyte composition. Once thawed, the cryo vials were quickly removed from the water bath, and their contents were gently poured into a vial containing DMEM+cryo (about 3-5 times volume of the pellet stack) and IsoPercoll (90% PERCOLL® in 10×PBS). The cryo vial was then rinsed with 1.5 mL of DMEM+, which was added to the pooled produc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com