Cyanine-containing compounds for cancer imaging and treatment
a technology of cyanine-containing compounds and cancer imaging, which is applied in the direction of biocide, drug composition, instruments, etc., can solve the problems that most cyanine dyes are not effective for in vitro treatment or imaging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0068]The synthesis of compound 8 is shown in Scheme 1.
[0069]Benz[c,d]indole-2(1H)-thione (2). This compound was obtained in an 93% yield; mp 146-148° C.; (reported: yield 82%, mp 156 dec).2,3
[0070]2-Methylthiobenz[c,d]indole hydroiodide (3). This compound was prepared by using the reported procedures.2,4 Since the product was unstable, it used in the next step without further purification.
[0071]2-(2,2-Dimethyl-4,6-dioxo-1,3-dioxane-5-yliden)1Hbenz[c,d]indole (4). This compound was obtained in an 85% yield; mp 220° C. (dec.); (reported: yield 94%, mp 223° C.).1,2
[0072]Ethyl 2-(2,2-dimethyl-4,6-dioxo-1,3-dioxan-5-ylidene)-1H-benz[c,d]indole-1-hexanoate (5). A mixture of compound 4 (3 g, 10.2 mmol), ethyl 6-bromohexanoate (5.5 g, 30.6 mmol) and K2CO3 (4.2 g, 30.60 mmol) were heated in DMF (40 mL) at 90° C. for 18 hr under a nitrogen.atmosphere. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified on s...
example 2
Preparation of MHI-148 (Compound 10)
[0075]As shown in Scheme 2, a solution of salt 9 (1.00 g, 2.82 mmol), Vilsmeier-Haack reagent 75 (507 mg, 1.4 mmol) and anhydrous sodium acetate (925 mg, 11.28 mmol) in acetic anhydride (30 mL) was heated to 70° C. for 1 h under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction progress was monitored by Vis / NIR spectroscopy. The green solution was cooled to room temperature, then poured into saturated solution of sodium iodide. The crude product was filtered off, washed with ether and recrystallized from methanol / ether providing 0.8 g (1.0 mmol, 71%); 1H NMR, δ 1.42 (m, 6H), 1.57 (m, 6H), 1.75 (m, 4H), 2.19-2.21 (m, 6H), 2.84 (m, 2H), 4.26 (m, 2H) 6.30-6.37 (m, 2H), 7.28-7.32 (m, 4H), 7.40-7.51 (m, 4H), 7.64 (m, 2H), 8.28 (d, J=8.3 Hz, 2H), ESI-MS m / z 742 ([M+], 100); ESI-HRMS calcd for C42H52N2O4Cl (M+-CH3COO−) 683.3616, found 683.3608. λmax Abs=780 nm and λmax FL=800 nm.
[0076]Synthesis of cyclopentene ring-containing structures can be carried out using method...
example 3
Evaluation of Organic Cyanine-Containing Compounds as Imaging Agents
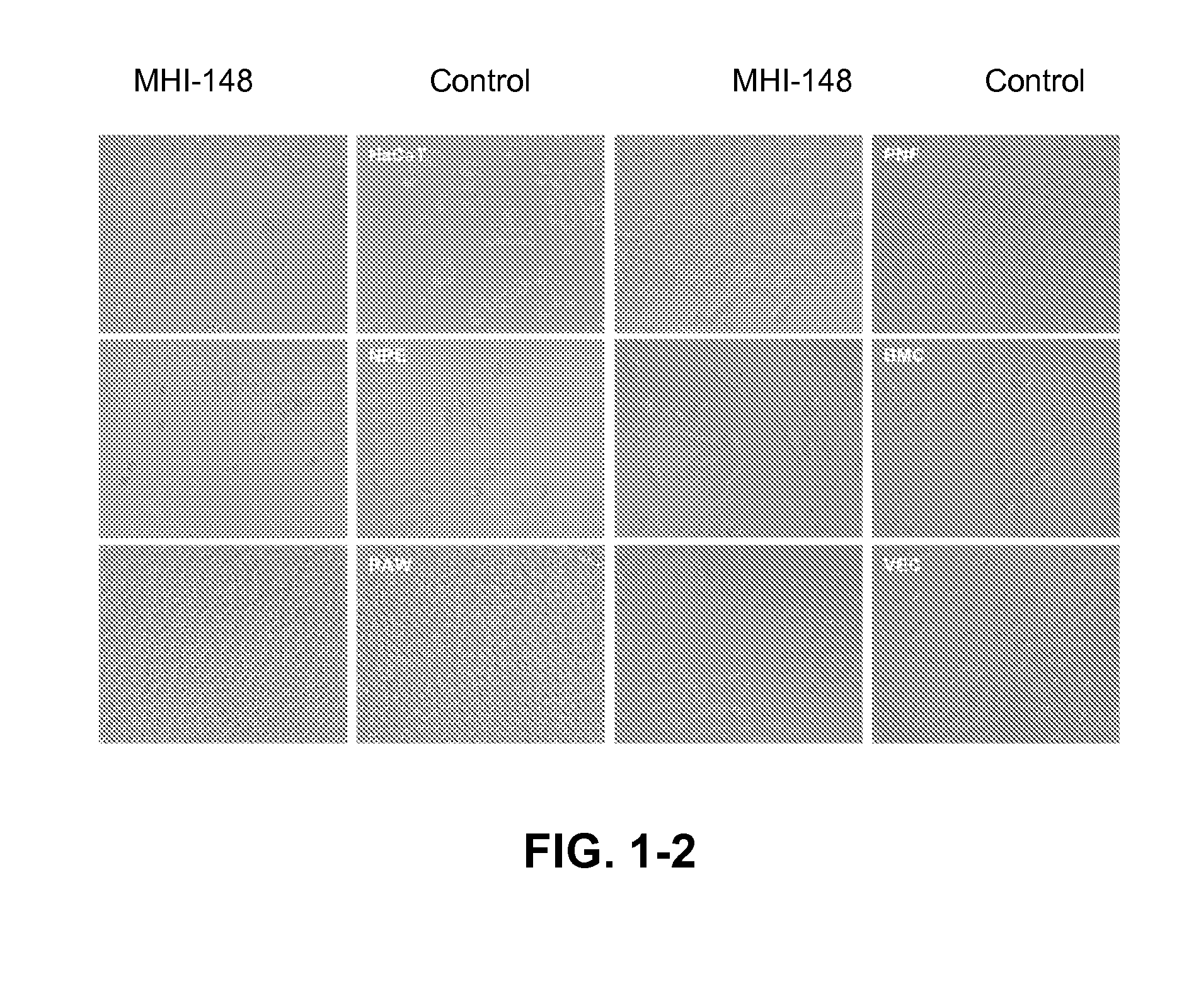
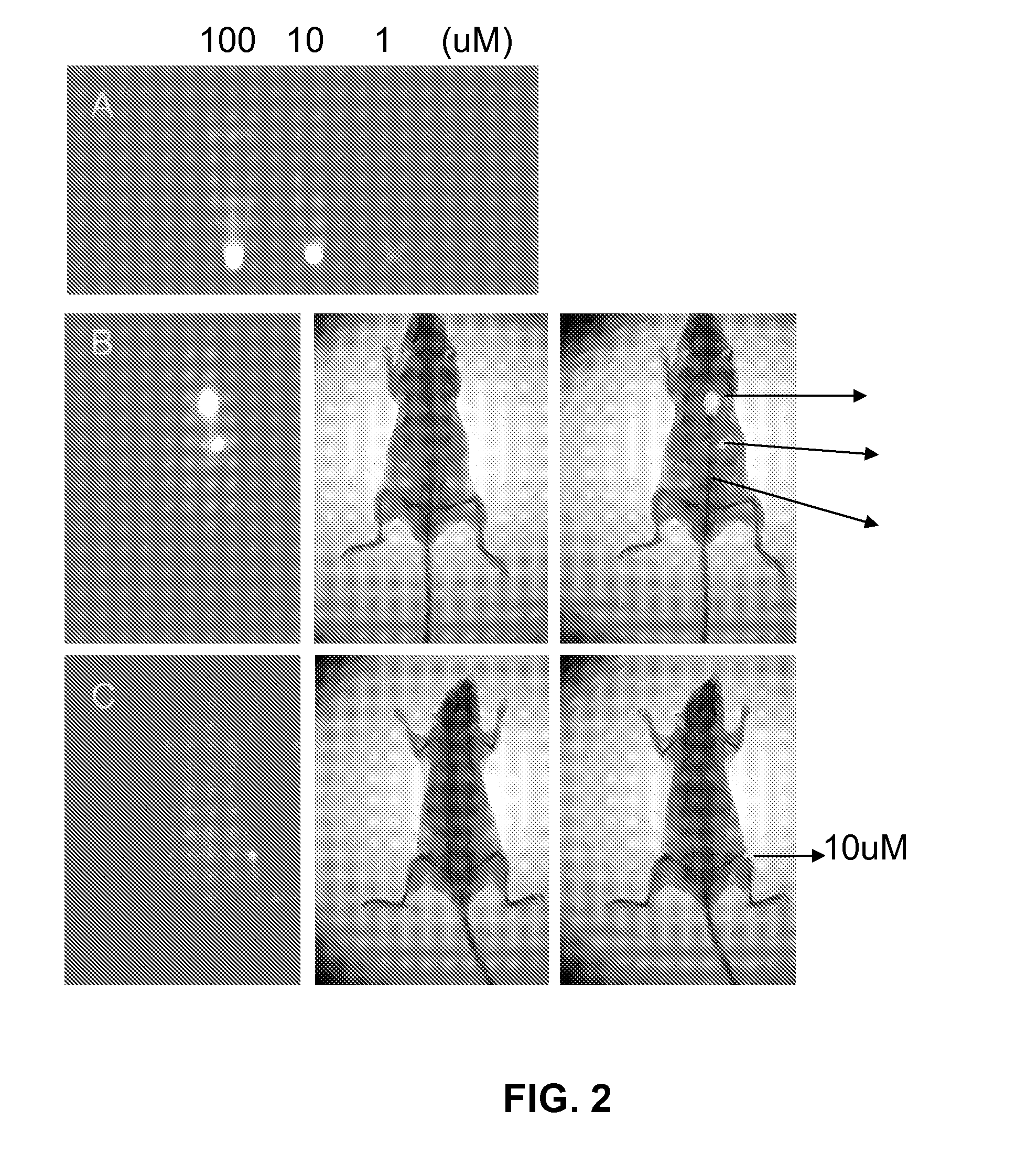
[0077]FIG. 1 shows imaging of human cancer cells including prostate (LNCaP, ARCaPE, ARCaPM, C4-2, PC-3), liver (HepG2), osteosarcoma (MG63), breast (MCF-7), kidney (RCC), bladder (T-24), cervical (HeLa), leukemia (K562) and lung (H358) with MHI-148. Cancer cells show a significant uptake of MHI-148 (dark color), while corresponding normal human or mouse cells (e.g. normal prostate fibroblasts, NPE; marrow stromal cells, BMC; normal vascular endothelial cells, VEC; or mouse macrophage RAW cells) failed to yield any time- or concentration-dependent uptake of MHI-148 in culture. Normal epithelial cells (e.g. normal prostate epithelial cells, NPE and normal human skin epithelial cells, HaCaT) showed a low uptake of MHI-148. All the cells were cultured with 100 μM MHI-148 in basal media (T-medium with 5% fetal bovine serum and 1% antibiotics) for two hours and were imaged under an inverted microscope. These conditions ar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| NIR wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| NIR wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com